LU 3.2b Intestinal & Liver Parasites II
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the general characteristics of helminths?
it is macroscopic in size for adult, often visible to naked eye
multicellular, bilaterally symmetrical, elongated round organisms
What are the two groups of helminths of medical importance to humans?
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)
Phylum Platyhelminthes (Cestodes and Trematodes)
What are the classification of trematodes?
Blood trematode
Liver trematode
Intestinal trematode
Lung trematode
What are the general differences between nematodes, cestodes and trematodes?
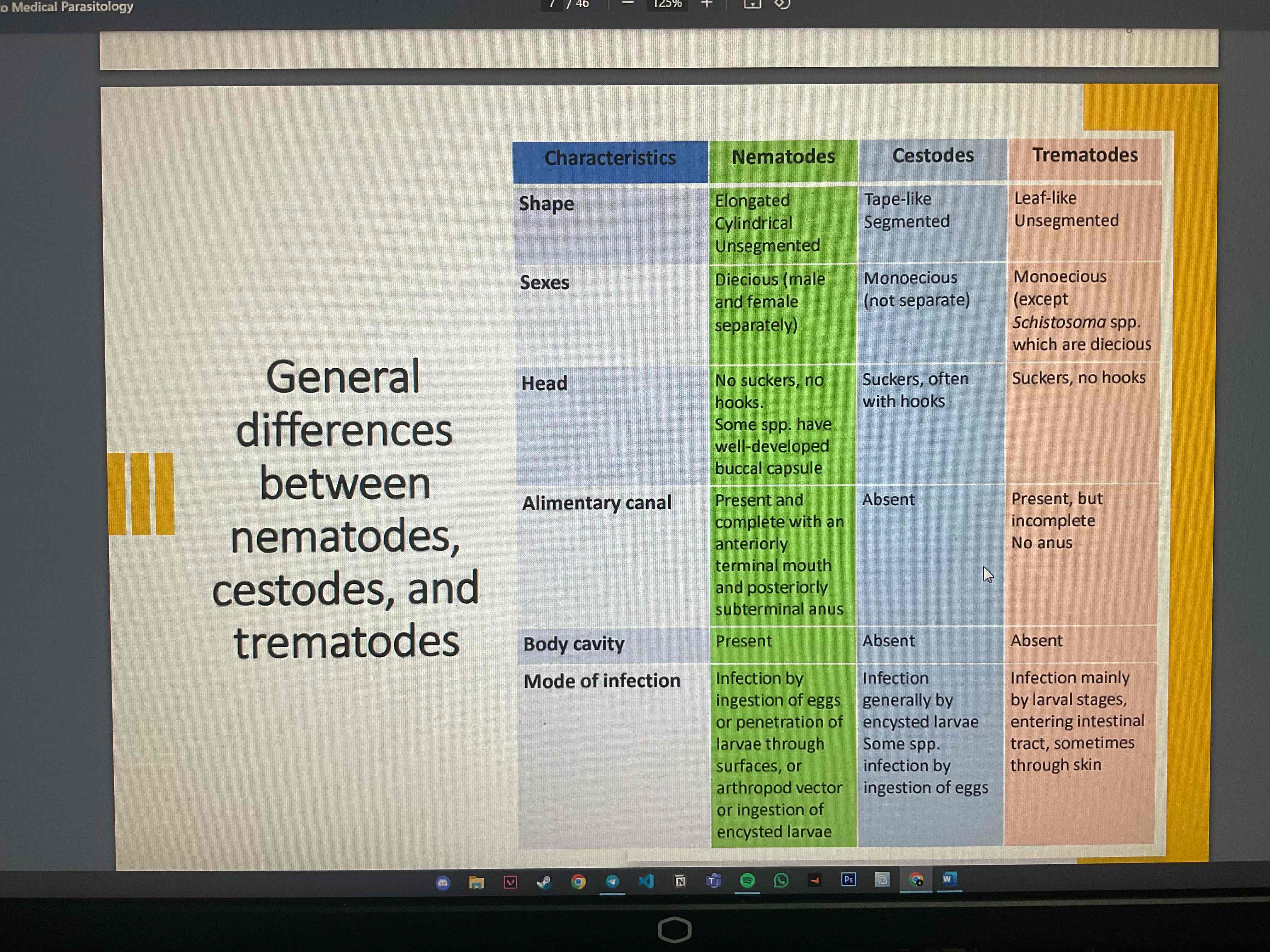
What are the general characteristics of trematode (Flukes) ?
