Archeology and Early Humans (History 11)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
How is information gathered when there is no written history?
Through archaeological findings (artifacts and fossils)

What is pre-history
time before writing
When did homonids begin using tools?
2.5 million years ago

Paleolithic Era
(Old Stone Age)
2 million - 10,000 y.a.

Neolithic Era
(New Stone Age)
10,000 - 4,000 BCE
- Advancements in clothing, art, tools, agriculture, and villages

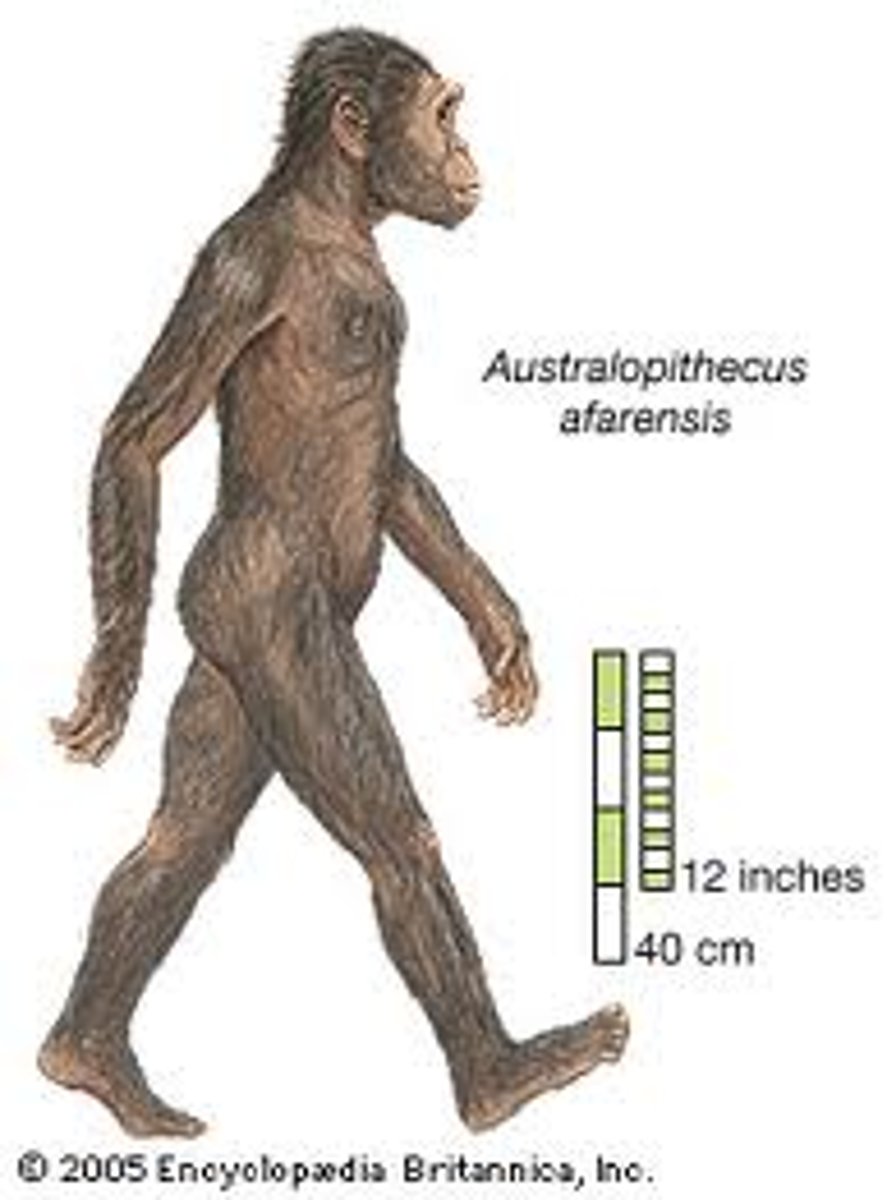
Australopithecus
(Lucy)
4 million y.a.
- Was the first biped (walking on two legs)
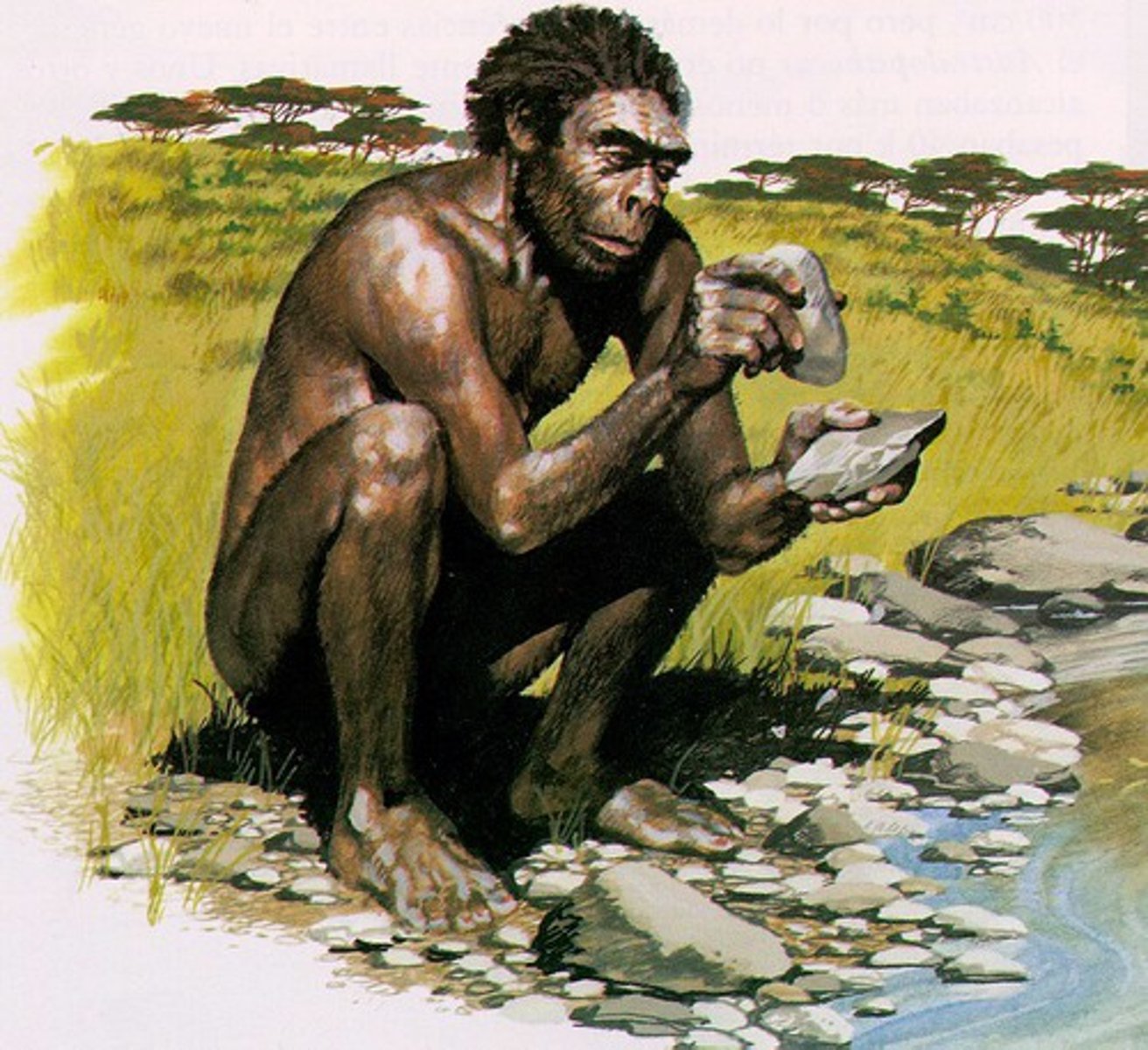
Homo Habilis
(Handy Man)
2 million y.a.
- Made tools, no fire or clothing
- Brain 2/3 of normal human

