b3 - organism level systems (copy)
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
what does the centeral nervous system consist of
brain and spinal cord
what are the central nervous systems main functions
take in sensory information,
process information
send out orders to the rest of the body
what does the peripheral nervous system consist of
nuerones, receptors and effectors
what is the peripheral nerous systems main functions
collecting information
sending it to the cns
acting on instructions from the cns
whats a nuerone
nerve cells which are adpated to carry electrical impulses from one place to another
whats a stimulus
a change in the enviroment we react to
whats a receptor
detects a stimulus and stimulate electrical impulses in response.
whats a sensory nuerone
Sensory neurones carry electrical signals - nerve impulses - towards the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain).
whats a motor nuerone
carry nerve impulses away from the central nervous system to the effectors.
what are effectors
a muscle/ gland which acts in response to a stimulus
whats the order of a reflex arc
stimulus →receptor → sensory nuerone → relay nuerone (CNS) → motor nuerone → effector → response
where are electrical pulses passed along a nuerone
the axon
why do nuerones have branched endings and what are they called
called dendrites and they mean they can connect with lots of other nuerones
whats a myelin
a fatty sheath surrounding some axons in a neuron which acts as an electrical insulator speeding up the electrical impulse
why is a long nuerone better than short ones joined together
connecting with another nuerone slows the impulses down
what is the gap between two nuerones called
synapse
how are electrical impulses sent between nuerones (synapse)
when an electrical impulse reaches the end of a neurone (dendrites) it causes the release of chemicals (neurotransmitters)
these chemicals then diffuse across the synapse and stimulate the next neurone to carry another electrical impulse
what are reflex actions
automatic actions to stop you from injuring yourself
how do reflex actions work
The receptor in the skin detects a stimulus - the change in temperature.
The sensory neurone sends nerve impulses to the spinal cord.
The relay neurone, which is located in the spinal cord, carries the nerve impulses from sensory neurones to motor neurones.
The motor neurone sends nerve impulses to the effector.
The effector - the biceps muscle in the arm - contracts so that the hand is moved away.
why are reflex actions so fast
they are automatic and dont involve conscious parts of the brain which allows us to be protected from harm
whats homeostatis
maintaining constant internal body conditions
whats a hormone
chemical messengers that are secreted by the glands in the endocrine system into the bloodstream
what are target cells
cells with the specific receptor for the hormone that produce an effect when the hormone binds
how does the endocrine system work
Glands are organs that release small chemicals called hormones.
These chemicals are normally released into the bloodstream, allowing them to travel around the body.
They can then bind to specific cells that have the correct receptors.
This will bring about some change within the cells.
what is adrenaline
a hormone produced by the adrenal glands (which are ontop of your kidneys)
when is adrenaline produced
during the flight or fight response when you get scared, stressed or need to exercise. It prepares the body for activity
What does adrenaline do ?
increases heart rate
increases breathing rate
increases blood pressure
increases blood flow to muscles
increases blood sugar (glucose levels) by stimulating liver to break down glyogen into glucose
When your brain detects a stressful situation what does it do ?
