PLP 130 MT2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:48 PM on 5/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
hypotheses to why secondary metabolism has evolved in fungi (and some plants)
1. competition theory
2. inc in pathogenic prowess
3. detoxification
4. maintenance of cell agility
5. evolution of primary metabolism
2
New cards
why are we interested in fungal SMs?
* mycotoxins to humans/animals
* disease on plants (phytotoxins)
* exploited in medicinal drugs eg Abx, anti-infective agents, immunosuppressants, anticancer agents
* disease on plants (phytotoxins)
* exploited in medicinal drugs eg Abx, anti-infective agents, immunosuppressants, anticancer agents
3
New cards
SMs as drugs
* statins = anti-cholesterol
* penicillin, chephalosporin = Abx
* cyclosporin A = immunosuppressant
* strobilurin = antifungal
* penicillin, chephalosporin = Abx
* cyclosporin A = immunosuppressant
* strobilurin = antifungal
4
New cards
Chaga
product of white rot fungus (Basidiomycetes) → makes sclerotia
* dark color bc antioxidant melanin → protects body against uncontrolled oxidation & free radicals
* SMs = betulin, sesquiterpenes, benzoic acid deriv
* used in many cultures
\
* contains a lot more antioxidants than acai, pomegranatas, blueberries
* dark color bc antioxidant melanin → protects body against uncontrolled oxidation & free radicals
* SMs = betulin, sesquiterpenes, benzoic acid deriv
* used in many cultures
\
* contains a lot more antioxidants than acai, pomegranatas, blueberries
5
New cards
Reishi mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum)
* used for chronic diseases ie arthritis, insomnia, etc
* wood degrading Basidiomycota (Ganoderma)
* wood degrading Basidiomycota (Ganoderma)
6
New cards
Otzi the Iceman carried _
* Piptoporus - as medicine to clear parasitic worms via agaric acid → causes diarrhea
* also hoof fungi → start/transport fires
* also hoof fungi → start/transport fires
7
New cards
acetate malonate pw
synthesis of polyketides & fatty acids
8
New cards
mevalonic acid pw
aka isoprenoid pw
synthesis of isoprenoids (terpenes, carotenoids, steroids)
synthesis of isoprenoids (terpenes, carotenoids, steroids)
9
New cards
shikimic acid & amino-acid derived pw
synthesis of non-ribosomal peptide & aa derivatives
10
New cards
SMs pw’s committing enzymes
need key enzymes that catalyze 1st committed step for each class:
* polyketides synthases (PKS)
* terpene synthase (TS)
* non ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS)
* polyketides synthases (PKS)
* terpene synthase (TS)
* non ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS)
11
New cards
complex SMs ex
combination of different pw → complex SMs
* indole alkaloids (ergots)
* derived from L-trypotophan via shikimic acid pw & dimethylalllyl pyroP
* indole alkaloids (ergots)
* derived from L-trypotophan via shikimic acid pw & dimethylalllyl pyroP
12
New cards
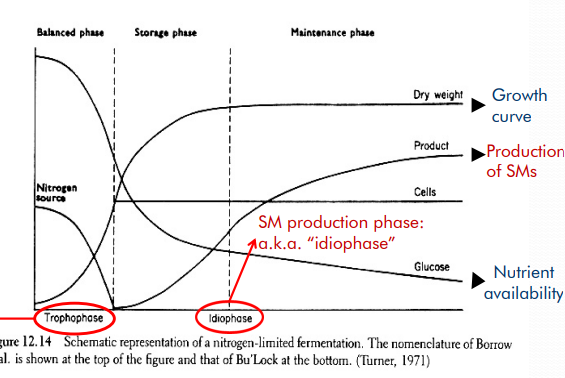
SMs production depends on _
* limited (esp nitrogen) nutrients
* idiophase = start where most SMs being made → make idiolites
* trophophase = feeding & growth phase; N is abundant
* idiophase = start where most SMs being made → make idiolites
* trophophase = feeding & growth phase; N is abundant
13
New cards
SM biosynthetic gene clusters
major components
* 1st committed enzyme (PKS, NRPS, TS): make backbone of SM
* additional tailoring enzymes: can be dozens, make specific modifications to backbone SMs
* transcription factors
* transporters: exporters
* other genes: defense
* 1st committed enzyme (PKS, NRPS, TS): make backbone of SM
* additional tailoring enzymes: can be dozens, make specific modifications to backbone SMs
* transcription factors
* transporters: exporters
* other genes: defense
14
New cards
aflatoxin or sterigmatocystin in Aspergilli fungi
* most carcinogenic mycotoxin
aflatoxin biosyn pw intermediates
* polyketide progenitors
* antraquionones
* xanthones
* bisfuranocoumarins (aflatoxins)
aflatoxin biosyn pw intermediates
* polyketide progenitors
* antraquionones
* xanthones
* bisfuranocoumarins (aflatoxins)
15
New cards
1st committed enzyme in Polyketides & Non-ribosomal synthetase pw
PKSs and NRPs are multimodular & multidomain enzymes = make core structure of many SM
16
New cards
polyketide syntheases
essential domains
* acyltransferase = selects extender untis (malonyl-/acetyl-/methylmalonyl-CoA) → transfers to ACP
* acyl carrier protein (ACP) = loads unit to extended product
* ketosynthases = accepts polyketide chain from upstream ACP & catalyzes decarboxylation condensation b/t this substrate & an extender unit attached to the ACP in the same module
