NAPLEX: Pharmacy Foundations Part 1: Basic Science Concepts
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System
1. Somatic (voluntary)
2. Autonomic (involuntary)
-Parasympathetic (Rest and Digest)
-Sympathetic (Fight or Flight)
What is the primary receptor that works in the somatic?
Ach acting on nicotinic receptors
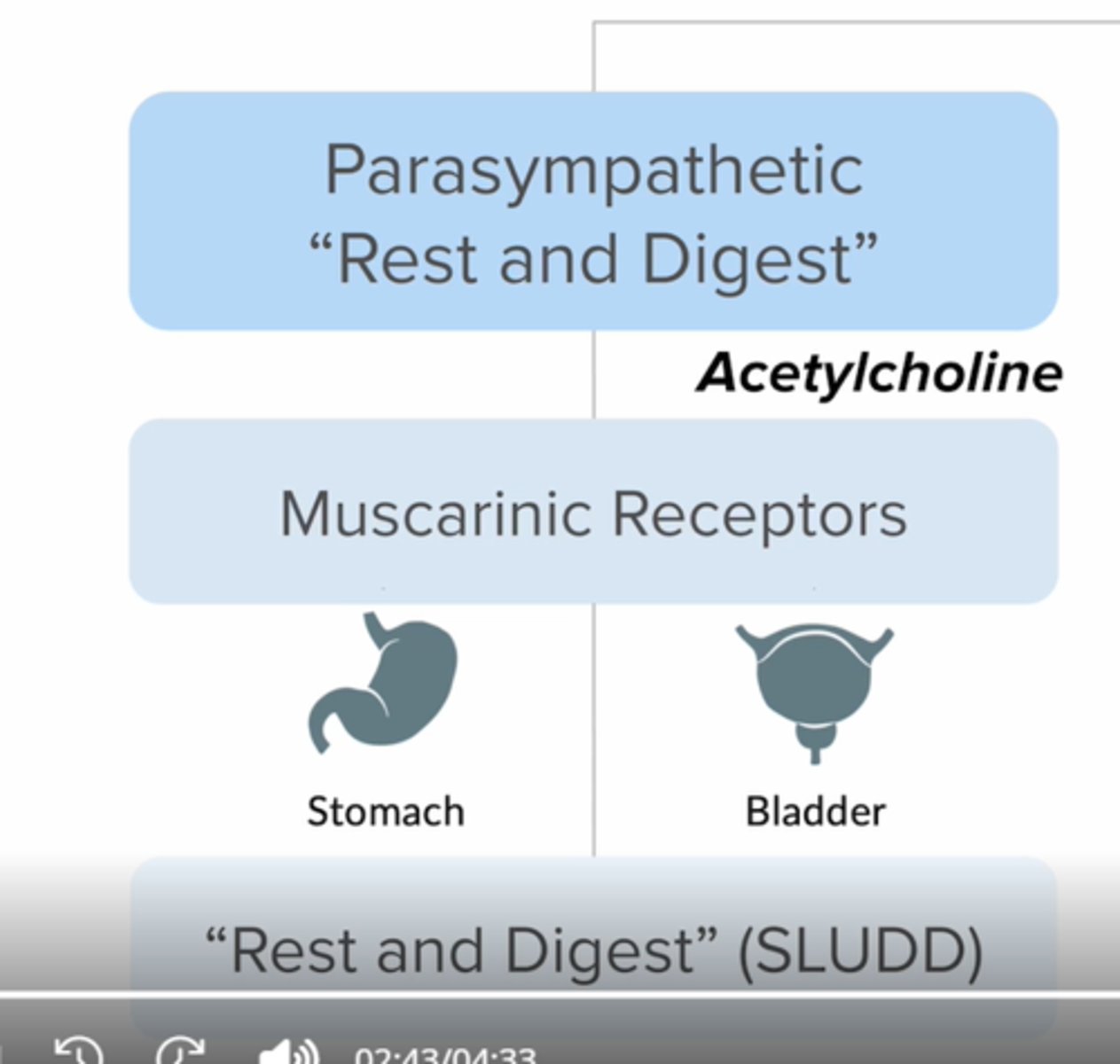
What happens in the parasympathetic nervous system?
Signal --> (Ach/N) --> (Ach/M) --[Most organs, smooth muscle & glands
Sympathetic Pathway through adrenal medulla
Signal --> (Ach/N)(adrenal medulla) ---[EPI/NE
sympathetic NS:
adrenergic receptors
