Year 9 Semester 2 Science (Electricity)
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Six Sheven
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What does the Law Of Conservation Of Energy state?
Energy can never be destroyed or created, only transformed from one form to another.
What is electricity?
The flow of electrons (in an electrical current)
What are the two main divisions of types of energy?
Kinetic Energy / Potential Energy
What are 5 types of kinetic energy?
Mechanical Energy
Electrical Energy
Sound Energy
Radiant Energy
Thermal Energy
What are 5 types of potential energy?
Gravitational Potential Energy
Electric Potential Energy
Elastic Energy
Chemical Energy
Nuclear Energy
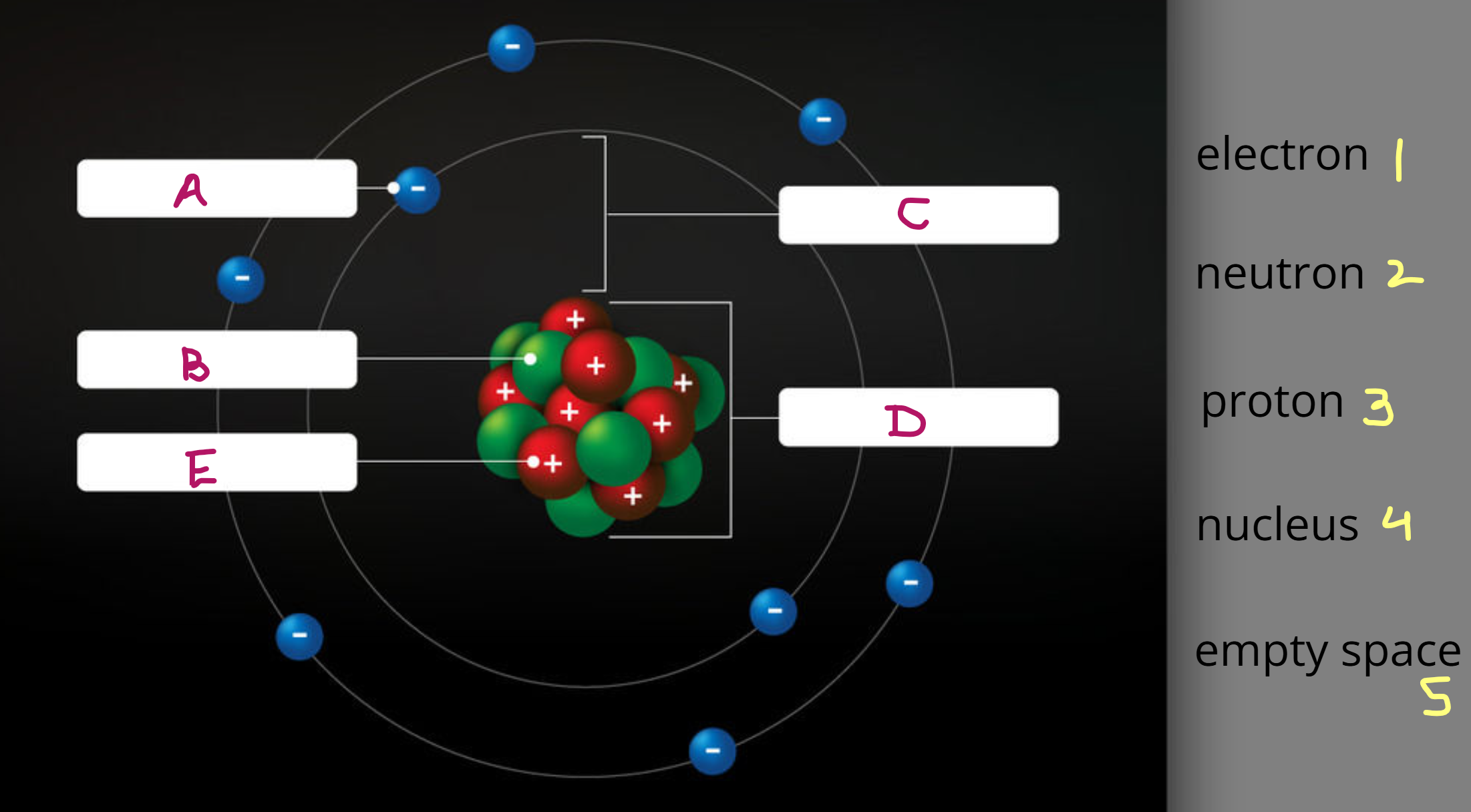
Fill in the blanks.
