Stimulants, headache and bipolar
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Bipolar Disorder
[Is there a genetic component?]
Genetic -- 80-90% of patients have 1st relative with mood disorder
![<p>Comorbidities of ADHD</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> <br></p><ul><li><p>Alpha-2 agonist</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7ead13a4-b937-4580-ab11-74d74d3d28ae.png)
Comorbidities of ADHD
[...]
Alpha-2 agonist
Tourette disorder
Non-Stimulant Agents
Clonidine Extended Release (Kapvay)
Clinical Pearls
Less effective than stimulants but can be used in combination
May be preferred if:
patient has active substance abuse problem, comorbid anxiety, tics, Tourette
OR has intolerable side effects to stimulants
More sedation than stimulants and atomoxetine
Better at ↓ [...] than [...]
May ↓ [...]
Monotherapy or with stimulants
hyperactivity
inattention
severity of tics
Non-Stimulant Agents
[...]
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
postsynaptic alpha2 agonist stimulation
regulation of subcortical activity in the prefrontal cortex
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 10-12 hours
Not a controlled substance
Adverse Effects:
sedation
bradycardia
hypotension
headache
Rebound HTN if stopped abruptly
Clonidine Extended Release (Kapvay)
Non-Stimulant Agents
Clonidine Extended Release (Kapvay)
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
postsynaptic [...] agonist stimulation
regulation of subcortical activity in the prefrontal cortex
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 10-12 hours
Not a controlled substance
Adverse Effects:
sedation
bradycardia
hypotension
headache
Rebound HTN if stopped abruptly
alpha2
Non-Stimulant Agents
Clonidine Extended Release (Kapvay)
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
postsynaptic alpha2 agonist stimulation
regulation of subcortical activity in the prefrontal cortex
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 10-12 hours
Not a controlled substance
Adverse Effects:
[does it make you drowsy?]
[brady or tachy]cardia
[hypo or hyper]tension
headache
Rebound HTN if stopped abruptly
sedation
brady
hypo

Non-Stimulant Agents
Clonidine Extended Release (Kapvay)
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
postsynaptic alpha2 agonist stimulation
regulation of subcortical activity in the prefrontal cortex
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 10-12 hours
Not a controlled substance
Adverse Effects:
sedation
bradycardia
hypotension
Rebound HTN
Non-Stimulant Agents
Atomoxetine (Strattera)
Adverse effects
CNS:
Dizziness
fatigue
drowsiness
Dermatologic
hyperhidrosis = abnormally excessive sweating
GI:
anorexia
upset stomach
nausea
CV: hypertension
Warnings
Cardiovascular events, including sudden death (same as stimulants)
May increase [...]
Contraindications
[...]
Severe cardiac disorders
Moderate-severe HTN
Use with or within 14 days of MAO inhibitors
Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
suicidal ideation
Glaucoma
![<p>Non-Stimulant Agents </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> <br></p><ul><li><p>Mechanism: </p><ul><li><p><span>selective norepinephrine <em><u>reuptake inhibitor</u></em></span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>PK/PD </p><ul><li><p>Onset of action: 2-4 weeks </p></li><li><p>Duration: 10-12 hours </p></li><li><p>Takes 6-12 weeks for max effect </p></li><li><p>May be used with stimulants</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4c6d640e-10b8-4b0b-8475-c0789efa3b8c.jpg)
Non-Stimulant Agents
[...]
Mechanism:
selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
PK/PD
Onset of action: 2-4 weeks
Duration: 10-12 hours
Takes 6-12 weeks for max effect
May be used with stimulants
Atomoxetine (Strattera)
![<p>Non-Stimulant Agents </p><ul><li><p><span>Atomoxetine (Strattera)</span> <br></p><ul><li><p>Mechanism: </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>PK/PD </p><ul><li><p>Onset of action: 2-4 weeks </p></li><li><p>Duration: 10-12 hours </p></li><li><p>Takes 6-12 weeks for max effect </p></li><li><p>May be used with stimulants</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/781a6b0d-14ed-4d2f-8dab-842d847027c1.jpg)
Non-Stimulant Agents
Atomoxetine (Strattera)
Mechanism:
[...]
PK/PD
Onset of action: 2-4 weeks
Duration: 10-12 hours
Takes 6-12 weeks for max effect
May be used with stimulants
selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Adverse effects
CNS: Dizziness, fatigue, drowsiness
Dermatologic: hyperhidrosis
GI: anorexia, upset stomach, nausea
CV: hypertension
Warnings
Cardiovascular events, including sudden death (same as stimulants)
May increase suicidal ideation
Contraindications
Glaucoma
Severe cardiac disorders
Moderate-severe HTN
Use with or within 14 days of MAO inhibitors
Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
![<p>Non-Stimulant Agents </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Clinical Pearls </p><ul><li><p>Less effective than stimulants </p></li><li><p>Option if patient has <strong><em><u>active</u></em></strong><em><u> substance abuse problem, anxiety, tics</u></em> OR has <strong>intolerable side effects</strong> to stimulants </p></li><li><p>Less growth suppression than stimulants </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d88669bb-576d-4d24-b0fd-1f211990ae0f.jpg)
Non-Stimulant Agents
[...]
Clinical Pearls
Less effective than stimulants
Option if patient has active substance abuse problem, anxiety, tics OR has intolerable side effects to stimulants
Less growth suppression than stimulants
Atomoxetine (Strattera)
Non-Stimulant Agents
[...]