alpha 1 receptor : blood vessels
beta 1: heart
beta 2: lungs
Functions of the parasympathetic nervous system
think acronym
Acetylcholine (bladder & stomach)
"rest and digest"
Increased SLUDD
-Salivation
-Lacrimation
-Urination
-Digestion
-Defecation
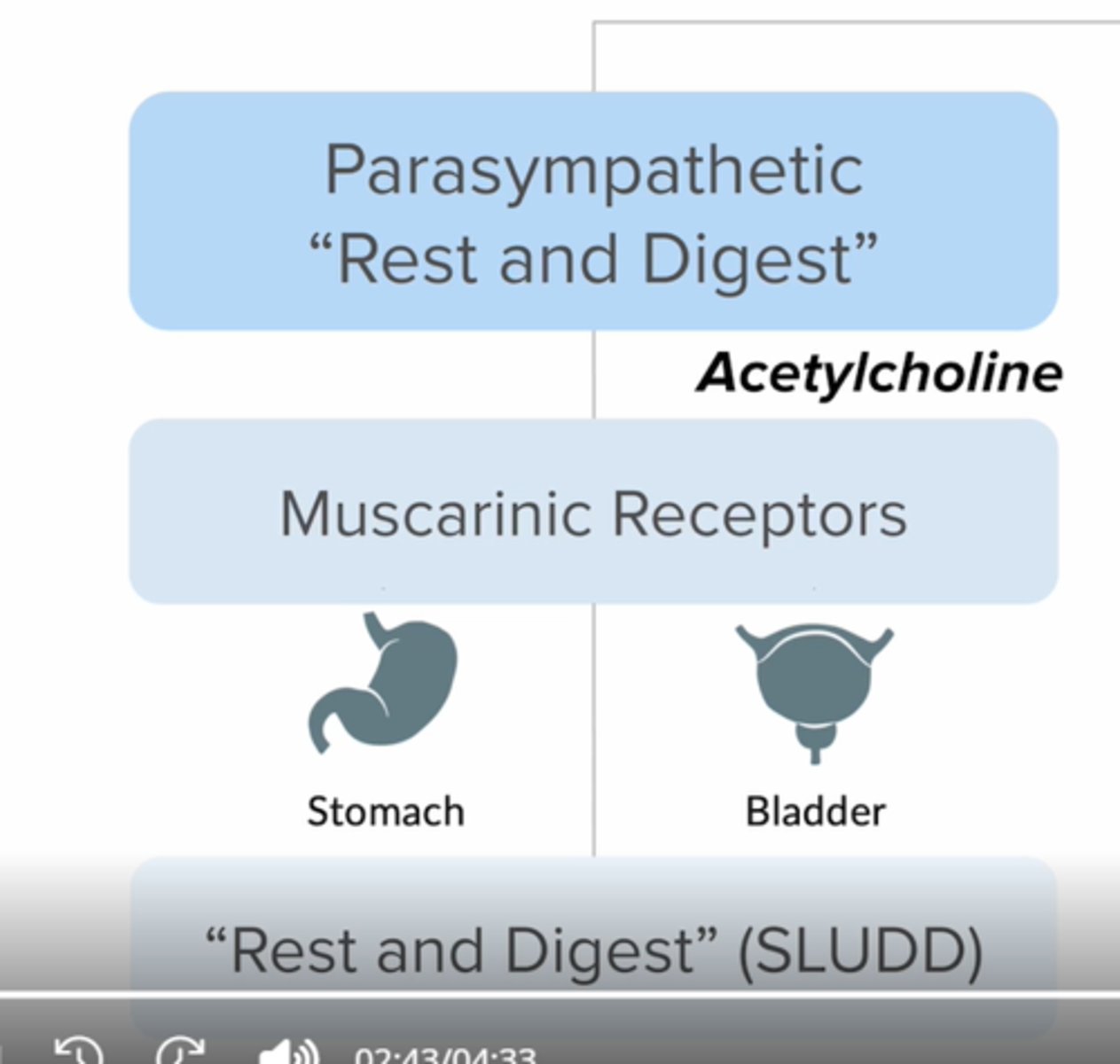
Functions of the sympathetic nervous system
Decreased:
Salivation
Urination
Peristalsis
Increased:
Pupil dilation
Glucose production
BP & HR
Bronchodilation
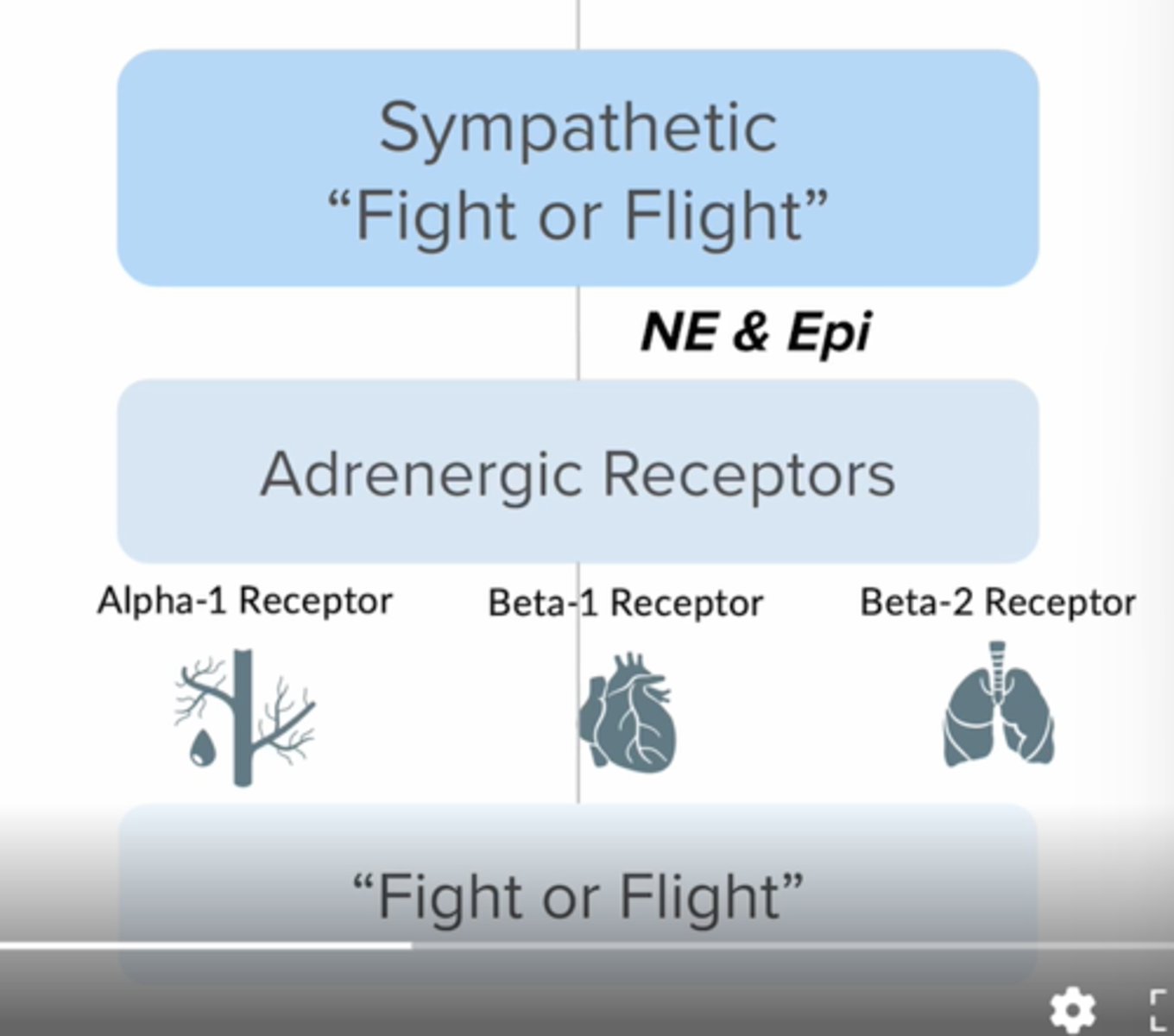
1 heart 2 lungs
Beta 1: heart
Beta 2: lungs
agonist
a substance that combines with a receptor to START reaction.
