Lec 4- Genetic Variability
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
What must be true for evolution by natural
selection to take place?
I. Heritable variation must exist in
population.
II. A source of new DNA mutations.
III. Some phenotypes reproduce more
than others.
IV. Sexual reproduction.
Heritable variation must exist in
population. Some phenotypes reproduce more
than others.
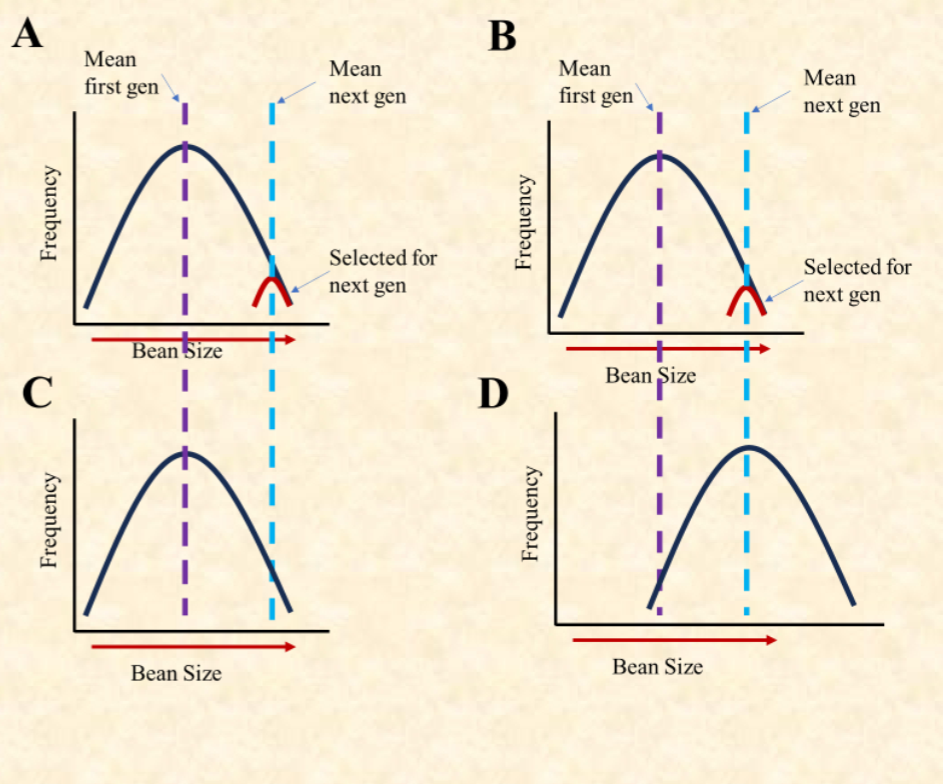
Why doesn’t the second generation
of beans from group A change mean
size?
A. Those beans are not subject
to evolution
B. This trait does not vary in a
heritable way.
C. Their trait is too complex
D. There was no selective
reproductive advantage
E. Beans don’t evolve, they
are content to
be-in the moment
10
This trait does not vary in a
heritable way.
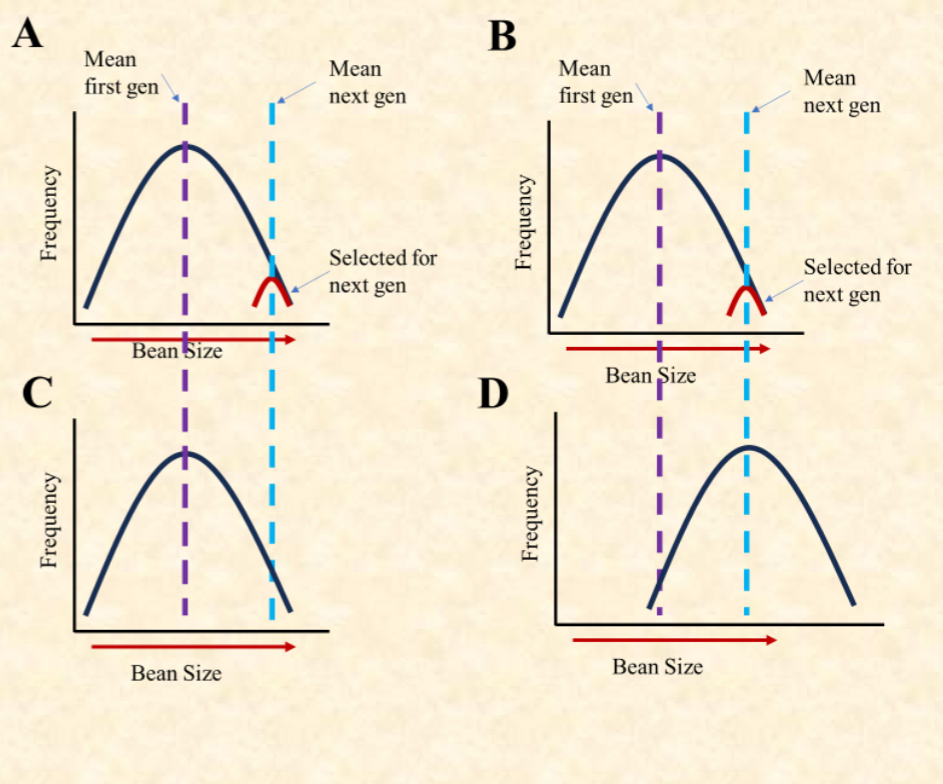
What happened between B and D?