\
auxiliary domains: optional domains ie enoyl reductases, dehydratase, ketoreductase
starter & termination domains = SAT is the starter ACP transacylase domain & thiolesterase the termination one
* acyltransferase = selects extender untis (malonyl-/acetyl-/methylmalonyl-CoA) → transfers to ACP
* acyl carrier protein (ACP) = loads unit to extended product
* ketosynthases = accepts polyketide chain from upstream ACP & catalyzes decarboxylation condensation b/t this substrate & an extender unit attached to the ACP in the same module
\
auxiliary domains: optional domains ie enoyl reductases, dehydratase, ketoreductase
starter & termination domains = SAT is the starter ACP transacylase domain & thiolesterase the termination one
17
New cards
reducing vs non-reducing PKS
* when auxiliary domains are present in PKS → reducing PKS
* only essent domains present → non-reducing PKS
* only essent domains present → non-reducing PKS
18
New cards
Type I, Iterative vs non-iterative (modular) PKS
non-iterative = multiple sequential modules, have extending & tailoring domains → each module does only one round of chain elongation (usually in bacteria)
\
iterative = single copy of each domain are made into 1 module, used repeatedly during biosynthesis, (in fungi)
\
iterative = single copy of each domain are made into 1 module, used repeatedly during biosynthesis, (in fungi)
19
New cards
Non-ribosomal peptide synthetases
essential domains
* adenylation domain
* peptidyl carrier protein (PCP)
* condensation domain
\
auxiliary domain
* methyltransferase, B-ketoacyl reductases, epimerization domains
\
starter & termination domains: PCP can function as starter domain & thiolesterase is termination one
* adenylation domain
* peptidyl carrier protein (PCP)
* condensation domain
\
auxiliary domain
* methyltransferase, B-ketoacyl reductases, epimerization domains
\
starter & termination domains: PCP can function as starter domain & thiolesterase is termination one
20
New cards
NRPSs Type A, B, C
linear NRPSs (type A): # & sequence of modules in NRPS matches the # and order of aa in the peptide
\
iterative NRPSs (type B): modules or domains are used more than once to synthesize the peptide, which consists of repeated sequences
\
nonlinear NRPSs (type C): seq of aa in generated peptide does not correlate to arrangement of modules on the template
\
iterative NRPSs (type B): modules or domains are used more than once to synthesize the peptide, which consists of repeated sequences
\
nonlinear NRPSs (type C): seq of aa in generated peptide does not correlate to arrangement of modules on the template
21
New cards
iterative hybrid PKS-NRPSs (iPKR-NRPSs)
single module of an iterative PKS is followed by a single NRPS module (Fusing the polyketide chain to an aa) and an off-loading domain
22
New cards
transcriptional regulational of SM clusters stimuli
stimuli include
* C & N-sources
* temperature
* light
* pH
* aa in environement
* C & N-sources
* temperature
* light
* pH
* aa in environement
23
New cards
SM physiological roles
assoc;d w/sporulation
* slow down germination spores until more favorable conditions
* toxic metabolites secreted to protect dormant spore from predators
* activate sporulation
* pigments for sporulation structures
* slow down germination spores until more favorable conditions
* toxic metabolites secreted to protect dormant spore from predators
* activate sporulation
* pigments for sporulation structures
24
New cards
most SM clusters are _ under lab conditions that don’t provide appropriate ecological triggers
silent or cryptic
25
New cards
regulation of SM gene clusters
pathway-specific = TFs that usually belong to clusters that factors regulate
\
global regulation = globally acting TF which are encoded by genes that don’t belong to any cluster, & which also regulate a # of genes that are not involved in secondary metabolism
\
global regulation = globally acting TF which are encoded by genes that don’t belong to any cluster, & which also regulate a # of genes that are not involved in secondary metabolism
26
New cards
transporters for secretion of SMs
efflux system of SMs
* major facilitator superfamily (MFS): use energy from electrochemical gradients across membranes
* ABC transprorters: use ATP hydrolysis
* major facilitator superfamily (MFS): use energy from electrochemical gradients across membranes
* ABC transprorters: use ATP hydrolysis
27
New cards
mycotoxins
low MW natural products made as SM by fungi → mycotoxosis
28
New cards
mycotoxin in food chain