can be exogenous or endogenous (mimicking an endogenous substrate)
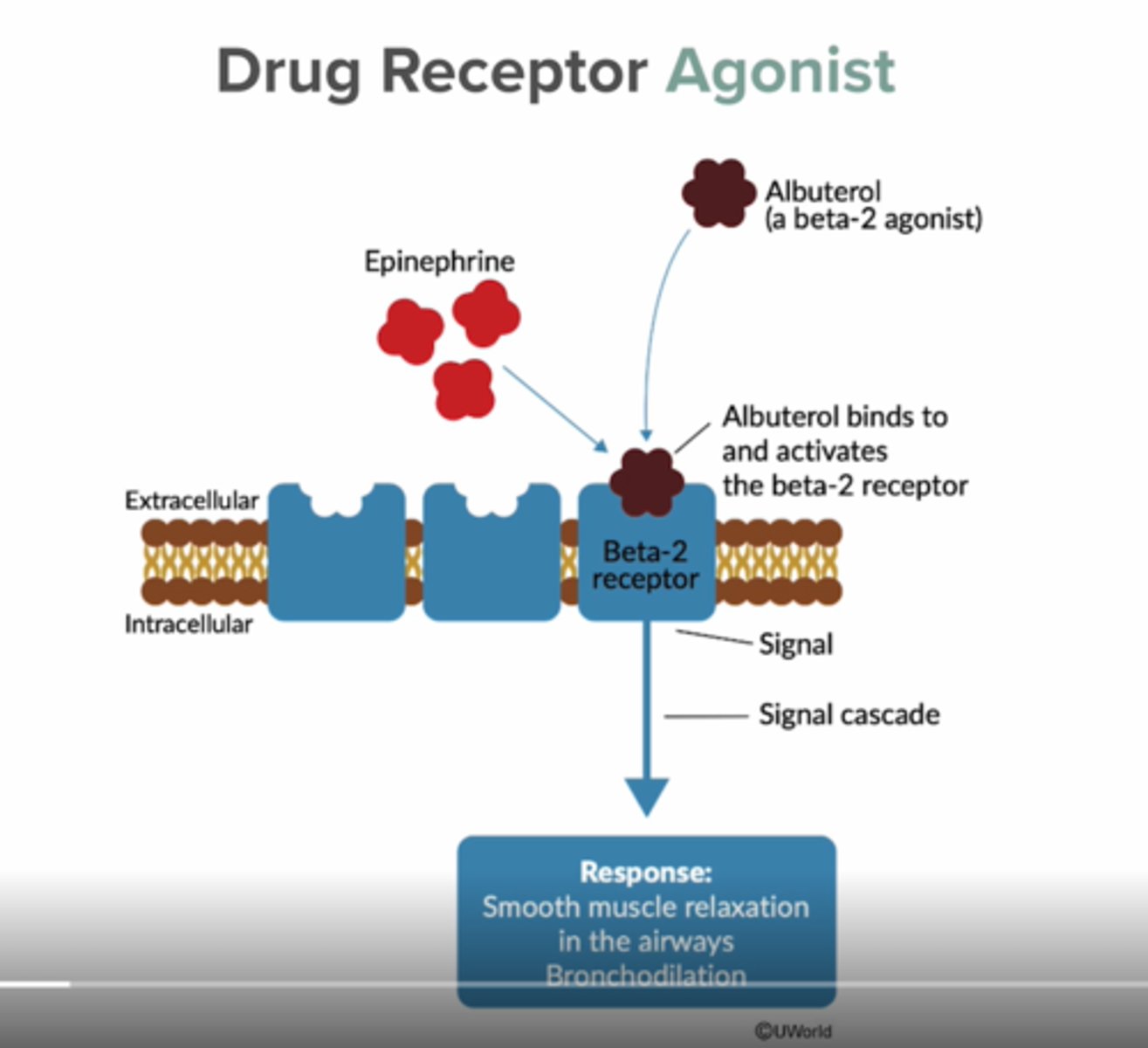
ligand (substrate)
A substance that creates a signal or produces an effect by binding to receptor enzyme or transporter
endogenous
A substrate that is produced by the body (such as a naturally produced substrate)
exogenous
A substance that is produced outside of the body such as a drug or other chemical
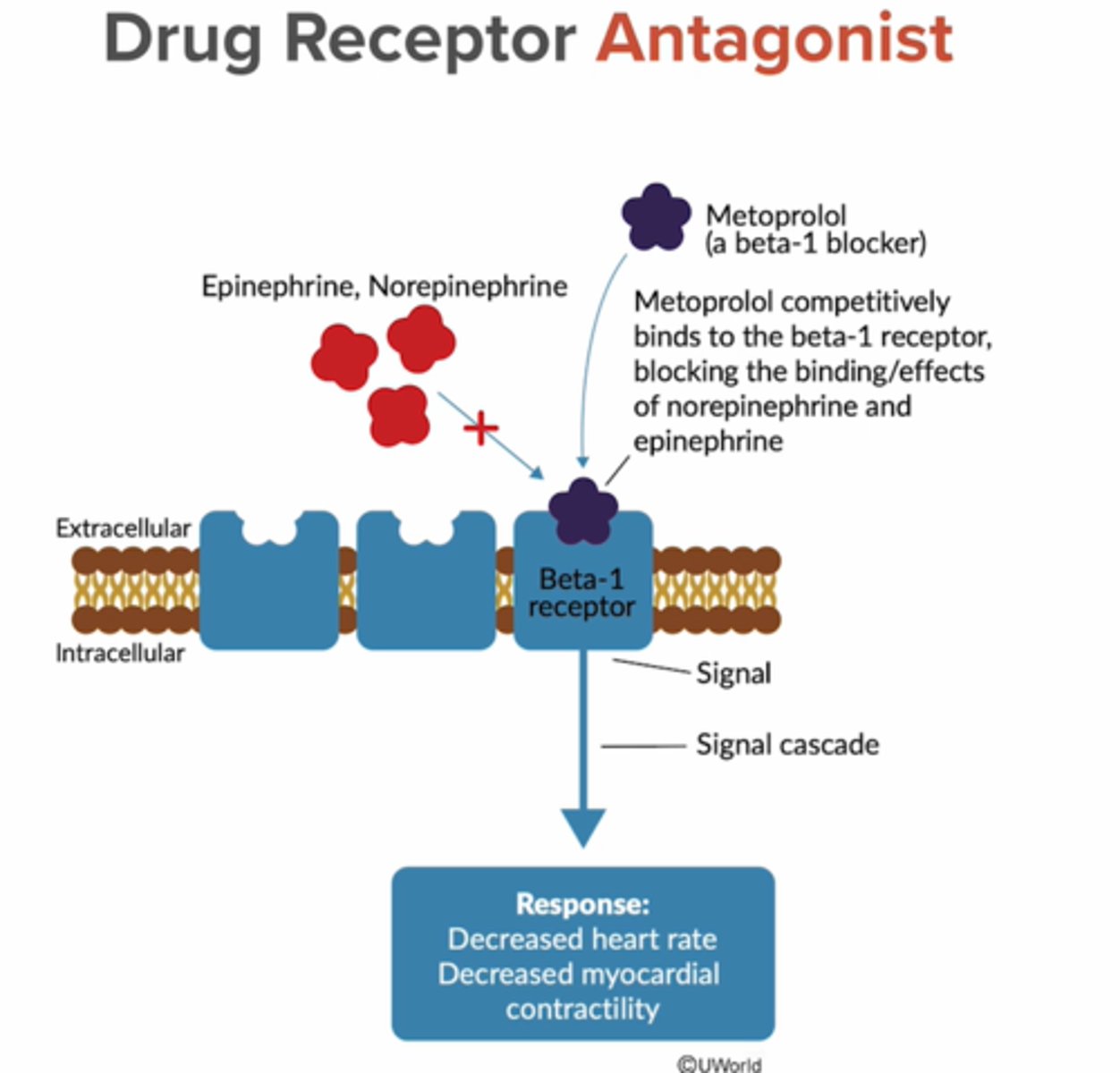
Antagonist
Antagonist A substance that reduces or blocks a reaction can be endogenous or exogenous
Induction
Induction When a substance increases the activity of an enzyme
