DSA32 - Movement Disorders
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
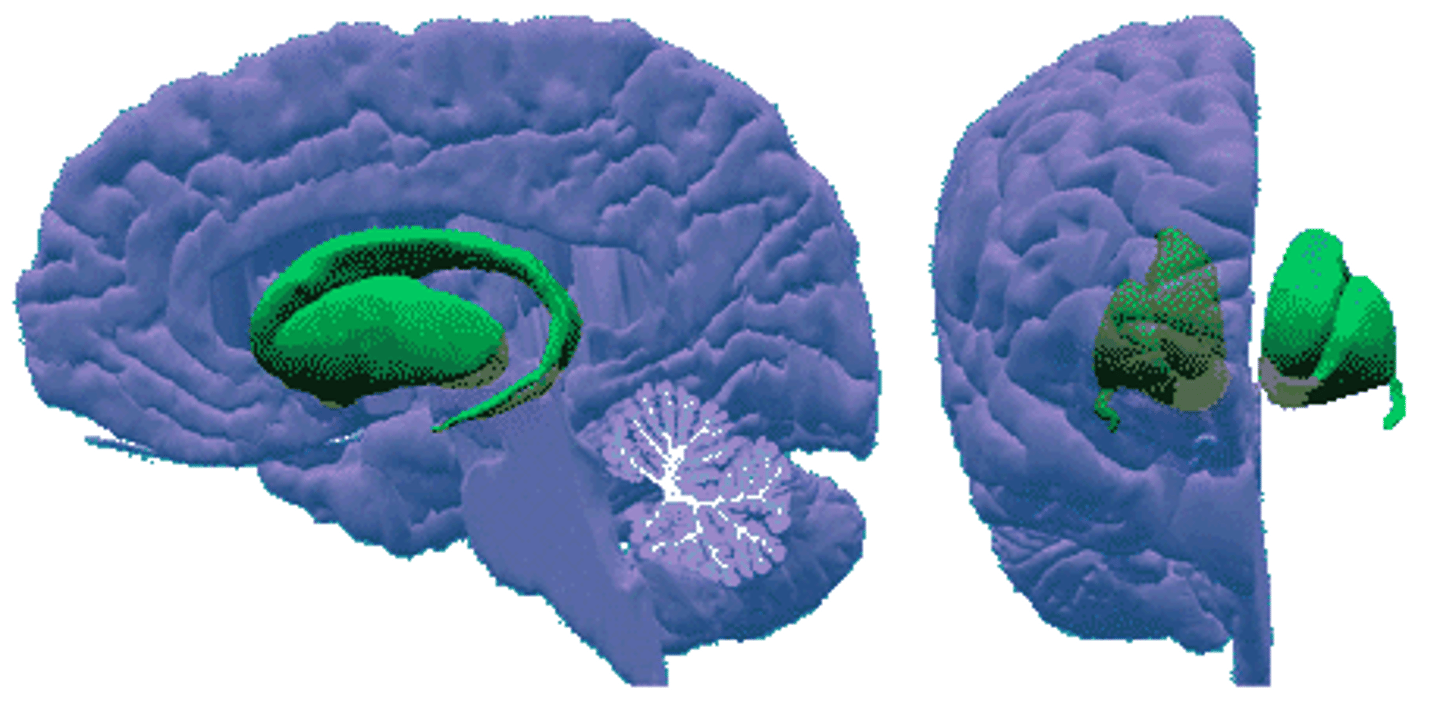
-Substantia Nigra
-Subthalamic Nucleus
-Striatum
-Thalamus
-Connects of system with the CST
The basal ganglia component of the Extrapyramidal Motor System consists of:
-Dopamine
-Glutamate
-GABA
-ACh
What are the major neurotransmitters of the Extrapyramidal Motor System?
Abnormalities of muscle tone abnormal body (tremors)
Disturbance of Extrapyramidal Motor System leads to what?
regular oscillation around a plane in space; can be physiologic or pathologic
Define Tremor
Physiologic tremors PERSIST during sleep (largely ballisto-cardiographic effect), but pathologic tremors DISAPPEAR during sleep (due to disease state)
What is the difference between physiologic tremors and pathologic tremors?
Postural Tremor ("Action/Essential Tremor")
Define Condition:
Most common movement disorder (ET); affects males & females equally; All ages, but more with older age; May be due to dysfunction of the purkinje cells in cerebellar cortex/projections to deep cerebellar nuclei
-Hx: Usually around 65 y/o; +FHx (Autosomal Dominant)
-Sx: BILAT & SYMM at ONSET; Starts in UE, but can affect all even head and neck (titubation) or jaw - increased by stress, fatigue or caffeine
-PE: Worse when limbs outstretched/maintaining posture, attempting delicate movement; may stop with complete relaxation (ex: reclining supine) --> (-)Archimedes Spiral w/o touching paper
-Dx: Normal Imaging
-Tx: Propanolol --> Alprazolam --> More intense like barbituate (Primidone), Botox, GABA)

Senile Tremor
When a Postural Tremor occurs in the elderly, it is known as a ()
Familial Tremor
When a Postural Tremor occurs in families, it is known as a ()
Benign Essential Tremor (ET)
When a Postural Tremor occurs in neither families nor is it elderly, it is known as a ()
B/c ET typically does not produce an ataxic gait like PD does
Why should gait (walking) and station (standing) ALWAYS be checked with ETs?