Unsegmented leaf-shaped worms, no body cavity
simple digestive system
excretory system is bilaterally symmetrical
reproductive system is highly developed system
Explain the life cycle of trematodes
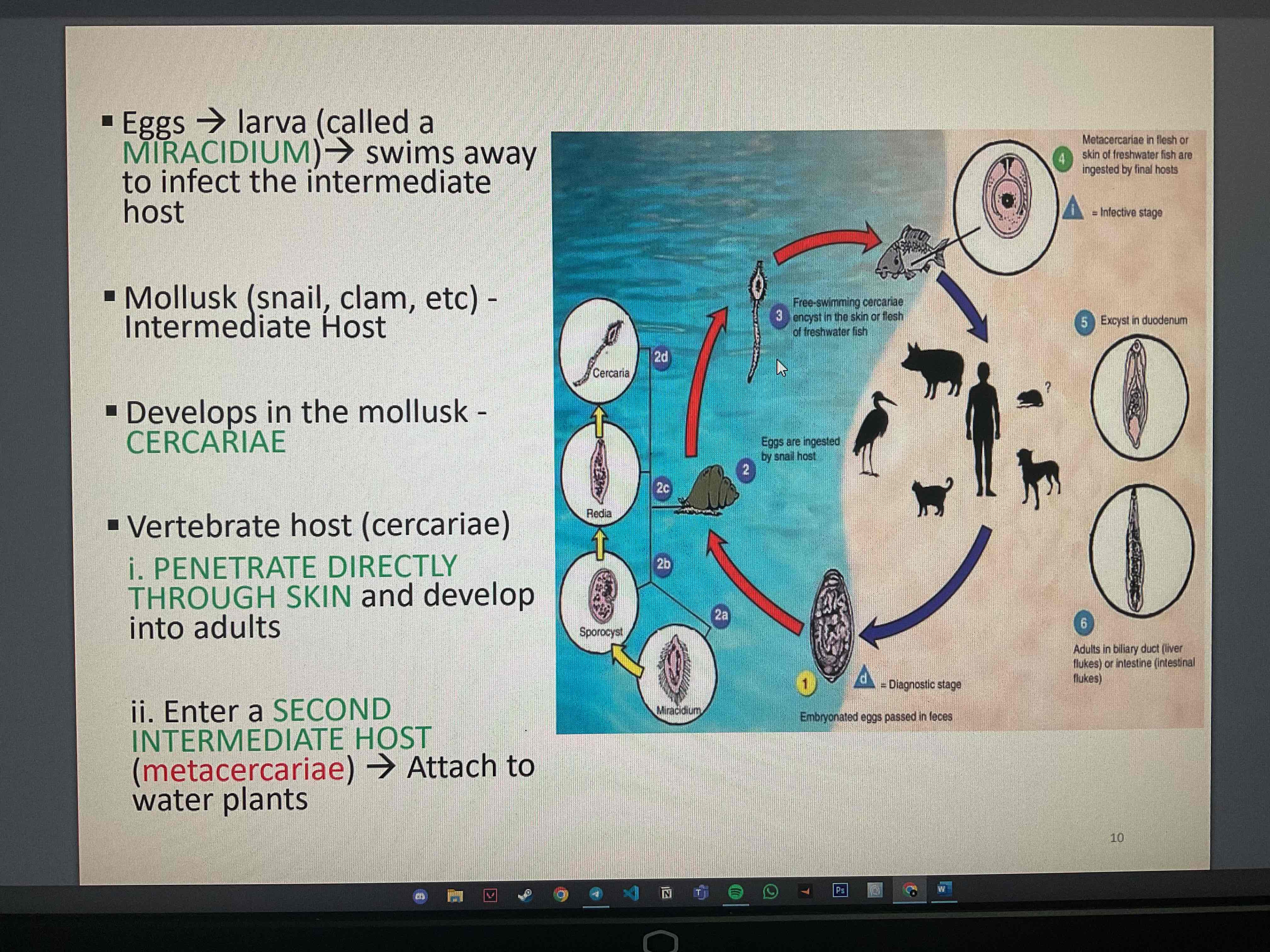
What are the mechanism of transmission of trematode?