Inhibition
Inhibition When a substance decreases or blocks the activity of an enzyme
Competitive inhibition
Antagonist binds to same active site as the endogenous substrate
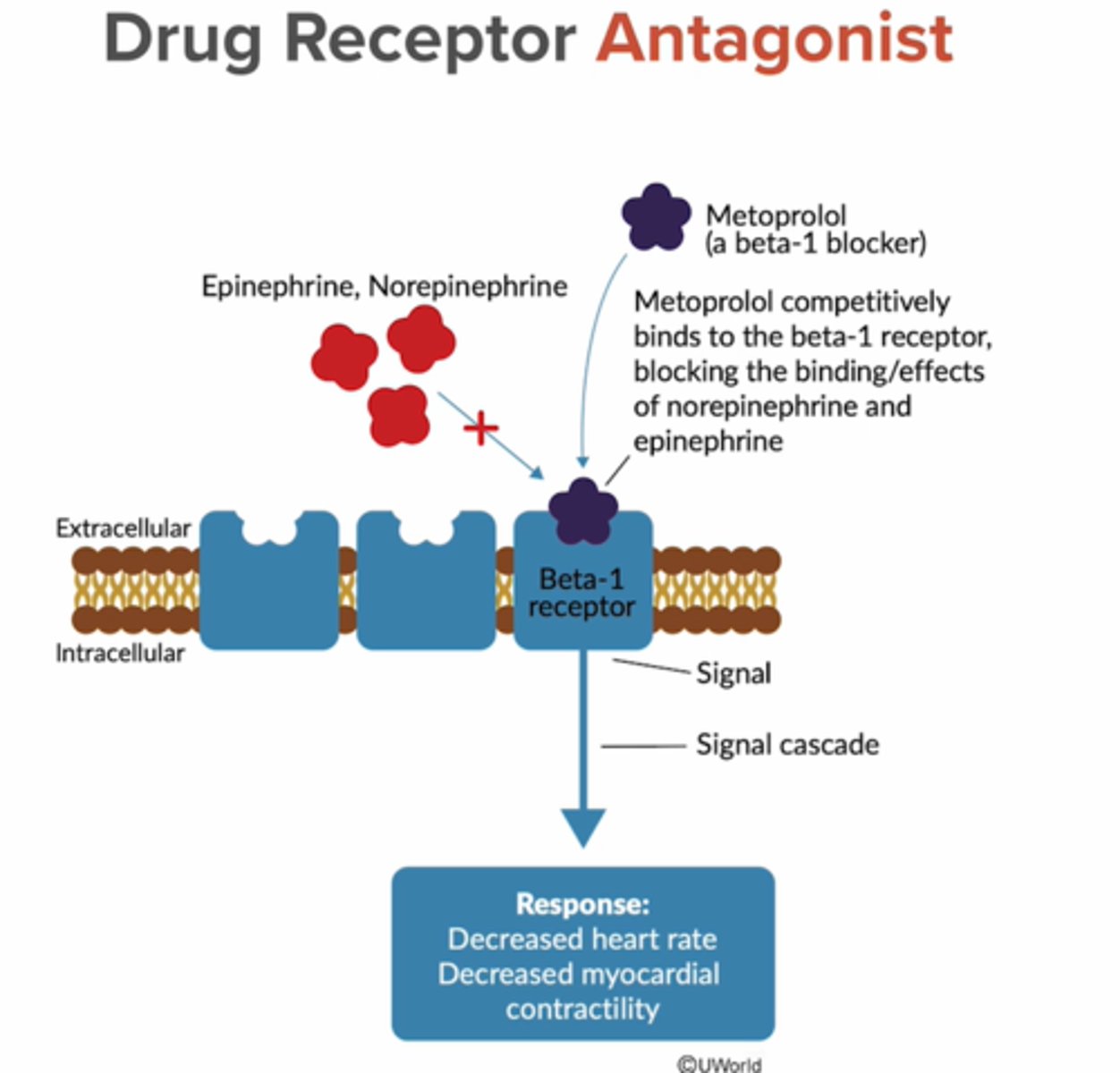
Noncompetitive inhibition
Antagonist binds to an allosteric site (not active site)
The active site shape is changed which does not allow endogenous substrate to bind
ach: muscarinic receptor response
agonist and antagonists
increase sludd
decrease sludd
-Salivation
-Lacrimation
-Urination
-Digestion
-Defecation
What happens when acetylcholine or agonists acts on nicotinic receptors?
antagonists?