A1 B2 C5 D4 E3
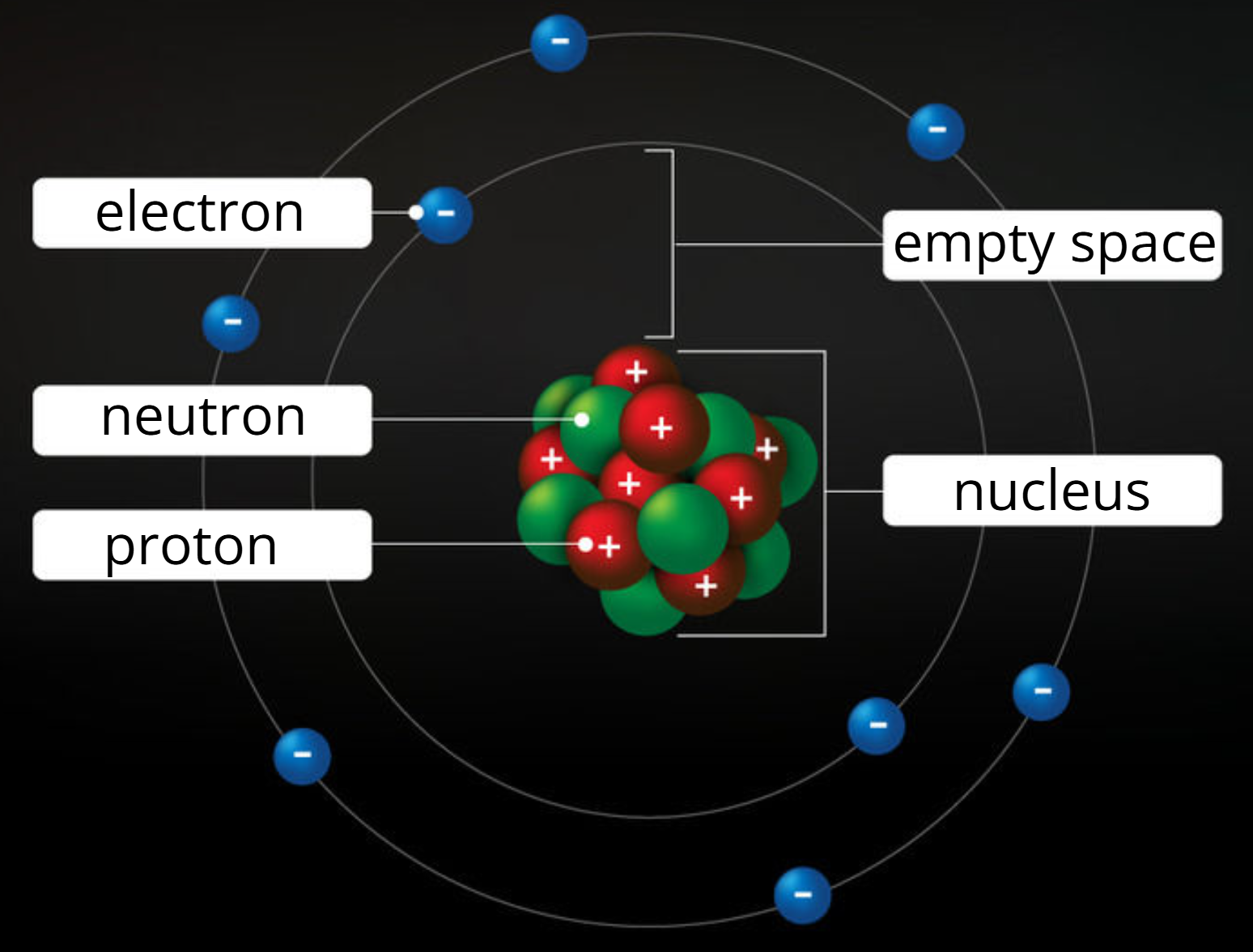
The charge of electrons are…
The charge of neutrons are…
The charge of protons are…
Negative
Neutral
Positive
What is the difference between a secondary energy source and a primary energy source?
Secondary energy sources are produced by the conversion of other primary energy sources (coal, gas, oil, fuel).
Give a brief overview of how an electrical generator works.
First a large machines called turbines are turned very quickly – this requires a lot of energy, such as heat, wind or moving water.
Next, the spinning turbines cause large magnets to turn within copper wire coils – these are the generators.
