ANT100 EVO
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Crepuscular
active at dawn and dusk
Cathemeral
active anytime day or night
Primates typically eat what?
Fruits, flowers, insects, (special ones eat leaves)
Large primates Diet is different...
they eat lots of non-nutritious food, compared to small ones that eat dense small meals
2 subcategories of Primate
Strepsirhini and Haplorhini
Strepsirhine Characteristics
Dental tooth comb, wet nose, unfused mandible, tapetum lucidum (see well), postorbital bar (bone around eye)
Sub families of Strepsirhini
Lemuriformes
-lemuroidea
-lorisoida
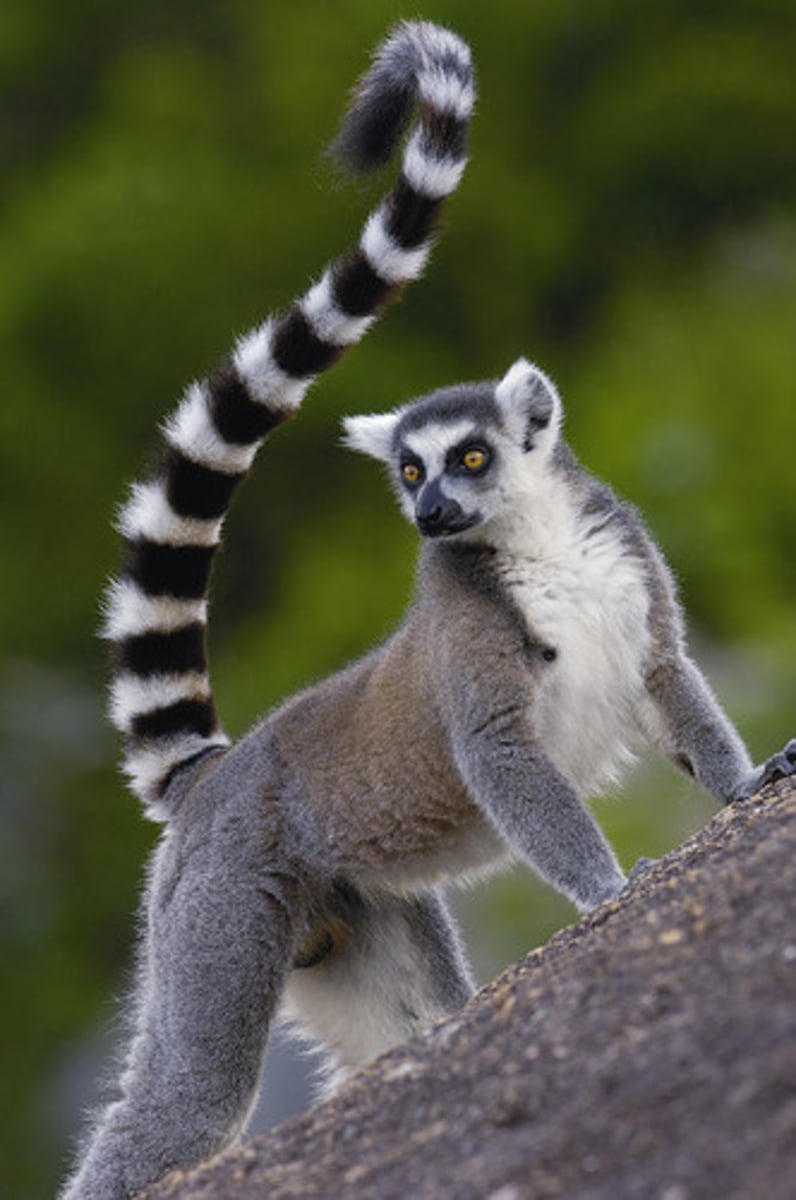
Lemuroidea basics