Increased HR and BP
neuromuscular blockade (paralysis)
what receptors do epi/ne act on?
alpha 1 (peripheral)
alpha 2 (central)
beta 1 (heart)
beta 2 (lungs)
What do alpha 1 receptors do?
-Peripheral
Smooth Muscle vasoconstriction =
Increased BP
What do alpha 2 receptors do?
Central (in brain mostly)
Less NE and Epi release
Decreased BP, HR (decreased sympathetic output = less ne/epi to act on peripheral receptors)
What do beta-1 receptors do?
Increase myocardial contractility, CO & HR
What do beta-2 receptors do?
Smooth muscle relaxation
Bronchodilation
Common Alpha-1 Agonists
-Phenylephrine
-Dopamin (high-dose)
Common Alpha-1 Antagonists
Alpha-1 Blockers
-Doxazosin, tamsulosin
-Phentolamine
Common Alpha-2 Agonists
-Clonidine
-Brimonidine (opthalmic)
decrease bp, hr
Common Alpha-2 Antagonists
-Ergot alkaloids
-Yohimbine
increase bp, hr
Common Beta-1 Agonists
-Dobutamine
-Dopamine (moderate-dose)
Common Beta-1 Antagonists
Beta-1 selective blockers
-metoprolol
decrease contractility, co, hr
Common Beta-2 Agonists
-albuterol
-terbutaline
Common Beta-2 Antagonists
Non-selective blockers
-propranolol
Common Dopamine Agonists
-Levodopa
-Pramipexole