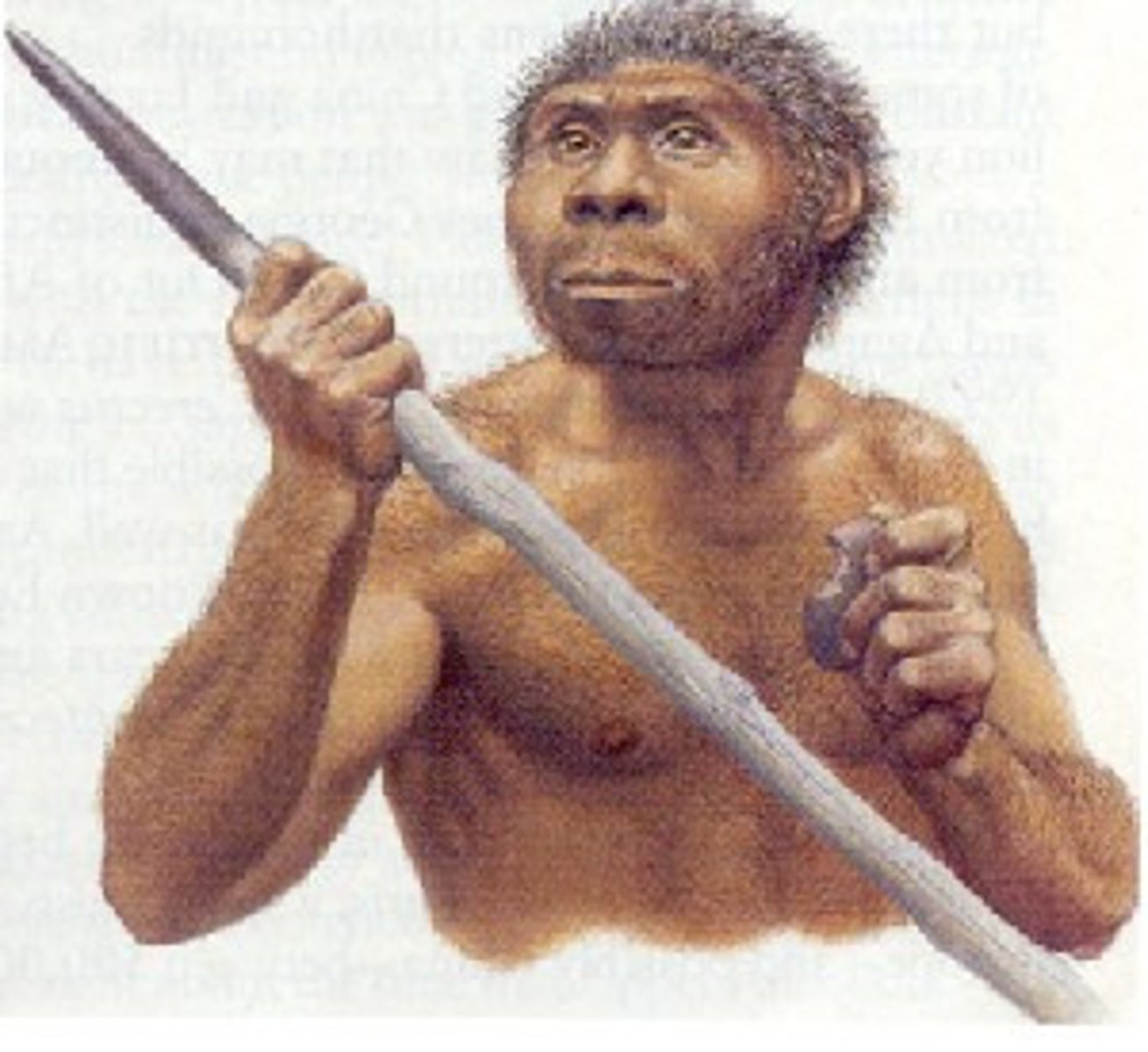
Homo Erectus
(Upright Man)
1.7 million y.a. (Africa)
- Used fire to cook animals
- More complex tools
- Larger brain

Homo Sapien
(The Thinker & Cro-Magnon)
400,000 y.a. (evolved from Erectus)
Complex society, language, tools, weapons, jewelry, art, clothing, etc.

