SWINE LABORATORY MIDTERMS REVIEWER
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
ADG (Average Daily Gain)
refers to the average amount of weight a pig gains per day over a specific period of time
AI (Artificial Insemination)
is a reproductive technique where semen is collected from a boar and manually inserted into the reproductive tract of a female pig (sow or gilt) using a catheter.
All-in/All-out
Is a system that keeps animals together in groups. Animals from different groups are not mixed during their stay on the farm. The groups are closely matched by age, weight, production stage and condition. The group is moved into a phase of production together.
Barrow
A castrated male pig used for meat production.
Boar
A matured male pig kept for breeding.
Carcass Index
This is a way to measure the quality of carcasses based on the amount of fat, protein, ash, and moisture it contains. It is also a determining factor for the value and price of the carcass at which it can be sold.
Carcass Yield
Termed as the proportion of the animal's live weight after it has gone through slaughtering. It is also called a dressing percentage. Factors such as age, bones, fats, and slaughtering procedures can affect the carcasses yielded.
Cross Foster
A technique used in animal husbandry where offspring are removed from their biological parent at birth and raised by different species, cross-fostering should be performed between 12 and 24 h after farrowing, before teat order has been established.
Cull
the process of removing or eliminating pigs from a herd that are no longer productive or healthy enough to remain.
Depopulation
is the act of removing or culling pigs from a specific barn or farm due to a disease or environmental disasters.
Repopulation
the process of introducing new pigs into a barn or farm after depopulation.
Down Time
The period of time when people are not allowed to enter the farm after coming in contact with other swine; the time when the barn is empty and undergoing cleaning and disinfecting.
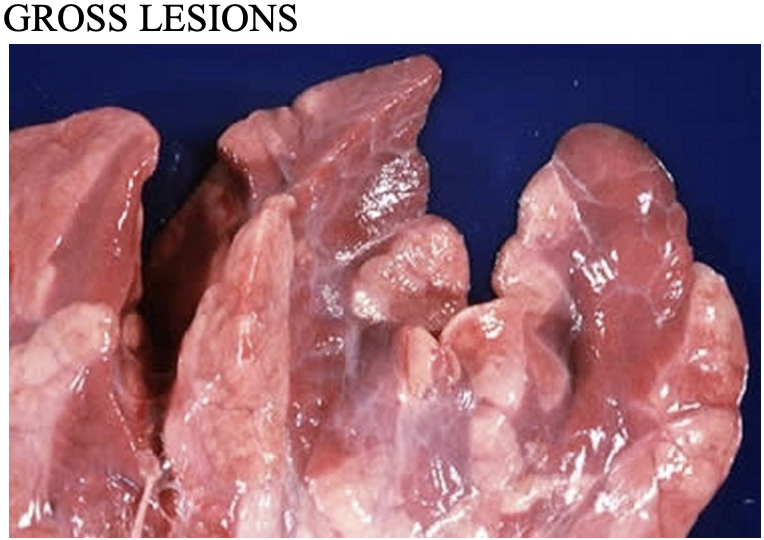
Enzoonotic Pneumonia (Mycoplasmal Pneumonia)
a chronic, mild infectious pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Characterized by persistent dry cough, impaired growth, and lung lesions.
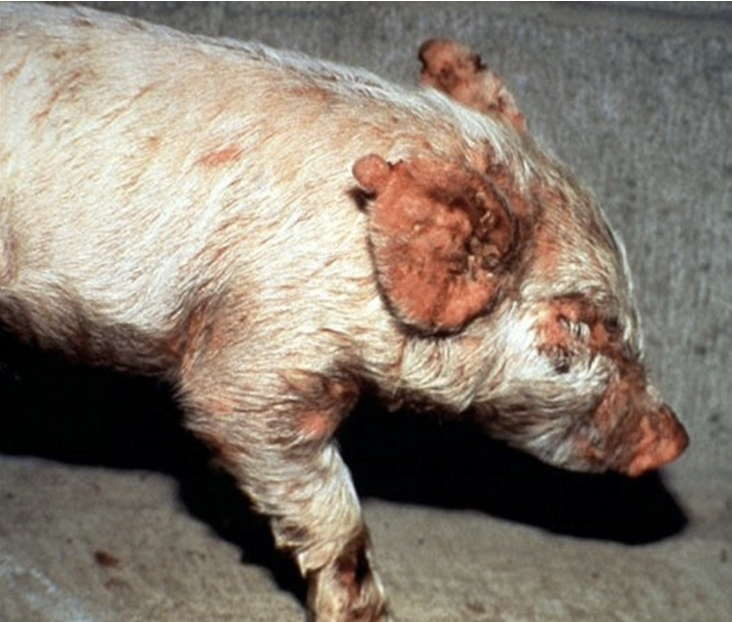
Greasy Pig Disease (Executive Epidermitis)
a staphylococcal infection affecting pigs aged 5 to 60 days, with morbidity ranging from 10–90% and mortality from 5–90%. It is more severe in suckling piglets but can also affect weaned pigs in a chronic form.