Madagascar, quadrupeds, female dominate

Lorisoida
Africa sahara, southeast asia, quadrupeds, nocturnal
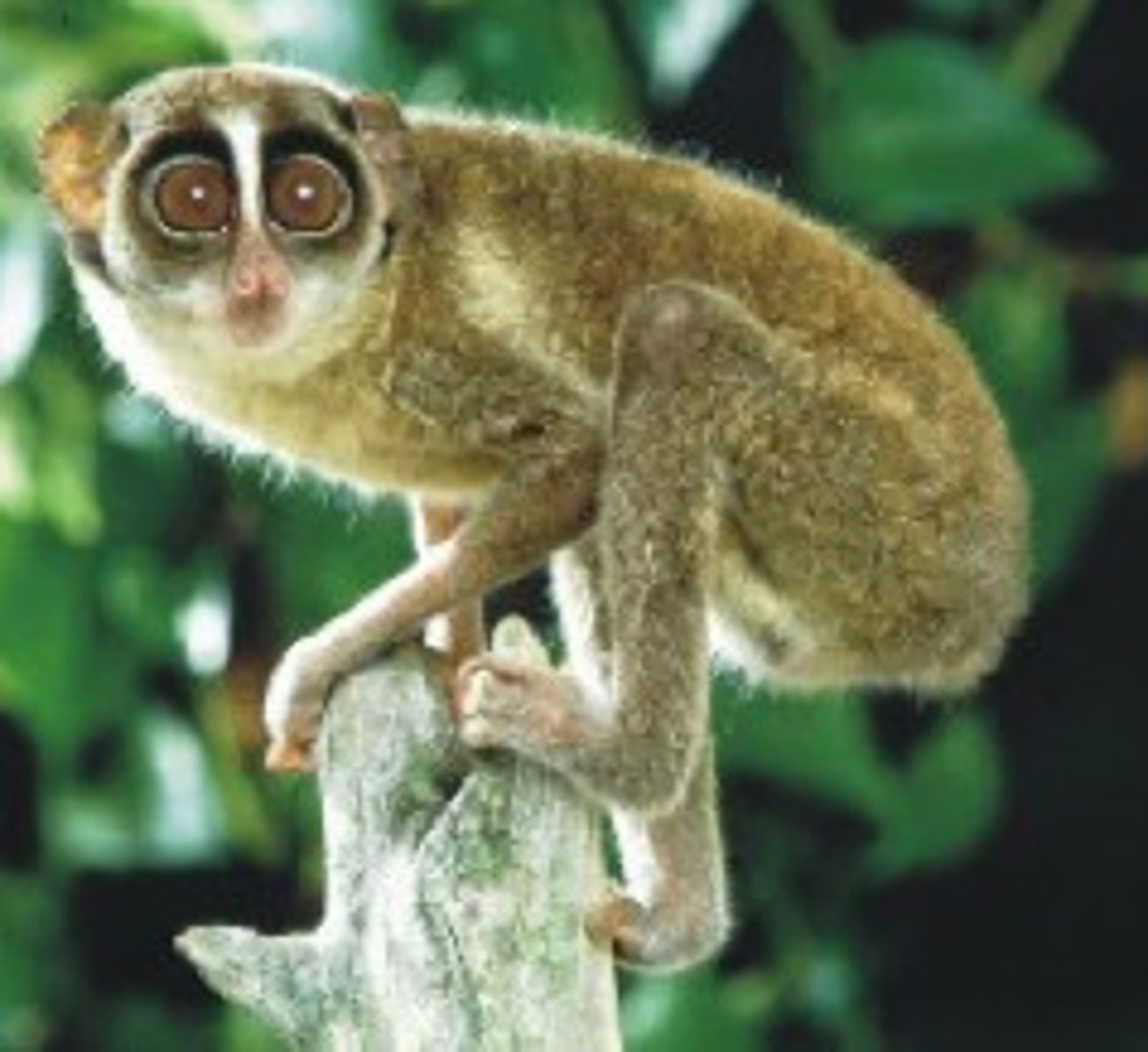

Haplorhine characteristics
Dry nose, retinal fovea, postorbital closure (eyes in bone), fused mandible and frontal symphyses
Haplorhine Sub categories
-Tarsiiformes
-Platyrrhini
-Catarrhini
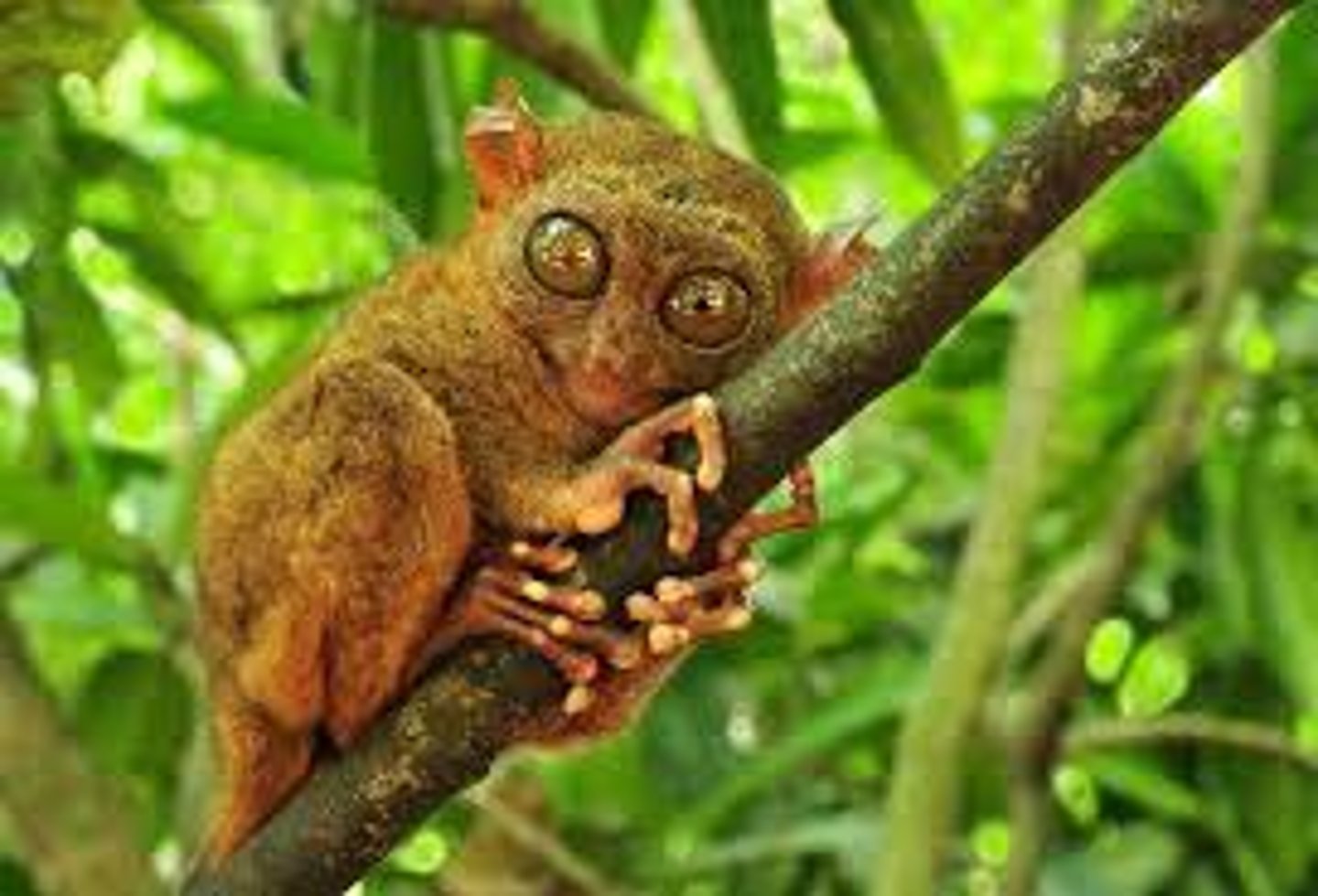
Tarsiiformes Characteristics
Small bodies, large eyes, Phillipines

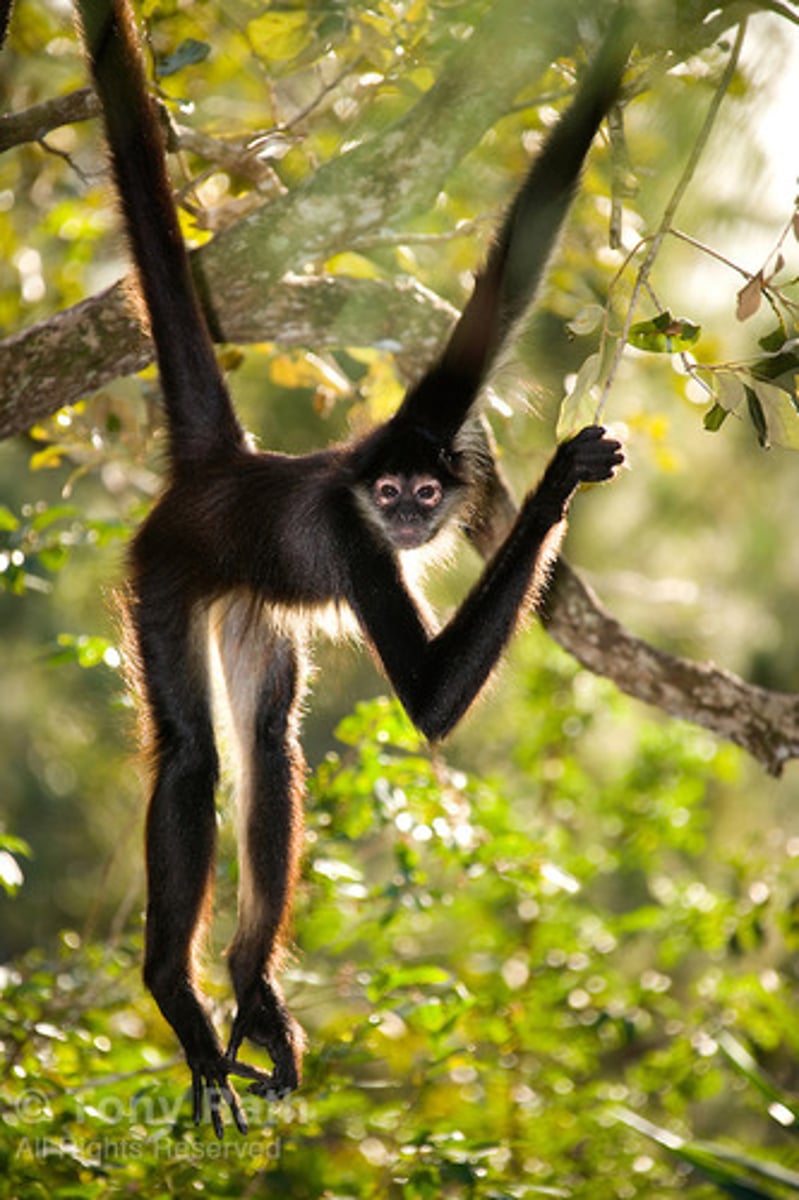
Platyrrhini Characteristics
South America, 11-11.4kg, Cebidae, atelidae + callitrichidae, prehensile tail (like a hand), arboreal

Catarrhini Characteristics
Africa + Asia, 1-175kg, old world monkey's, Variety diets, social

Primate Ranging Patterns (name them)
Home range, core area, territories (do not defend), daily path (where they go in 24hrs), day range (their limit)
Primates social ways (name them)
Deception, Female-male choice, homosexuality, warfare, kin recognition, friendship
Social Grooming is for?
establishing + maintaining social bonds then hygiene
Social organizations
Foraging laws, mate laws, housing, Female/Male philopatry (leaving at sexual maturity)
Epochs in Order
Paleocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene, Pliocene, Pleistocene, Holocene
Paleocene Climate and famous hominin
Hot and Humid, following the break up of pangea.
