MCB 2610 Exam #2 - Eukarya and Antibacterials
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Clostridium botulinum
Gram-positive
Obligate anaerobes
Bacillus
Produce heat resistant endospores
Ferments sugars or Amino Acids
Causative agent of botulism
C. botulinum Locations
Soil, lake sediments, and decaying vegetation.
Botulism
Paralytic illness caused by a nerve toxin produced by C. botulinum.
Foodborne Botulism
Caused by eating foods that contain the botulinum toxin
Wound Botulism
Caused by a wound infected with C. botulinum, typically caused by injecting drugs or traumatic injury.
Inadvertent Botulism
Accidental overdoes of botulinum toxin
Infant Botulism
Caused by a child consuming spore or bacteria, which germinate in the intestine and release toxin.
Adult Intestinal Colonization Botulism
Caused by an adult consuming spores, which germinate in the intestine and release toxin.
Botulism Toxin Effect on Acetylcholine (Ach)
Blocks SNARE proteins from guiding Ach to the nerve membrane, leading to forced muscle relaxation and muscle paralysis.
Known Botulism Toxins
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and F/A Hybrid.
A is most common in the United States; most responsible for foodborne outbreaks.
Harmful Effect of Botulism Toxin
Can travel into the central nervous system causing paralysis.
C. botulinum Symptoms
Double vision, Blurred vision, Drooping eyelids, Slurred speech, Difficulty Swallowing, Dry Mouth, and Muscle Weakness.
Infant C. botulinum Symptoms
Lethargy, Poor feeding, Constipation, Weak cry, and Poor Muscle Tone.
Untreated C. botulinum
Progress to cause paralysis of respiratory muscles and airway obstructions, later leading to death.
Foodborne Botulism Onset
4 to 36 Hours
Dr. Justinus Andreas Christian Kerner (1800s)
Performed experiments on himself by eating small amount of sour sausage and then documented the signs and symptoms.
1895
C. botulinum isolated from a Belgium scientist
Dr. Vernon Brooks (1950)
Find that C. botulinum blocks the release of acetylcholine from motor nerve terminals.
1989
BOTOX approved by the US FDA in December 1989 for muscle spasms.
C. botulinum Epidemiology (2024)
Foodborne: 9
Infant: 67
Wound: 12
Other: 5
Total: 93 cases
C. botulinum Diagnosis
Serum analysis looking for Botulism Toxin
Needs to be caught early
C. botulinum Treatments
Treated with an antitoxin that blocks the action of the toxin circulating in the blood. --> Only available from food.
If from food, inducing vomiting or enemas to remove food.
Supportive care
Antibiotics for Infection Site (Wounds)
Several Months of Medical care
Patients who survive will have fatigue and shortness of breath for years after.
C. botulinum Prevention
Boil home-canned foods for 10 minutes before eating
When in doubt, throw it out.
Eukaryotic Glycocalyx
Sticky carbohydrate extending from animal plasma membrane.
Bound to proteins and lipids in membrane --> Glycoproteins.
Eukaryotic Glycocalyx Function
Strengthens the cell surface, helps attach cells together, and cell-cell recognition.
Eukaryotic Flagella and Cili
Make the cell move or "beat" via microtubules.
Propel the cell through water.
Pseudopodia/Pseudopods
a temporary foot-like projection of the cytoplasm
Contains cytoplasm
Used for cellular locomotion
Eukaryotic Flagella
Few and long
Eukaryotic Cilia
Short and Many
Microtubule Array
Nine parallel pairs of microtubules surrounding a central pair of microtubules, 9+2 array.
Hollow Tube.
Microtubule Protein
Tubulin
How Does Eukaryotic Flagella Move
Whip-like motion.
Sliding of microtubules relative to each other causes flagellum to bend.
Powered by ATP.
Eukaryotic Cell Wall
Simpler than bacterial.
Eukaryotes that lack this have some kind of protective layer on them.
Plant Cell Wall Component
Cellulose
Fungus Cell Wall Component
Chitin and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) units.