What is the order of the homonids?
Australopithicus (Lucy), Homo Habilis (Handy man), Homo Erectus (Upright Man), Homo Sapien (The Thinker), Neanderthal
Neanderthal
100,000 y.a. (In Europe)
- Type of early modern human
- Strong 💪

What are the three parts of the Stone Age
Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic
What are some firsts from the Homo Erectus?
- First to create fire
- First to migrate into Europe and Asia
How did we know that Homo Habilis was a homonid?
Brain size and teeth

What did Homo Sapiens create?
Spoken language and complex tools
Cro-Magnons meaning
The name of the cave where Homo Sapiens were discovered.
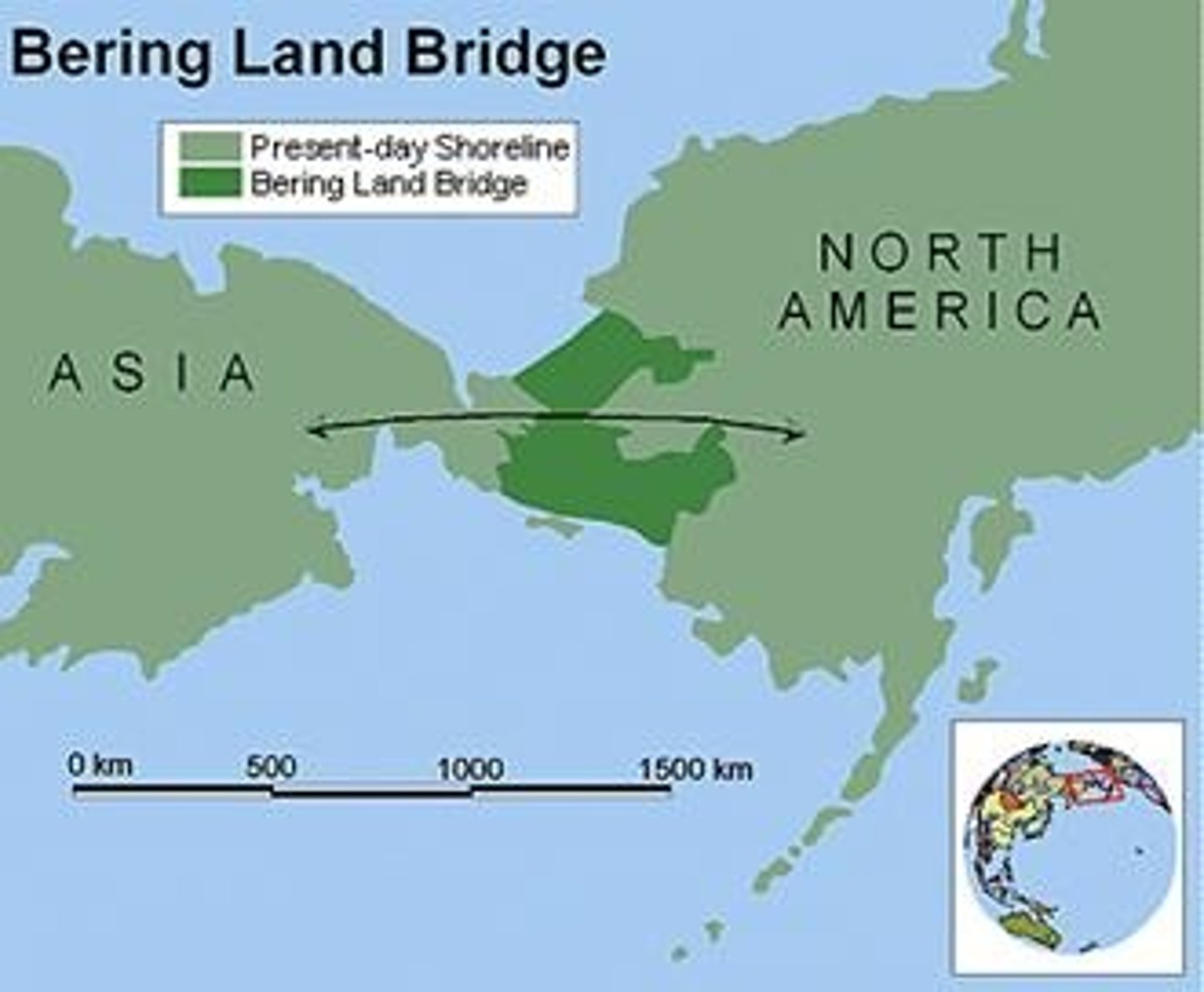
When did Homo Sapiens move to Americas?
30,000 y.a. across the Bering Strait
Between what years did Neanderthals exist?
230,000 to 30,000 y.a.
What are some theories to the disappearance of Neanderthals?
Modern humans conquered them, new diseases, inbred with modern humans, couldn't compete with modern humans.
When did modern humans move to Europe?
40,000 y.a.
The Great Leap Forward
35,000 y.a.
Beginning of innovative behavior and the creation and innovation of many art and culture pieces
Innovations of the Great Leap Forward
- Complex weapons and tool
- Trade for raw materials and ornaments
- Artistic objects for beauty and religion
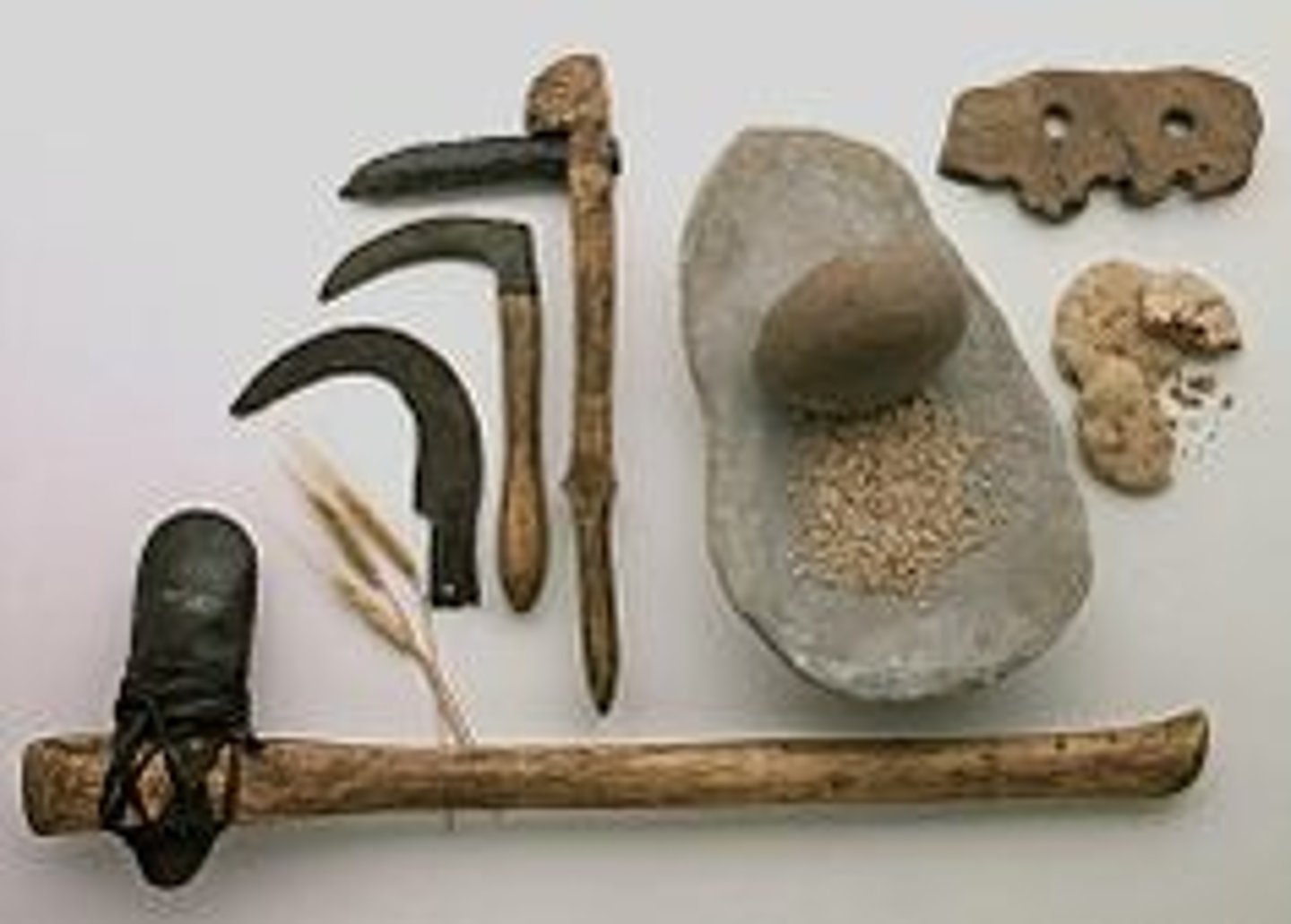