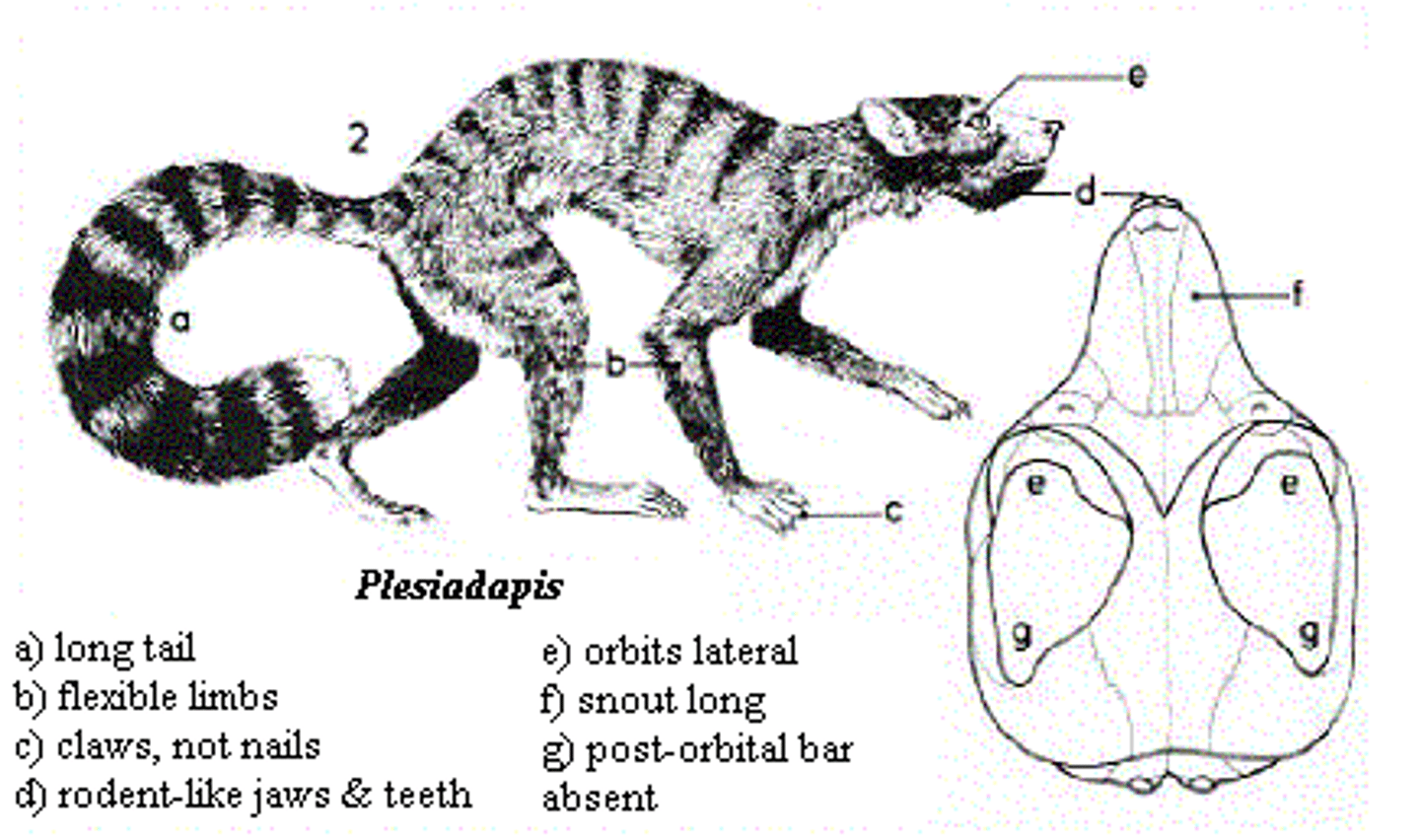
-Plesiadapiformes
Plesiadapiformes Characteristics
ARE Not PRIMATES. Body size, Niche: Nocturnal, Eat bugs and seeds, used to be primates comparing teeth, not earlier primates
Eocene Climate and famous hominin
Cooling down, land hasn't made contact yet
-Adapidae
-Omomyidae
Adapidae Characteristics
100-6900g, quadpeds leapers, fruits, bugs, leavesm led to lemurs

Omomyidae Characteristics
45-2500g, leaper teeth, soft fruits, insects, ancestor of tarsiers