improve parkinsons
Common Dopamine Antagonists
-1st generation antipsychotics
-metoclopramide
worsen parkinsons
Common Serotonin Agonists
-triptans
Common Serotonin Antagonists
-5HT-3 antagonists like ondansetron
-2nd generation antipsychotics
drugs with multiple receptor effects
isoproterenol: b1/b2 agonist
carvedilol: alpa 1, b1/b2 aantagonist
NE: alpha 1, b1
Catecholamine Metabolism
Dopamine ---> NE --- EPI ---> Harmless metabolites
Tryptophan --> 5-HT ---> Harmless metabolites
Acetylcholinesterase
The enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- Donepezil (Aricept, Aricept ODT)
- Rivastigmine (Exelon, Exelon Patch)
- Galantamine (Razadyne, Razadyne ER)
Angiotensin Pathway
Liver released angiotensinogen // Renin is released from the kidney ---> Angiotensin I ---> angiotensin II ---[Aldosterone secretion/Vasoconstriction]
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
Breaks down levodopa
COMT inhibitors
Entacapone
Tolcapone
Cyclooxygenase (COX)
Converts arachidonic acid into prostaglandins (inflamation/pain) and thromboxanes (platelet aggregation)
What blocks COX enzymes?
NSAIDS
MAO inhibitors
Phenelzine
Isocarboxazid
Selegiline
