C22 - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

20 Terms
2nd law of thermodynamics (entropy)
All processes in the Universe increase entropy
2nd law of thermodynamics (Clausius statement)
Heat transfer will not occur from a colder area to a warmer area (w/o some input work)
2nd law of thermodynamics (Kelvin-Planck statement)
No heat engine can output work equivalent to the energy input
i.e. there must be some leakage
e (engine efficiency)
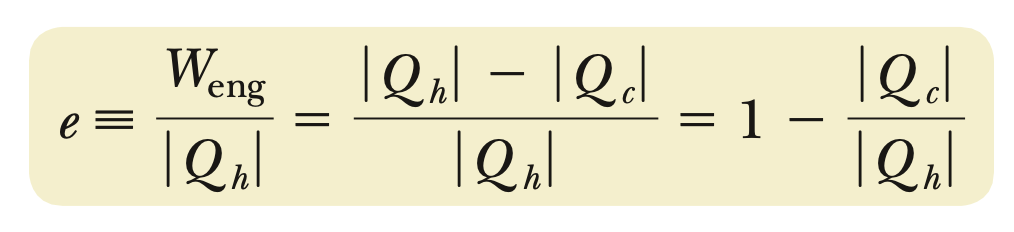
COPcooling

COPheating

reversible process
process which can be returned to its initial state (no change in energy or entropy)
irreversibilities: real-life processes preventing reversibility (friction, deformation, chemical rxn, etc.)
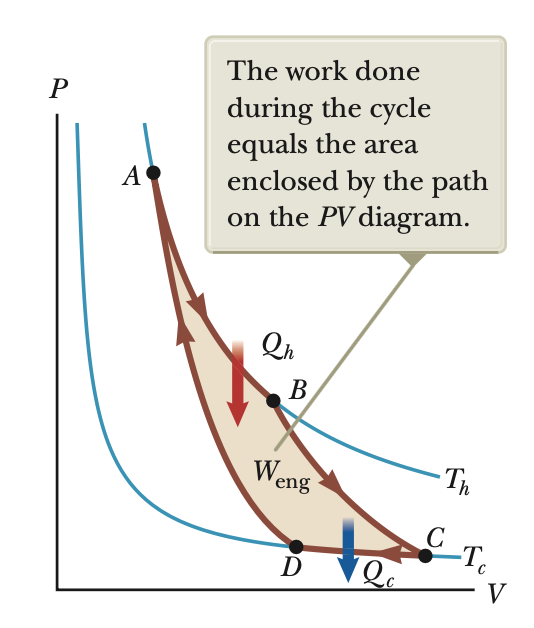
Carnot engine
Ideal, reversible engine with max efficiency possible
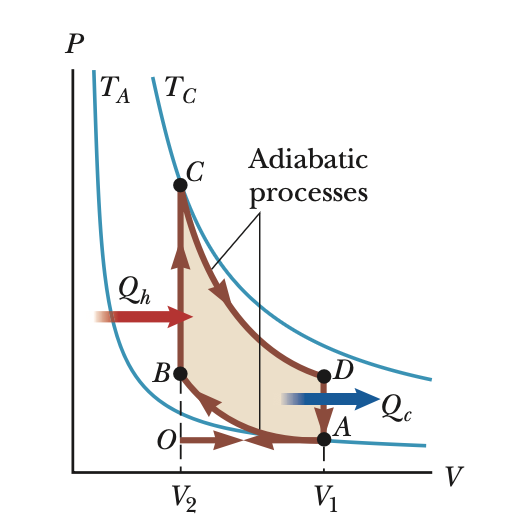
A: isothermal expansion (Th)
B: adiabatic expansion
C: isothermal compression (Tc)
D: adiabatic compression
PV diagram (carnot)
Q → T relationship (Carnot cycle)
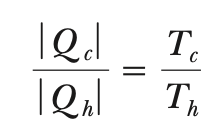
e (Carnot cycle)
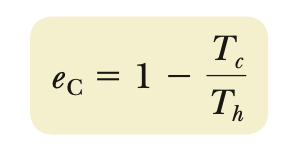
COPC, cooling
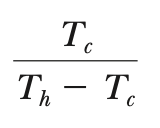
COPC, heating
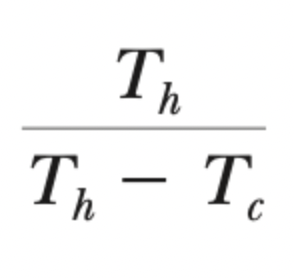
Otto cycle
Idealized cycle for 4-stroke spark-plug piston engine
Intake: valve opens to let combustion gases in
Compression: increase in pressure
Power: after pressurized gases are combusted, piston pushed & work is done
Exhaust: after release, piston rises to spit out exhaust gases
PV diagram (otto)
eOtto
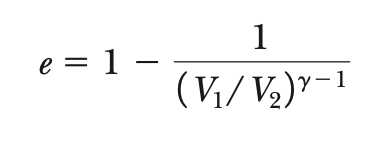
Entropy
The amount of microstates/uncertainty given by any given arrangement of a system
Macrostate = overall characteristic
Microstate = one of many possibilities within a macrostate
S = kBln(W) = nRln(V/Vm)
∆S
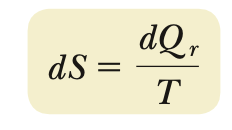
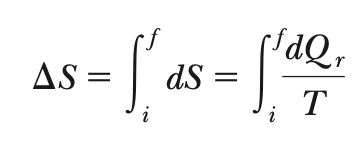
∆Sreversible
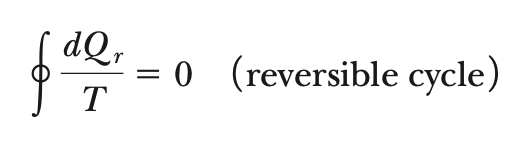
hp → watts
1 hp = 746 W