Finally the moving magnets within the coil of wire cause electrons (charged particles) to move within the wire – this is electricity.

What the john does this have to do with the stile lesson
Idk bro bro bro your boat you tell me
What are some types of renewable energy?
Solar, Wind, Hydro, Geothermal, Biomass
What is a conductor?
Materials that permit electrons to flow freely from particle to particle
What is an insulator?
Materials that obstruct the free flow of electrons from atom to atom and molecule to molecule
What conductor and insulator can be found in wires in electrical circuits?
Copper as a conductor
Rubber as an insulator
Why do we cover wires in rubber?
Wires that are carrying electricity that are not covered in rubber could be very dangerous. If somebody touched them they could get an electric shock, or the heat energy that they produce could cause a fire

Not a flashcard, but a useful note.
What are some physical properties of metals?
Conductive
Ductile
Solid
Malleable
Lustre (Shiny)
What are some physical properties of metalloids?
SEMI Conductive
NOT Ductile
NOT Solid (Durable)
NOT Malleable
Lustre (Shiny)
What are some physical properties of non metals?
NOT Conductive
NOT Ductile
Brittle Solid
NOT Malleable
Dull (Usually)
Gaseous
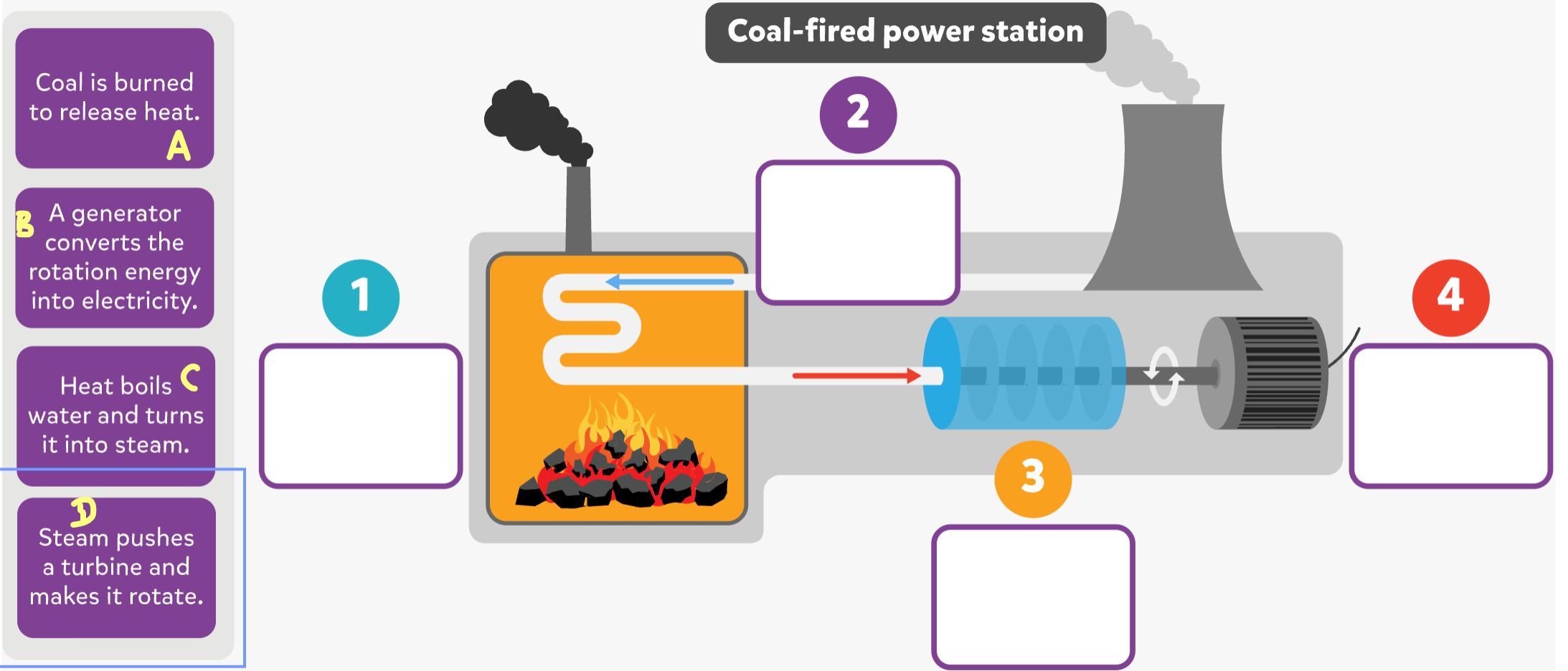
Fill in the blanks to how a coal fired power station works.