Tranylcypromine
Phosphodiesterase
Converts cAMP (smooth muscle relaxant) to AMP
PDE-5 inhibitors
Sildenafil
Vardenafil
Tadalafil
Vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR)
Coverts Vitamin K into active form which is used to make Factor II, VII, IX, X
VKORC1 inhibitor
Warfarin
Xanthine Oxidase (XO) Pathway
Hypoxanthine --> Xanthine --> Uric Acid --> Allantoin
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors
Allopurinol
Febuxostat
What do MAOi cause?
Build of of 5-HT, NE, EPI
MAOIs used for depression
**SPIT**
Selegiline
Phenelzine
Isocarboxazid
Tranylcypromine
What risks can MAOi's lead to when combined with other drugs that increase NE and Epi?
Hypertensive Crisis (Increased BP, HR, agitation & death)
Common Drugs:
-Bupropion
-SNRIs
-TCAs
-Amphetamines/stimulants
-Linezolid
-Methylene blue
-Tyramine-rich foods
What risks can MAOi's lead to when combined with other drugs that increase 5-HT?
common drugs (lots)
Serotonin Syndrome
(Agitation, Tachycardia, Diaphoresis, Mydriasis, Hyperreflexia, Clonus, Tremor, N/V/D, HTN)
Common Drugs:
-SSRIs
-SNRIs
-TCAs
-Mirtazapine
-Trazodone
-St. John's Wort
-Opioids
-Tramadol
-Antiemetics (ondansetron)