Paleolithic Religion
- Burials had jewellery and spears
- Afterlife?
How did we move to the Neolithic?
It got warmer
Neolithic Age
- Agriculture (end of stone age, so population increased)
- Permanent towns and cities (Jericho)
- Trade by the barter system
- Development of Hierarchy, jobs
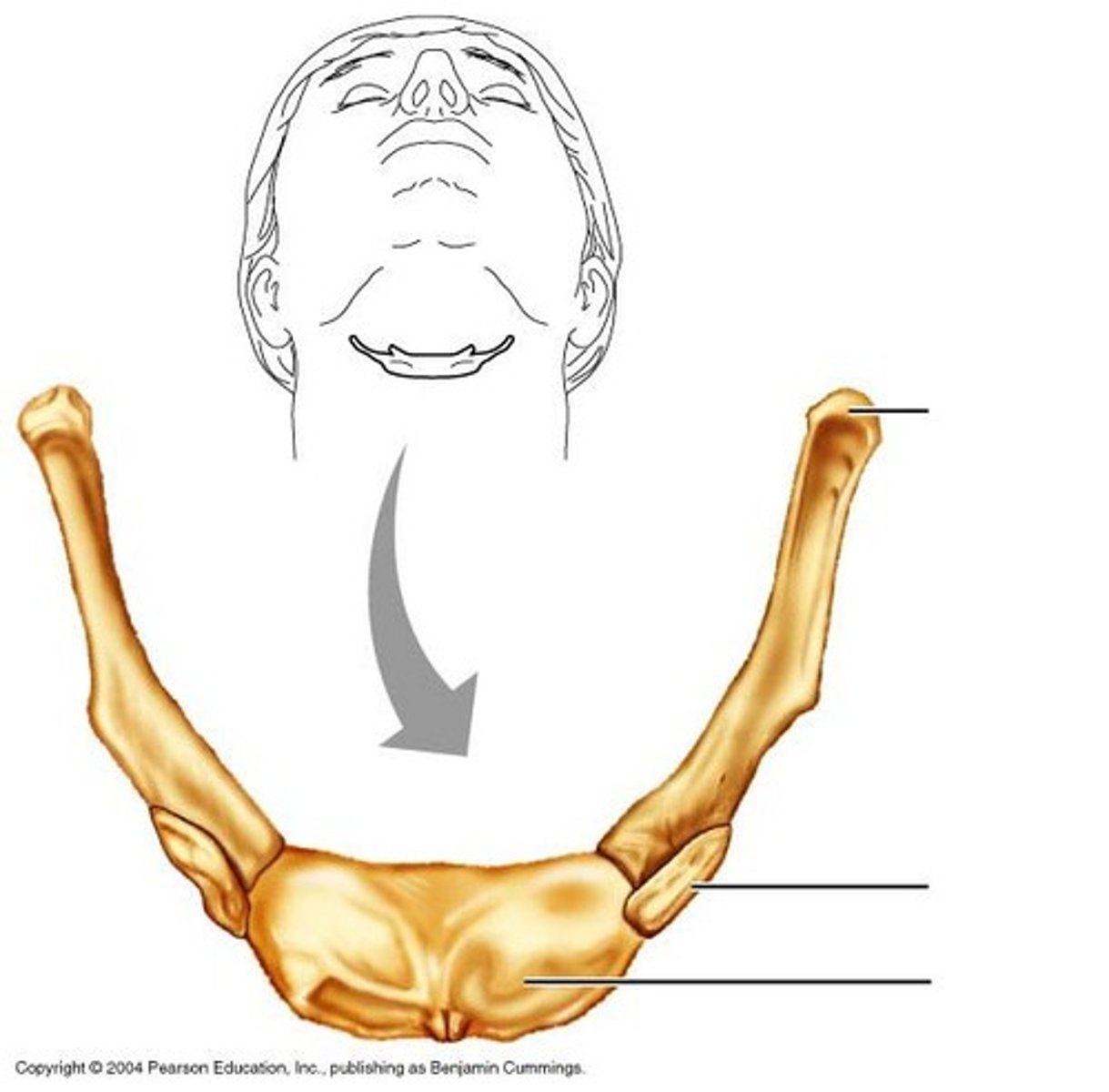
Hyoid Bone
- Fossilizes and can show whether people in the Stone Age could or not could speak
- 60,000 years ago, a Neanderthal hyoid bone was indistinguishable from our own and shows us that they had the ability to speak just like us, not that they did.
Fire
- Homo erectus first made it 1.4 million years ago by rubbing sticks
- Allowed them to move to colder regions
- No more raw food
- Made weapons more efficient and better for hunting