A1
B4
C2
D3
What force do magnets use to attract materials?
Magnets use a fundamental non-contact force called magnetism to attract materials.
What are examples of magnetic materials?
Iron, nickel, and cobalt are examples of magnetic materials.
What are examples of non-magnetic materials?
Aluminium and wood are examples of non-magnetic materials.
What is electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism is the interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields
What is electromagnestis’s two main relationships?
Electric currents produce magnetic fields
Changing magnetic fields can produce electric currents
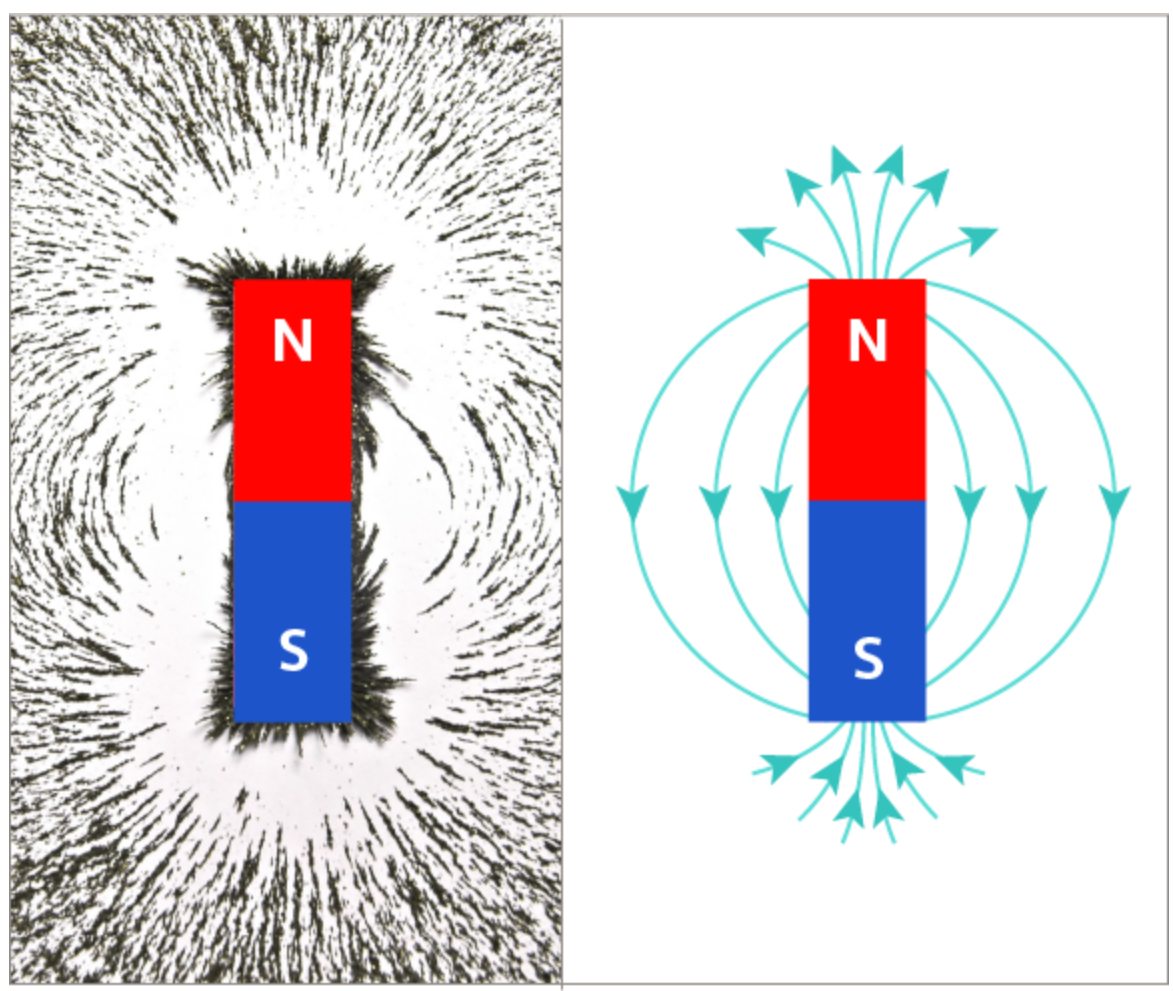
What are the four main rules when drawing magnetic fields?