contamination of food/feed can occur at any stage during food production
* causes many economic losses
* 56% of rejection to food to EU is due to mycotoxins
* causes many economic losses
* 56% of rejection to food to EU is due to mycotoxins
29
New cards
factors influencings mycotoxin production
* climatic & environment: high T & humidity
* fungal strain
* plant variety
* damage of crop by other factors eg insects, mechanical
* substrate on which fungus is growing (idiophase)
* xs use of pesticides/fungicides that leads to resistance & induction of stress
* fungal strain
* plant variety
* damage of crop by other factors eg insects, mechanical
* substrate on which fungus is growing (idiophase)
* xs use of pesticides/fungicides that leads to resistance & induction of stress
30
New cards
mycotoxin exposure sources
* food
* water damaged buildings
* outdoors
* vehicles
* water damaged buildings
* outdoors
* vehicles
31
New cards
health effects of mycotoxins depend on
* animal sp
* type of mycotoxin
* fitness of animal
* dosage & duration
* synergistic effects w/other mycotoxins
* type of mycotoxin
* fitness of animal
* dosage & duration
* synergistic effects w/other mycotoxins
32
New cards
acute mycotoxicosis
after a single v severe exposures
* GI disturbances
* abortions
* skin irritation
* GI disturbances
* abortions
* skin irritation
33
New cards
chronic mycotoxicosis
* after periodic exposure to low doses over a long period of time
* hepatotoxicity (liver cancer is most prominent)
* nephrotoxicity
* genotoxicity
* etc
* hepatotoxicity (liver cancer is most prominent)
* nephrotoxicity
* genotoxicity
* etc
34
New cards
symptoms of mycotoxin exposure
\
same happens to aniamls
\
hard to diagnose bc of same symptoms of other diseases
same happens to aniamls
\
hard to diagnose bc of same symptoms of other diseases
35
New cards
MOA (modes of action) of mycotoxins
* damage membranes in intestines → impair absorption of nutrients & barrier to bloodstream
* target protein synthesis pw esp DNA/RNA structure
* induce immunosuppression
* disrupt microbiota homeostasis
* act as a neurotoxin
* target protein synthesis pw esp DNA/RNA structure
* induce immunosuppression
* disrupt microbiota homeostasis
* act as a neurotoxin
36
New cards
mycotoxin in the GIT & leaky gut syndrome
* most mycotoxins absorbed in duodenum
* encounter GITs epithelium
* epithelial cells allow selective absorption of nutrient & are a barrier to pathogens & toxins into the bloodstream
\
leaky gut syndrome
* leads to minor: bloating & gas, cramps, fatigue
* severe: autoimmune conditions, depression
\
* death or illness can result
* encounter GITs epithelium
* epithelial cells allow selective absorption of nutrient & are a barrier to pathogens & toxins into the bloodstream
\
leaky gut syndrome
* leads to minor: bloating & gas, cramps, fatigue
* severe: autoimmune conditions, depression
\
* death or illness can result
37
New cards
mycotoxin amplification in enterohepatic cycle
part of mycotoxins can re-enter GIT via bloodstream & hepatic portal vein → prolonged retention in GIT → amplify damage to host
* can cause oxidative damage to liver
* bloodstream → spread to other organs
* can cause oxidative damage to liver
* bloodstream → spread to other organs
38
New cards
mycotoxin & effect on gut microbiota
* can alter microbiota in gut → growth of pathogens in GIT & inflammation
39
New cards
mycotoxin detection
* hard to prevent contamination
* v stable
* can be masked by other nutrients
* can act synergistically to enhance toxicity
* v stable
* can be masked by other nutrients
* can act synergistically to enhance toxicity
40
New cards
mysterious turkey X disease
in UK 1960s; 100K turkey poults died
* all had same liver damage
* all got fed same peanuts from Brazil - contaminated w/Aspergillus flavus→ aflatoxins
* all had same liver damage
* all got fed same peanuts from Brazil - contaminated w/Aspergillus flavus→ aflatoxins
41
New cards
aflatoxins
* polyketide mycotoxin; produced by Aspergillus flavus & Aspergillus parasiticus
* common: B1, B2, G1, G2 types
* toxicity: highest AfB1 > G1 > B2 >G2 lowest
\
* AfM1 & M2 were 1st isolated from milk of lactating animals fed on aflatoxin grains
* common: B1, B2, G1, G2 types
* toxicity: highest AfB1 > G1 > B2 >G2 lowest
\
* AfM1 & M2 were 1st isolated from milk of lactating animals fed on aflatoxin grains
42
New cards
aflatoxin & hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
* primary disease ass’d w/aflatoxin intake is HCC
* mostly in Asia & Africa
* even 0.04g/kg could be dangerous
\
how?