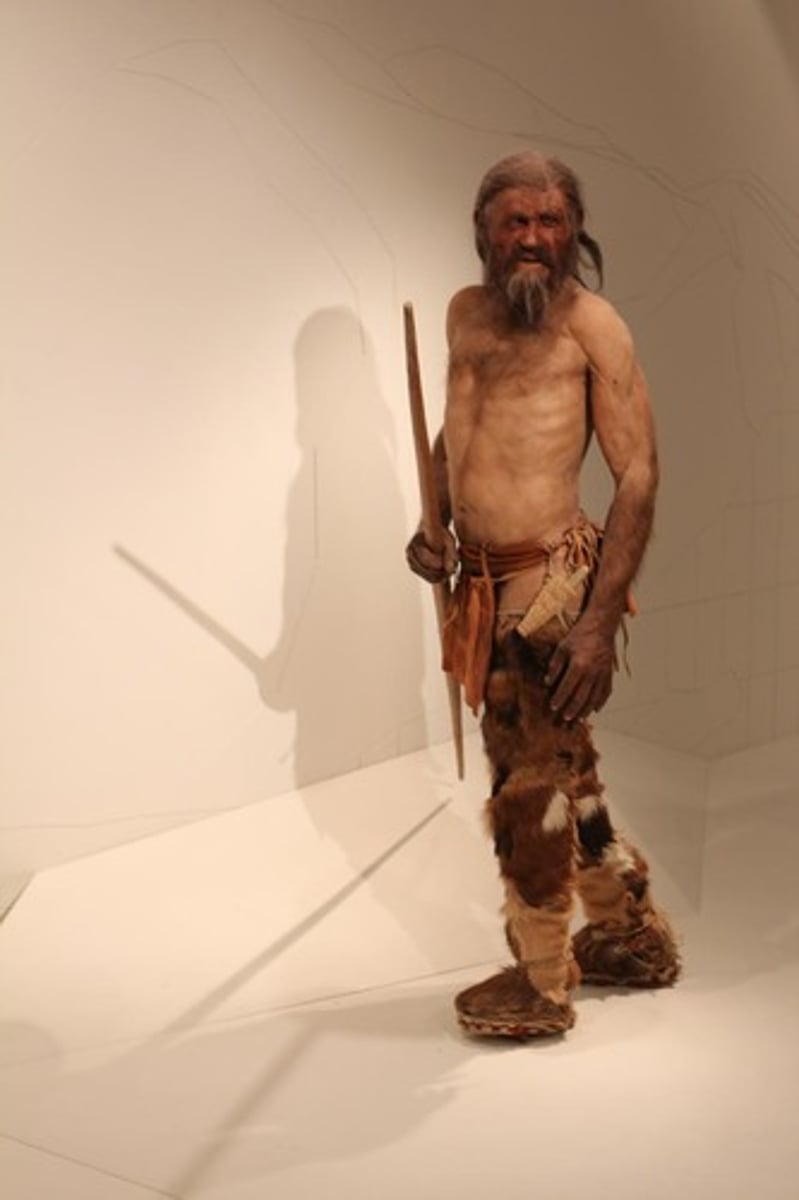
Where was Otzi found?
European Alps
How long ago did Otzi die?
5,300 years ago.
What was found in Otzi's back?
An arrowhead but no body of the arrow. This shows that he was murdered by somebody, but they did not want to be identified and so they took out the arrow and also did not steal anything from him.
Why is the Copper Axe for Otzi so significant?
The copper axe is significant since it was believed at this time that people in the Neolithic age could not smelt copper and create tools from it, but this finding showed that they were way more advanced than we thought.
What did the pollen in Otzi show?
Trees in the upper mountain are hornbeam, and the trees in the lower mountain are conifer.
He was found to have a layer of hornbeam, a layer of conifer, and then another layer of hornbeam in his stomach. This shows that he was on the run soon before his death and went up and down the mountain several times.
What does Otzi's last meal tell us?
His last meal was a blend of ibex meat, Einkorn, and fat which shows that he was in a small farming community but still did hunting.
What diseases did Otzi have?
He had arthritis, lactose intolerance, sclerosis, lyme disease which caused arthritis.