A. Artificial selection
B. Natural selection
C. Genetic drift (random loss of
alleles)
D. Gene flow (new alleles from
outbreeding)
Artificial selection
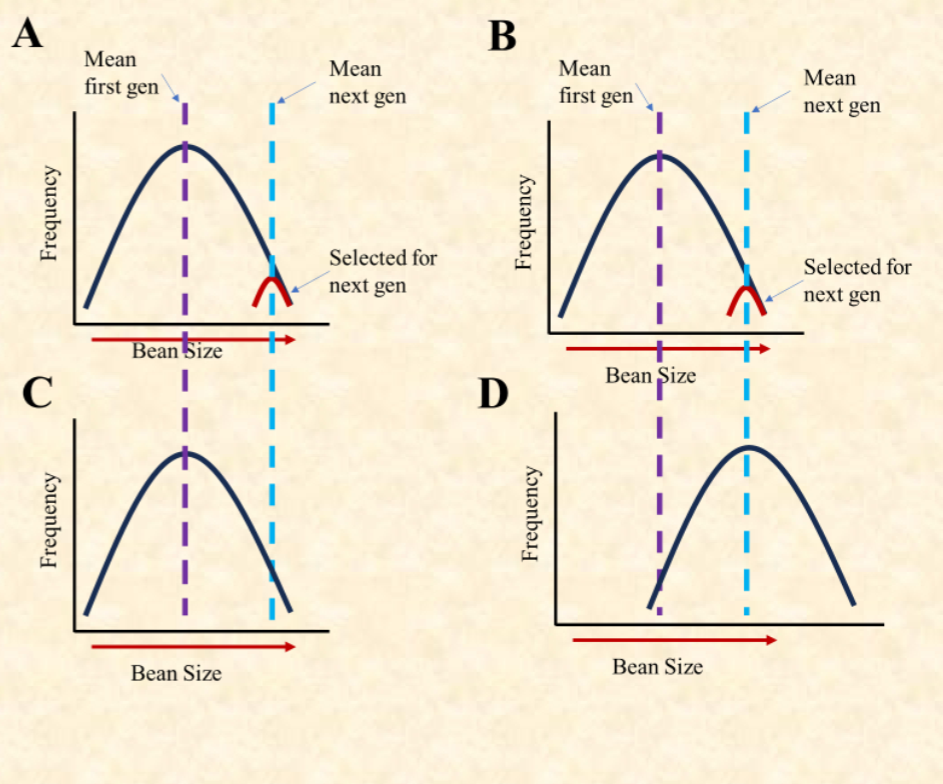
How can there be various sizes of A beans
when the trait isn’t heritable?
A. Somatic (non-germ line) mutations
B. Differences in growth conditions
C. Some beans were more fit than others
D. Experimental error
Differences in growth conditions
How can we measure the genetic
diversity of a population?
A. Assess how many genes there are in the
population.
B. See how many chromosomes the organism
has.
C. See how many different alleles there are
for all the genes in the population.
D. Assess phenotypic diversity in the
population
E. Ask them
See how many different alleles there are
for all the genes in the population.