* AfB1 is pro-carcinogen: P450 transforms to AFBO (in humans) → binds to DNA
* DNA mutations
* induces mutations in P53 tumor suppressor gene → liver cancer
\
\[insert aflatoxin pic\]
* mostly in Asia & Africa
* even 0.04g/kg could be dangerous
\
how?
* AfB1 is pro-carcinogen: P450 transforms to AFBO (in humans) → binds to DNA
* DNA mutations
* induces mutations in P53 tumor suppressor gene → liver cancer
\
\[insert aflatoxin pic\]
43
New cards
aflatoxins in milk
AfB1 → M1 in milk → Kwashiorkor disease in human babies
44
New cards
Aflatoxin & peanuts & other crops
* 1/2 of peanuts are contaminated by Aflatoxins
* if contaminated → may re-enter as animal feed or local open markets
\
* rice, maize
* if contaminated → may re-enter as animal feed or local open markets
\
* rice, maize
45
New cards
aflatoxin regulation
* food testing set by FDA
* PCR, ELISA,
* PCR, ELISA,
46
New cards
other common mycotoxins
* Ochratoxin A (in wine) from Aspergillus ochraceus
* patulin (in fruit) A. clavatus
* fumonisin (corn)
* Trichothecenes (corn)
* patulin (in fruit) A. clavatus
* fumonisin (corn)
* Trichothecenes (corn)
47
New cards
Trichothecenes (TCNs)
* most common in USA
* made by Fusarium mostly
* Type A > Type B in toxicity
* Type A: lead to alimentary toxic aleuka (ATA)
* eg T-2
* TYpe B: cause changes of intestinal immune & nervous systems
* eg DON
* made by Fusarium mostly
* Type A > Type B in toxicity
* Type A: lead to alimentary toxic aleuka (ATA)
* eg T-2
* TYpe B: cause changes of intestinal immune & nervous systems
* eg DON
48
New cards
TCN: Deoxynivalenol (DON, vomitoxin)
* most common in USA
* Fusarium sp infects corn, wheat, sorghum
* DON can cross the BBB
* in swine: moldy corn toxicosis
* Fusarium sp infects corn, wheat, sorghum
* DON can cross the BBB
* in swine: moldy corn toxicosis
49
New cards
TCN: T-2
\
Mycotoxins as biowarfare
* Yellow Rain controversy & gulf war syndrome
\
Mycotoxins as biowarfare
* Yellow Rain controversy & gulf war syndrome
* powerful inhibitor of protein synthesis & neurotoxin
* made by Fusarium sp
* often in poultry
* inhibits synth of DNA/RNA, induce apoptosis
\
* yellow rain: air attacks in Laos by Russian military after WWII
* T-2 was proposed as cause of Gulf War syndrome
* made by Fusarium sp
* often in poultry
* inhibits synth of DNA/RNA, induce apoptosis
\
* yellow rain: air attacks in Laos by Russian military after WWII
* T-2 was proposed as cause of Gulf War syndrome
50
New cards
Managing at Governmental Level: Hazard Analysis for critical control points (HACCP)
includes streategies for prevention, control, and quality from farm to fork
\
Primary prevention: prevent fungal infestations, most important
* use of disease resistant plant strain
* chemical control
Secondary: stop existing infn
* protect stored products from conditions that favor fungus
Tertiary: when heavily infested by toxic fungi, less effective
\
\
Primary prevention: prevent fungal infestations, most important
* use of disease resistant plant strain
* chemical control
Secondary: stop existing infn
* protect stored products from conditions that favor fungus
Tertiary: when heavily infested by toxic fungi, less effective
\
51
New cards
mycotoxin exposure routes
consumption of contaminated food: direct & in-direct (animals feed mycotoxins)
\
breating in: stachybotrys, toxic black mold in carpets
\
skin or eyes (TCNs)
* via pillows?
