Recreational drugs
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Opiates
Can derive morphine, codeine and thebaine
Naturally occuring alkaloids
- morphine, codeine
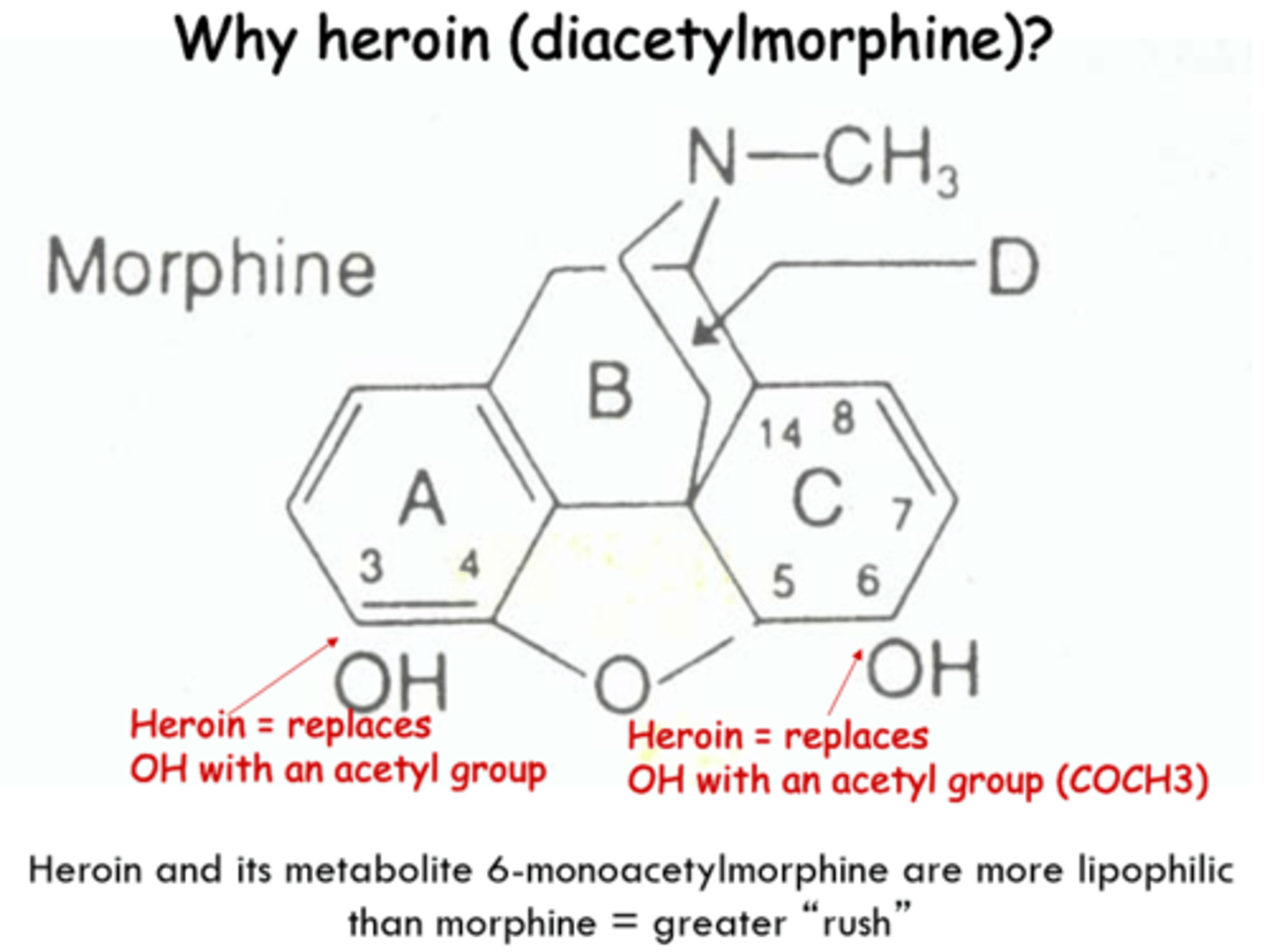
Heroin
Diacetylmorphine
- diacetyl derivative of morphine
- in body --> deacetylated to morphine
- replace OH with acetyl group on morphine --> heroin
Morphine metabolites
- M3G, M6G
Heroin metabolite
- 6-monoacetylmorphine
- penetrates brain more = lipophilic
- marker for heroin use in forensics
Pharmacological effects of opioids
Analgesia
- major use
Euphoria
- contributes to addiction
Impaired cough reflex
- anti-tussive
Constipation
- anti-diarrhoeal
N&V
Tolerance and dependence
Respiratory depression
Heroin MOA
Converted to morphine in the body
Acts on mu receptors
Needle syringe program
Provides sterile equipment to prevent blood-borne viruses
Injecting drug users major mode of HIV transmission
Fentanyl
80-100x more potent as morphine
IV drug users remove fentanyl from patches to inject
Major killer in US
Methamphetamine
Synthetic homologue of amphetamine
- highly addictive
MOA
- release of DA
- blocks monoamine transporters
- can last several hours (long t1/2)
Pharmacological effects
- euphoria, increased alertness
- increased energy, libido
- appetite suppressant
ADRs
- increased HR, breathing
- hypertension
- irregular body temperature
- cognitive and emotional changes
Meth long term ADRs
Meth mouth
- dry mouth
- tooth decay
- teeth grinding
Addiction
Overdose risk even at low doses from cardiac failure
Neurotoxicity
- long-term emotional and cognitive impairments
- due to damage to DA and 5HT neurons and transporters
- loss of gray matter
- altered BBB
History of cocaine use
Derived from coca plant where its leaves were chewed
Initially used a local anaesthetic, in Coca-Cola
Increasing lifetime use
Cocaine
Often used in binges, followed by severe crash with intense depression, lethargy and hunger
MOA
- inhibits NA and 5HT transporters
- blocks DA reuptake transporter --> more DA in synapse
Pharmacological effects
- euphoria, appetite suppressant