Cercariae : free swimming larvae
Metacercariae : water plants, fish
Explain the general characteristics of Intestinal Trematode : Fasciolopsis buski
is is the largest trematode infecting human
diseases : fasiolopsiasis
definitve host : human & pig
transmission : consumption of under-cooked water plants containing metacercariae
Explain the adult and eggs stage of fasciolopsis buski
Adult : i) fleshly dark red and elongated oval fluke ii) live in small intestine iii) life span about 1 year
Eggs : broadly ellipsoidal, operculated, light yellowish brown
Explain the mechanism of transmission of fasciolopsis buski
human become infected by ingesting waterplants containing metacercariae
after ingestion, metacercariae excyst in duodenum and attached to the intestinal wall
What are the clinical manisfestation/effects of fasciolopsis buski
Clinical manisfestations : heavy infections can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomitting and fever
Explain the general characteristics of liver trematode : Fasciola hepatica
it is large leaf-like fluke
brown to pale in colour
disease : fascioliasis
definitive host : humans, sheep, goats
transmission : consumption of under-cooked watercress containing metacercariae
Explain the general characteristics of adult and eggs of fasciola hepatica
Adult : i) large leaf-like fluke ii) brown to pale in colour iii) bilaterally symmetrical iv) life span about 10 years
Eggs : i) large, yellowish brown ii) thin and smooth surface shell
Explain the mechanism of transmission of fasciola hepatica
human become infected by ingesting metacercariae-contaminated vegetation
after ingestion, metacercariae excyst in duodenum and penetrate through intestinal wall into peritoneal cavity
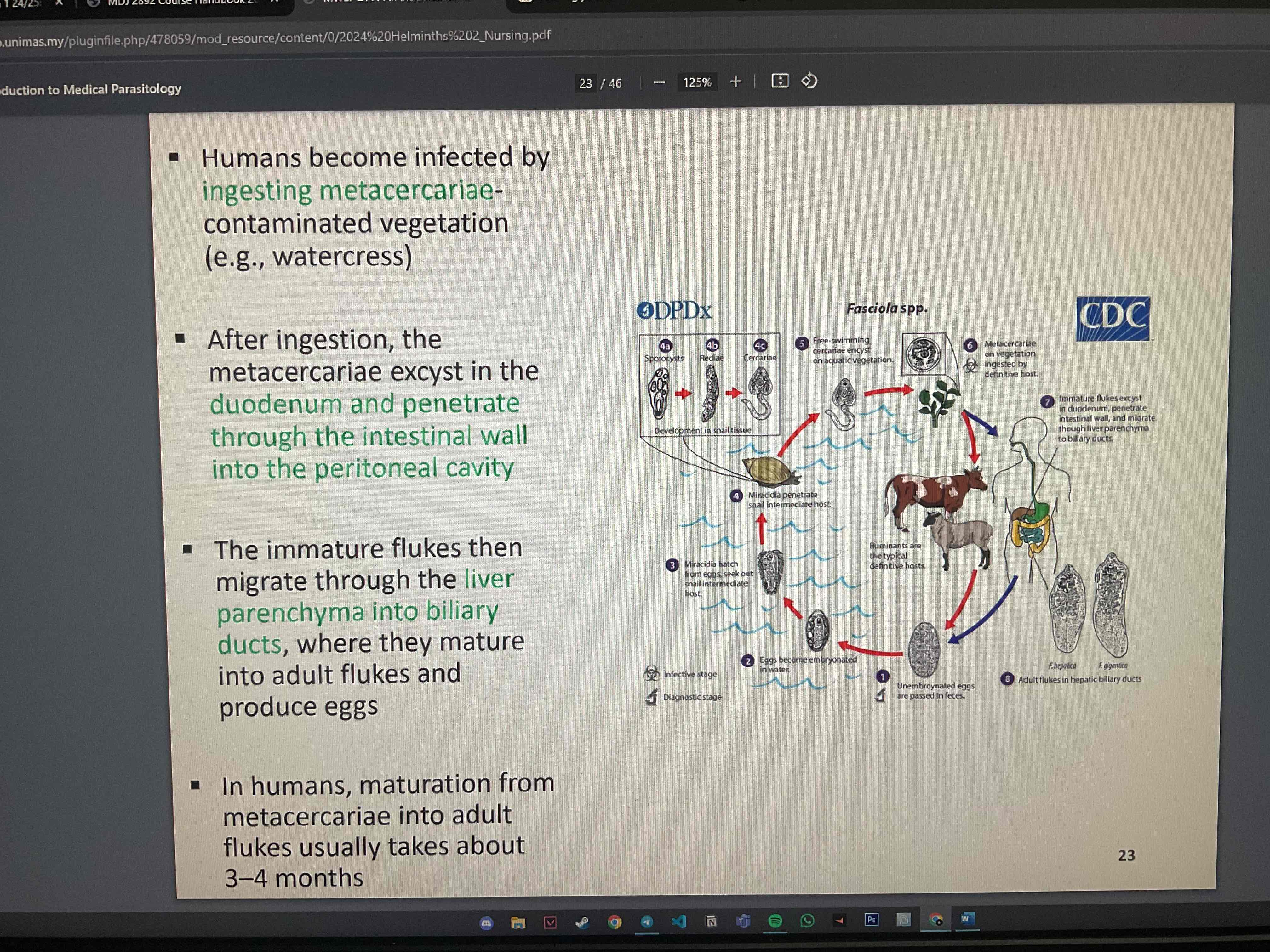
What are the clinical manisfestations/effects of fasciola hepatica during
early phase
chronic phase
Early phase : i) inflammation, tissue destruction, allergic reactions ii) nonspecific signs/ symptoms : abdominal pain, nausea, vomitting
Chronic phase : i) inflammation of bile ducts and also pancreas
What are the general characteristics of Liver Trematode : Fasciola gigantica?
it is the largest human liver trematode