\
breating in: stachybotrys, toxic black mold in carpets
\
skin or eyes (TCNs)
* via pillows?
52
New cards
exposure in houses
* Stachybotrys chartarum - produces TCNs most assoc’d w/houses
* Aspergillus, Penicillium, Trichoderma, Cladosporium
* Aspergillus, Penicillium, Trichoderma, Cladosporium
53
New cards
Stachybotrys chartarum (aka S. atra) or Black mold
* causes “sick-building syndrome”
* over 170 mycotoxins, including cytoxic TCN
* chemotype S strain: 30-40%
* chemotype A: do not make TCN, 70-60%
* most common on cellulite (wallpaper, carpets)
* over 170 mycotoxins, including cytoxic TCN
* chemotype S strain: 30-40%
* chemotype A: do not make TCN, 70-60%
* most common on cellulite (wallpaper, carpets)
54
New cards
health assoc’d risks w/mold in indoors
* allergic rxn: asthma, hay fever, pneumnoitis
* infectious: aspergillosis or histoplasmosis
* toxic: disruption of cellular fxn & interaction w/DNA, cancer
* infectious: aspergillosis or histoplasmosis
* toxic: disruption of cellular fxn & interaction w/DNA, cancer
55
New cards
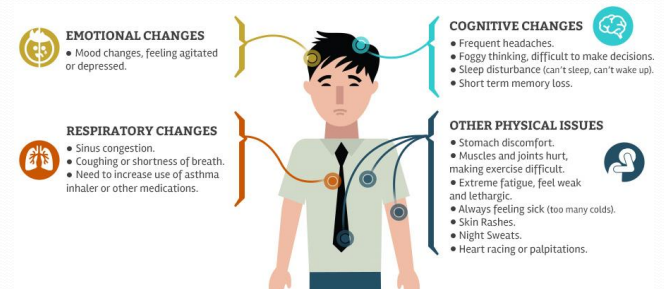
symptoms & mycotoxins in urban environment
emotional changes, respiratory changes, cognitive changes, physical issues
56
New cards
diagnosing a ‘sick building’
* mold growth & condensation
* off smell in particular rooms
* temperature always feels wrong
* off smell in particular rooms
* temperature always feels wrong
57
New cards
mycotoxins & human society
* ergot: plant disease, St. Anthony’s fire; cuased by Caviceps purpurea
* grows on rye crops
* infected ovary is replaced by scleortium = ergot → produces toxic alkoids
* grows on rye crops
* infected ovary is replaced by scleortium = ergot → produces toxic alkoids
58
New cards
Ergotism
* convulsive ergostism: nervous dysfxn, tremors, hallucinations
* gangrenous ergostism: victim lose limbs, fingers, toes to dry gangrene
* gangrenous ergostism: victim lose limbs, fingers, toes to dry gangrene
59
New cards
ergot alkaloids
* indole alkaloids
* mode of action: toxicity attributed to interaction of ergot alkaloids w/adrenergic, serotonergic & dopaminergic R in brain
* can be used as med drug in low doses
* mode of action: toxicity attributed to interaction of ergot alkaloids w/adrenergic, serotonergic & dopaminergic R in brain
* can be used as med drug in low doses
60
New cards
ergot alkaloids in folklore
* Salem Witch trials (madness like symptoms)
* flying ointments
* dance mania
* 27 y/o Peloponnesian War - contaminated wheat → killed many in Athens
* failed war from Peter the Great
* flying ointments
* dance mania
* 27 y/o Peloponnesian War - contaminated wheat → killed many in Athens
* failed war from Peter the Great
61
New cards
**products of fungi**
food themselves
use as microbial cell factories
agricultural biotechnology & bioremediation
use as microbial cell factories
agricultural biotechnology & bioremediation
62
New cards
fungal hydrolyzing enzymes
* amylases, glucoamylase, glucose isomerases
* catalases: dyeing process
* cellulaase: digest jean fiber ‘fungal washing”
* xylanasaes, peroxidase, ligninases (paper)
\
* catalases: dyeing process
* cellulaase: digest jean fiber ‘fungal washing”
* xylanasaes, peroxidase, ligninases (paper)
\
63
New cards
primary metabolites or secondary metabolites
primary
* citric acid
* gluconic acid
* itaconic acid
\
secondary
* terpenoids in fragnance & flor industry, black/brown pigments, food, pharma, textiles
* pharm: antiallergic, antioxidants, antitumor
* citric acid
* gluconic acid
* itaconic acid
\
secondary
* terpenoids in fragnance & flor industry, black/brown pigments, food, pharma, textiles
* pharm: antiallergic, antioxidants, antitumor
64
New cards
major pharm drugs of fungal origin
\
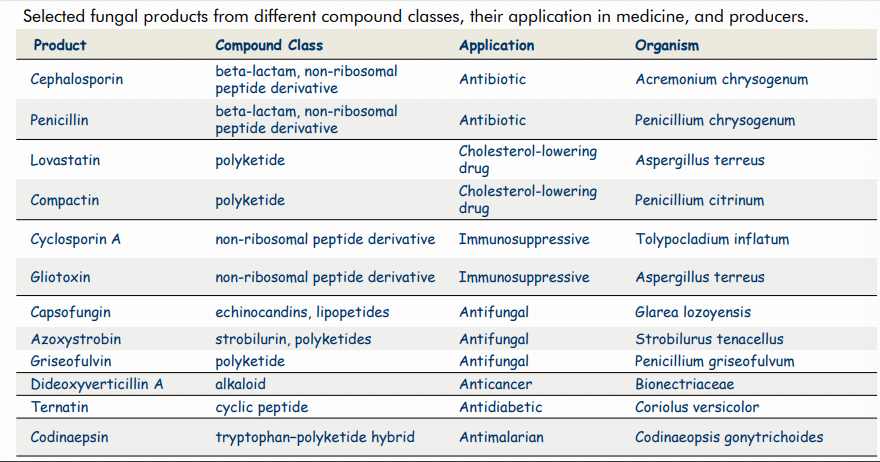
65
New cards
penicillin
* Beta-lactam Ab are effective against G+ bacteria
* B-lactam ring = responsible for Ab activity via interfering w/bacterial CW biosynthesis by preventing the cross-linking of peptidoglycan