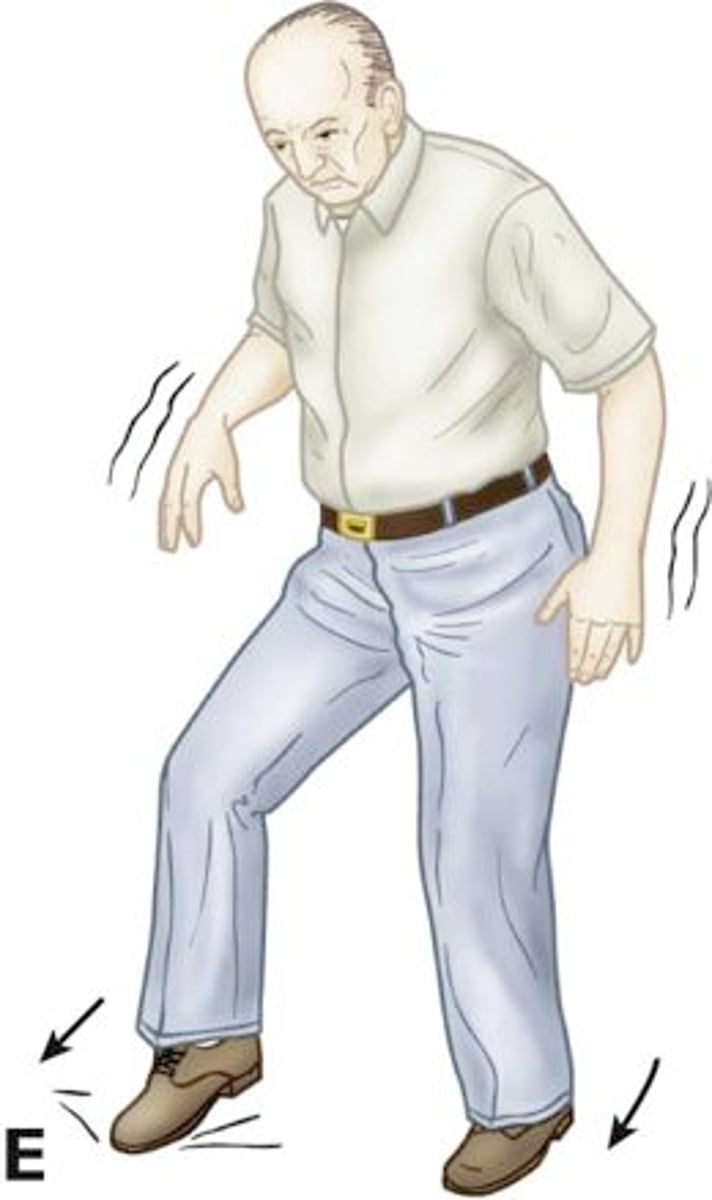
Resting Tremor (a/w Parkinsons)
Define Condition:
Loss of the pigmented neurons of the parscompacta of the substantia nigra in the midbrain --> overactivity of local-circuit, cholinergic neurons
-Hx: Older adults
-Sx: Usually begins as ASYMMETRIC; Preceded by slowness (bradykinesia) and stiffness (rigidity in FLEXION), Possible Depression/REM sleep disorder/Anosmia
-PE: (+)"Pill Rolling", Decrease with action/increase at rest
-Dx: Normal Imaging, except DaT scan (shows abnormal dopamine uptake)
-Tx: Carbidopa /Levodopa (Sinemet), Dopamine Agonists, MAOi, Anticholinergics +/- Pallidotomy +/- Thalamotomy +/- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Neurodegenerative disorder primarily caused by degeneration of the substantia nigra in the basal ganglia --> Not enough Dopamine to suppress inhibition → overactivity in inhibitory functions = lower ability to initiate movement
Define Parkinson's Disease
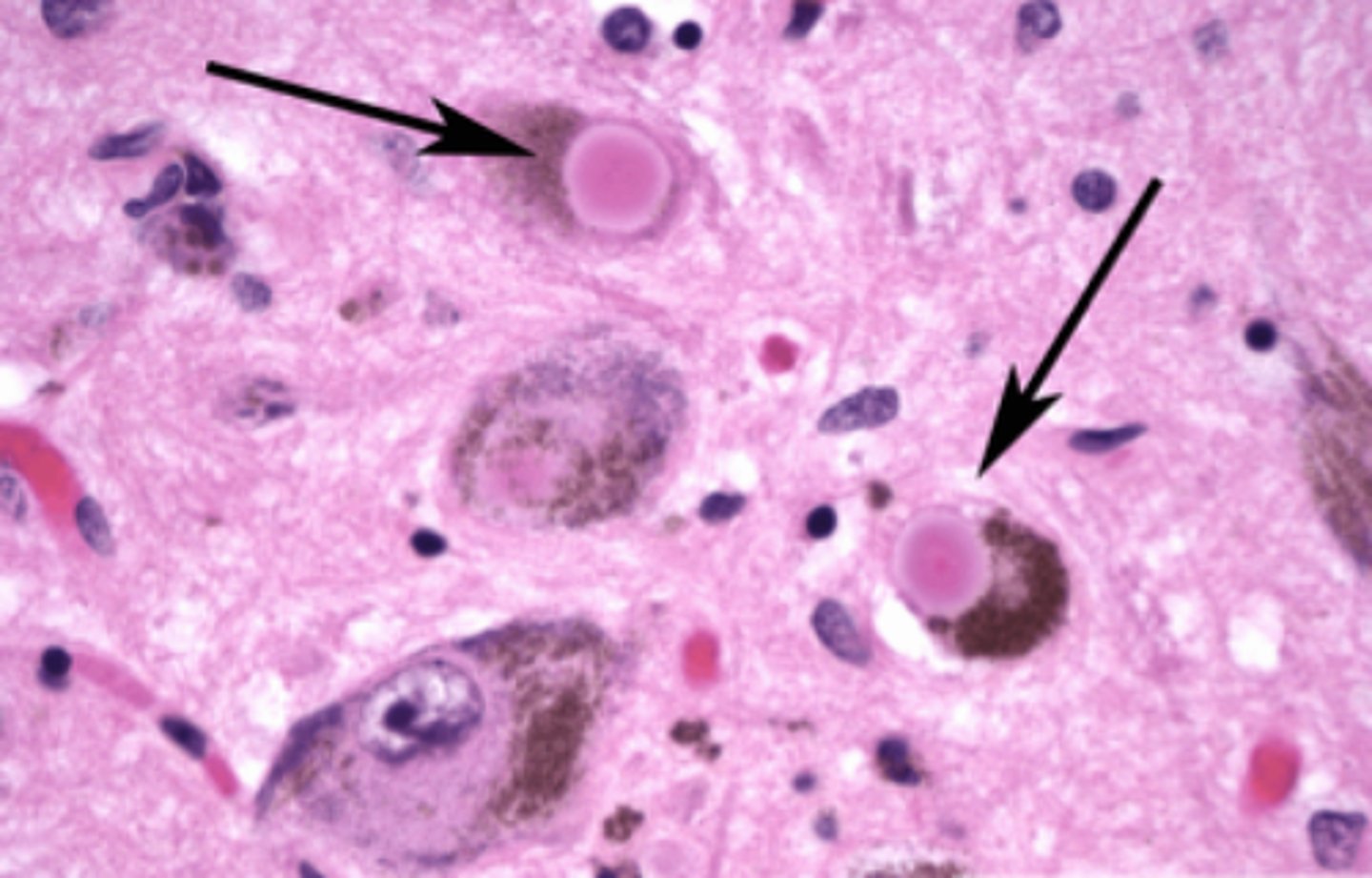
Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion body with a dense core consisting of a-synuclein protein; found in the cytoplasm of nigrostriatal neurons in people with Parkinson's disease
Define Lewy Bodies
-Resting Tremor
-Bradykinesia
-Rigidity in FLEXION