- increased alertness
- confidence
- increased HR, BP
- local anaesthesia
ADRs of repeated use
- eating and sleeping disorders
- sexual dysfunction
- kidney failure
- convulsions
Cocaine side effects
Low purity --> unknown potentially toxic fillers
Damage to nasal membranes if snorted
Tissue damage due to vasoconstriction when injected
Chronic use can lead to
- psychotic episodes
- heart failure
Excessive dosages
- tremors, convulsions
- respiratory depression
- cardiac arrhythmias
History of MDMA
First used as appetite suppressant and aid psychotherapy
Increasing lifetime use
MDMA
MOA
- binds to 5HT transporter, blocks reuptake of 5HT
--> increases 5HT release
- inhibits VMAT, MAO
- increase oxytocin
ADRs
- acute psychosis
- panic attacks
- insomnia
- involuntary teeth clenching
- seizures
Role of 5HT
Roles
- hallucination, mood
- aggression, impulsivity
- eating, sleeping
- arousal, sensory and pain transmission
Does MDMA cause brain damage?
Long term 5HT neurotoxicity
- in animals, causes reduction in 5HT receptors and transporters
- axonal damage
Elevated body temperature accelerate neuronal damage
5HT depletion with heavy use
--> impulsivity, depression, memory loss
Cannabis use
Use has increased among older people
Top indications
- pain
- anxiety
- depression
- sleep disorder
- PTSD
Main way accessing cannabis
- least with prescription
- greatest with dealer
WHO recommendations of cannabis
Cannabis and cannabis resin to be deleted from prohibition schedule
Pure CBD is unscheduled
THC
Main intoxicant
- CB1/CB2 receptor partial agonist
- moderate affinity
CBD
Non-intoxicant
- anticonvulsant, anxiolytic
- antipsychotic
- anti-inflammatory, wakefulness
Cannabis effects
The good
- euphoria
- appetite stimulation
- analgesia
The bad
- anxiety
- memory impairment
- sedation
The ugly
- schizophrenia
- addiction
Cannabis MOA
CB1
- found in CNS and periphery
CB2
- found in periphery (immune cells)
THC binds to CB1 receptors
--> psychotropic effects
Endocannabinoids
Naturally occurring cannabis found in body
- anandamide
- 2AG
Act as messengers in CNS