-Buspirone
-Lithium
-Triptans
-Ergotamines (migraine drugs)
-Dextromethorphan (HD)
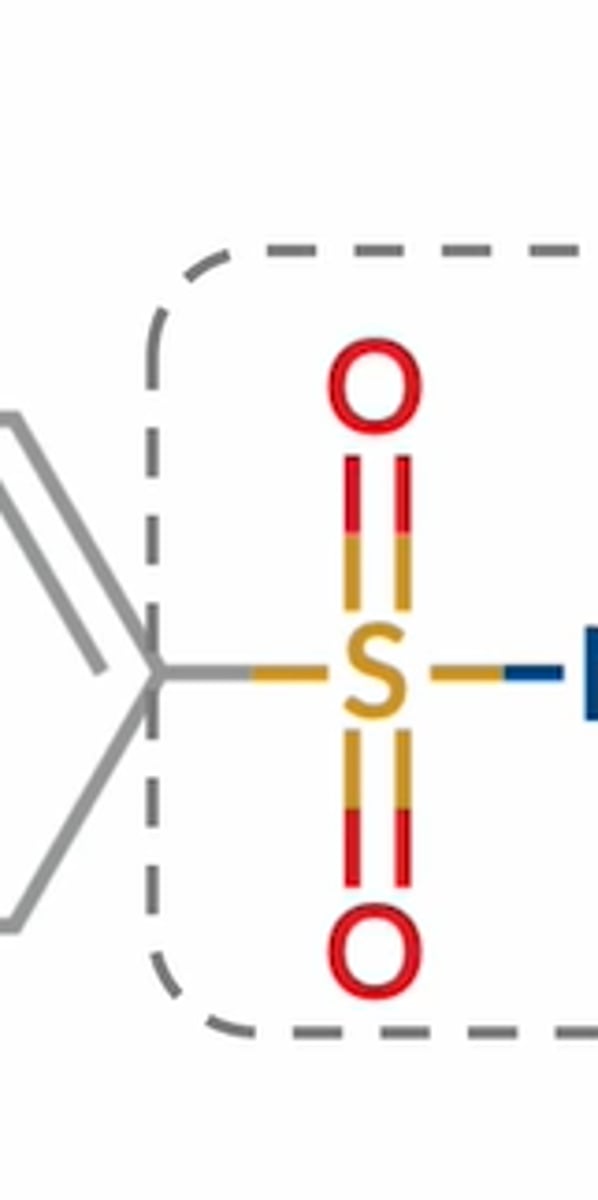
Drugs with a sulfonamide group
Celecoxib
Sulfamethoxazole
Loop diuretics (bumetanide & furosemide)
Triptans
Thiazide diuretics
Acetazolamide
Sulfonylureas (chlorpropamide, acetohexamide)
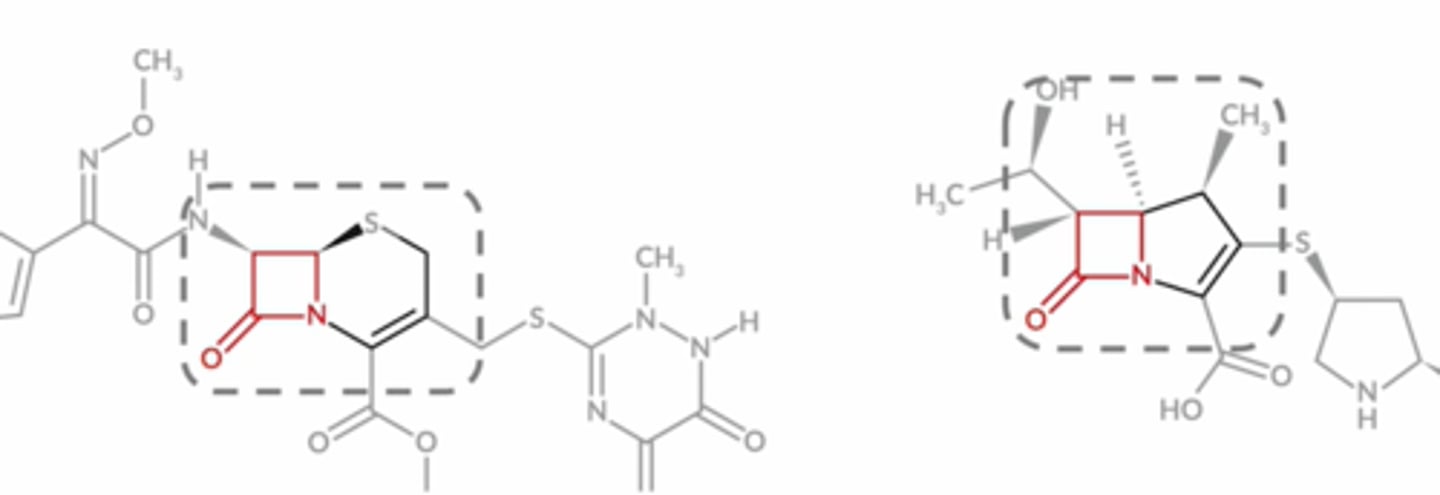
What does a beta-lactam look like?
Square with N component and double bonded O fused to another 5 or 6 sided ring
what do nsaids look like?
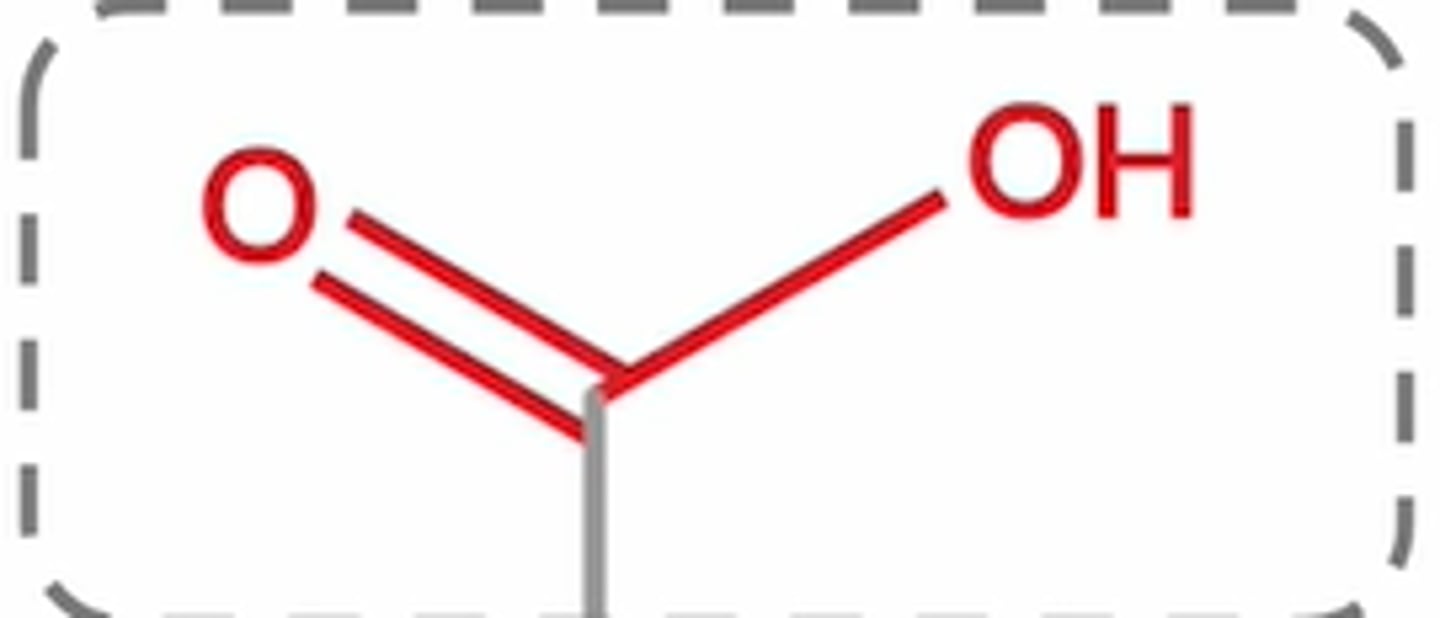
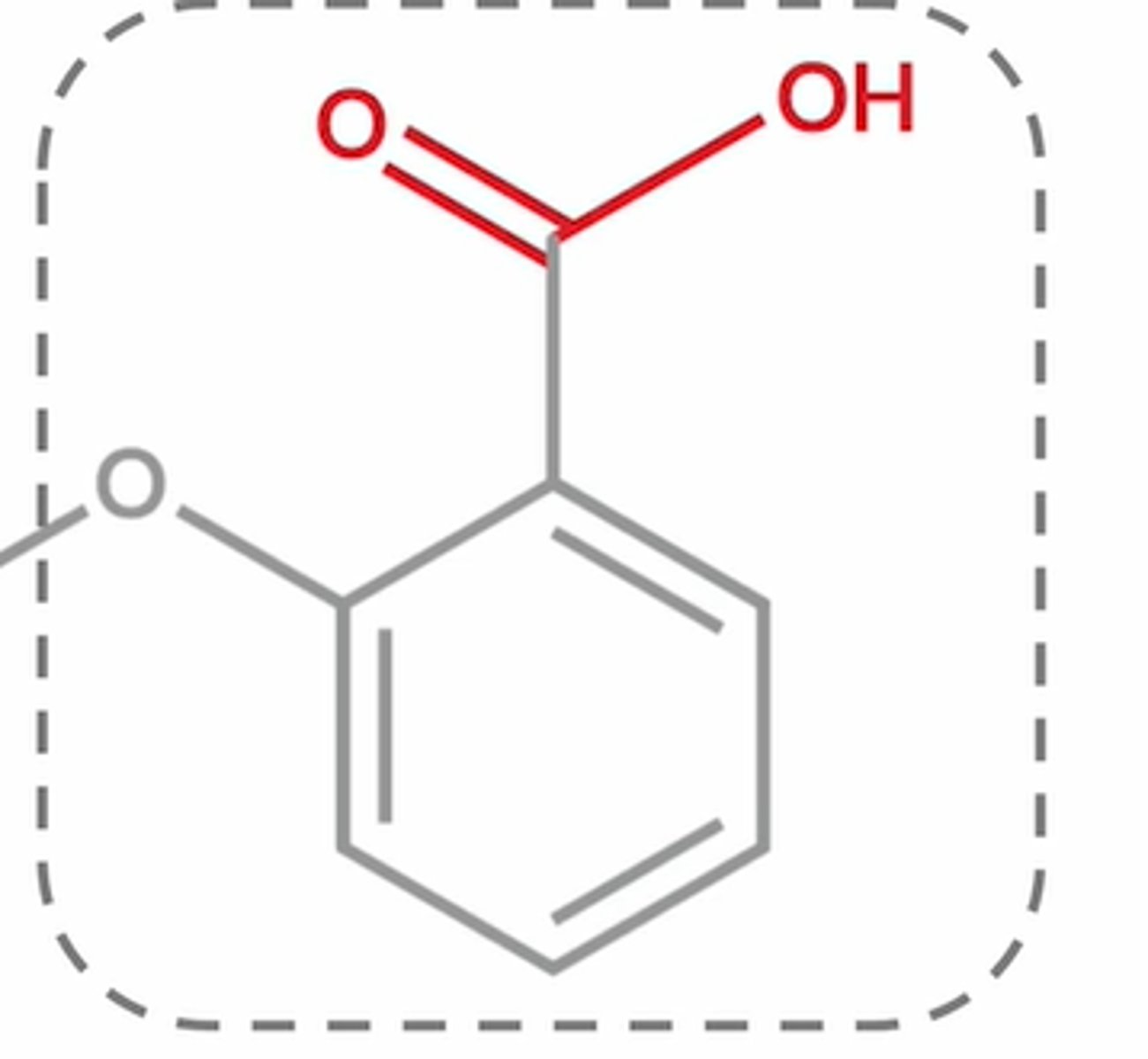
what does aspirin (salicylate) look like
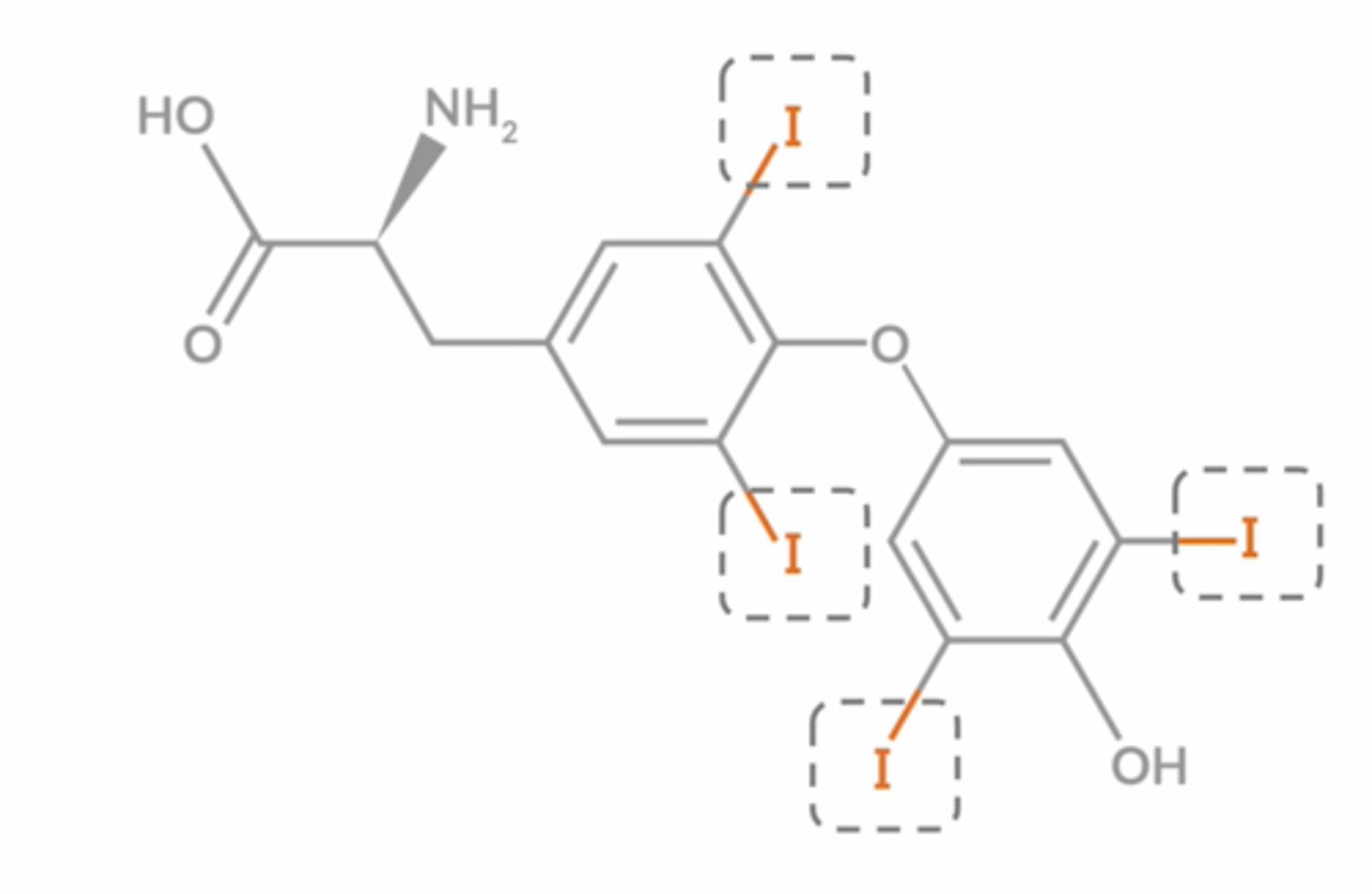
What compounds contain Iodine?
Levothyroxine
Amiodarone
contains and "i" in the structure
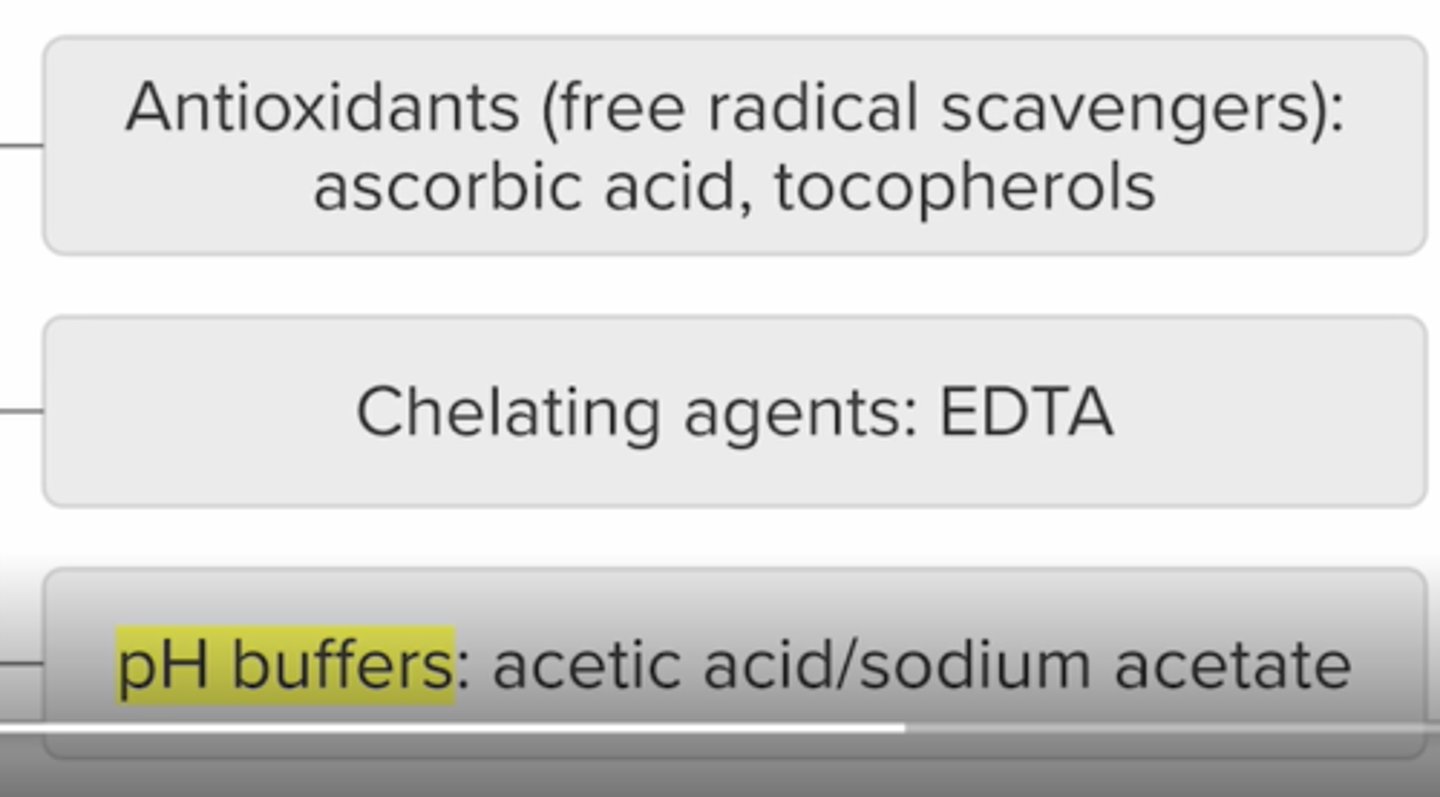
Degradation reactions:
Oxidation hydrolysis photolysis
oxidation
transfer of electrons
drugs with oh on aromatic ring are at risk
protect from light, heat metal ions to extend exp date
hydrolysis
breakdown by water
esters, amides, lactams at risk
protect from moisture
photolysis
breakdown by light
ascrobic acid, nitroprusside, phytonadione at risk
protect from light