* discovered accidentally by Fleming
* B-lactam ring = responsible for Ab activity via interfering w/bacterial CW biosynthesis by preventing the cross-linking of peptidoglycan
* discovered accidentally by Fleming
66
New cards
penicillin’s discovery & development
1) Fleming discovered accidentally → isolated & classified Penicillium notanum → low yield
2) WWII casualities from bacterial wounds; Chain and Florey
3) Florey; 2nd largest R&D project of WWII after Manhattan project; isolated strain from moldy cantaloupe → NRRL 1951 was a high producer of penicillin
→ induce mutations to get higher production & improved extraction procedures
2) WWII casualities from bacterial wounds; Chain and Florey
3) Florey; 2nd largest R&D project of WWII after Manhattan project; isolated strain from moldy cantaloupe → NRRL 1951 was a high producer of penicillin
→ induce mutations to get higher production & improved extraction procedures
67
New cards
limitations of natural penicillin
* limited range
* unstable in acidic environment
* painful, but be injected
* allergic
* sensitive to Beta-lactamases
* unstable in acidic environment
* painful, but be injected
* allergic
* sensitive to Beta-lactamases
68
New cards
composition of penicillin & improving penicillin
penicillin is composed of
* a thiazolidine ring, a B-lactam ring, free carboxyl acid group, one or more aa side chains
* position 6: variations are limited to acyl aide chain
\
\
improving
* planting & selecting natural mutants
one way to change is vary acyl side chain by adding diff carboyxlic acids to fermentation medium
* corn steep liquior → pen G
* phenoxy-acetic acid → pen V (1st oral form)
* a thiazolidine ring, a B-lactam ring, free carboxyl acid group, one or more aa side chains
* position 6: variations are limited to acyl aide chain
\
\
improving
* planting & selecting natural mutants
one way to change is vary acyl side chain by adding diff carboyxlic acids to fermentation medium
* corn steep liquior → pen G
* phenoxy-acetic acid → pen V (1st oral form)
69
New cards
classes of drug derivatives
1. natural (penicillin G)
2. biosynthetic: eg fermentation changes
3. semisynthetic (ie ampicillin, amoxycillin): cmpds are further chemically modified in lab after isolated from natural processes
4. synthetic: fully synthesized chemically
70
New cards
immunosuppressant drugs: Cyclosporine A (CsA)
* MOA
* MOA
CsA is only member used clinically
used in BM transplants
\
MOA
* inhibits fxn of several proteins involved in activation of T-cells at transcription level
used in BM transplants
\
MOA
* inhibits fxn of several proteins involved in activation of T-cells at transcription level
71
New cards
Cyclosporine MOA
\[insert pic\]
* cyclophylin (CpN) blocks fxn of phosphatase enzyme cacineurin (CaN) → CaN fails to deP TF, NF-ATc ----→ T cells do not produce IL-2 → don’t activate full T-cell activation & immunity
* cyclophylin (CpN) blocks fxn of phosphatase enzyme cacineurin (CaN) → CaN fails to deP TF, NF-ATc ----→ T cells do not produce IL-2 → don’t activate full T-cell activation & immunity
72
New cards
statins
inhibit ergosterol bspw
* interact w/LDL cholesterol (bad - clogs veins) & lower triglycerides in blood
* some can inc also HDL (good) cholesterol
* interact w/LDL cholesterol (bad - clogs veins) & lower triglycerides in blood
* some can inc also HDL (good) cholesterol
73
New cards
statins development
* change strain, fermentation media
* discovered accidentally in Penicillum
* discovered accidentally in Penicillum
74
New cards
statin controversy
media reports of muscle pain and weakness → the Lancet reported that positives outweigh the negatives
75
New cards
common fungal-dervied enzymes in industry
cellulase:
glucosidase
laccase
amylase
pectinase
lipase
protease
chitinase
xylanase
glucosidase
laccase
amylase
pectinase
lipase
protease
chitinase
xylanase
76
New cards
textile industry
biostoning: use cellulases instead of pumice to degrade the jeans
* cellulase from Trichoderma reesei
\