sends nerve impulses to adrenal glands, respond by secreting adrenaline
where is thyroxine produced
produced by the thyroid gland found in your neck
what does thyroxine do
its main role is to increase your metabolic rate (the rate at which chemical reactions are taking place)
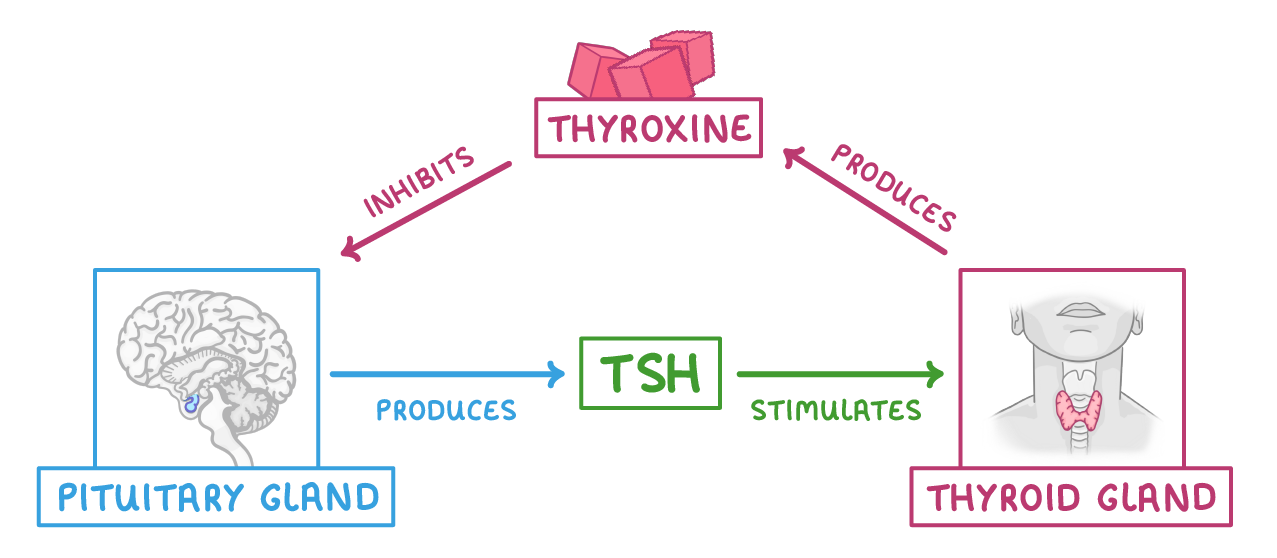
how is the production of thyroxine regulated
the pituatry gland produced TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine.
thyroxine then inhibits the production of TSH from the pituitary gland
what happens if your thyroxine levels are too low
the pituitary gland will release TSH.
This then stimulates the thyroid gland to release more thyroxine so thyroxine levels in the blood increase back up to normal.
what happens if your thyroxine levels are too high
the thyroxine will inhibit the pituitary gland from producing TSH.
Less TSH means that the thyroid gland won't release as much thyroxine so thyroxine levels in the blood fall back to normal.
how is the control of thyroxine levels an example of negative feedback
If levels of thyroxine rise too high, it will bring about changes to lower the levels, and if they fall too low, it brings about changes to raise them back up.
how does the endocrine system work
is a network of glands
glands release hormones into the blood stream
these hormones can then bind to specific cells with the correct receptors which will bring about some change in the cells
What is a gland ?
organs that release chemicals called hormones
What are hormones ?
Chemicals produced in various glands which bind to receptors on a target cell
what is a target cell
any cell that has the correct receptor for a particular hormone to bind to
what does the pituitary gland do in the endocrine system
is the master gland and tells other glands to secrete their hormone in the endocrine system
what does the pancreas do in the endocrine system
regulates blood glucose
what do the testes do in the endorcine system
only found in males , secrete testosterone
what do the ovaries do in the endorcine system
in females, secrete oestrogen
whats negative feedback
When your body detects that the level of a substance has gone above or below the normal level, it triggers a response to bring the level back to normal again. e.g. thyroid regulating the metabolic rate
Name the two sex hormones secreted by the ovaries
oestrogen, progesterone
name the two sex hormones secreted by the pituitary gland
FSH, LH
what is FSH and LH
FSH(follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luetinising hormone) are released from the pituitary gland and help support the menstrual cycle
What does FSH do ?
