
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
solubility
hydrophobic molecules
fatty acids and their derivatives are insoluble in water
triglycerols/triglycerides and waxes
used as energy stores
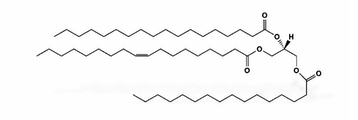
phospholipids
found in membranes
used as structural molecules
2 ethyl chains
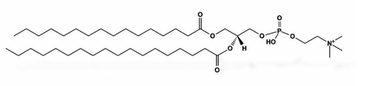
other lipids
steroids, act as signals, co-factors (vitamin E,K) and pigments (carotene, chlorophyll)
carotene:
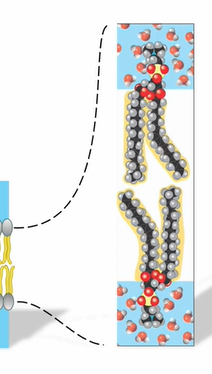
hydrophobic tails of fatty acids
can be made of 4-36 carbons in length (always an even number)
head group: made of a carboxylic acid
saturated and unsaturated varieties
unsaturated; kinks in the chain due to double C=C bonds
stores of energy; triglycerols/triglycerides
glycerol linked by an ester bond to 3 fatty acids
triglyceride made of glycerol moiety
each of the hydroxyls in glycerol in glycerol will be linked to an aliphatic tail to form the tri
saturated fats
fully hydrogenated
no double bonds in the carbon backbone
close packing molecules
often found in mammals
unsaturated fats
one or more fouble bonds in teh carbon backbone
double bonds result in kinks in teh fatty acid ‘tail’
close packing is hindered by the kinks
typically stored in plants
phospholipids
structural lipids
composed of a glycerol molecule linked to 2 fatty acid molecules and a phosphate group
this structure provides them with amphipathic properties ( hydrophilic phosphate head; polar, hydrophobic fatty acid tail; non-polar)
membranes
Phospholipids arranged into a bilayer
Hydrophobic tails shielded from water
Hydrophilic heads exposed to water
Major component: Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
Membranes perform vital functions in cells
membranes
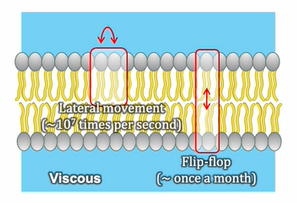
fluid structures
Phospholipid molecules are not covalently linked together in the membrane
Lipid molecules are in constant lateral motion
Unsaturated phospholipids enhance membrane fluidity
Saturated phospholipids are closely packed and less fluid due to the lack of double bonds
The ratio of saturated : unsaturated lipid determines the membrane fluidity and can change with an organism's environment