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
preferentially binds postsynaptic alpha2A-adrenoreceptors in prefrontal cortex
delays firing of prefrontal cortex neurons
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 18 hours
Dosed once daily
Clinical Pearls
Same as clonidine
Longer-acting than clonidine
AE: same as clonidine
Rebound HTN if stopped abruptly
Guanfacine ER (Intuniv)
Non-Stimulant Agents
Guanfacine ER (Intuniv)
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
preferentially binds postsynaptic [...] in prefrontal cortex
delays firing of prefrontal cortex neurons
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 18 hours
Dosed once daily
Clinical Pearls
Same as clonidine
Longer-acting than clonidine
AE: same as clonidine
Rebound HTN if stopped abruptly
alpha2A-adrenoreceptors
Non-Stimulant Agents
Guanfacine ER (Intuniv)
Mechanism:
unknown
Possibly:
preferentially binds postsynaptic alpha2A-adrenoreceptors in prefrontal cortex
delays firing of prefrontal cortex neurons
PK/PD
Onset: up to 2 weeks
Duration: 18 hours
Dosed once daily
Clinical Pearls
Same as clonidine
[Shorter or Longer]-acting than clonidine
AE: same as clonidine
[...] if stopped abruptly
Longer
Rebound HTN
44-87% of children with ADHD have at least one other disorder such as:
[...]
[...]
[...]
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)
Anxiety disorder
Tics and Tourette Disorders
ODD = people who yell out, act out against their parents, etc
Tics = repeated motion
Anxiety, social anxiety disorder, etc are more prevalent in these patients -tend to act out more, deviant behavior
-90% of patients with terrets will have ADHD too
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Anticonvulsants
Increases GABA (inhibitory neurotransmitter) to brain neurons and may enhance GABA at postsynaptic receptor sites
Many potential side effects; both are teratogenic!
Preferred in [...] or [...]
Drug of choice
[...]
[...]
seizure disorder or bipolar illness
Divalproex
Topiramate
![<p>Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis</p><ul><li><p>Beta-Blockers and Verapamil </p><ul><li><p>Reduces frequency ~50% in more than half of patients </p></li><li><p><strong><em><u>Modulates adrenergic and serotonergic to</u></em>ne </strong>making patients less susceptible to migraines </p><ul><li><p>Preferred in <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> or <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>Drug of choice: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f177e806-d70e-4483-87c5-a42e8c40aed3.jpg)
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Beta-Blockers and Verapamil
Reduces frequency ~50% in more than half of patients
Modulates adrenergic and serotonergic tone making patients less susceptible to migraines
Preferred in [...] or [...]
Drug of choice: [...]
HTN or angina
Propranolol
Typically takes 2-3 months to determine effectiveness
Continue for 6-12 months after improvement is seen
May taper and discontinue
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
New Drugs – Migraine Prophylaxis
Galcanez[...] (Emgality)
Epitinez[...] (Vyepti)
Eren[...] (Almovig)
Fremanez[...]-vfm (Ajovy)
Mechanism
Binds to calcitonin-gene related peptide (CGRP)
modulates trigeminovascular pain transmission
umab
umab
umab
umab
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
New Drugs – Migraine Prophylaxis
Galcanezumab (Emgality)
Epitinezumab (Vyepti)
Erenumab (Almovig)
Fremanezumab-vfm (Ajovy)
Mechanism
Binds to [...]
modulates [...] pain transmission
calcitonin-gene related peptide (CGRP)
trigeminovascular
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
NSAIDs
Used sparingly due to a risk of rebound
For [...]
e.g. [...]
Initiate 1-2 days prior to onset
Before headache is expected to occur
Discontinue when high risk period is over
recurrent, predictable migraines
menstrual associated migraines
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Options -- [...] will help determine choice
Beta-blockers
Tricyclic antidepressants
Anticonvulsants
NSAIDs



Typically takes 2-3 months to determine effectiveness
Continue for 6-12 months after improvement is seen
May taper and discontinue
Co-morbidities
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Options -- Co-morbidities will help determine choice
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]



Typically takes 2-3 months to determine effectiveness
Continue for 6-12 months after improvement is seen
May taper and discontinue
Beta-blockers
Tricyclic antidepressants
Anticonvulsants
NSAIDs
![<p>Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis</p><ul><li><p>Tricyclic Antidepressants </p><ul><li><p><strong><em><u>Down regulates serotonin and NE receptors</u></em></strong> – exact mechanism unknown </p></li><li><p>TCAs are associated with <strong><em><u>more side effects</u></em></strong> therefore tolerability may prevent use </p></li><li><p>Preferred if patient has <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> or <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>Drug of choice: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/200073ed-8848-4c64-9bd2-3528aceec0e7.jpg)
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Tricyclic Antidepressants
Down regulates serotonin and NE receptors – exact mechanism unknown
TCAs are associated with more side effects therefore tolerability may prevent use
Preferred if patient has [...] or [...]
Drug of choice: [...]
depression
insomnia
Amitriptyline
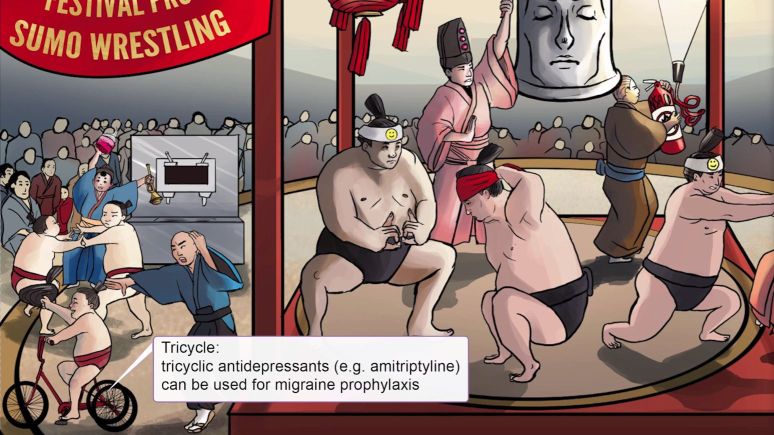
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Cluster Headache: Treatment and Prophylaxis
Treatment
[...] (relieves pain in 50-85% of patients)
Triptans:
SQ and intranasal sumatriptan and intranasal zolmitriptan may also effective
100% Oxygen
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
[For what type of headache]: Treatment and Prophylaxis
Treatment
100% Oxygen (relieves pain in 50-85% of patients)
Triptans:
SQ and intranasal sumatriptan and intranasal zolmitriptan may also effective
Cluster Headache
Migraine Medications: [...]