-Postural Disequilibrium
What are the 4 Cardinal Signs of Parkinson's? (dx is based on 2/4 of these signs)
Involves the coordination of movement strategies to stabilize the centre of body mass during both self-initiated and externally triggered disturbances of stability (ex: difficulty getting out of low chair)
Define Postural Disequilibrium
Antidopaminergic Drugs (antipsychotic drugs and anti-emetics such asmetoclopramide and compazine)
DRUG INDUCED Parkinsonism is a common S/E for what kind of drugs?
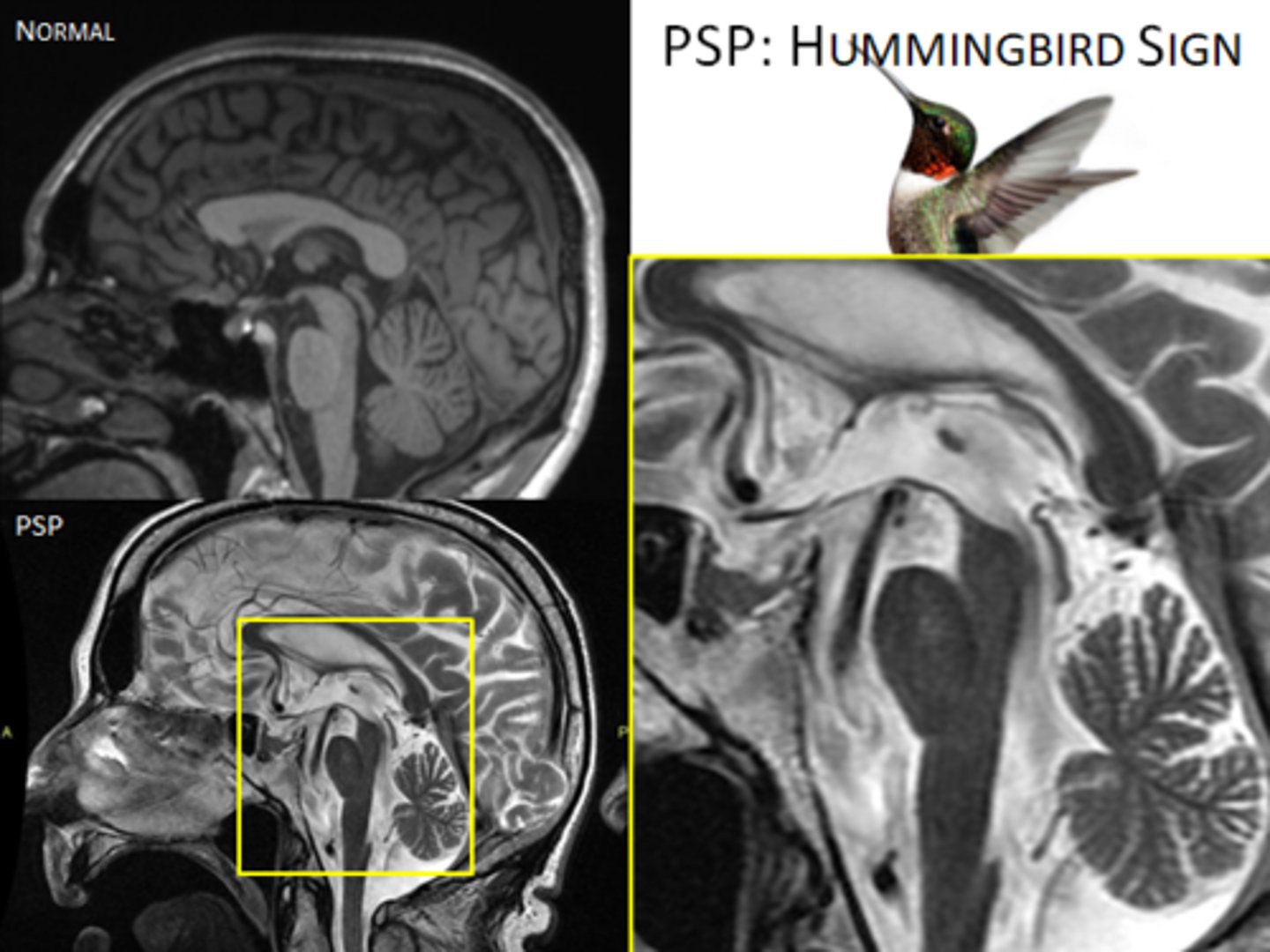
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy/PSP
Define Condition:
*Mistaken as PD*
-Hx: Usually > 60 y/o; Gradual onset
-Sx: Gait instability/Falls, Disturbance of speech articulation and swallowing, Impairment of eye movements (issues seeing)
-PE: Parkinsonism w/o tremor, Rigidity in EXTENSION Increased AXIAL muscle tone, Unstable gait/falls, dysarthric speech, dysphagia, Impaired eye movements (Downward vertical, conjugate ophthalmoplegia with intact VOR = “supranuclear lesions”), Intellect preserved until very late
-Dx: Brain MRI (r/o other disorders but may show classic midbrain atrophy, "hummingbird sign")
-Tx: Supportive Tx --> Full Care
Intention Tremor
Define Condition:
Occurs with attempt at purposeful movement; due to disturbances of the cerebellum or connections to the cerebellum
-Hx: May have FHx of similar issues
-Sx: Occurs with balance issues, gait problems, and speech/eye issues (*If lesions are FOCAL = Sx are ipsilateral*)
-PE: Worsens as target is reached (increases in amplitude/frequency) --> disappears at rest; May see cerebellar dysfunction (limb ataxia, dysmetria, dysarthria, nystagmus, hypotonia, etc)
-Dx: MRI (Cerebellar Lesions or Atrophy)
-Tx: Depends on etiology; MUST prevent injuries from ataxia; DBS may help if severe
postural
If the neuro exam is normal besides the tremor, it is likely a(n) (postural/resting/intention) tremor
Resting/Parkinsonian
If the neuro exam shows rigidity, slowness of movement, and/or postural disequilibrium, it is likely a(n) (postural/resting/intention) tremor
Intention
If the neuro exam shows ataxia, it is likely a(n) (postural/resting/intention) tremor
Guide center for movement - provides for coordinated, fluid and precise movement
What is the function of the Cerebellum?
-Visual System
-Vestibular System
-Proprioceptive system
From where does the Cerebellum RECEIVE input?
Pyramidal motor system (CST)
Where does Cerebellar input go to?
Cerebellar Ataxia
Define Condition:
-Hx: Child/adult onset, ACUTE = trauma/stroke, SUBACUTE = Intoxication/Abscess, CHRONIC = hereditary/degenerative/Neoplastic; May have neg FHx if recessive
-Sx/PE (ispilat to lesion): Limb/Gait ataxia (looks drunk), Dysmetria (past pointing), Dysarthria, Nystagmus, Scanning Speech, Hypotonia, Intention Tremor = Dysdiadochokinesia (Ex: can't quickly pronate/supinate)
-Dx: MRI WWOC (to view posterior fossa/cerebellum)
-Tx: Genetic counseling if hereditary, Surgery for hemorrhage/neoplasm, Tx if MS, Rehab if traumatic

When Speech is "slowed" or "staccato"
Define Scanning Speech
Define Scanning Speech
Spinocerebellar Ataxia/SCA
Define Condition:
-Hx: Rarely purely spinal; +FHx (ex: Machado-Joseph’sDisease = AD/14q, Friedreich’s Ataxia = ar/9q)
-Sx/PE (*IF SPINAL, no dysarth/nystag): +/- Nystagmus & Dysarthric Speech, Gait ataxia (looks drunk), Intention Tremor = Dysdiadochokinesia (Ex: can't quickly pronate/supinate), Dysmetria (past pointing), Hypotonia, Dysdiadochokinesia (Ex: can't quickly pronate/supinate) + SC sensory and motor disturbances
-Dx: MRI (may show spinal and/or cerebellar degeneration/atrophy, or white matter changes)
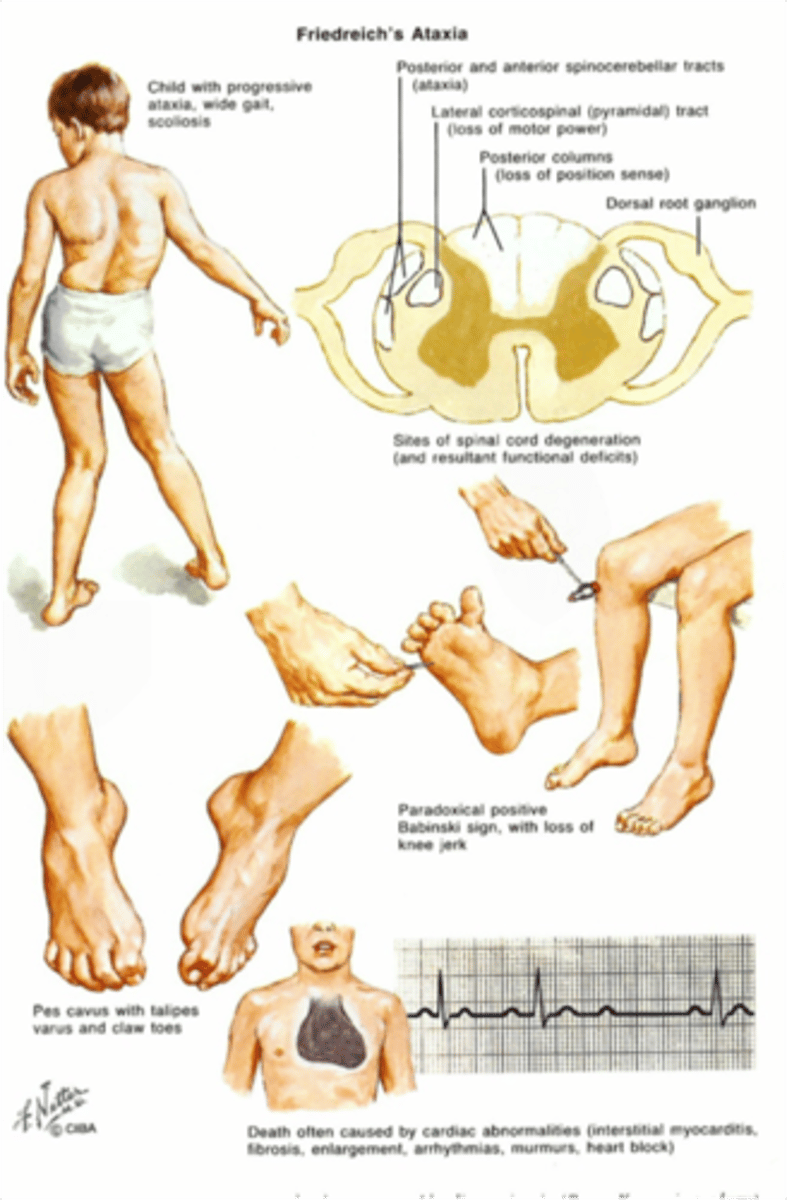
Friedreich's Ataxia
Define Condition:
MOST COMMON SCA in YOUNG PEOPLE; Due to Autosomal recessive trinucleotide repeat disorder (GAA, frataxin gene). Leads to impairment in mitochondrial functioning & destruction of myelin in Spinal Cord.
-Sx/PE: Ataxia/frequent falling, nystagmus, dysarthria, pes cavus, hammer toes, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (Cause of death). Presents in childhood with kyphoscoliosis.
Sensory Ataxia
Define Condition:
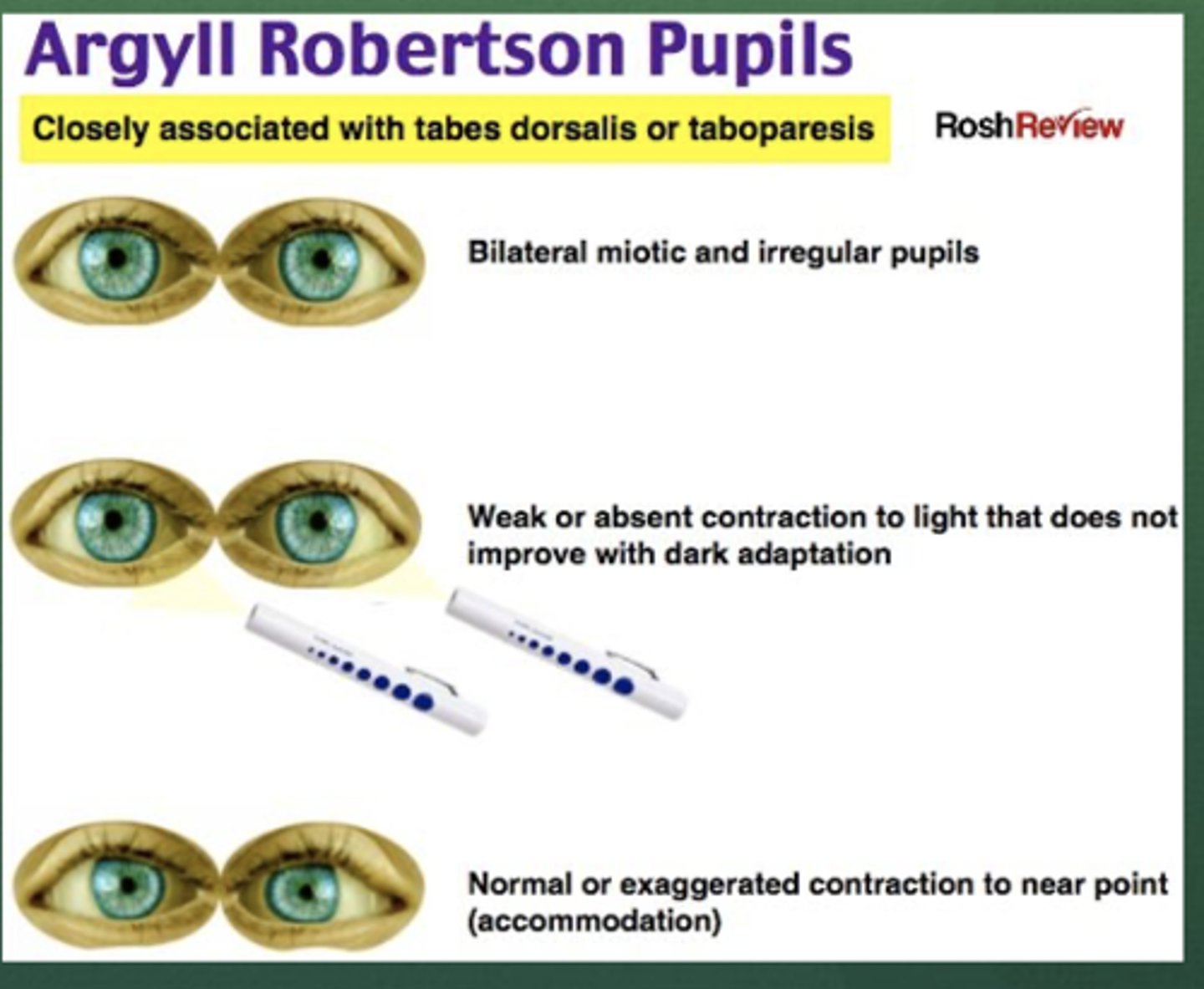
-Hx: Subacute or Chronic, +/- FHx; +/- Hx Alcoholism, STD (Tabes Dorsalis), Peripheral Neuropathy
-Sx: Numbness, Tingling, Pain in feet, frequent tripping/stumbling on irregular surfaces
-PE: Ataxia WORSE in dark (loss of proprioception --> balance depends on sight), Sensory deficit in LE (feet), Decreased vibratory/joint position in feet, (+) ROMBERG, Argyll-Robertson Pupils (Tabes Dorsalis), ABSENT RELFEXES
-Dx: Labs for neuropathy (DM, Hypothyroid, B12, +HIV, +RPR), EMG/NCV (neuropathic), Nerve biopsy for etiology
-Tx: Depends on etiology
When pupils reactive to accommodation but not to light, associated with tabes dorsalis
Define Argyll-Robertson Pupils
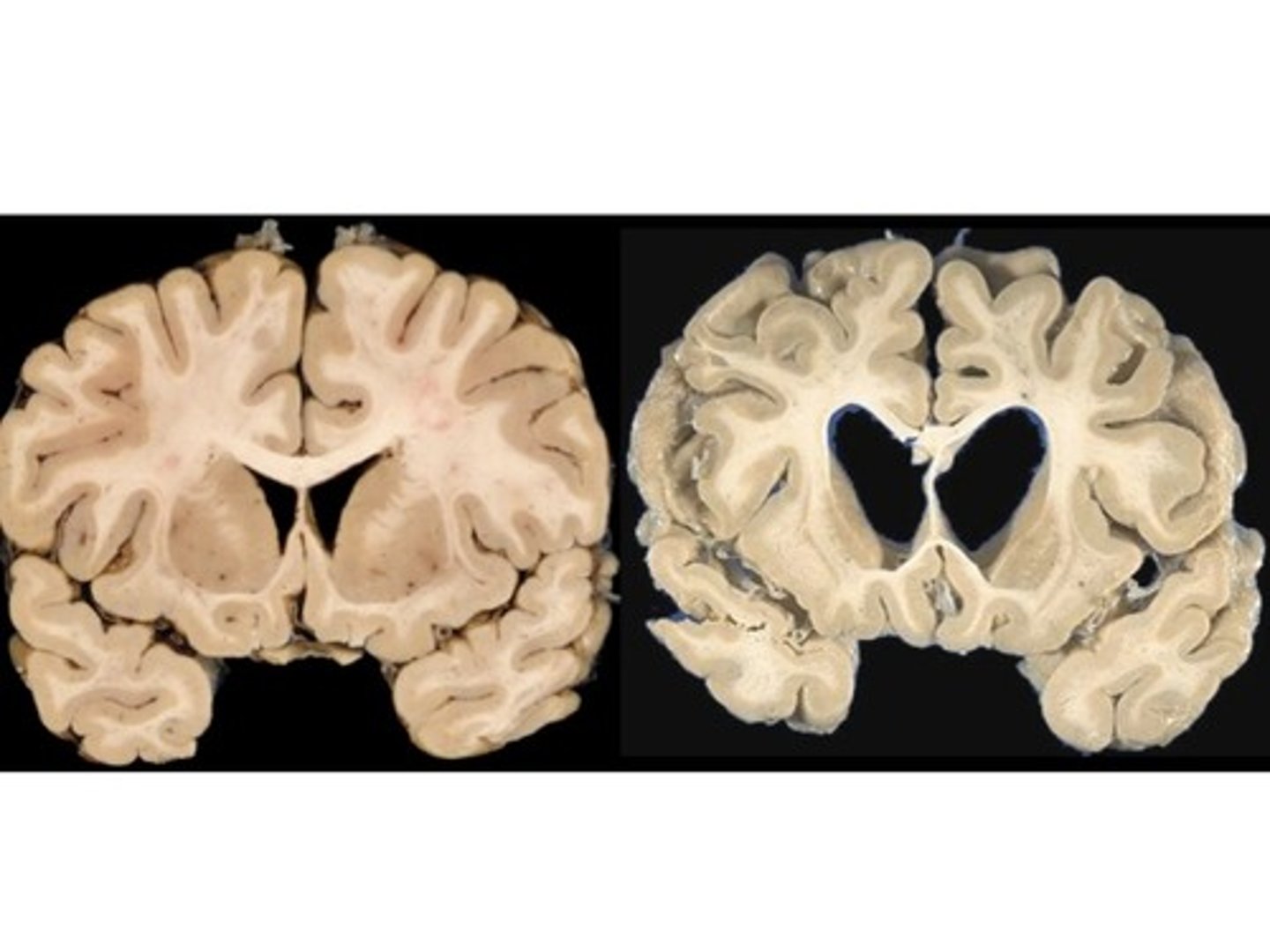
Huntington's Chorea/Disease
Define Condition:
Trinucleotide repeat produces a “toxic gain of function,” affectingthe protein “Huntingtin,” on Chromosome 4p.