What does Otzi's last meal tell us about his death?
His last meal tells us that he was not prepared to die and he could have been killed by someone he trusted to be around. This is because his last meal was quite large and not something someone would eat before going off to die.
Assemblage
A collection of artifacts from a given site
Artifacts
object made by human beings, either hand-made or mass-produced
Sample
A controlled collection of bone, seeds, shells
Features
structures including remains of dwellings
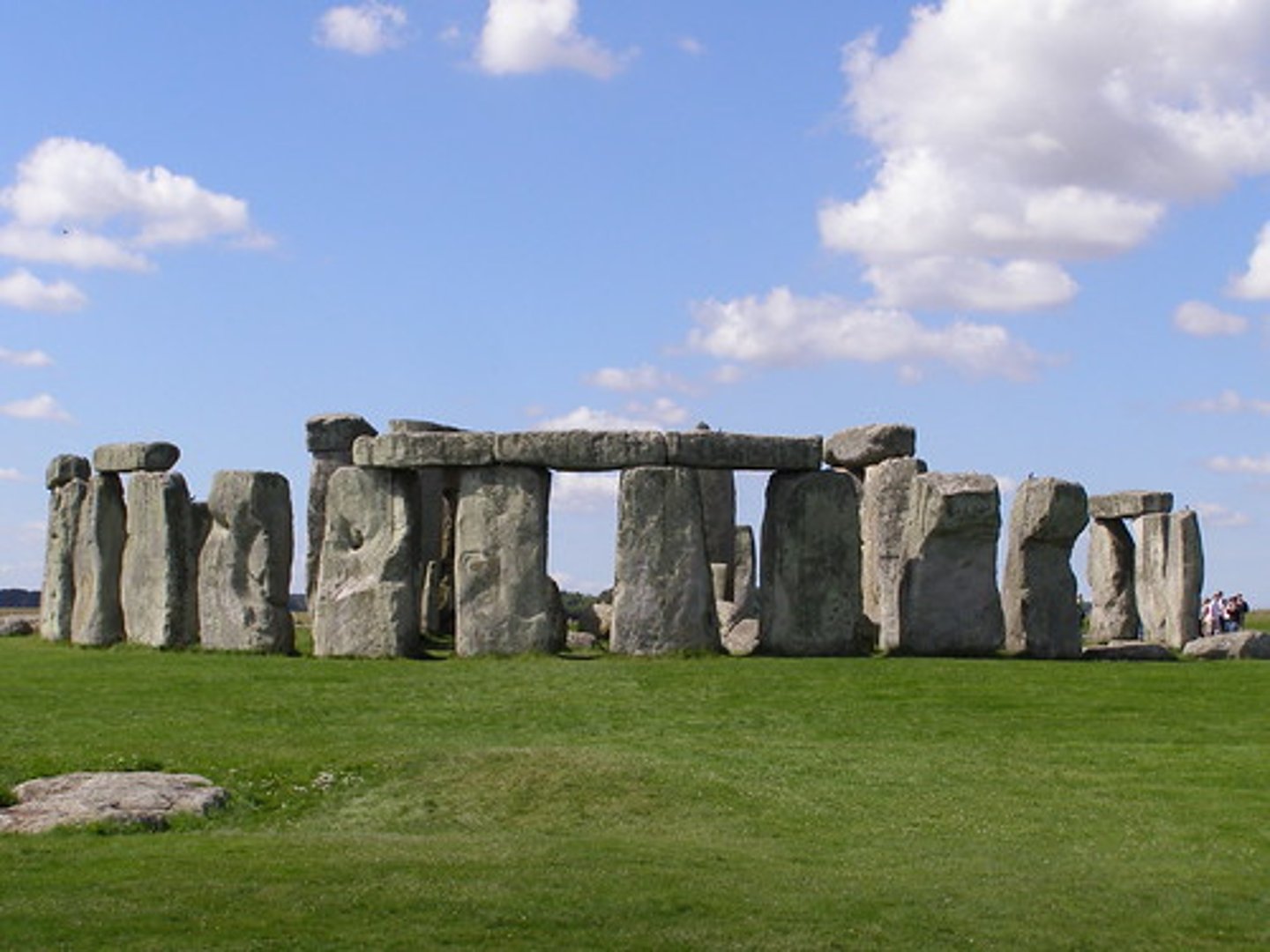

What conditions should exist for discoveries to be preserved?
Hot and dry or cold and dry climates

First step of archaeology
Establish a site, must have importance or reason for investigation
After establishing a site, what must be done
A map and grid must be created with scale dimensions
Excavation
Excavate the deposits and make sure they're on your grid

Interpret your evidence
Connect past information with current obtained information and make a sequence of events and build a model of the site

What is Stratigraphy
study of layered rock successions and the concept that the farther down the discovery, the older it is