Oligocenes Climate and famous hominin
Warms again, india yet to hit
-3 haplorhini features appeared. frontal lobe, postorbital bar, mandible
-Parapithecidae. Propliopithecidae. and Platyrrhini
Miocene Climate and famous hominin
Mediterranean Dried up, cooling lands
-Early: Monkey in africa
-Mid: Ape-like catarrhines Eurasia
-Late: Ape become rare (forest gets dry)
-Monkey's may have rafted or migrated before the continents split
Pliocene Climate and famous hominin
Lands still moving, still open at panama, fluctuations in temperature, and the Mediterranean is filled
-Fossil Cercopithecinae
-Fossil Colobinae
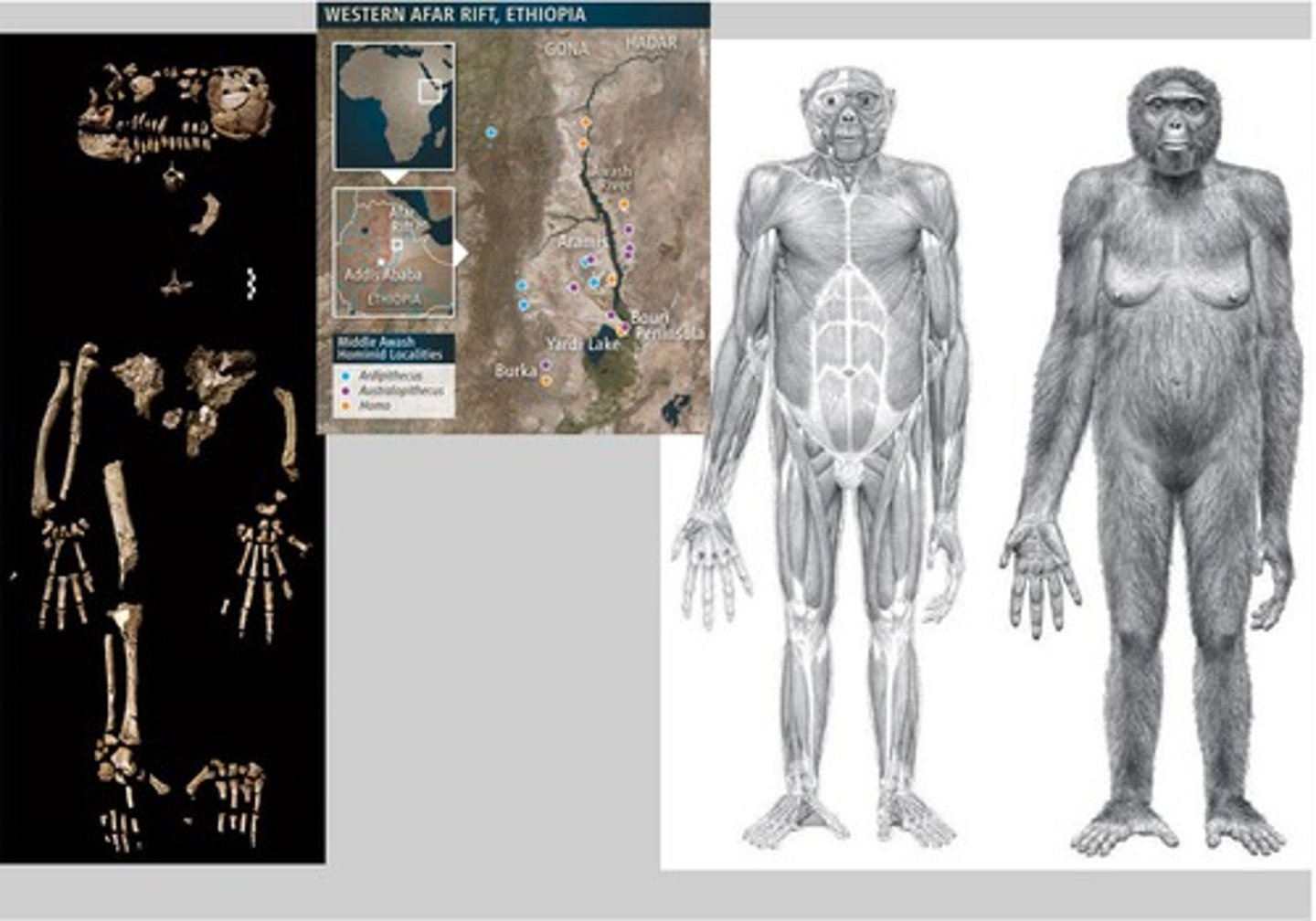
Australopithecus Afrarensis
4.2-3 MYA Ethiopia, smart, Laetoli footprints, ape (sagital crest) and hominin like (valgus knee)
-Salem: 3yrs female 3.2MYA

Ardipithecus Ramidus
Ethiopia 4.4MYA, walking on hands and feet, ape (thin enamel) and human like (small canine, bipedal)
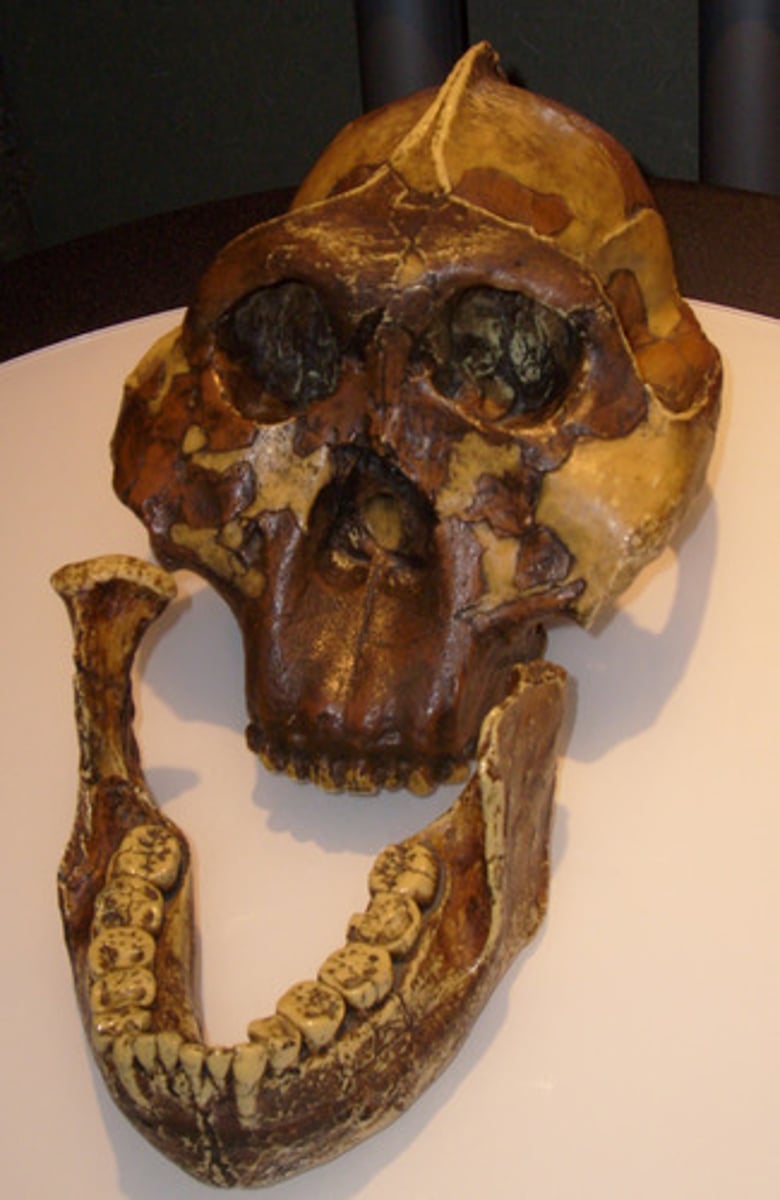
Australopithecus Aethiopicus