Yeast Cell Wall Component
Glucan and Mannan
Animal Cell Wall
Does not exist.
Protozoa Cell Wall Homolog
Flexible outer protein covering called a pellicle.
Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane
Very similar to Prokaryotic.
Contains carbohydrates for attachment sites.
Contains sterols/cholesterol for resistance to osmotic lysis and increase flexibility.
Phospholipid bilayer.
Transport Methods of Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane
Simple Diffusion, Facilitative Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport, and Endocytosis.
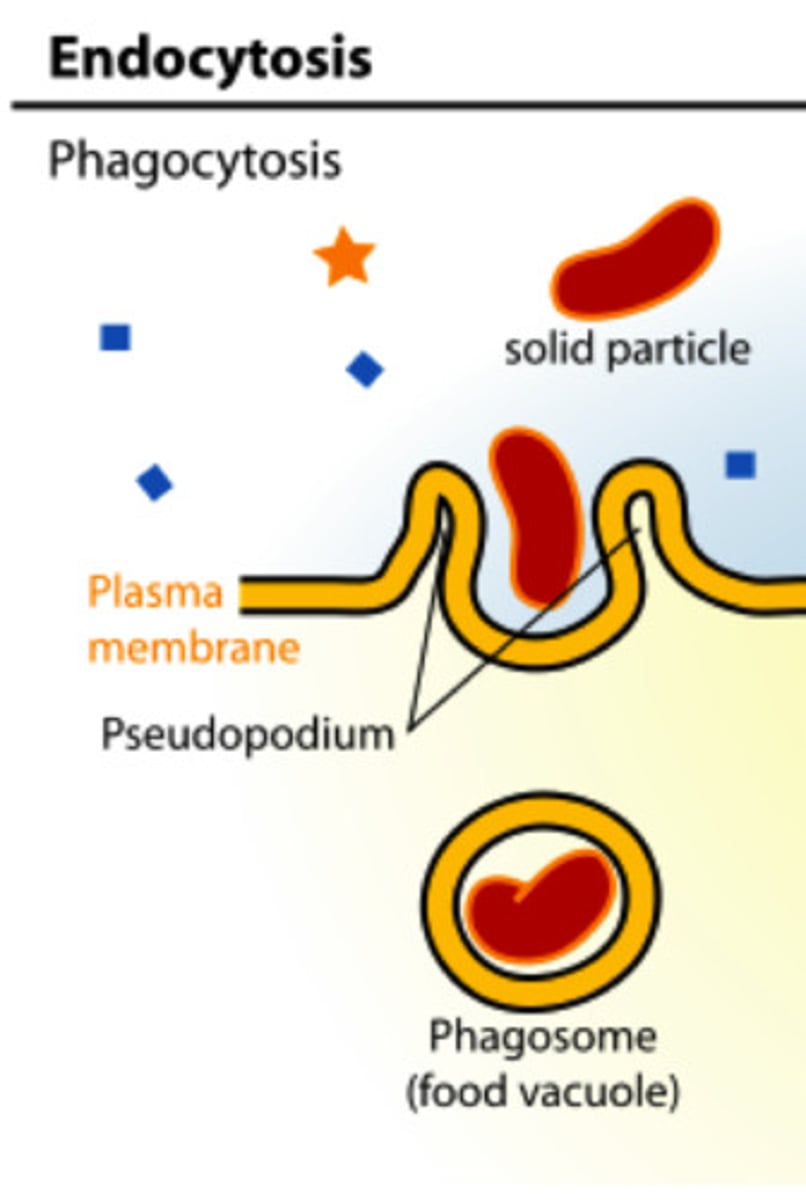
Phagocytosis
Pseudopods extend and and engulf particles
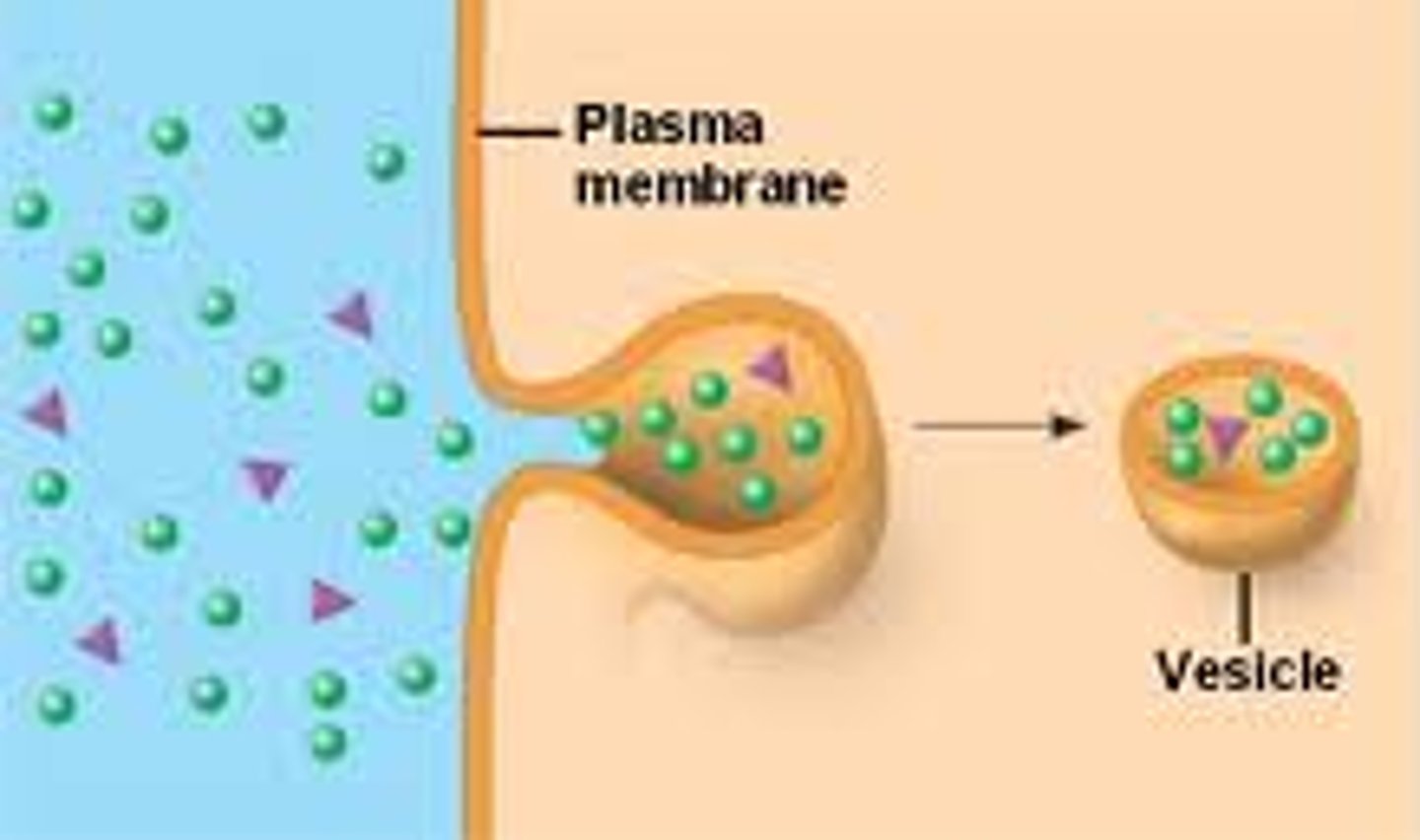
Pinocytosis
Membrane folds inward, bringing fluid and dissolved substances
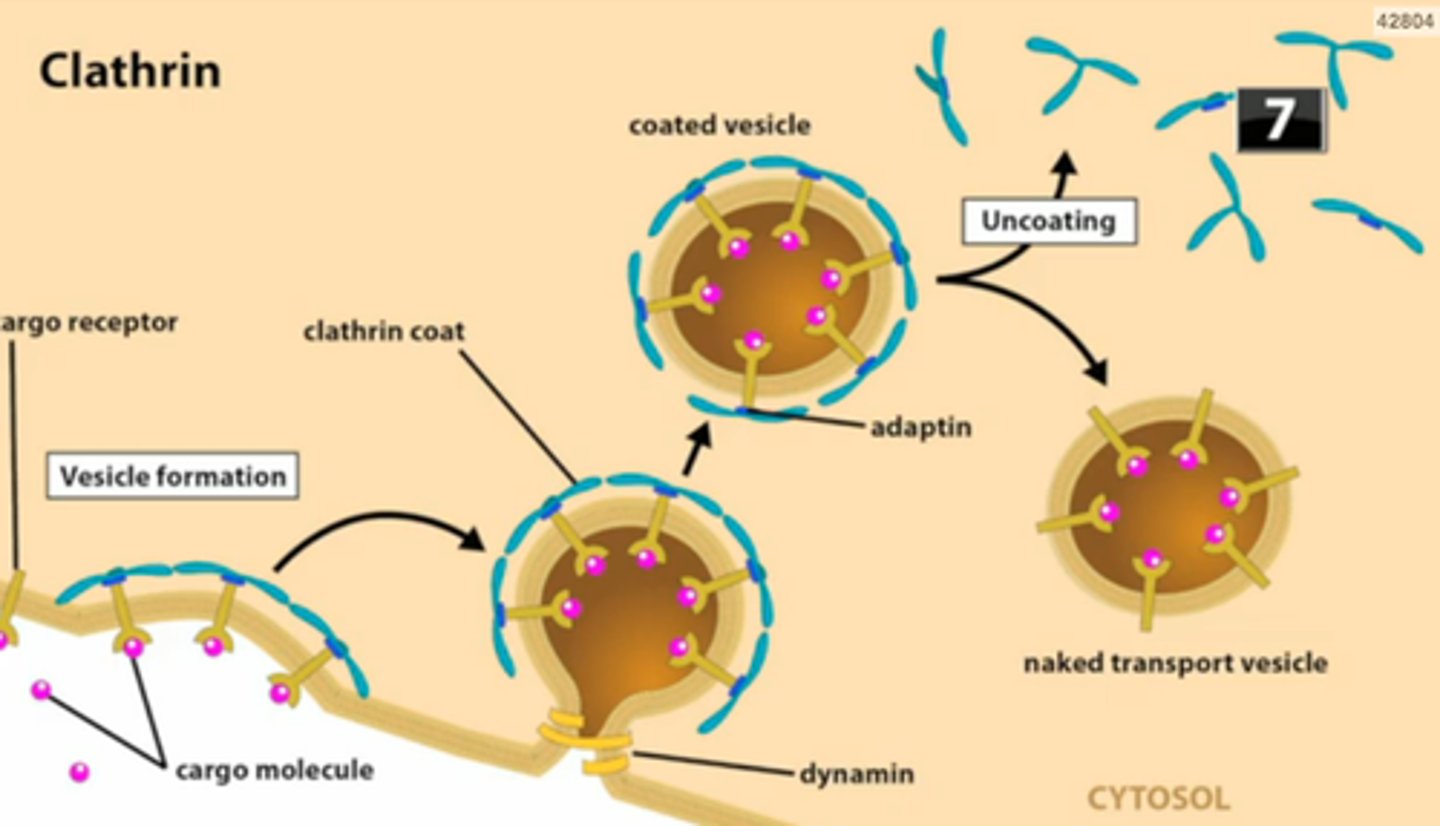
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Binding to a receptor then membrane folds in.
What is the nature of eukaryotic cytoplasm?
Semifluid, gelatinous, nutrient matrix
What are the complex internal structures found in eukaryotic cytoplasm?
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
Where do most metabolic reactions occur in eukaryotic cells?
In the cytoplasm
What functions does the eukaryotic cytoplasm provide?
Support, shape, and assists in solute/ion transport
What does eukaryotic cytoplasm contain?