Carbon-14 Dating/Radiocarbon
A dating system based on the decay of C-14 in an organism from the past. The half life of C-14 is 5730 years. Smart big brained scientists have found a way to use the ratio of C-14 atoms in Carbon in an organism to date organisms from the past.
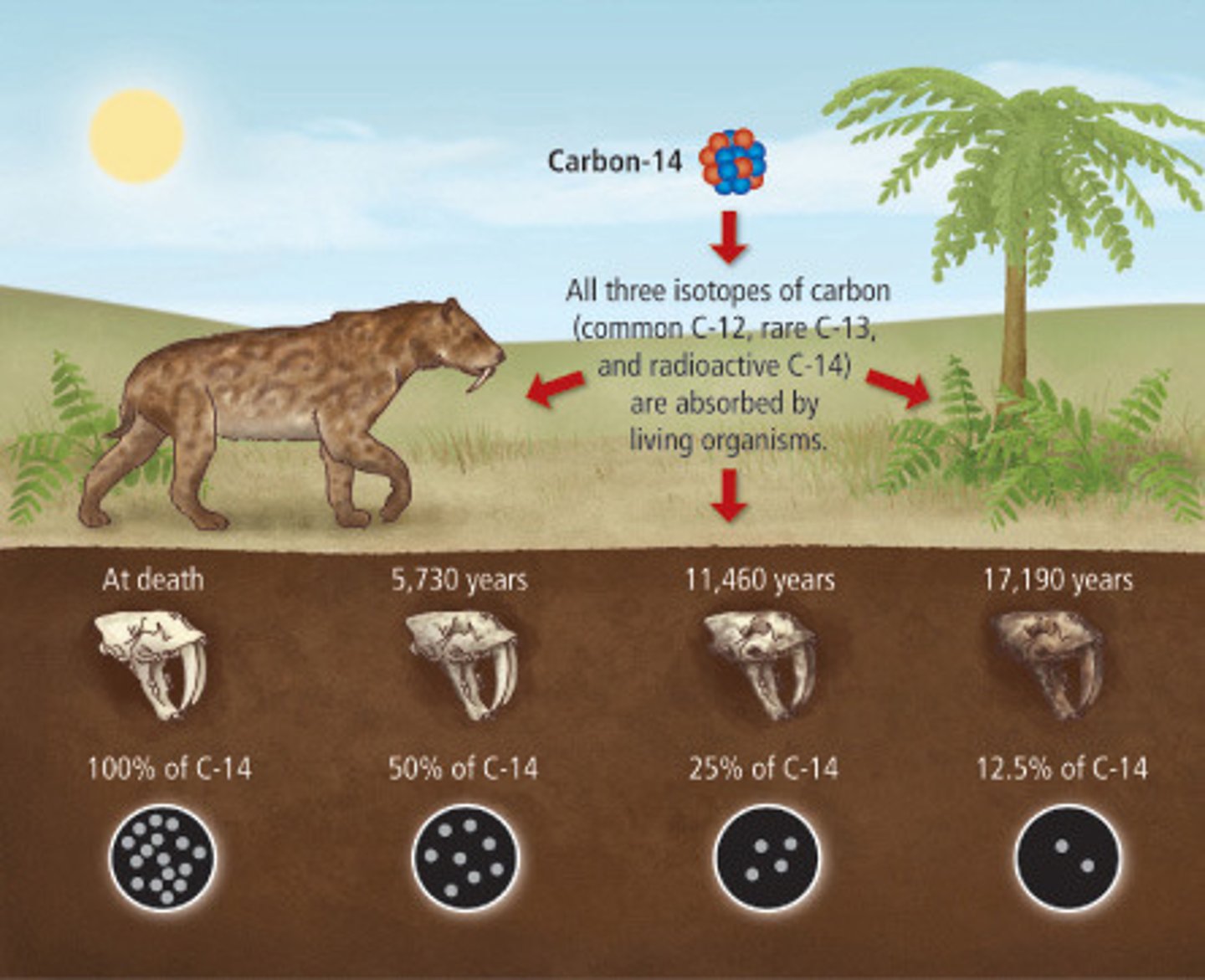
List reasons why archaeology is not perfect
Limited sources due to tainting and destruction from climate and humans
Government in power may limit archaeological finds or interpretations
Personal ambiitions or bias may taint the interpretations of artifacts
Over-excitement may impair judgement and interpretation
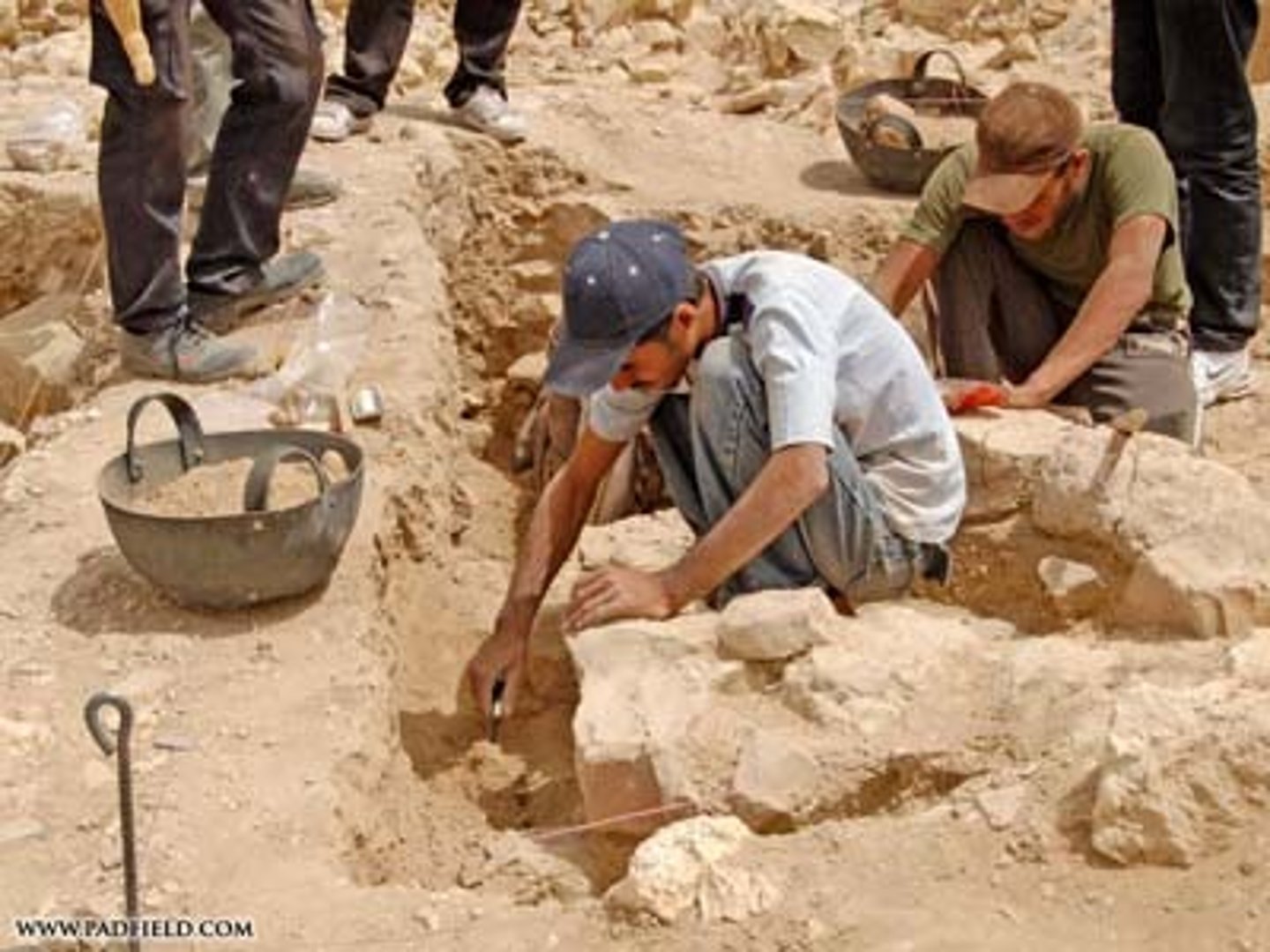

What was life in the stone age generally like?
- They lived in small groups and were nomadic
- They survived by hunting and gathering
Civilization
A settled society