Farrowing rate
the percentage of sows that farrow to a given number of matings.
Growth Rate
The speed at which a pig's body mass grows over time.
Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR)
measures how efficiently an animal converts feed into body mass. It is computed by dividing the feed consumed by the weight gained over a specific time period.
Finisher
the final stage of pig production, during which pigs are fed high-energy diets until they achieve market weight, which is typically 100-120 kg. Starting at 50-60 kg.
Grower
A pig between weaning and sale or transfer to the breeding herd, sold for slaughter or killed for rations.
Hand Breeding
usually a practice of breeding sows or gilt to a boar alongside Pen Breeding.
The practice involves 2-3 times of mating in gaps of 24 hours per estrous.
PCV AD (Porcine Circovirus Associated Diseases)
Porcine Circovirus emerged in the early 20th century from a North American swine. This virus is the most common virus in the world;
However, from its history, it developed with two prototypes: PCV and PCV2.
PCV or the prototype 1 is nonpathogenic, even though it has contaminated cell cultures or samples. The PCV2 or prototype 2 started from the post-weaning of piglets wherein symptoms appear just right the separation of piglets to their dam which is known by the name of Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting syndrome too.
SYMPTOMS:
- Gradual Wasting
- Unthriftiness
- Rough Hair Coat
- Dyspnea
- Icterus
- Polypnea
- Lesions to Granulomatous inflammations in
organs
Pig density
Also known as stocking density, is the number of pigs per unit of space.
Pig flow
The systematic approach to raising pigs in a multi-site production system, in terms of where the pigs are housed and how long they are fed
Starter ration / Creep feed
A type of feed given to young animals to help them adapt to solid food and grow.
Processing
Refers to routine procedures performed on piglets shortly after birth to promote their health and welfare.
Ridgling
a cryptorchid; a male animal with one or both testicles undescended.
Savage/ Savaging
a term used in the study of ethology that refers to aggressive behavior displayed by the mother towards the offspring.
Aggressive behavior includes being rough with, injuring, biting, attacking, crushing and killing (maternal infanticide) of the offspring.
Scour
refers to diarrhea or loose stools, which can lead to dehydration and other health issues.
SPF
This term can be used to describe a pig or pigs, a herd or a disease control program.
Back Pressure Test
also known as riding test; a procedure used to determine if a pig is in heat and ready to conceive by applying pressure to the loin's area and then gently sitting on its back to see if it stands up.
Conception Rate
percentage of sows that become pregnant after insemination and can be influenced by a number of factors, such as fertility rate, semen quality and age of gilt.
Cull Rate
percentage of pigs that are removed from a breeding herd each year, whether voluntary or involuntary
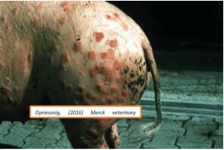
Diamond Skin Disease
a skin condition in swine caused by the bacterium Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae.
It is characterized by diamond-shaped, raised, red to purple lesions on the skin, typically on the ears, neck, and abdomen.
Double Mating
refers to a breeding strategy where a female animal is mated with two different males during a single estrus cycle.
Gilt Pool
a group of female pigs (gilts) that are managed together for breeding purposes.
Leptospirosis
a contagious disease caused by an infection with any one of a large group of spiral-shaped bacteria Leptospira interrogans.
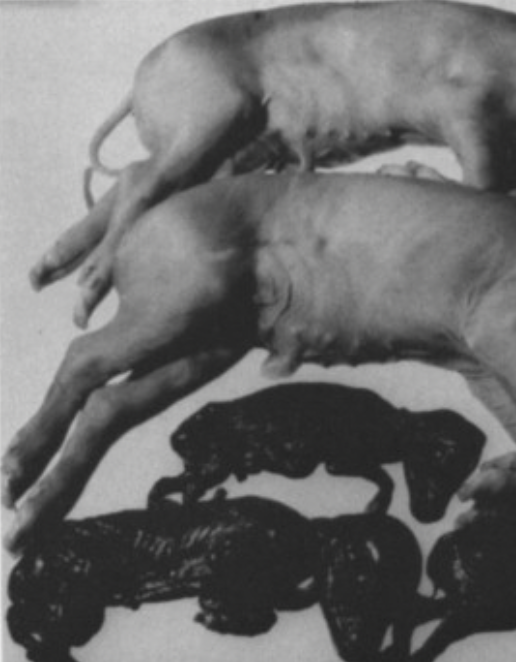

Porcine parvovirus (PPV)
can cause reproductive failure in native dams. It is characterized by the occurrence of large numbers of mummified fetuses
Return to estrus
when a sow or gilt comes into heat again after giving birth or being weaned.
Seasonal Infertility
a reduction in fertility and fecundity that occurs during certain times of the year, usually in the summer and early fall.
Service
act of mating a sow with a boar or inseminating a sow with semen to make her pregnant.
The term can also refer to the number of heat cycles between pregnancies.