Scheduled medication to decreased frequency, severity and duration of migraines
May improve response to acute therapy
When to use
4 or more attacks per month
Intermittent use for predictable pattern such as in:
Menstrual migraine
Exercise induced migraine
Prophylaxis
Migraine Medications: Prophylaxis
Scheduled medication to decreased frequency, severity and duration of migraines
May improve response to acute therapy
When to use
4 or more attacks per month
Intermittent use for predictable pattern such as in:
[...]
[...]
Typically takes 2-3 months to determine effectiveness
Continue for 6-12 months after improvement is seen
May taper and discontinue
Menstrual migraine
Exercise induced migraine
[...]
Chronic illness that causes periodic shifts in mood through episodes of dysthymia, depression, hypomania, and mania
Not from substance use
Not caused by another medical condition
Symptoms typically presents in early adulthood
Rare before puberty and after 65
Usual age range of onset 18-44 years
No predilection for race, sex, or ethnicity
1/3 attempt suicide
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder
Chronic illness that causes periodic shifts in mood through episodes of dysthymia, depression, hypomania, and mania
Not from substance use
Not caused by another medical condition
Symptoms typically presents in early adulthood
[Is it common] before puberty and after 65
Usual age range of onset 18-44 years
No predilection for race, sex, or ethnicity
1/3 attempt suicide
Rare
Amphetamines
Formulations
All available as [which formulation?]
Onset of action ≤ 60 mins; variable with formulation
Duration
Short-acting (6 hrs.) → 1-2 doses per day
Mixed amphetamine salts (Adderall)
Long-acting (10-12 hours)
Mixed amphetamine salts extended-release (Adderall ER)
Lis-dexamphetamine (Vyvanse)
Lysine bound to amphetamine in order to prevent degradation
oral
![<p>Amphetamines </p><ul><li><p>Formulations</p><ul><li><p>All available as <span>oral</span> </p></li><li><p>Onset of action ≤ 60 mins; variable with formulation </p></li><li><p>Duration </p><ul><li><p>Short-acting (6 hrs.) → 1-2 doses per day </p><ul><li><p>Mixed amphetamine salts (<span><strong>[...]</strong></span>) </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Long-acting (10-12 hours) </p><ul><li><p>Mixed amphetamine salts extended-release (<span><strong>[...]</strong></span>) </p></li><li><p>Lis-dexamphetamine (<span><strong>[...]</strong></span>)</p><ul><li><p>Lysine bound to amphetamine in order to prevent degradation </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/707952df-d1f2-4241-96b5-b6363cd2b776.png)
Amphetamines
Formulations
All available as oral
Onset of action ≤ 60 mins; variable with formulation
Duration
Short-acting (6 hrs.) → 1-2 doses per day
Mixed amphetamine salts ([...])
Long-acting (10-12 hours)
Mixed amphetamine salts extended-release ([...])
Lis-dexamphetamine ([...])
Lysine bound to amphetamine in order to prevent degradation
Adderall
Adderall ER
Vyvanse
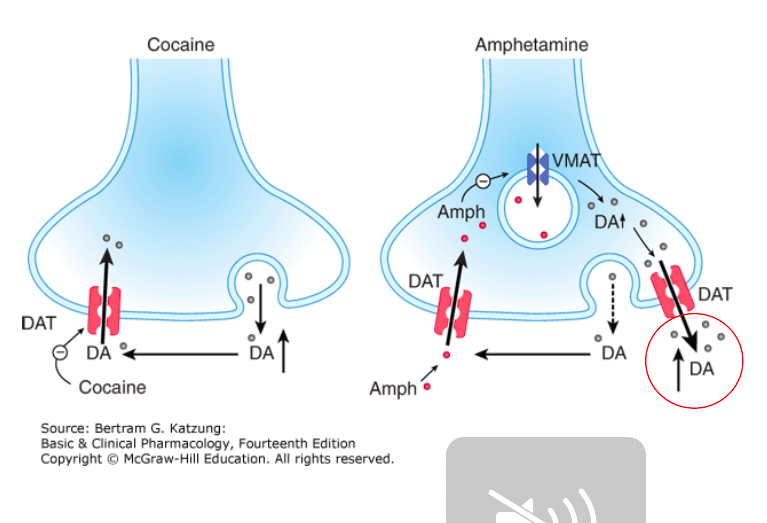
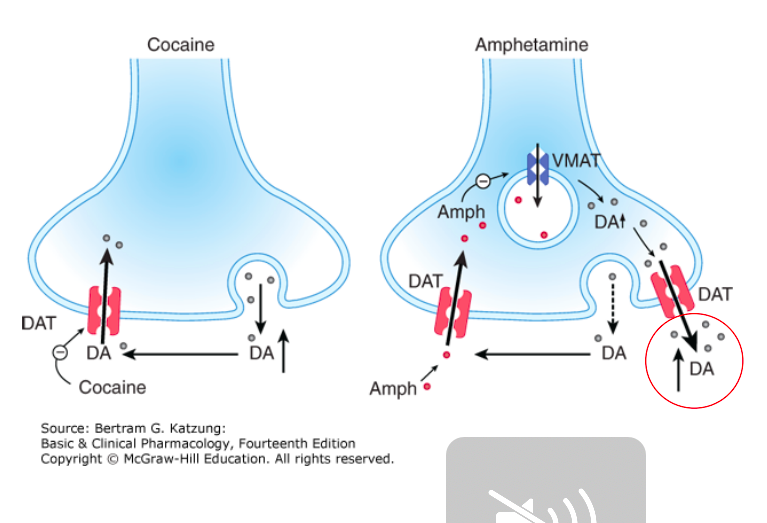
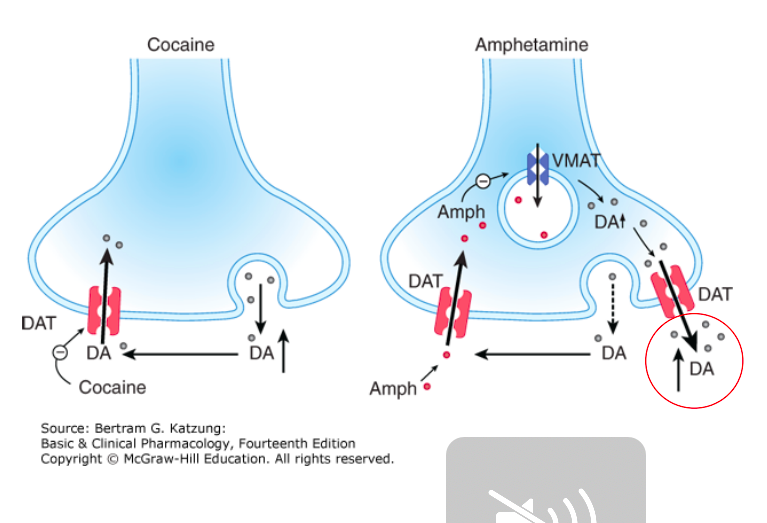
Amphetamines
Mechanism of action
[...]