Storage granules and organelles
Eukaryotic Ribosome
Site for Protein Synthesis
80s
Small Eukaryotic Ribosomal Subunit
40s
Large Eukaryotic Ribosomal Subunit
60s
Free Ribosome
Suspended in the cytosol, makes proteins that function in the cytosol.
Bound Ribosome
Attached to the outside of the Rough ER, makes proteins for insertion into membranes.
Chloroplast and Mitochondria Ribosomes
70s, endosymbiont theory.
Nucleus
Contains chromosomes
DNA
Nuclear Envelope
Encloses the nucleus, covered in pores.
Pore Complex
Regulates entry and exit of proteins and RNAs, as well as large complexes of macromolecules.
Chromosomes
Area where DNA is organized.
Structures that carry genetic information.
Each one contains one long linear DNA molecules associated with many proteins/histones.
Eukaryotic DNA Histone Complex
Octamer, 160 Nucleotide Base Pairs.
Chromatin
Histones and DNA together.
Characteristic of A Particular Species
The number and composition of chromosomes and the number of genes on each chromosome.
Human (46), Elephants (56), Nematodes (11)
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Transport network
Golgi Complex
Membrane formation and secretion
Lysozyme
Digestive Enzyme
Membranous sac with acid environment.
Lysozyme Function
Hydrolytic enzymes that digest various molecules without harming cytoplasmic components of the cell.
Can digest bacteria.
Vacuole
Brings food into cells and provides support.
Mitochondria
Powerplant, powerhouse, energy factories of the cell.
Found in all eukaryotic cells.
ATP molecules are produced within by cellular respiration.
Number depends on activities of the cell, can grow and divide independently.
Endosymbiont Theory Based On Eukaryotic Mitochondria
Double membranes, Contain ribosomes to produce their own proteins, Circular DNA, and grow independent within the cell.
Chloroplast
Photosynthesis
Peroxisome
Oxidation of fatty acids; destroys H2O2
Centrosome
Consists of protein fibers and centrioles, important for cell division
Tsetse Flies Endosymbiont
Wigglesworthia, Fly has a specialized organ for it, Sodalis glossinidius
Paramecium Endosymbiont
Ingesting algae and using them for photosynthesis.
Protozoa Harmful Microorganisms
Small amount needed to cause disease
Can be intracellular or extracellular
Unable to withstand drying --> cannot be free in environment
Arthropod Vectors
Examples of Protozoa
Plasmodium falciparum, Trypanosoma brucei, Giardia lamblia, and Toxoplasma gondii
Protozoa
Nonphotosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms.
Unicellular
Free-living
More animal-like than plant-like.
Protozoa Locations
Soil and water
Protozoa Motility
Divided into groups based on their method of locomotion.
Amebae
Pseudopodia
Ciliates
Cilia
Flagellates
Flagella
Amoeboid
Entamoeba histolytica; Parasite in GI tract
Flagellated Protozoans
Giardiasis
Trypanosomiasis
- African sleeping Disease (Tsetse flies)
- Chagas Disease (Kissing Bugs)
Ciliated Protozoans
Balantidium coli
Spore-forming Protozoans
Malaria (Plasmodium)
Helminths
Harmful Eukaryote whose life cycle is part microscopic, when it is typically spread.
Helminths Example
Roundworms and Flatworms
Taeniasis
adult tapeworm infects the intestine; from livestock.
Mycology
Study of Fungi
Fungi
Some are harmful, some are beneficial.
Yeasts, molds and mushrooms.
Not photosynthetic.
Fungi Cell Membrane
Ergosterols; antifungal drugs.
Fungi Growth
Unicellular and Hyphae
Fungal Spores
Help classify, either asexual or sexual.
Harmful fungal spore
Blastomycosis; Blastomyces dermatitidis
Yeast Locations
Soil and water, On skins of produce, and On Humans
Used in baking.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Most frequent yeast isolated from human clinical specimens
Candida albicans
Mycosis
fungal infection
Fungal Pathogen Cycle
Between Hyphae and yeast-like (Dimorphic)
Fungal Diseases
Chronic (long lasting)
Fungi grow slow
Hard to treat