Causes egg to mature
stimulates ovaries to produce oestrogen
what is oestrogen
main female sex hormone produces in the ovaries which is involved in mesntrual cycle and devloping femal charcteritics (e.g. breasts)
what does oestrogen do ?
causes lining of uterus to thicken
stimulates production of LH
inhibits production of FSH so that only one egg is released in each cycle
What does LH do ?
stimulates release of egg (ovulation)
indirectly stimulates progesterone production
what is progesterone
hormone produced in the ovaries to help support ovaries and also is involved in the menstrual cycle
what does progesterone do ?
maintains uterus lining. when level falls and there's low oestrogen -lining breaks down
inhibits production of FSH and LH
low levels allow FSH to increase- whole cycle starts again
what happens in stage 1 of the menstrual cycle
menstruation - period of bleeding as the uterus lining breaks down
what happens in stage 2 of the menstrual cycle
building up of the uterus lining
what happens in stage 3 of the menstrual cycle
ovulation - release of the egg from the ovaries
what happens in stage 4 of the menstrual cycle
maintenance of the uterus lining
what does testosterone do
stimulate sperm production from the testes
why would low levels of FSH cause infertility ?
some women have low levels of FSH so there eggs can't mature- no ovulation takes place- cant get pregnant
how can ovulation be stimulated ?
by injection of FSH and LH
explain how ivf works
First, a woman is given FSH and LH to stimulate their eggs to mature.
These eggs can then be collected from the woman's ovaries. Sperm is also collected from the male.
The eggs are then fertilised by the sperm.
These fertilised eggs are then left to grow into embryos in a laboratory incubator.
Once the embryos are large enough, they are transferred to the women's uterus, so that they can develop into a foetus.
what are contraceptives used for ?
to prevent pregnanacy
name the types of hormonal contraception that use progesterone and how long they are effective for
injection -up to 3 months
implant- inserted beneath skin if the arm for 3 years
the coil (ius) - t shaped piece of plastic inserted into uterus 3-5 years
mini pill( progesterone only pill) has to be taken every day
how do contraceptive methods involving progesterone work
stimulates production of thick cervical mucus making it less likey for the sperm to get through
thins lining of uterus to make it less likely for egg to implant
prevents ovulation by inhibiting production of lh and fsh
name the methods of hormonal contraception using progesterone and oestrogen
combined pill - taken in a 21 day pill, 7 days no pill cycle
patch- worn in skin in 4 week cycle
how does oestrogen prevent pregnancy ?
prevents ovulation by inhibiting FSH
what is a barrier method is contraception?
stop the egg and sperm meeting
Name the barrier methods of contraception
condoms, female condoms and diaphragm
what are the no hormonal methods of contraception
intrauterine devices-IUDS
natural planning
sterilisation
how does an iud work
its non hormonal t shaped device made from copper inserted into the uterus and it works by stopping the sperm and egg from surviving in the womb or fallopian tubes.
whats natural planning
not having sex when the womans most fertile
whats sterilisation
surgical procedure to cut/tie tubes in reproductive system
what are bad things about hormonal methods of contraception
side effects
possibility of doing/taking it wrong so is ineffective
dont protect against sti’s
name advantages of hormonal methods of contraception
long lasting methods- don't have to worry about it every day
what is diabetes ?
Diabetes is a disease in which the body is unable to produce any or enough insulin causing elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
whats type 1 diabetes
the pancreas produces little or no insulin
how do you treat type 1 diabetes
through insulin therapy - injecting insulin several times a day (often at mealtimes)
stops level of glucose in blood from getting too high- very effective
what is type 2 diabetes ?
the body cells lose their sensitivity ( no longer respond to insulin being produced)
makes it difficult to control blood glucose levels
how is type 2 diabetes treated
healthy diet, exercising regularly ( increases amount of energy used up by body and decreases amount of stored body fat) and losing weight if necessary
what can increase the chance of getting type 2 diabetes ?
being overweight
too much saturated fat which increases blood cholesterol
whats does insulin do and wheres it made
lowers blood glucose levels and made in pancreas
what does glucagon do and wheres it made
increases blood sugar levels and made in pancreas
whats glucose and wheres it made
a sugar used to make energy and is made in the liver
whats glycogen
Glycogen is a carb stored in liver and muscles. It's a quick energy source made up of glucose molecules.
what happens of your blood glucose levels are too high
pancreas is stimulated
insulin is secreted
insulin stimulates glucose uptake from blood
blood glucose level falls
what happens of out blood glucose levels are too low
pancreas is stimulated
glucagon is secreted
glucagon stimulates liver to release glucose
blood glucose level rises