bleach clean up: catalase to get white fabric via splitting H2O2
\
bioscouring: uses pectinases to remove impurities ie pectin & wax
\
biopolish: cellulase to removes microhairs
\
desizing w/amlyases: removing applied size material ie starch that were added to improve strength of yarn for weaving
* cellulase from Trichoderma reesei
\
bleach clean up: catalase to get white fabric via splitting H2O2
\
bioscouring: uses pectinases to remove impurities ie pectin & wax
\
biopolish: cellulase to removes microhairs
\
desizing w/amlyases: removing applied size material ie starch that were added to improve strength of yarn for weaving
77
New cards
6 major enzyme classes
oxidoreductases
transferase
hydrolases
lyases
isomerases
ligases
transferase
hydrolases
lyases
isomerases
ligases
78
New cards
CAZymes structure
1. carbohydrate-binding domain (CDM): keeps CD nearby substrate
2. catalytic (hydrolyzing) domain (CD): does cleavage
3. a linker domain: seq of aa connecting cellulose BD & CD = flexible hinge to allow indep fxn of each domain
79
New cards
fungal isoenzymes of CAZymes
types of CAZymes
* endocellulases: hydrolyzes glycosidic bonds w/in a chain
* exocellulases: ““ from ends of chains or free ends generated by endoglucanases
* beta-glucosidases: cleave cellobiose into glc monomers
* endocellulases: hydrolyzes glycosidic bonds w/in a chain
* exocellulases: ““ from ends of chains or free ends generated by endoglucanases
* beta-glucosidases: cleave cellobiose into glc monomers
80
New cards
research areas on fungal enzymes
enzyme discovery
* exploitation of natural biodiv/screening, genome seq, metagenomics
\
enzyme engineering
* rationale design, directed evolution
\
selected applications
* industrial, environmental, biomedical
* exploitation of natural biodiv/screening, genome seq, metagenomics
\
enzyme engineering
* rationale design, directed evolution
\
selected applications
* industrial, environmental, biomedical
81
New cards
enzyme discovery
conventional culture-dependent & bioactivity-based approach
* enrichments
* disadvantages: screening is against a library of predefined substrates, costly, laborious, limited to only culturable organism
\
genomics approach (genome mining)
* sequence, annotate, look for CAZymes
* databases
* dbCAN: for CAZymes
* Gene Ontology
* KEGG
* antiSMASH & SMURF
* disadvantages: need to isolate DNA, loses majority of diversity
\
metagenomics
* enrichments
* disadvantages: screening is against a library of predefined substrates, costly, laborious, limited to only culturable organism
\
genomics approach (genome mining)
* sequence, annotate, look for CAZymes
* databases
* dbCAN: for CAZymes
* Gene Ontology
* KEGG
* antiSMASH & SMURF
* disadvantages: need to isolate DNA, loses majority of diversity
\
metagenomics
82
New cards
metagenomics
sequences-based screening: uses enzyme-encoding genes based on seq homology (genome-mining)
\
activity-based screening (functional metagenomics): req cloning of environmental DNA into vectors to screen clones expressed selected enzymatic activity
\
activity-based screening (functional metagenomics): req cloning of environmental DNA into vectors to screen clones expressed selected enzymatic activity
83
New cards
enzyme engineering
improve
* rate of catalytic activity
* stability and robustness
* substrate specificity; reduction in side activity
* enantioselectivity
* rate of catalytic activity
* stability and robustness
* substrate specificity; reduction in side activity
* enantioselectivity
84
New cards
enzyme engineering approaches
rational design: mutants designed based on protein structure, prep by site directed mutagenesis
directed evolution: prep of large library of mutant genes, transformation & expression, screening for mutants w/desired properities is conducted & selected mutants are tested
directed evolution: prep of large library of mutant genes, transformation & expression, screening for mutants w/desired properities is conducted & selected mutants are tested
85