Minor pathway: [...]
Formulations
Amphetamine
Dextroamphetamine
Mixed salts – d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine (3:1)
Lis-dexamphetamine (lysine-bound)
Promote release of dopamine and norepinephrine from their storage sites in the presynaptic nerve terminals
blocks reuptake
![<p>Amphetamines </p><ul><li><p>Metabolism <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> via:</p><ul><li><p>oxidation</p></li><li><p>deamination</p></li><li><p>CYP2D6 </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Various active metabolites </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Elimination </p><ul><li><p>via <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/726fa56a-4379-4985-8253-3dfc24663b9f.png)
Amphetamines
Metabolism
[...] via:
oxidation
deamination
CYP2D6
Various active metabolites
Elimination
via [...]
Hepatic
urine
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Anticonvulsants
Carbamazepine
[Why is this drug notorious for drug-drug interactions?]
Also is a 3A4 substrate!
Black Box Warnings
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)
Toxic Epidermal Necrosis Syndrome (TENS) (HLA-B*1502)
Aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis
Strong CYP3A4 INDUCER
Carbamazepine -- has three a's
aplastic anemia
agranulocytosis
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Anticonvulsants
Carbamazepine
Strong CYP3A4 INDUCER
Also is a 3A4 substrate!
Black Box Warnings
[...]
[...]
[...] and [...]
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)
Toxic Epidermal Necrosis Syndrome (TENS) (HLA-B*1502)
Aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Anticonvulsants
Divalproex -- anti-epilectic drug
Black Box warnings
[...]
[...]
[...]
Hepatotoxicity
Pancreatitis
Teratogenicity
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Anticonvulsants
Lamotrigine
Black Box Warnings
[...]
[...]
only two L's in LLama --> two black box warnings
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)
Toxic Epidermal Necrosis Syndrome (TENS)
![<p><span>Bipolar Disorder Medications </span><br></p><ul><li><p>Lithium<br></p><ul><li><p>Adverse Effects -- LITHIUM<br></p><ul><li><p>L -- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>I -- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>T -- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>H-- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>I -- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>U -- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>M -- <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f3180930-6f3f-4323-9d6d-5cf6fb6fe00f.png)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Adverse Effects -- LITHIUM
L -- [...]
I -- [...]
T -- [...]
H-- [...]
I -- [...]
U -- [...]
M -- [...]
Leukocytosis
Insipidus
Tremor, teratogen
Hypothyroidism
Increased weight
Ugh…nausea and vomiting
Misc. CNS, cardia
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Conditions causing Li toxicity
Sodium restriction
Activities that cause you to be [...]
Dehydration
Vomiting/diarrhea
Heart failure
Heavy exercise
Sauna baths, hot weather, fever
Medical illnesses prone to dehydration
dyhydrated
![<p><span>Bipolar Disorder Medications </span><br></p><ul><li><p>Lithium<br></p><ul><li><p>Drug Interactions and Pregnancy <br></p><ul><li><p>Several drug interactions <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Increases or decreases]</strong></span> <strong><em>serum lithium</em></strong> & <span><strong>[Increases or decreases]</strong></span> renal elimination<br></p><ul><li><p><span>Diuretics</span> </p></li><li><p><span>ACE-inhibitors </span></p></li><li><p><span>NSAIDs</span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[Increases or decreases]</strong></span> <strong><em>serum lithium</em></strong> & <span><strong>[Increases or decreases]</strong></span> renal elimination<br></p><ul><li><p>Theophylline </p></li><li><p>Caffeine </p></li><li><p>Pregnancy</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d3b596af-ad54-4098-b1d2-9710e75a3f8b.jpg)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Drug Interactions and Pregnancy
Several drug interactions
[Increases or decreases] serum lithium & [Increases or decreases] renal elimination
Diuretics
ACE-inhibitors
NSAIDs
[Increases or decreases] serum lithium & [Increases or decreases] renal elimination
Theophylline
Caffeine
Pregnancy
Increases
decreases
decreases
increases
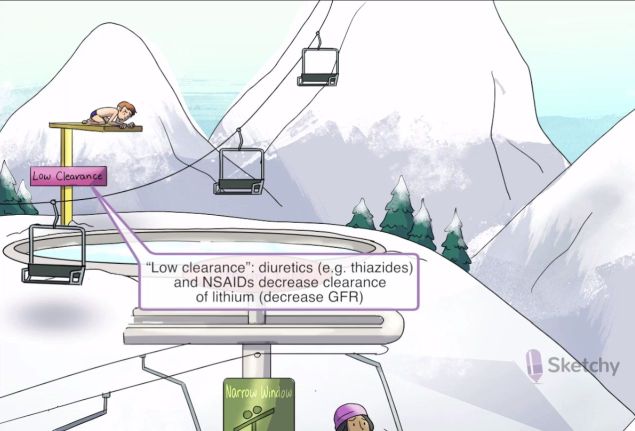
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Drug Interactions and Pregnancy
Several drug interactions
Increases serum lithium & decreases renal elimination
[...]
[...]
[...]