-Hx: +FHx of early-onset dementia w/ dyskinesias due to AD of high penetrance; Onset in 40s-50s (but issues in childhood)
-Sx: Gradual onset of "fidgetiness" (choreiform ataxia) --> jerky movements, Personality changes
-PE: Jerks becoming incapacitating + personality changes
-Dx: Brain MRI (atrophy of the caudate nuclei + large ant horns of ventricles) + Genetic Testing (CAG trinucleotide repeats > 38)
-Tx: Tx Chorea with Tetrabenazine (deplete monoaminergic synaptic vesicles, thus resetting a balance between dopamine/NE and ACh)
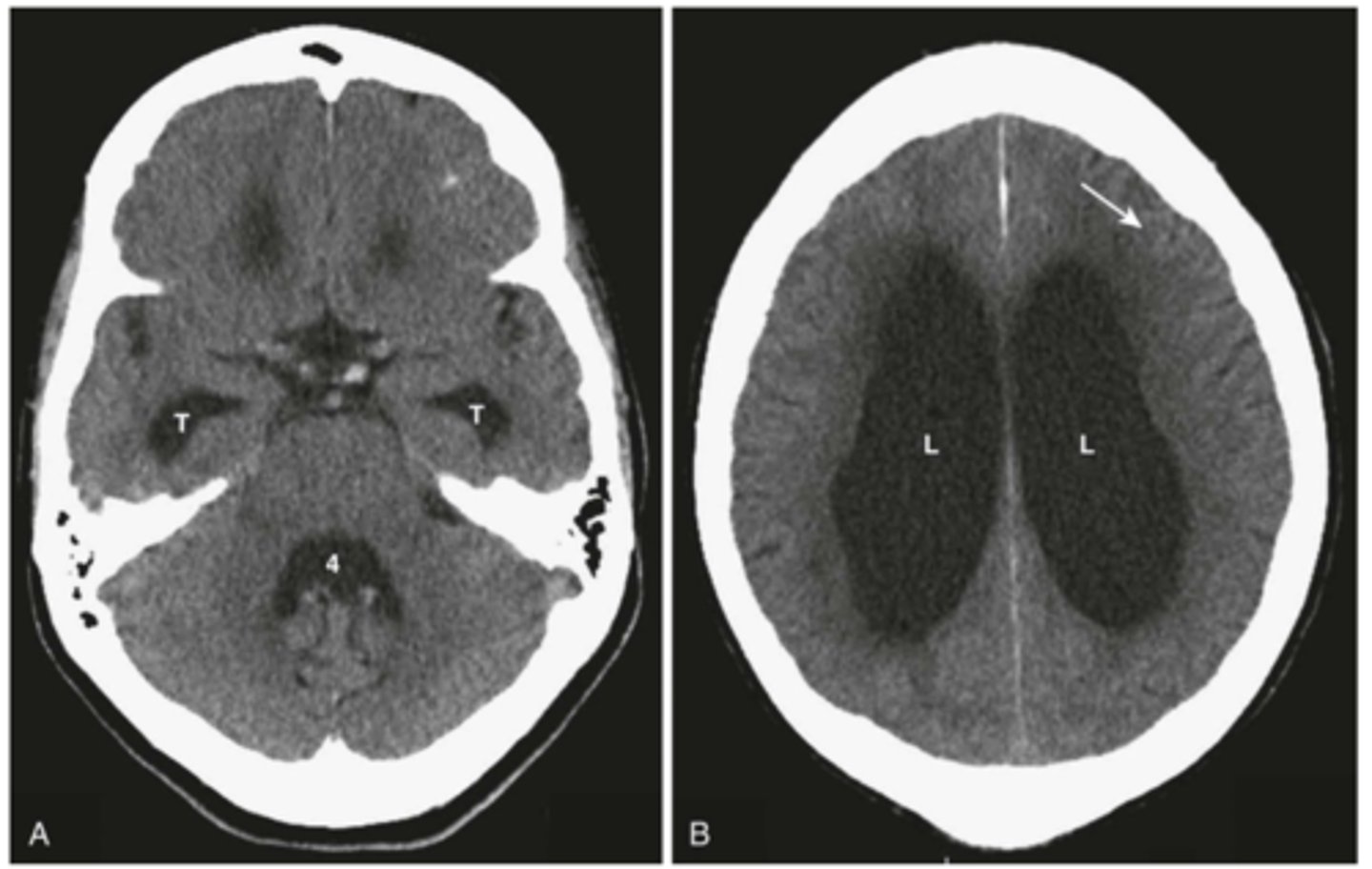
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus/NPH
Define Condition:
-Hx: Adult onset (45-75 y/o), +/- Hx of meningitis/SDH/TBI affecting CSF reabsorption
-Sx: Urinary incontinence, Gait Ataxia (falls), cognitive decline (dementia)
-PE: Frontal Lobe ataxia (magnetic gait - "stuck to the floor"), LE hypertonia, NO PAPILLEDEMA (*think "wet, wacky, wobbly"*)
-Dx: CT WOC (ENLARGED LATERAL VENTRICLES but NO ATROPHY)/Brain MRI (communicating hydrocephalus WITHOUT atrophy - VENTRICULAR ENLARGEMENT) + LP (normal, or 5-20 cm H2O)
-Tx: VPS/ventriculo-peritoneal shunt within 2 yrs of onset
These conditions can scar the arachnoid granulations that allow for egress of CSF
Why might Ataxia due to NPH be more common in patients who have a prior history of head trauma, meningitis, or subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Ataxia = INCOORDINATED movements; Dyskinesia = ABNORMAL movements
Distinguish Ataxia vs Dyskinesia
Dyskinesia
Define Condition:
Abnormal movement that is not tremors or chorea; often irreversible - focal, asynchronous muscle movements which may occur in any muscle groups but are particularly common in the oro-facial-lingual and limb muscles
-Hx: ACUTE with drug reactions, but usually Subacute or Gradual; Hx of Anti-Dopa or Antipsych/Anti-emetics
-Dx: Normal
-Tx: STOP any drug implicated (if it can be safely stopped), Sometimes Botulinum Toxin
discontinuation
Acute iatrogenic dyskinesias begin shortly after beginning or increasing the causative agent --> will cease with () of agent
Tardive
() dyskinesias are usually seen in patients taking certain drugs chronically
True
T/F - Phenothiazine can induce Extrapyramidal Symptoms like dyskinesia or dystonia
Basal Ganglia
What lesions typically cause Involuntary Dyskinesia (tremors when pt isn't doing anything)?
