Atomic Structure
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
describe the atom
nucleus made up of protons and neutrons
electrons orbiting in shells, take up most space in the atom
what makes up most of an atoms mass
nucleus
relative charge of all subatomic particles
proton, +1
neutron, 0
electron, -1
relative mass of all subatomic particles
proton, 1
neutron, 1
electron, 1/1840
mass number definition
total number of protons and neutrons
atomic/proton number definition
number of protons
why are all atoms neutral
number of protons = number of electrons
ion definition
atoms which have lost or gained electrons = charged atom
what does proton number determine
the element
what do electrons determine
reactivity properties
what determines physical properties
number of protons, neutrons and its electron configuration (determines bonding)
define isotope
elements with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
what do different isotopes have
differ in physical properties due to different number of neutrons
first hypothesis for atoms
atoms are spheres,
different elements are made from different spheres,
indivisible
who made the first hypothesis for atoms
greeks
J.J. Thompson theory for atoms
discovered the electron
atom wasn't solid and was made of other particles
positive atom with electrons embedded
ernest rutherford nuclear model
discovered the nucleus, found it was very small and positive
found atom was empty space
positive nucleus with negative electrons orbiting
gold leaf experiment and findings
positive alpha particles fired at thin gold leaf
most went through, showing mostly empty space
some deflected, showing small positive nucleus
what problem did niels bohr find with rutherford model
the cloud of electrons could collapse into the positive nucleus
what did niels bohr find
fixed energy levels: shells
what did James Chadwick find
neutrons
describe nuclear model
positive nucleus with protons and neutrons
electrons orbit in fixed energy levels
existence of sub shells
Erwin Schrödinger theory
orbitals
steps of time of flight mass spectrometry
1. vaporisation
2. ionisation
3. acceleration
4. ion drift
5. detection
two types of ionisation
electrospray
electron impact
describe electron impact
vaporised sample,
high energy electrons fired by an electron gun to form a positive ion,
electrons knocked off,
fragmentation occurs
describe electrospray ionisation
sample dissolved in a high, volatile solvent,
sample injected into a fine hypodermic needle and an aerosol is created,
high voltage is passed through causing loss of electron
acceleration
positive ions are passed through an electric field, particles with a lower m/z ratio will accelerate quicker
ion drift
particles travel through with a constant speed and kinetic energy
particles with lower m/z travel faster
detection
ions hit negative detector plate and produce a current as they gain an electron
how is abundance measured in tof mass spec
abundance is directly proportional to size of current
electron impact equation
X(g)→ X+ (g) + e-
electrospray ionisation equation
Xg) + H+ (g) -> XH+(g)
relative atomic mass
average mass of an atom of an element, relative to 1/12th of an atom of carbon 12
relative molecular mass
average mass of a molecule, relative to the mass of 1/12th of carbon 12
relative isotopic mas
mass of an atom of a particular isotope compared to one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
relative atomic mass equation
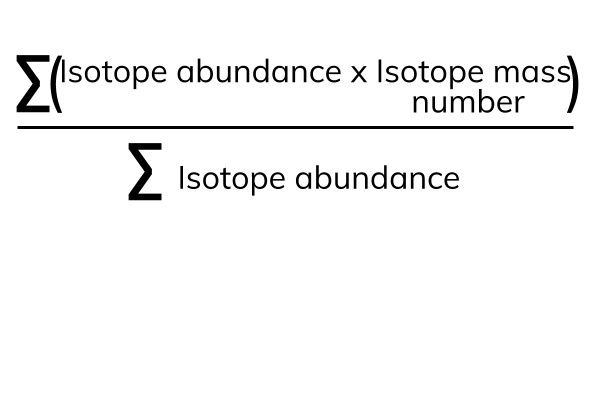
draw a mass spectra produced by tof
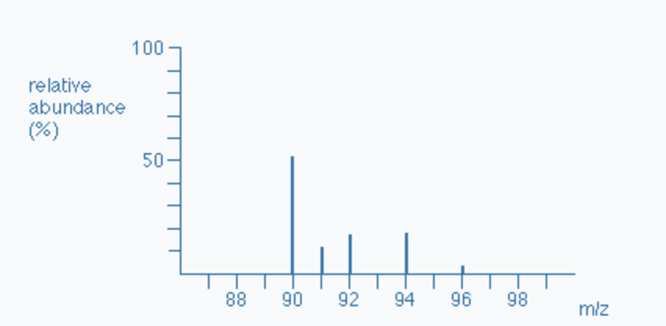
what does a mass spectra show
abundance of different isotopes present
how are molecules different in mass spec
fragments are created, molecular ion peak is equal to the relative atomic mass
what is the molecular ion peak
last significant peak on a mass spectra, equal to relative atomic mass peak at 100
4 sub shells
s,p,d,f
how many electrons in an s sub shell
2
how many electrons in a p sub shell
6, 3 pairs
how many electrons in a d sub shell
5 pairs, 10 electrons
how do electrons fill in orbitals
separately first, then they pair up
electron configuration for chromium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s1
one 4s moves to 3d so it is half full and more stable
electron configuration for copper
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1
define ionisation energy
minimum amount of energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of atoms in the gaseous state
write first ionisation energy equation for sodium
Na (g) -> Na+ (g) + e-
is ionisation endo or exothermic
endothermic, it requires energy = positive value
how does shielding effect ionisation energy
more electron shells between positive nucleus and negative electron = less energy required to remove,
weaker electrostatic attraction
3 factors that affect ionisation energy
shielding, atomic size, nuclear charge
how does atomic size impact ionisation energy
bigger the atom the further away the outer electrons are from the nucleus, attractive force between electrons and nucleus reduces = easier to remove electron
how does nuclear charge impact ionisation energy
more protons in nucleus = bigger attraction between nucleus and outer electrons = more energy required to remove the electron
define successive ionisation
removal of more than 1 electron from the same atom
define second ionisation energy
energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of +1 gaseous ions, producing one mole of 2+ gaseous ions
reasons for jumps in ionisation energy
removing electrons from shells closed to the nucleus
why is there an increase in successive ionisation energy
removing an electron from an increasingly more positive ion
1st ionisation energy trend down a group
decreases
why does ionisation energy decrease down a group
atomic radius increases, outer electrons are further from the nucleus, attractive force is weaker = less energy required
- shielding increases, more shells = attractive force is weaker = less energy required
1st ionisation trend across a period
increases
why does ionisation energy increase across a period
nuclear charge increases as protons increase, increasing nuclear attraction
shielding doesn't change
atomic radius slightly decreases as atom is compressed from increased nuclear charge = stronger attraction
exceptions in period 3
decrease at aluminium = evidence for sub shells
- was not explained by Niels Bor atomic model
- slight decrease from P to S
how is a decrease at aluminium evidence for atoms having sub shells
decrease of 1st ionisation energy across period 3
- outer electron sits at a higher energy sub shell, further from the nucleus compared to magnesium = decrease
- magnesium: outer electron in 3s
- aluminium: outer electron in 3p
what is the decrease at sulfur from phosphorus evidence for
electron repulsion
why does ionisation energy slightly decrease between phosphorus and sulfur
both have outer electrons in 3p, shielding is the same
- sulfur: 3p4 (1 pair of electrons in a sub shell)
- phosphorus: 3p3 (electrons = unpaired)
- electrons repel, so less energy is needed to remove an electron from an orbital with 2 in than 1
why do electrons pair up with opposite spins
so the atom is as stable as possible
what is produced if electron spins are unpaired and unbalanced
natural repulsion = unstable,
atoms may take a different arrangement to improve stability