more oblong with a longer posterior end than F. hepatica
pathology, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment and control and preventive measures are similar to F.hepatica
What are the general characteristics of liver trematode : Clonorchis sinensis?
important foodborne pathogen and cause of liver disease
Disease : clonorchiasis
transmission : ingestion of undercooked, salted, pickled or smoked freshwater fish containing metacercariae
Explain the general characteristics of adult and egg of Clonorchis sinensis
Adult : i) flattened and leaf-shaped fluke ii) the body is slightly elongated and slender iii) 2 large branches of testes iv) lifespan about 25-30 years
Eggs : i) small and oval in shape ii) yellowish brown
Explain the mechanism of transmission of Clonorchis sinensis
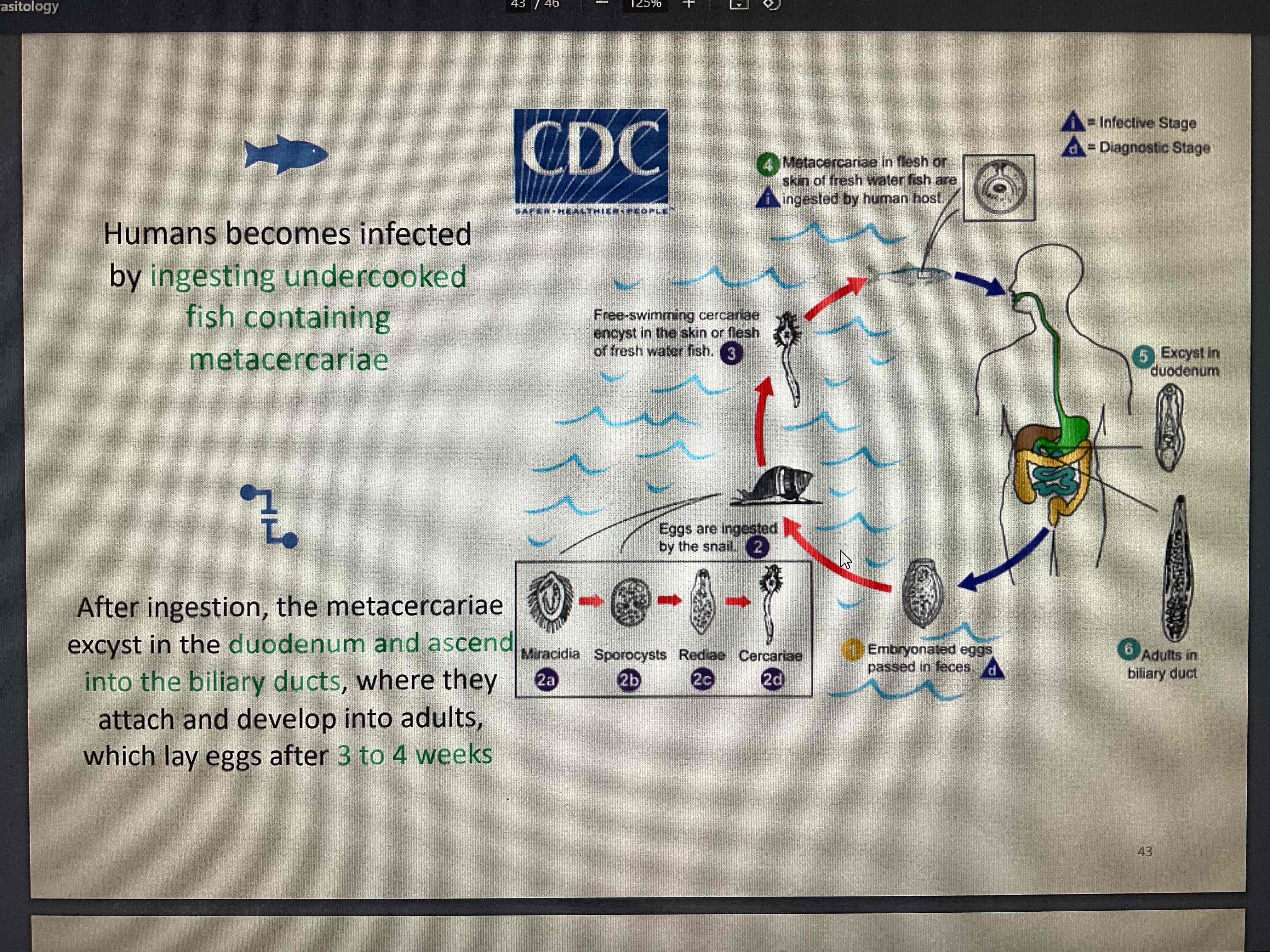
human become infected by ingesting undercooked, salted, pickled, or smoked freshwater fish containing metacercariae
after ingestion, metacercariae excyst in duodenum and ascend into the biliary tract
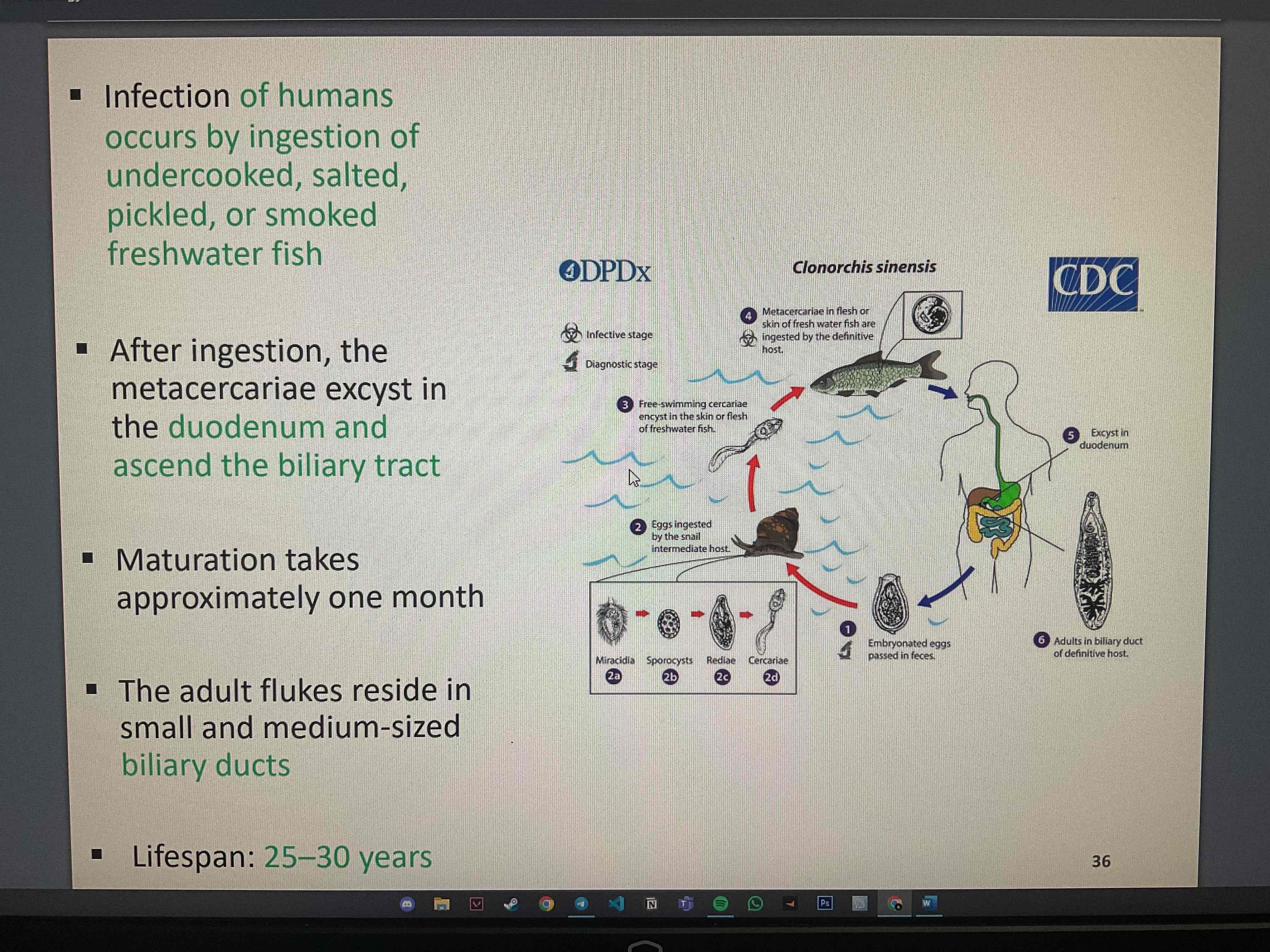
What are the clinical manisfestations/effects & s/s of clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrine
cause mechanical injury and bile duct obstruction
symptoms : fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, diarrhea
severe chronic disease results in obstructive jaundice
What are the general characteristics of Liver Trematode : Opisthorchis viverrine?
adults live in biliary and pancreatic ducts
disease : opisthorchiasis
definitive host : humans and other mammals
transmission : ingesting undercooked fish containing metacercariae
Explain the mechanism of transmission of Opisthorchis viverrine
human become infected by ingesting undercooked fish containing metacercariae
after ingestion, metacercariae excyst in duodenum and ascend into the biliary tract
What are the diagnosis for all the trematodes?
Identification of eggs in the feces
What are the treatment for all trematode?
Praziquantel
What are the prevention and control for all types of the trematodes?
Fasciola gigantica & Fasciola hepatica & Fasciolopsis buski : Avoid eating raw water vegetables
Opisthorchis viverrine & Clonorchis sinensis: Avoid from eating raw uncooked fish