Decreases serum lithium & increases renal elimination
Theophylline
Caffeine
Pregnancy
Diuretics
ACE-inhibitors
NSAIDs
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Indications:
Acute [...]
Acute [...]
Maintenance of [...]
First line agent
Monotherapy or in combination with anticonvulsants or antipsychotics
Seems to work best for bipolar I
Efficacious (50%-70% response)
decreases the frequency and severity of both manic and depressive attacks
Use is limited by tolerability and safety
Requires close monitoring
Therapeutic level
Safety monitoring
mania
bipolar depression
bipolar I and II
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Indications:
Acute mania
Acute bipolar depression
Maintenance of bipolar I and II
[What line of therapy]
Monotherapy or in combination with anticonvulsants or antipsychotics
Seems to work best for bipolar I
Efficacious (50%-70% response)
decreases the frequency and severity of both manic and depressive attacks
Use is limited by tolerability and safety
Requires close monitoring
Therapeutic level
Safety monitoring
First line agent
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Lithium-associated [...]
Lithium interferes with action of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
ADH is responsible for free water reabsorption in the collecting tubule
Usually reversible but can be irreversible with long- term use
30-50% of patient develop DI
Management
Amiloride (potassium-sparing diuretic) -- if lithium cannot be stopped
Decreases lithium concentration at the collecting ducts
Diabetes Insipidus
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Lithium-associated Diabetes Insipidus
Lithium interferes with action of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
ADH is responsible for free water reabsorption in the collecting tubule
Usually reversible but can be irreversible with long- term use
30-50% of patient develop DI
Management
[...] (potassium-sparing diuretic) -- if lithium cannot be stopped
Decreases lithium concentration at the collecting ducts
Amiloride
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Lithium-associated Diabetes Insipidus
Lithium interferes with action of [...]
[...] is responsible for free water reabsorption in the collecting tubule
Usually reversible but can be irreversible with long- term use
30-50% of patient develop DI
Management
Amiloride (potassium-sparing diuretic) -- if lithium cannot be stopped
Decreases lithium concentration at the collecting ducts
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
ADH
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Mechanism:
exact mechanism unknown -- Mood stabilizing effects
Appears to be neuroprotective:
decreasing [...]
enhancing [...], etc
glutamate
neurotropic factors
Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Monitoring
Therapeutic levels
Acute mania [...] to [...] mEq/L
Maintenance: [...] to [...] mEq/L
Toxic Concentrations
>1.5 mEq/L
tremor, N/V, blurred vision, vertigo, confusion, decreased deep tendon reflexes
>2.5 mEq/L
seizures, coma, cardiac dysrhythmia, permanent neurological impairment
>3.5 mEq/L
potentially fatal
Baseline and periodically:
BMP, CBC, renal, thyroid function, urinalysis, electrocardiogram
Pregnancy test for all females -- because it is highly teratogenic
0.5
1.2
0.6
1
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Monitoring
Therapeutic levels
Acute mania 0.5 to 1.2 mEq/L
Maintenance: 0.6 to 1 mEq/L
Toxic Concentrations
[...] mEq/L
tremor, N/V, blurred vision, vertigo, confusion, decreased deep tendon reflexes
[...] mEq/L
seizures, coma, cardiac dysrhythmia, permanent neurological impairment
[...] mEq/L
potentially fatal
Baseline and periodically:
BMP, CBC, renal, thyroid function, urinalysis, electrocardiogram
Pregnancy test for all females -- because it is highly teratogenic
>1.5
>2.5
>3.5
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Monitoring
Therapeutic levels
Acute mania 0.5 to 1.2 mEq/L
Maintenance: 0.6 to 1 mEq/L
Toxic Concentrations
>1.5 mEq/L
tremor, N/V, blurred vision, vertigo, confusion, decreased deep tendon reflexes
>2.5 mEq/L
seizures, coma, cardiac dysrhythmia, permanent neurological impairment
>3.5 mEq/L
potentially fatal
Baseline and periodically:
BMP, CBC, renal, thyroid function, urinalysis, electrocardiogram
[should females take special precautions?]
Pregnancy test for all females -- because it is highly teratogenic
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
PK
High absorption from GI tract (80-100% bioavailable)
No protein binding, no metabolization
95% of a single dose is eliminated via urine
Half-life ~ 24 hours
Steady state ~5 days; onset of action takes more time!
Elimination via [...]
Li+ competes with Na+ for [...]
Li+ retention can be [increased or decreased] by Na+ loss
Example of Na+ loss: sweating!
kidneys
tubular
reabsorption
increased
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
PK
High absorption from GI tract (80-100% bioavailable)
No protein binding, no metabolization
95% of a single dose is eliminated via urine
Half-life ~ 24 hours
Steady state ~5 days; onset of action takes more time!
Elimination via kidneys
Li+ competes with Na+ for tubular reabsorption
Li+ retention can be increased by Na+ loss
Example of Na+ loss: [...]!
sweating
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Lithium
Treatment
Ideally, use in patients with normal cardiac and renal function
Therapeutic levels must be maintained
Compliance is challenging
May take 1-2 weeks for [...] effects
Antipsychotics and benzodiazepines used as adjuncts to “bridge”
May take 6-8 weeks for [...] effects
antimanic
antidepressant
![<p>Bipolar Disorder Medications </p><ul><li><p>Main 3 Classes<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>Carbonate </p></li><li><p>Citrate </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>Divalproex</p></li><li><p>Carbamazepine</p></li><li><p>Lamotrigine </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>Aripiprazole</p></li><li><p>Olanzapine</p></li><li><p>Quetiapine</p></li><li><p>Lurasidone, etc. </p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Adjunct Therapy <br></p><ul><li><p><span>Benzodiazepines</span> </p></li><li><p><span>Antidepressants</span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/53a635d4-e4d7-435f-9605-662aa1f68a37.jpg)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Main 3 Classes
[...]
Carbonate
Citrate
[...]
Divalproex
Carbamazepine
Lamotrigine
[...]
Aripiprazole
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Lurasidone, etc.