Cerebellar
What lesions typically cause Voluntary Dyskinesia (tremors ONLY when using body/limbs)?
Dystonia
Define Condition:
Abnormal movement that is not tremors or chorea; often irreversible - prolonged muscle contractions more like increased muscle tone in specific muscle groups
-Hx: ACUTE with drug reactions, but usually Subacute or Gradual; Hx of Anti-Dopa or Antipsych/Anti-emetics
-Sx/PE: Cervical (torticollis, aka "wry neck"), Generalized ("Dystonia musculorum deformans"), Focal Limb ("writer's cramp")
-Dx: Normal - EXCEPT in Wilson's Disease
-Tx: STOP any drug implicated (if it can be safely stopped), Anticholinergic Drugs (ex: Benadryl), Benzodiazepines, Sometimes Botulinum Toxin
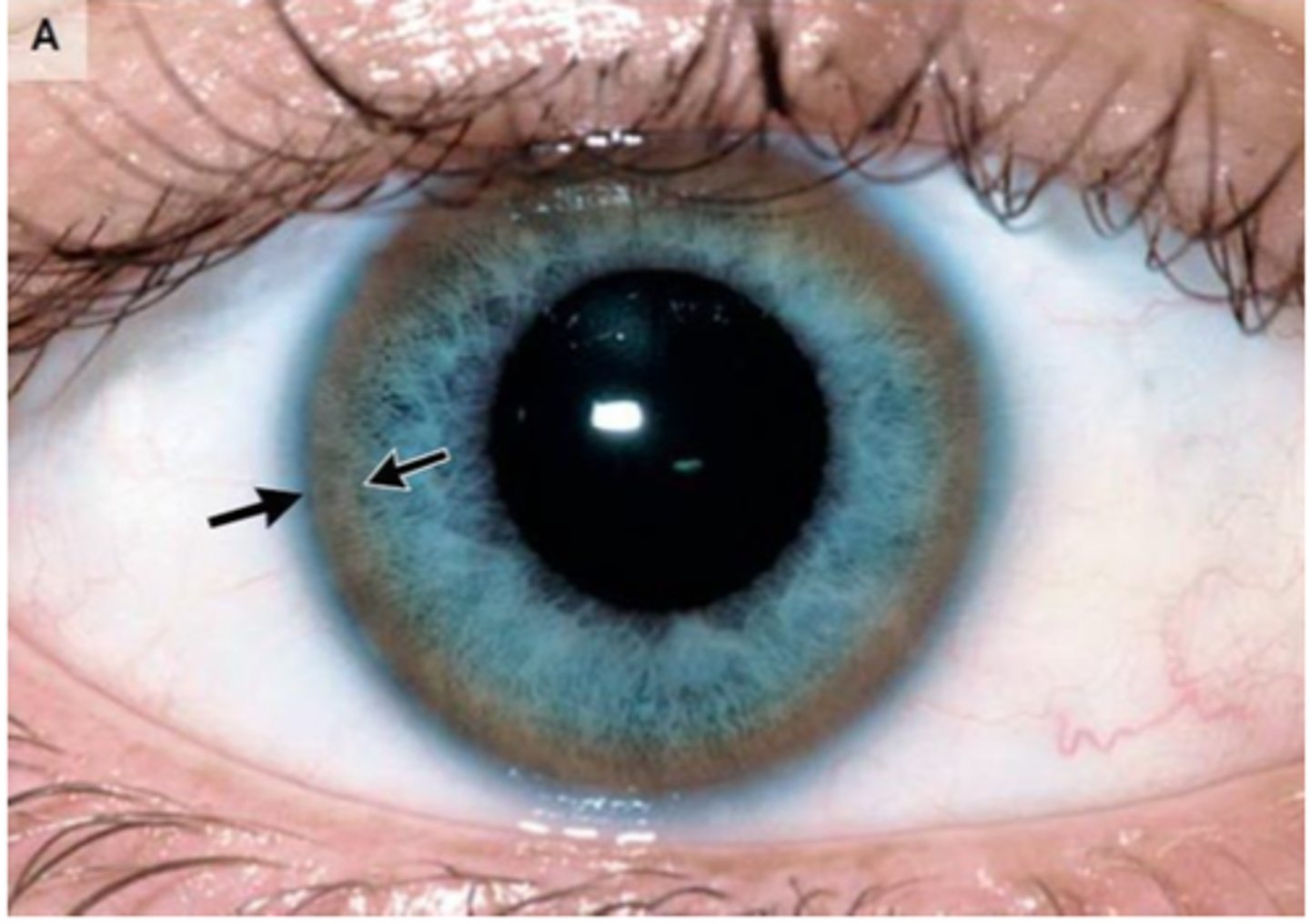
Wilson's Disease
Define Condition:
Hepatolenticular degeneration due to genetic defect, “ar” on Chromosome 13 causing abnormal metabolism and deposition of copper
-Hx: +FHx, Young Onset
-Sx/PE: Unexplained dyskinesia/tremor (typically produces dystonic tremors); deposition of copper in brain, liver (cirrhosis) & eye (kaiser-flesher ring)
-Dx: Labs for 24 hr copper UA (high) and serum ceruloplasmin (low) + Liver Biopsy
-Tx: Chelation Therapy