New cards
fungal biotech violins
increase acoustic properties of violin wood by making v small holes
86
New cards
biofuels
1st gen: from edible plants, ethanol/butanol via yeast fermentation
2nd gen: from lignocellulosic material from non-food crops ie wood to feed microbes
3rd gen: from algae, resilient organisms that can be grown from sunlight, CO2, doesn’t use arable land, fastest growing sources, C-neutral
4th gen: genetic engineering
2nd gen: from lignocellulosic material from non-food crops ie wood to feed microbes
3rd gen: from algae, resilient organisms that can be grown from sunlight, CO2, doesn’t use arable land, fastest growing sources, C-neutral
4th gen: genetic engineering
87
New cards
1st gen biofuels
starch (amylose or amylopectin) from corn, sugar cane, cassava →high-yielding ethanol source
* via fermentation w/S. cerevisiae, but lack amylolytic activity → initial degradation of starch into fermentable sugars → ferment
* via fermentation w/S. cerevisiae, but lack amylolytic activity → initial degradation of starch into fermentable sugars → ferment
88
New cards
2nd gen biofuels
* need ligninases, cellulases, hemicelluloses to degrade lignin in cobs, stalk, leaves to make ethanol
* lignocellulolytic enzymes are for pretreatment of material or enzymatic hydrolysis to make fermentable sugars
* lignocellulolytic enzymes are for pretreatment of material or enzymatic hydrolysis to make fermentable sugars
89
New cards
consolidated bioprocessing
CBP-enabling microbe bust be able to solubilize a practical biomass substrate & produce desired products at high yield → need genetic engineering
* native strategy: begin w/microbes w/native ability to use cellulosic biomass
* recombinant strategy: begin w/microbes that do not have ability → require heterologous expression of a saccharolytic enzyme system
* native strategy: begin w/microbes w/native ability to use cellulosic biomass
* recombinant strategy: begin w/microbes that do not have ability → require heterologous expression of a saccharolytic enzyme system
90
New cards
Asperigillus niger
produces pectinases → clarified fruit juices
91
New cards
bread w or w/o yeast
unleavened = w/o yeast, flat bread
leavened = w/yeast
leavened = w/yeast
92
New cards
chemistry of bread-making
glc → yeast will make CO2 and ethanol
amylopectin & amylose = need amylose to break down starch → maltose → glc
amylopectin & amylose = need amylose to break down starch → maltose → glc
93
New cards
enzymes in baking industry
amylase: alpha & beta, glucoamylases
lipase
protease
xylanase
\
externally added bc yeast is a poor producer of amylases
lipase
protease
xylanase
\
externally added bc yeast is a poor producer of amylases
94
New cards
amylases family
alpha
\
beta
\
glucoamylase: most high demand → get glucose syrup from starch
\
beta
\
glucoamylase: most high demand → get glucose syrup from starch
95
New cards
glucose isomerase
production of high fructose sugar → 2x sweeter than glucose
* come from corn
* fructose → obesity epidemic in US, bc fructose is lipogenic, glc is preferred
* come from corn
* fructose → obesity epidemic in US, bc fructose is lipogenic, glc is preferred
96
New cards
fructose negative health effects
* fructose is only metabolized in the liver →
* tooth decay
* leaky gut
* fatty liver
* type II diabetes
* etc
* tooth decay
* leaky gut
* fatty liver
* type II diabetes
* etc
97
New cards
fungal consumption history
fungal consumption is almost 20,000 years ago
98
New cards
Monascus pigments
* makes red fermented rice
* pigments are added into food or textiles
* therapeutic uses, antimicrobial, anticancer
* pigments are added into food or textiles
* therapeutic uses, antimicrobial, anticancer
99
New cards
food products from fungi
cheese, salami, red yeast rice, miso, tempeh
100
New cards
edible mushrooms
* B vitamins & D (if exposed to UV)
* Agaricus mushrooms (button mushrooms) are >95% of total US mushrooms
* Agaricus mushrooms (button mushrooms) are >95% of total US mushrooms