Skin Pigmentation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Freckles (normal Variant)
Accumulations of melanin

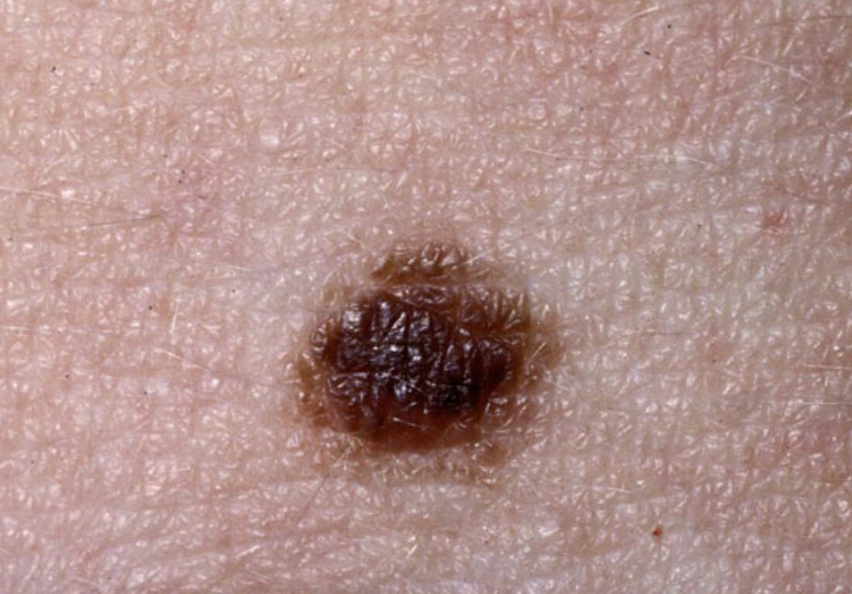
Nevus (normal variant)
Moles; concentrated areas of melanocyte. Should be monitored for any changes indicating cancerous overgrowth
Poliosis (normal variant)
A white patch of hair that lacks of melanin

Albinism (disorders)
A lack of melanin production due to double recessive gene- impigmentation

Vitiligo (Disorders)
autoimmune damage to melanocytes causing them to cease producing melanin. This condition tends to progress over time. There’s no cure.

Melanoma(Disorder)
Skin cancer of melanocytes

Flushing/Blushing
occurs with the vessels of skin dilate and bring a surge of blood flow
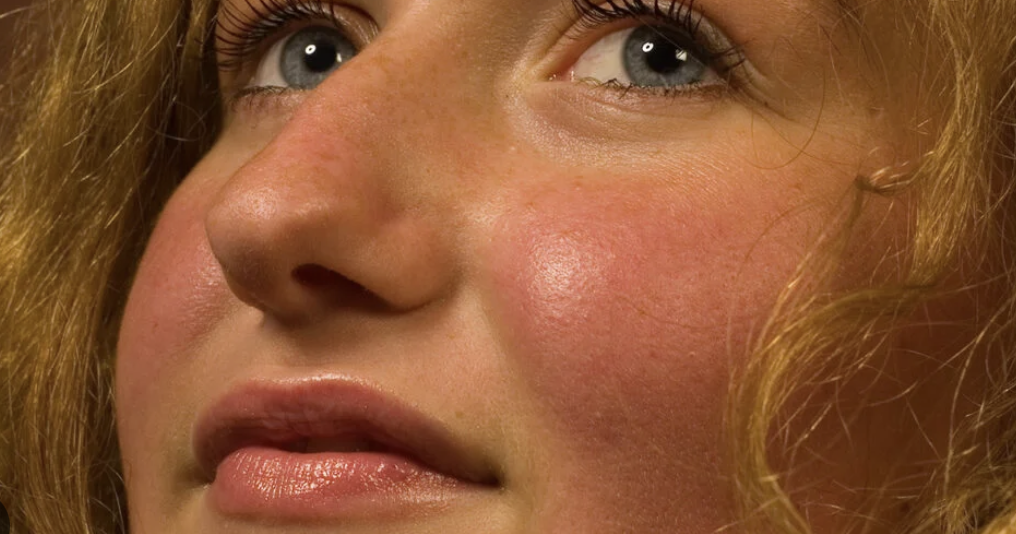
Cyanosis
Skin takes on a blueish tint when the body is oxygen deprived. Most easily noticed around lips and finger tips

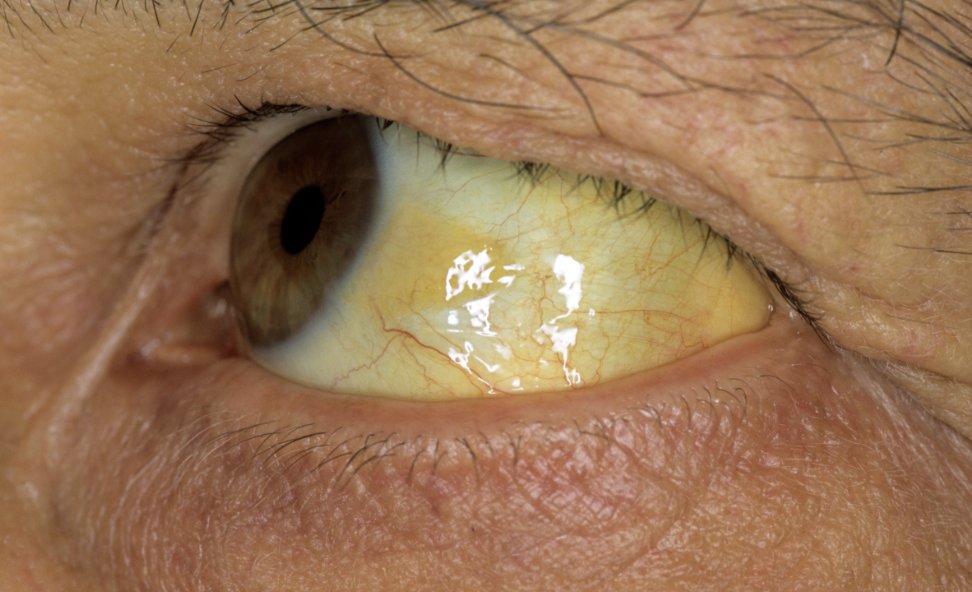
Jaundice
A toxic buildup of unconjugated bile slats from the liver will cause skin and eye scleras to take a yellowish tint. Eyes and anterior wrists are early indicators, common in newborns.
Palor
Cold, extreme fright, anemia, and other situations where there is lower blood or less oxygenation of the skin resulting in pale tone.
Addison’s disease
Adrenal insufficiency leads to “bronzing” hyperpigmentation. (odd, unusual color)