Adjunct Therapy
Benzodiazepines
Antidepressants
Lithium
Anticonvulsants
Antipsychotics

![<p>Bipolar Disorder Medications </p><ul><li><p>Main 3 Classes<br></p><ul><li><p><span>Lithium</span> </p><ul><li><p>Carbonate </p></li><li><p>Citrate </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span>Anticonvulsants</span> </p><ul><li><p>Divalproex</p></li><li><p>Carbamazepine</p></li><li><p>Lamotrigine </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span>Antipsychotics</span> </p><ul><li><p>Aripiprazole</p></li><li><p>Olanzapine</p></li><li><p>Quetiapine</p></li><li><p>Lurasidone, etc. </p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Adjunct Therapy <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2378bf83-96b1-4de4-a720-03ea5589a085.jpg)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Main 3 Classes
Lithium
Carbonate
Citrate
Anticonvulsants
Divalproex
Carbamazepine
Lamotrigine
Antipsychotics
Aripiprazole
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Lurasidone, etc.
Adjunct Therapy
[...]
[...]
Benzodiazepines
Antidepressants

![<p>Bipolar Disorder Medications </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>mood-stabilizing drugs that reduce manic and depressive episodes </p></li><li><p>Monotherapy or adjunct </p><ul><li><p>Can be used in combination +/- lithium +/- antipsychotic</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Drugs </p><ol><li><p><span>Divalproex</span> </p></li><li><p><span>Carbamazepine</span> </p></li><li><p><span>Lamotrigine</span> </p></li></ol></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/68697bf0-0eb3-4fdc-a52a-6e96dec1553c.jpg)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
[...]
mood-stabilizing drugs that reduce manic and depressive episodes
Monotherapy or adjunct
Can be used in combination +/- lithium +/- antipsychotic
Drugs
Divalproex
Carbamazepine
Lamotrigine
Anticonvulsants

![<p>Bipolar Disorder Medications </p><ul><li><p><span>Anticonvulsants</span> </p><ul><li><p>mood-stabilizing drugs that reduce manic and depressive episodes </p></li><li><p>Monotherapy or adjunct </p><ul><li><p>Can be used in combination +/- lithium +/- antipsychotic</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Drugs </p><ol><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ol></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1c60a33c-6b08-44c7-9ca9-6f93f83d155d.jpg)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Anticonvulsants
mood-stabilizing drugs that reduce manic and depressive episodes
Monotherapy or adjunct
Can be used in combination +/- lithium +/- antipsychotic
Drugs
[...]
[...]
[...]
Divalproex
Carbamazepine
Lamotrigine

Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
Antidepressants
Controversial
[why?]
Not to be used as monotherapy
Used in combination with mood stabilizer
Considered “3rd line”
If used, SSRIs and bupropion are preferred
potential for switching to manic phase (especially in bipolar I)
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
Antidepressants
Controversial
potential for switching to manic phase (especially in bipolar I)
Not to be used as monotherapy
Used in combination with mood stabilizer
[what line of therapy?]
If used, SSRIs and bupropion are preferred
Considered “3rd line”
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
Bipolar depression Drugs
[...]
[...]
[...]
MOA:
blockade of D2 receptors in CNS
Quetiapine (Seroquel)
Olanzapine-fluoxetine (Symbyax)
Lurasidone (Latuda)
for acute and mixed mania
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
Bipolar depression Drugs
Quetiapine (Seroquel)
Olanzapine-fluoxetine (Symbyax)
Lurasidone (Latuda)
MOA:
[...]
blockade of D2 receptors in CNS
for acute and mixed mania
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
Useful for [...] or [...] episodes
Monotherapy or +/- mood stabilizer +/- BZD
Quick onset, making it useful as bridge therapy
Often used in combination regimens for acute treatment of mania
acute or mixed mania
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
[...]
Useful for acute treatment of mania/hypomania
Used in combination with mood stabilizer or antipsychotic
Helpful for agitation, insomnia, hyperactivity
Not effective at core symptoms or prevention of relapse
Long-term therapy is not recommended
Benzodiazepines
adjunt therapy -- used to bridge the gap between anti-maniac and anti-depression effects of Lithium
Bipolar Disorder Medications
Antipsychotics
Benzodiazepines
Useful for acute treatment of mania/hypomania
Used in combination with mood stabilizer or antipsychotic
Helpful for agitation, insomnia, hyperactivity
Not effective at core symptoms or prevention of relapse
[Is Long-term therapy recommended?]
Long-term therapy is not recommended
adjunt therapy -- used to bridge the gap between anti-maniac and anti-depression effects of Lithium
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]:
At least one manic episode, which may have been preceded by and may be followed by hypomanic or major depressive episode(s)
Bipolar I disorder
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]:
At least one hypomanic episode and a current or past major depressive episode
Bipolar II disorder
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]:
Chronic fluctuations between mild depression and hypomania, none of which meet the criteria for mania or major depressive episode
Cyclothymic disorder
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]
A distinct period of persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting throughout at least 4 days, that is clearly different from the usual nondepressed mood
Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
Decreased need for sleep
More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
Flight of ideas or racing thoughts
Distractibility
Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have high potential for painful consequences
Hypomanic Episode
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
Hypomanic Episode
A distinct period of persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting throughout [for how long], that is clearly different from the usual nondepressed mood
Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
Decreased need for sleep
More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
Flight of ideas or racing thoughts
Distractibility
Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have high potential for painful consequences
at least 4 days
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]
5 or more of the following in same 2-week period
Several other symptoms need to be present for diagnosis
Depressed mood
Diminished interest/pleasure in most/all activities
Significant weight change
Feelings of worthlessness
Psychomotor agitation or retardation
Insomnia or hypersomnia
Fatigue
Diminished ability to think
Recurrent thoughts of death
Major Depressive Disorder
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]
Distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary)
Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
Decreased need for sleep
More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
Flight of ideas or racing thoughts
Distractibility
Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have high potential for painful consequences
Manic Episode
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
Manic Episode
Distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting [how long] (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary)
Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
Decreased need for sleep
More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
Flight of ideas or racing thoughts
Distractibility
Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have high potential for painful consequences
at least 1 week
Bipolar Disorder: Definitions
[...]:
concurrent features of mania and depression
Mixed Episode
![<p>Methylphenidate </p><ul><li><p>Formulations</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Onset of action: </p><ul><li><p>≤ 60 mins</p></li><li><p>except Ritalin SR, 1-3 hrs </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Duration </p><ul><li><p><span>Short-acting</span> (3-5 hrs.) → 2-3 doses per day</p></li><li><p><span>Intermediate</span> (6-8hrs.) → 1dose per day</p></li><li><p><span>Long-acting</span> (8-12 hrs.) → 1 dose per day </p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Can be placed on the hip for <span>up to 9 hours</span> </p><ul><li><p><strong>Effects last ~12 hours</strong> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Onset of action: 1-2 hours </p></li><li><p>Adverse reactions </p><ul><li><p>Same as oral </p></li><li><p>Skin reactions e.g. contact sensitization </p></li><li><p>Excessive absorption exposed to heat</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/eaa1b4d6-1e17-4e02-9c52-479dd344e1d7.jpg)
Methylphenidate
Formulations
[...]