2.7-2.3 MYA East Africa

Australopithecus Boisei
2.2-1.2 MYA East Africa
Australopithecus Robustus
2.0-1.0 MYA South Africa
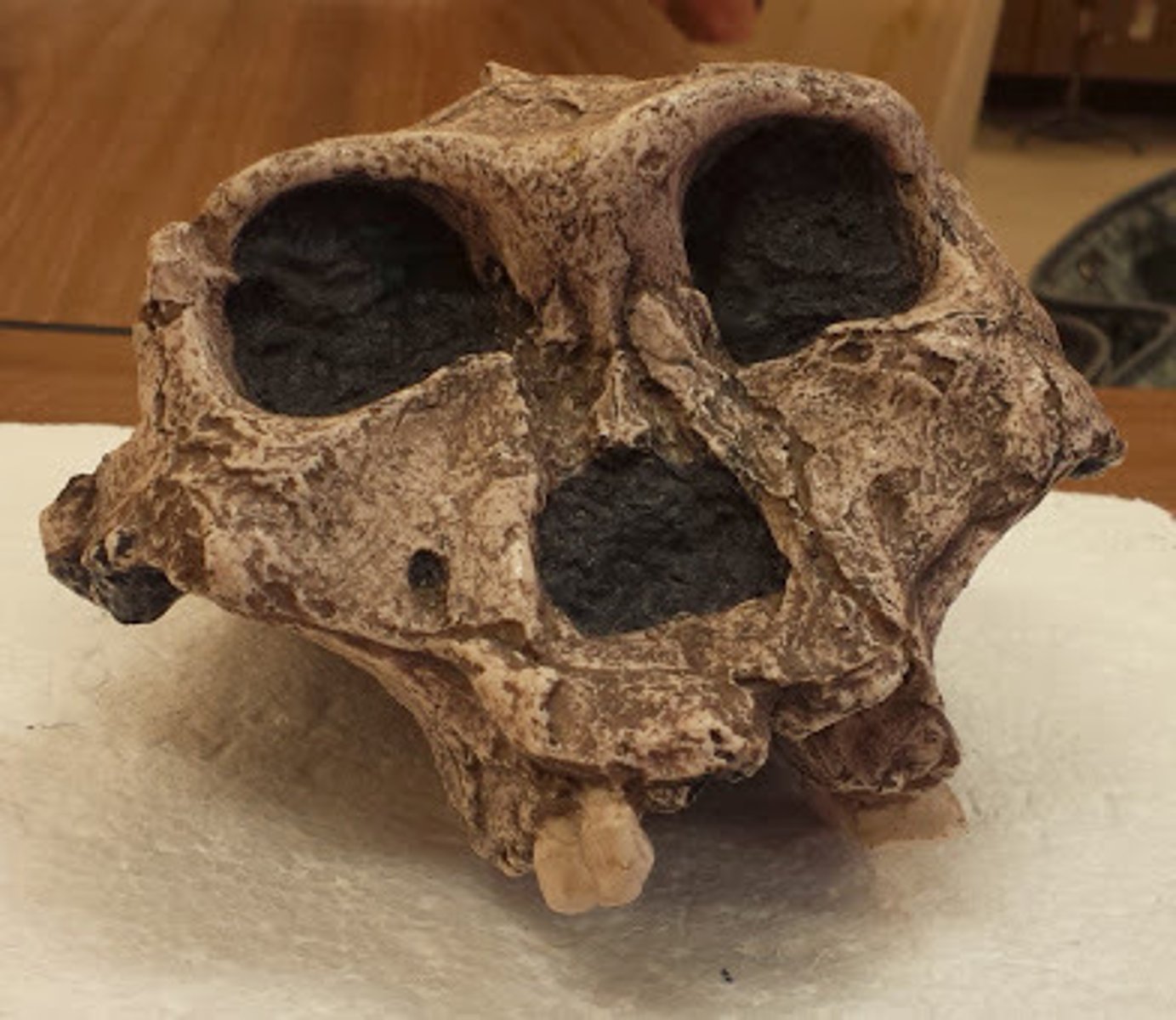

Australopithecus Sediba
Malapa South Africa 1.98MYA, 9 year old boy, human like (brain, pelvis, bipedal), had ape grappers
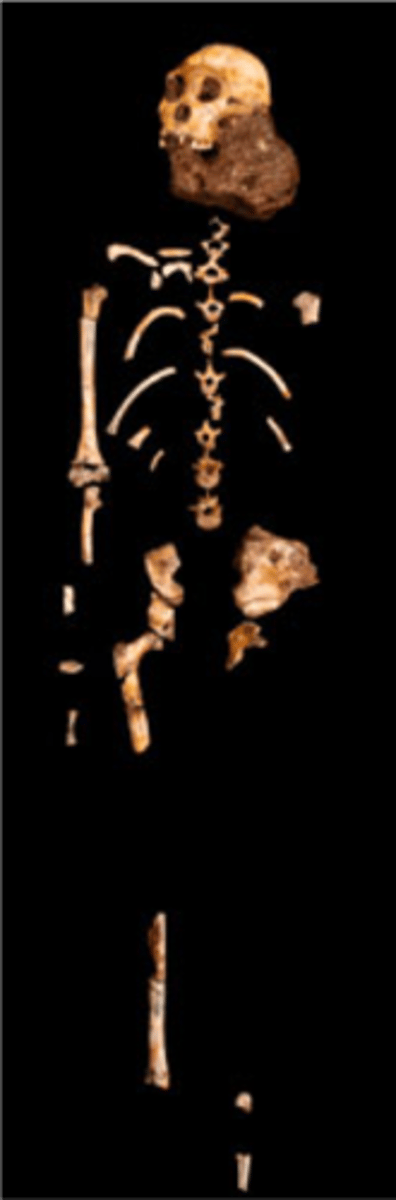
Homo Habilis
"Handy Man" they were found near tools, Form tanzania, kenya, ethopia, first species of homo.

Homo Rudolfensis
Koobi Fora, Kenya. Confused with habilis