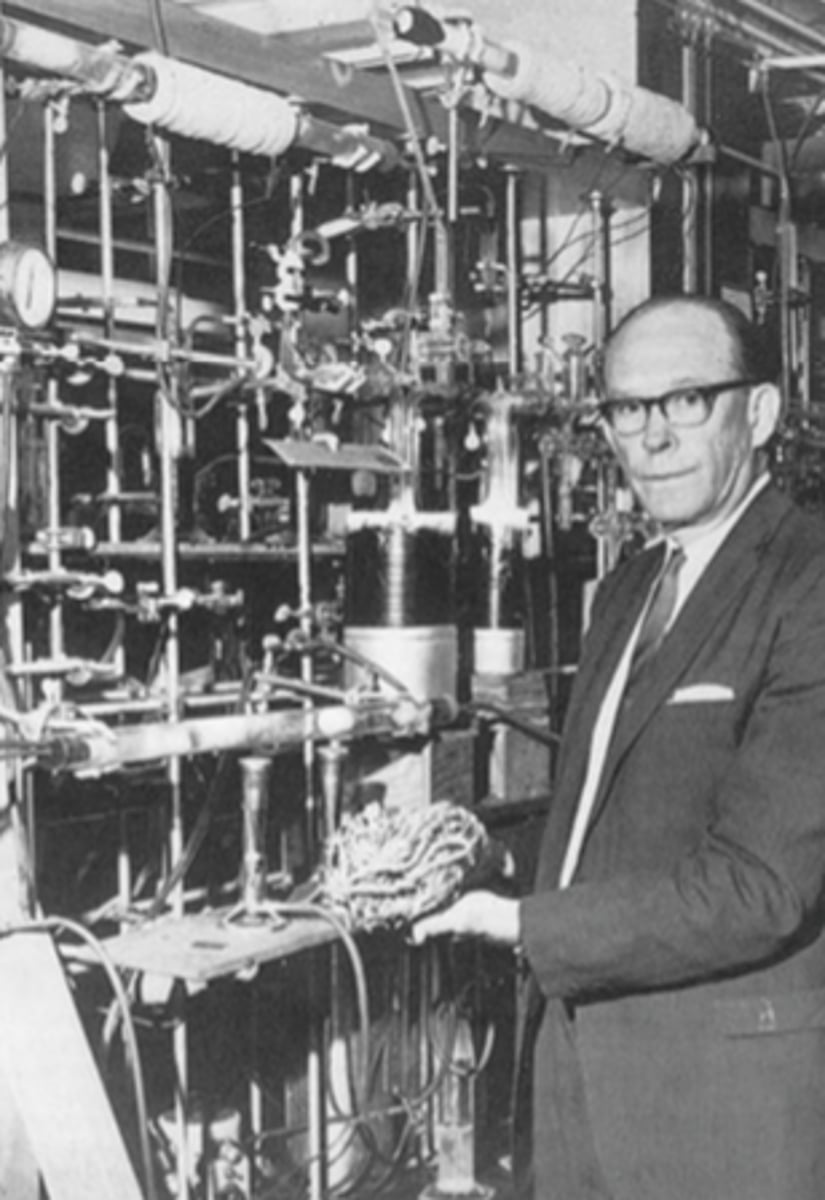
Who invented C-14 dating?
1948 - Willard R. Libby

What did Richard Leakey discover?
He discovered the most complete skeleton of a 12 year old Homo Erectus.

How did they find out Otzi's cause of death?
They found an arrowhead in his back which stroke an artery.

Why did they have trouble extracting the arrowhead?
It was blocked by tissue
Rise Factors to Civilization
Trade, Patriarchy, Hierarchy, Centralized Government, Excess food, Arts and Culture, Religion, Writing, Cities
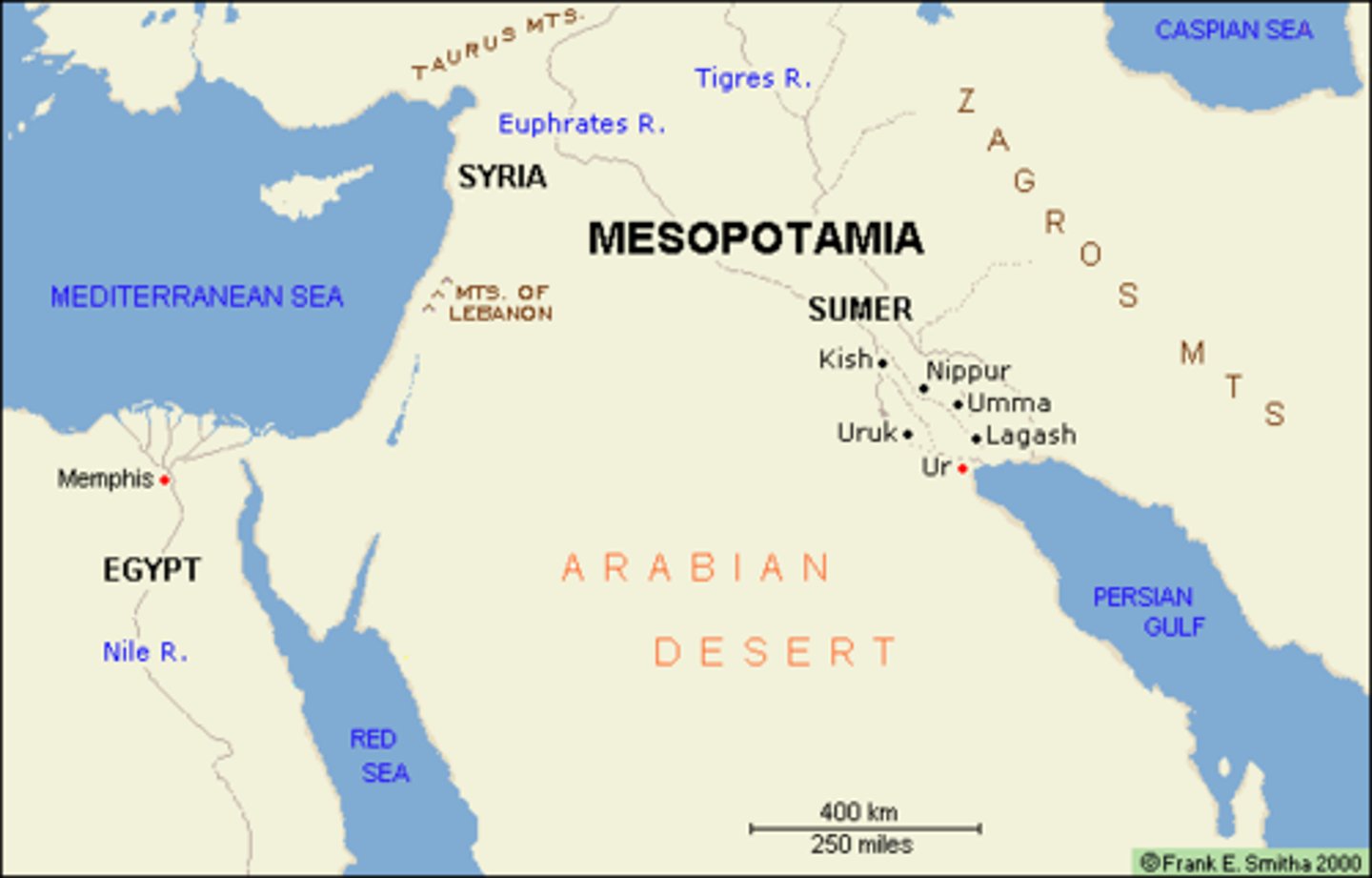
Importance of Water to civilization
Water is needed to humans and there must be an abundance of it wherever humans live. This makes it so many of the cities and civilizations from early history are near water, and cities nowadays still follow this trend.