The lines connect the two poles of a magnet in a doughnut-like shape.
The lines never cross each other.
The arrows show the direction of the magnetic field, always pointing away from the north pole and towards the south pole.
The spacing of the lines indicates the strength of the magnetic force, with greater distance between lines meaning a weaker force.
What is an electromagnet, and how is it made?
An electromagnet is a temporary magnet made by running an electric current through a copper wire, which creates a magnetic field.
What happens in a combustion reaction?
The reactants are always a fuel and oxygen.
The products is always carbon dioxide, water and energy.
What are the issues with combustion reaction?
It produces carbon dioxide which is greenhouse gas. It traps heat from the sun in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming. If done incomplete, can make soot (carbon) and carbon monoxide, which is very poisonous.
What is the cause of incomplete combustion?
Incomplete combustion happens when there isn’t enough oxygen, so not all carbon and hydrogen atoms in fuels like fossil fuels can fully combine with it.
How do we get acid rain?
Acid rain forms when sulfur impurities in coal and oil burn to create sulfur dioxide, which dissolves in rain to make sulfuric acid, and when nitrogen from the air burns in hot furnaces and engines to produce nitrogen dioxide, both contributing to acid rain that harms forests and water.
What are the requirements for an electrical current to flow?
An electrical current must have a closed pathway or circuit to flow around, an energy source like a power station, generator, or battery to cause the current to flow, and flow through certain parts or components of the circuit that can use the energy for something useful, like a light globe, motor, or computer.
How does a battery work in a circuit?
A battery holds chemical energy that moves to electrons when its two metal ends are connected by a circuit, letting electrons flow from the negative to the positive end and pass energy to things like light bulbs, motors, and heaters.
Describe voltage with an example.
Voltage is the amount of energy given to moving electrons in a circuit, measured in volts, and can be compared to the pressure that pushes water through pipes in a house, with a higher voltage supplying a bigger "push" to the electrons.
What is the direction in which electrons travel?
In a circuit, electrons travel from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
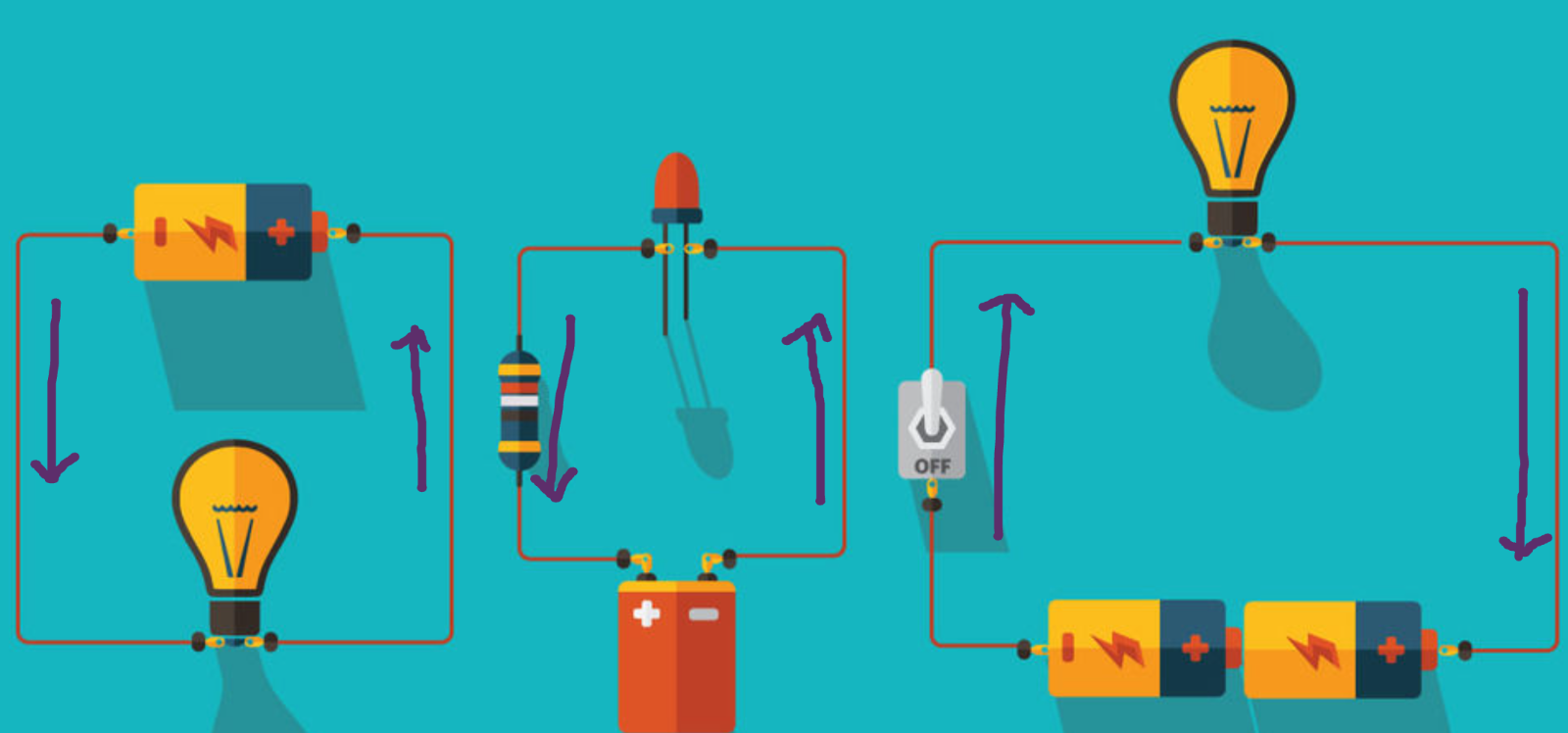
What is a circuit and what does it need for electrons to flow?
A circuit is a pathway for electricity to flow through, and it needs an unbroken path for electrons to flow.
What are electrical conductors and why are metals used in circuits?
Electrical conductors are materials that allow electrons to flow through them, and metals are used in circuits because they are good electrical conductors.
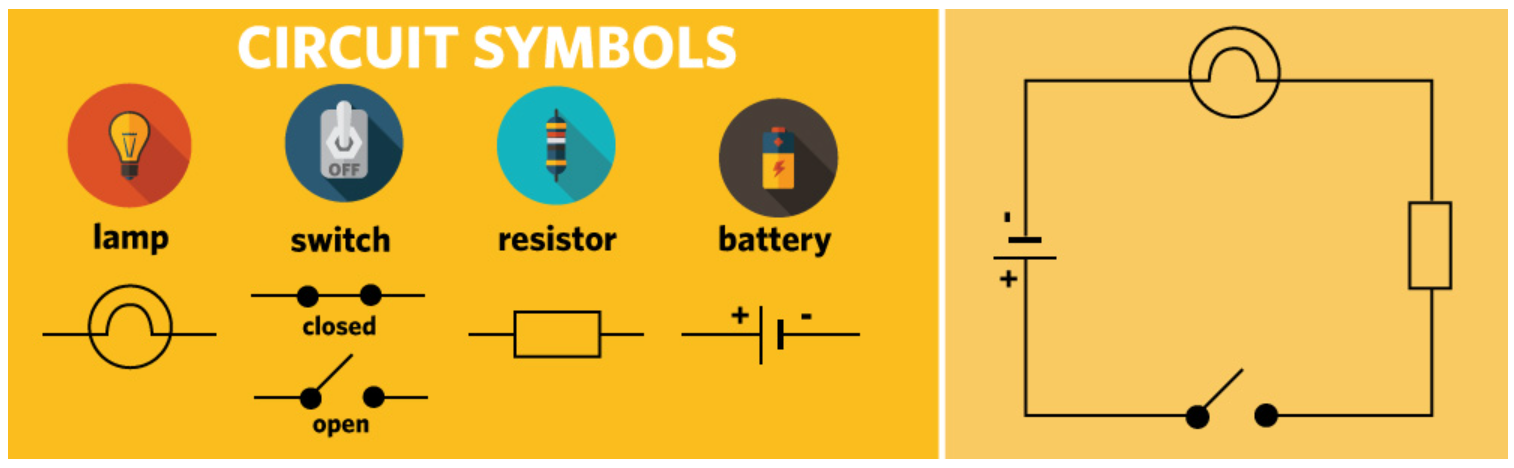
Not a question, but circuit symbols you must know.
Not a question, but circuit symbols you must know.