Onset of action:
≤ 60 mins
except Ritalin SR, 1-3 hrs
Duration
Short-acting (3-5 hrs.) → 2-3 doses per day
Intermediate (6-8hrs.) → 1dose per day
Long-acting (8-12 hrs.) → 1 dose per day
[...]
Can be placed on the hip for up to 9 hours
Effects last ~12 hours
Onset of action: 1-2 hours
Adverse reactions
Same as oral
Skin reactions e.g. contact sensitization
Excessive absorption exposed to heat
Oral
Transdermal (Daytrana)
Methylphenidate
Formulations
Oral
Onset of action:
≤ 60 mins
except Ritalin SR, 1-3 hrs
Duration
[...] (3-5 hrs.) → 2-3 doses per day
[...] (6-8hrs.) → 1dose per day
[...] (8-12 hrs.) → 1 dose per day
Transdermal (Daytrana)
Can be placed on the hip for up to 9 hours
Effects last ~12 hours
Onset of action: 1-2 hours
Adverse reactions
Same as oral
Skin reactions e.g. contact sensitization
Excessive absorption exposed to heat
Short-acting
Intermediate
Long-acting
Methylphenidate
Formulations
Oral
Onset of action:
≤ 60 mins
except Ritalin SR, 1-3 hrs
Duration
Short-acting (3-5 hrs.) → 2-3 doses per day
Intermediate (6-8hrs.) → 1dose per day
Long-acting (8-12 hrs.) → 1 dose per day
Transdermal (Daytrana)
Can be placed on the hip for [how long? Is it longer than the oral?]
Effects last ~12 hours
Onset of action: 1-2 hours
Adverse reactions
Same as oral
Skin reactions e.g. contact sensitization
Excessive absorption exposed to heat
up to 9 hours
![<p>Methylphenidate </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[What]</strong></span> line therapy </p></li><li><p>Mechanism of action<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>Metabolism <br></p><ul><li><p><span>Hepatic</span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Elimination <br></p><ul><li><p><span>78%-97% eliminated via urine as inactive metabolites</span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a4bbbffa-31ee-471d-863a-9fa447ea7b89.jpg)
Methylphenidate
[What] line therapy
Mechanism of action
[...]
Metabolism
Hepatic
Elimination
78%-97% eliminated via urine as inactive metabolites
First
Blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into presynaptic neurons
Concentrates in brain more than plasma
![<p>Methylphenidate </p><ul><li><p><span>First</span> line therapy </p></li><li><p>Mechanism of action<br></p><ul><li><p><span><u>Blocks the reuptake</u> of norepinephrine and dopamine into presynaptic neurons</span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>Metabolism <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Elimination <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d1aa80ff-22d8-482d-935d-bedc72d14d9f.jpg)
Methylphenidate
First line therapy
Mechanism of action
Blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into presynaptic neurons
Metabolism
[...]
Elimination
[...]
Hepatic
78%-97% eliminated via urine as inactive metabolites
Concentrates in brain more than plasma
Non-Stimulants
[...] and [...]
[...]
Options if:
Stimulants caused intolerable side effects
Contraindications to stimulants
Stimulants failed or inadequate response
Abuse/dependence issues with stimulants
Clonidine
guanfacine
Atomoxetine
![<p>Stimulants Warnings </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[What scheudle is it?]</strong></span>: </p><ul><li><p>High potential for abuse and dependence. </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/afdfd366-9f16-4460-bc30-f6a25d4afe45.png)
Stimulants Warnings
[What scheudle is it?]:
High potential for abuse and dependence.
C-II
Administration for prolonged periods may lead to drug dependence
Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy
![<p>Stimulants Warnings </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> <br></p><ul><li><p>Prolonged (>4 hrs) erection </p></li><li><p>Often painful </p></li><li><p>Surgical intervention may be necessary</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/009f27c1-2eb6-47ae-84be-50c244d2cebc.png)
Stimulants Warnings
[...]
Prolonged (>4 hrs) erection
Often painful
Surgical intervention may be necessary
Priapism
![<p>Stimulants Warnings </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Peripheral vasculopathy </p></li><li><p>Typically mild and intermittent </p></li><li><p>Rare: digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2a7556ab-d2a1-41e7-b0f0-827f324098df.png)
Stimulants Warnings
[...]
Peripheral vasculopathy
Typically mild and intermittent
Rare: digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown
Raynaud phenomenon
Stimulants: Adverse Effects
In general:
Poor growth
weight loss
decreased appetite
CNS:
Jitteriness
Sleep disturbance
Irritability
Headache
Rare: psychosis
CV:
Tachycardia
Palpitations
Increased BP and HR
GI
[...]
[...] -- dry mouth
Upset stomach and nausea
Anorexia
Xerostomia
Stimulants: Contraindications
Symptomatic cardiovascular disease
Moderate to severe [hypo or hyper]tension
[hypo or hyper]thyroidism
Known hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines
[specific disease?]