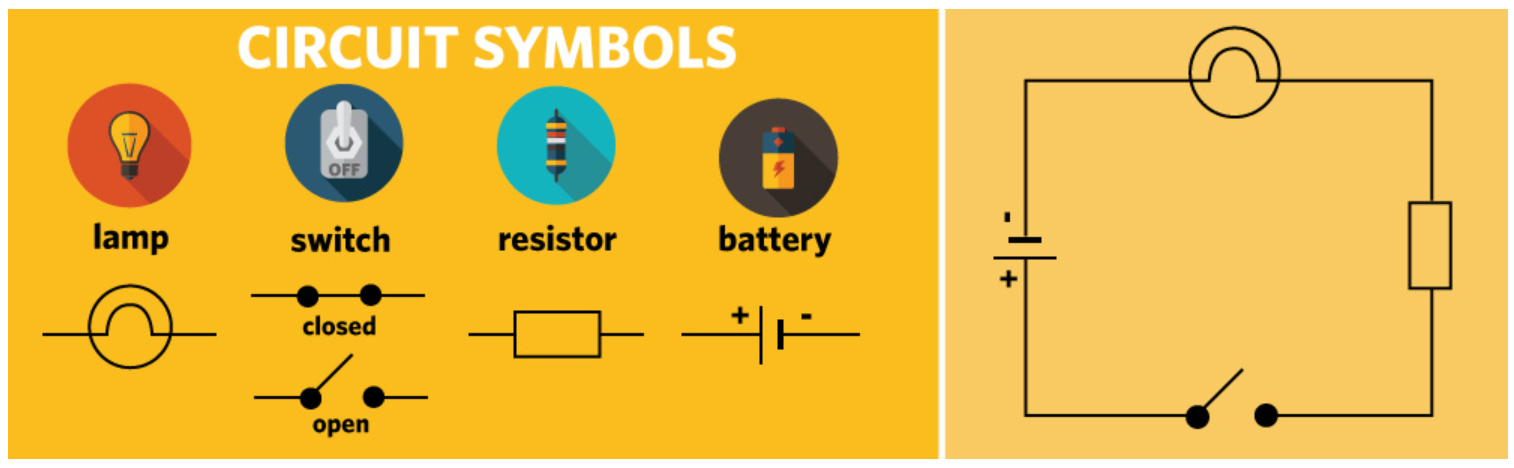
How would you define current?
The number of electrons passing a given point in one second.
What is power in physics and how is it measured?
Power in physics is the rate of transfer of electrical energy in a circuit and is measured in watts.
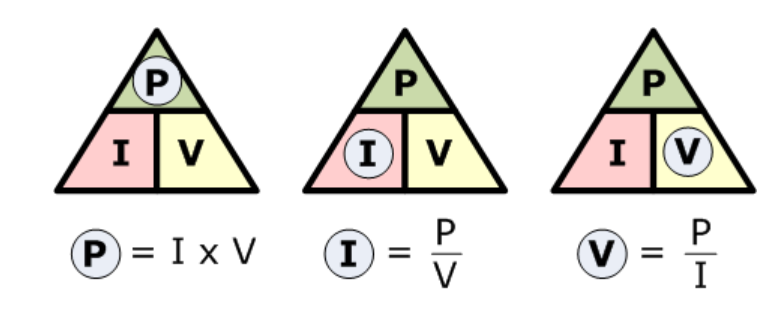
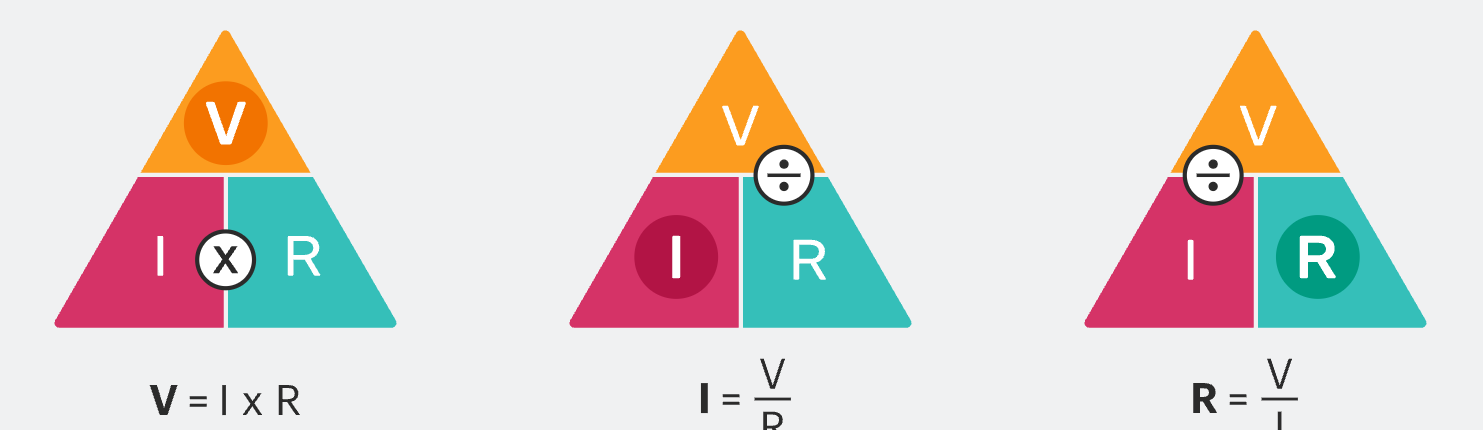
How would you make the PIV Triangle with P as power measured in watts, I as current measured in amperes, and V as voltage measured in volts.