Marked anxiety, tension and agitation
History of drug abuse
Concurrent use or use within 14 days of the administration of [...]
hyper
hyper
Glaucoma
monoamine oxidase inhibitors
[...]
Characterized by a considerable degree of inattentiveness, distractibility, impulsivity, and often hyperactivity
ADHD
Adults must have childhood-onset, persistent, and current symptoms of ADHD to be diagnosed
Headaches: General Principles
Primary headaches
[...]
Secondary headaches
[...]
recurrent, not caused by underlying disease
caused by underlying disease
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Simple Analgesics
Used for:
[...]
[...]
Choices:
Acetaminophen
Combination
Acetaminophen (APAP), aspirin, caffeine
MOA
APAP:
not completely understood
may activate descending serotonergic inhibitory pathways in the CNS
Caffeine:
CNS stimulant
vasoconstrictor on cerebral vessels
Aspirin:
inhibits prostaglandin synthesis in CNS
Mild-moderate migraines
tension headaches
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Simple Analgesics
Used for:
Mild-moderate migraines
tension headaches
Choices:
Acetaminophen
Combination
Acetaminophen (APAP), aspirin, caffeine
MOA
APAP:
not completely understood
may activate [...] pathways in the CNS
Caffeine:
CNS stimulant
vaso[dilator or constrictor] on cerebral vessels
Aspirin:
inhibits [...] in CNS
descending serotonergic inhibitory
constrictor
prostaglandin synthesis
![<p>Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment </p><ul><li><p>Treatment options<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Misc. agents </p><ul><li><p>oxygen -- used primarily for <span><strong><em><u>[...]</u></em></strong></span><strong><em><u> </u></em></strong></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fe89d355-1673-41bf-baa1-b20333d24a67.jpg)
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Treatment options
[...]
[...]
[...]
Misc. agents
oxygen -- used primarily for [...]
Simple analgesics
Triptans
Ergot alkaloids
cluser headaches

Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Adverse Effects
[...] (common)
Worse with ergotamine
Administer with an antiemetic
Paresthesia
Weakness and fatigue
Abdominal pain
Chest tightness
Peripheral ischemia and painful extremities (rare)
Nausea and vomiting
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Adverse Effects
Nausea and vomiting (common)
Worse with [which ergot type?]
Administer with an [...]
Paresthesia
Weakness and fatigue
Abdominal pain
Chest tightness
Peripheral ischemia and painful extremities (rare)
ergotamine
antiemetic
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Contraindications
[...]
Use of [...] with 24 hours
Use with [...]
Hepatic dysfunction
Renal dysfunction
Coronary artery disease
Cerebrovascular disease
Peripheral vascular disease
Pregnancy/lactation (category X)
triptan
a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Mechanism:
migraine effects due to:
vaso[constriction or dilation] via [...]
inhibition of [...] --> preventing inflammation
Also [...] vaso[constriction or dilation]
constriction
5-HT1B/1D receptor
vasoactive peptide release
alpha-1
constriction
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Types of Ergots
[...]
Sublingual and rectal suppository
[...]
Better tolerated than above
Intranasal, IV/IM/SC
Start ASAP at onset of migraine attack
Can be combined with caffeine or simple analgesics
Triptans contraindicated within 24 hours of an ergot
PK:
hepatically metabolized and eliminated via bile
Contraindications
Pregnancy/lactation (category X)
Hepatic dysfunction
Renal dysfunction
Coronary artery disease
Cerebrovascular disease
Peripheral vascular disease
Use of triptan with 24 hours
Use with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor
Ergotamine
Dihydroergotamine (DHE 45)
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Types of Ergots
Ergotamine
Sublingual and rectal suppository
Dihydroergotamine (DHE 45)
[Better or worse] tolerated than above
Intranasal, IV/IM/SC
Start ASAP at onset of migraine attack
Can be combined with caffeine or simple analgesics
Triptans contraindicated within 24 hours of an ergot
PK:
hepatically metabolized and eliminated via bile
Better
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Types of Ergots
Ergotamine
Sublingual and rectal suppository
Dihydroergotamine (DHE 45)
Better tolerated than above
Intranasal, IV/IM/SC
Start ASAP at onset of migraine attack
Can be combined with caffeine or simple analgesics
[...] contraindicated within 24 hours of an ergot
PK:
hepatically metabolized and eliminated via bile
Triptans
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Types of Ergots
Ergotamine
Sublingual and rectal suppository
Dihydroergotamine (DHE 45)
Better tolerated than above
Intranasal, IV/IM/SC
Start ASAP at onset of migraine attack
Can be combined with caffeine or simple analgesics
Triptans contraindicated within 24 hours of an ergot
PK:
[...] metabolized and eliminated via [...]
hepatically
bile
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Warnings
Cardiovascular
[...] due to vasospastic reactions
[...]
Evaluate patients that complain of [...]
Watch out for signs of decreased arterial flow such as in:
[...]
[...]
Cerebrovascular events have occurred (rarely) after injection
Avoid concurrent use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
Increases vasospasms
will be on exam
Peripheral ischemia
Myocardial ischemia
angina
Raynaud syndrome
Ischemic bowel
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Ergot Alkaloids
Warnings
Cardiovascular
Peripheral ischemia due to vasospastic reactions
Myocardial ischemia
Evaluate patients that complain of angina
Watch out for signs of decreased arterial flow such as in:
Raynaud syndrome
Ischemic bowel
Cerebrovascular events have occurred (rarely) after injection
Avoid concurrent use with [...]
Increases vasospasms
will be on exam
strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
Migraine Medications: Acute Treatment
Opioids and Barbiturates
[What line of option?]
Lack of quality evidence
Potential for abuse, tolerance, dependence, addiction, overdose
Relevant Drug
Fioricet (includes butalbital, APAP, caffeine)
Indicated for tension headaches
Prone to overuse headache
Limited data to support efficacy
Schedule III (butalbital)
Last-line options (“rescue”)