What is resistance and how does it affect electrons?
Resistance is the difficulty electrons face when flowing through a component, measured in ohms (Ω), and the higher the resistance, the harder it is for electrons to flow and the more energy they lose.
How would you make the VIR Triangle with R as resistance in ohms, I as current in amperes, and V as voltage in volts.
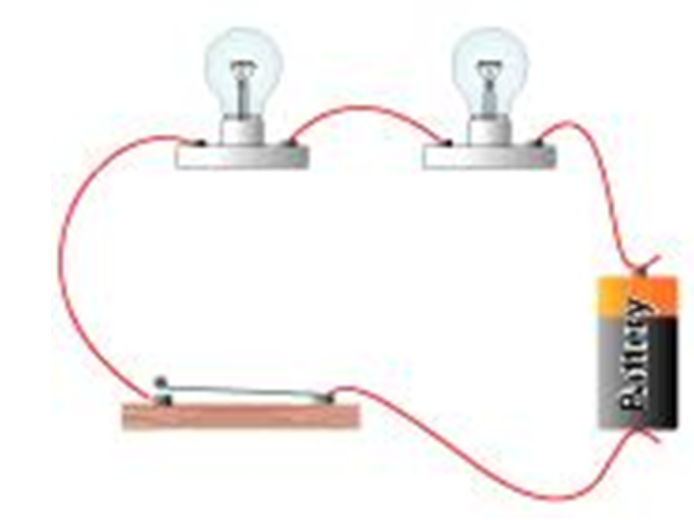
Define a series circuit.
The components are connected end-to-end, one after the other. They make a simple loop for the current to flow round.
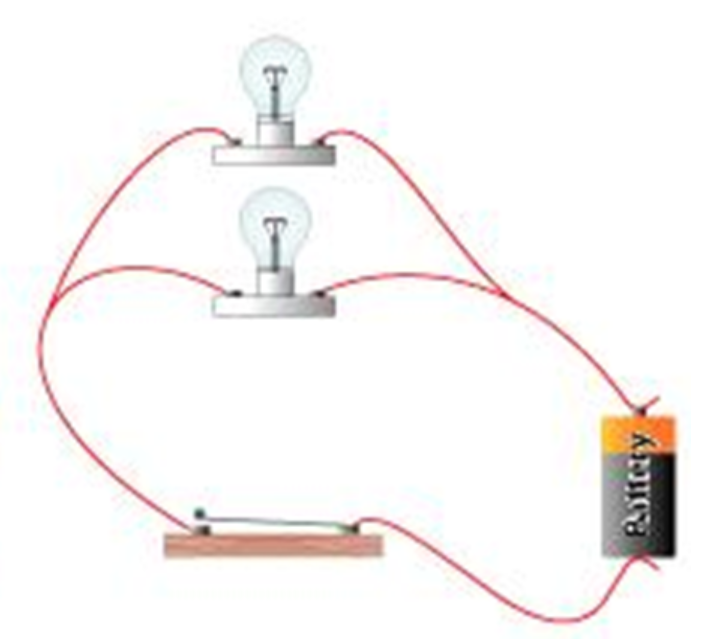
Define a parallel circuit.
The components are connected side by side. The current has a choice of which wire it travels in, this means the resistance doesn't add up.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of series circuits?
A: Series circuits are simpler, takes less time to design and sometimes cheaper.
D: If one component breaks, the entire circuit breaks and stops. The resistance builds up.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of parallel circuits?
A: If one component breaks, the circuit still works as it can take another path. The resistance wont add up.
D: They require more wiring and more planning and sometimes higher power consumption.