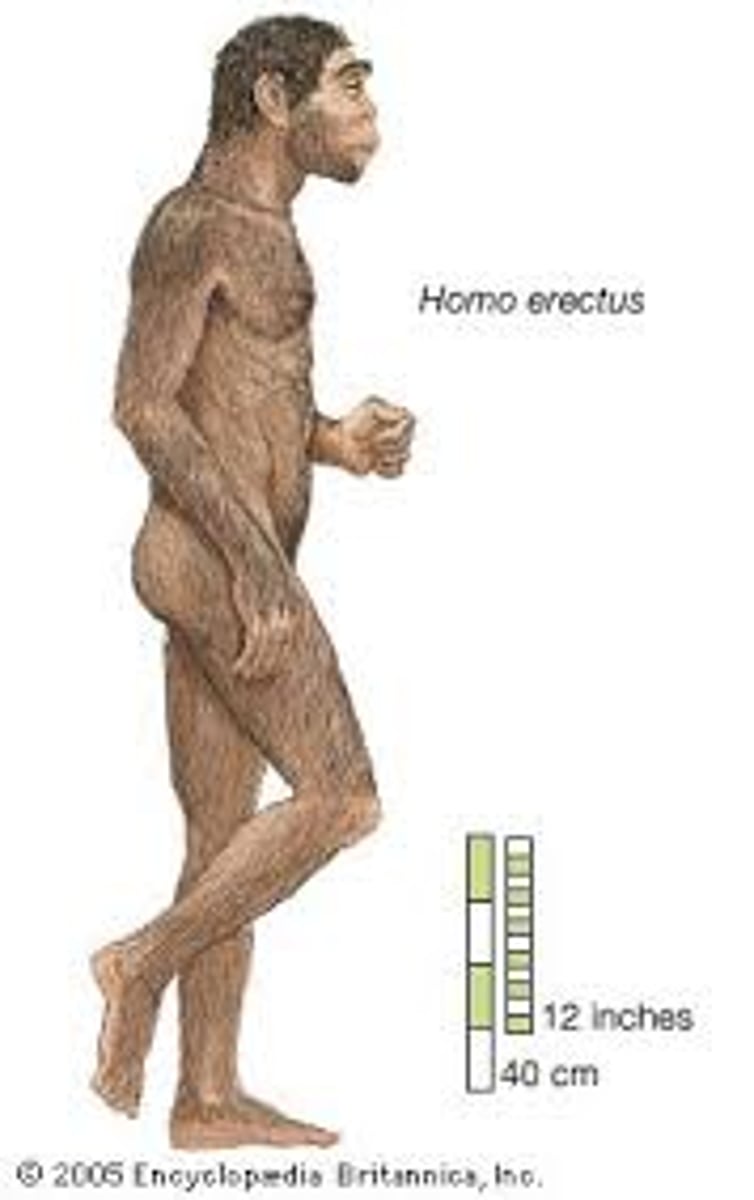
Homo Erectus
South East Asia and Africa, 1.8MYA-27KYA. mirgated to asia first. Bigger brain and short and thick, used fire (smoking out predators and cooking)

Homo Ergaster
East South Africa, 1.8-1.3MYA. thinner skull than erectus no suborbital foramen
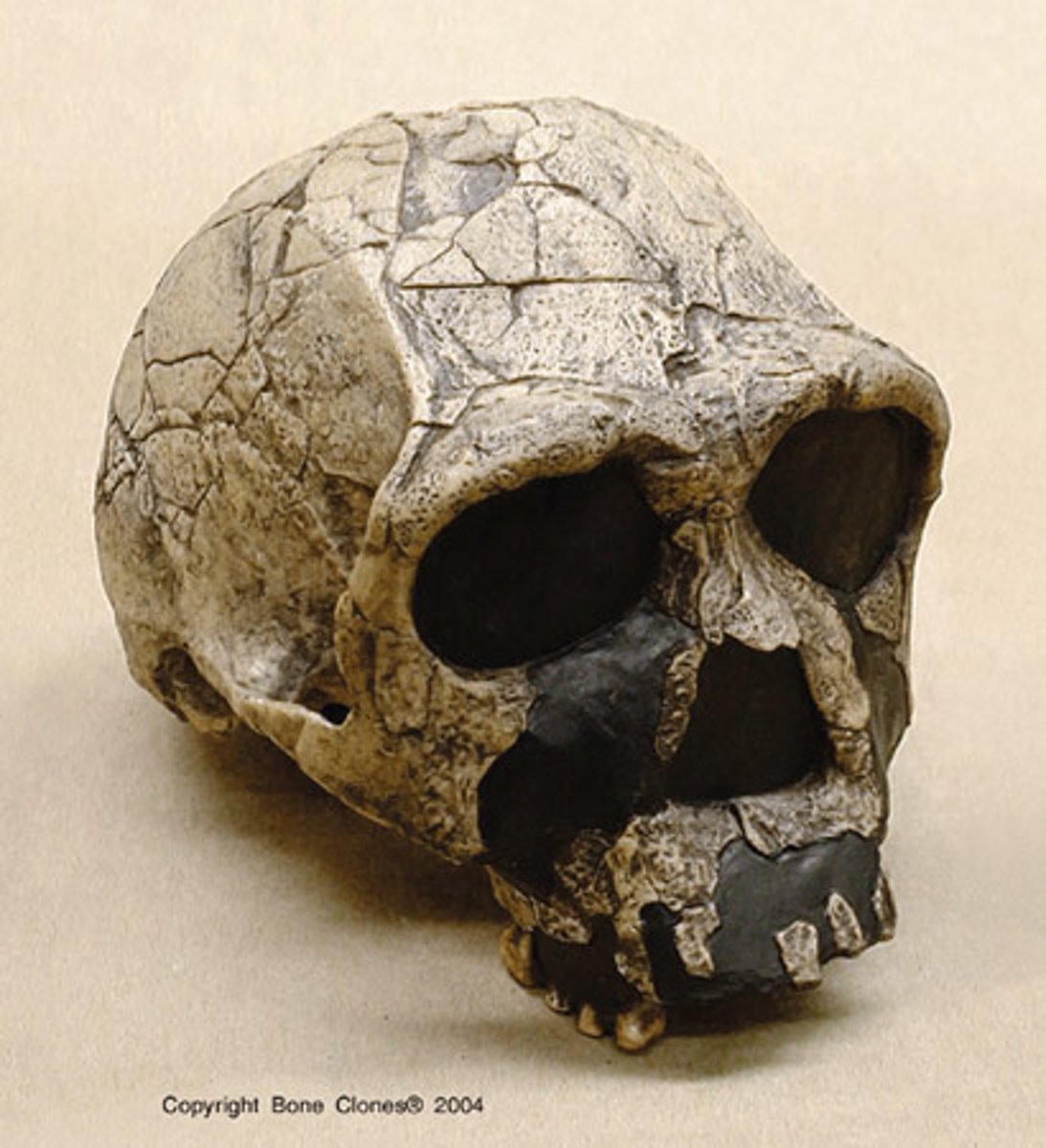
Homo Heidelbergensis
Europe and Africa, 700-130 KYA. from erectus, bigger brain and body

Homo Antecessor
Spain, 1.2 MYA-800KYA, first hominin in europe
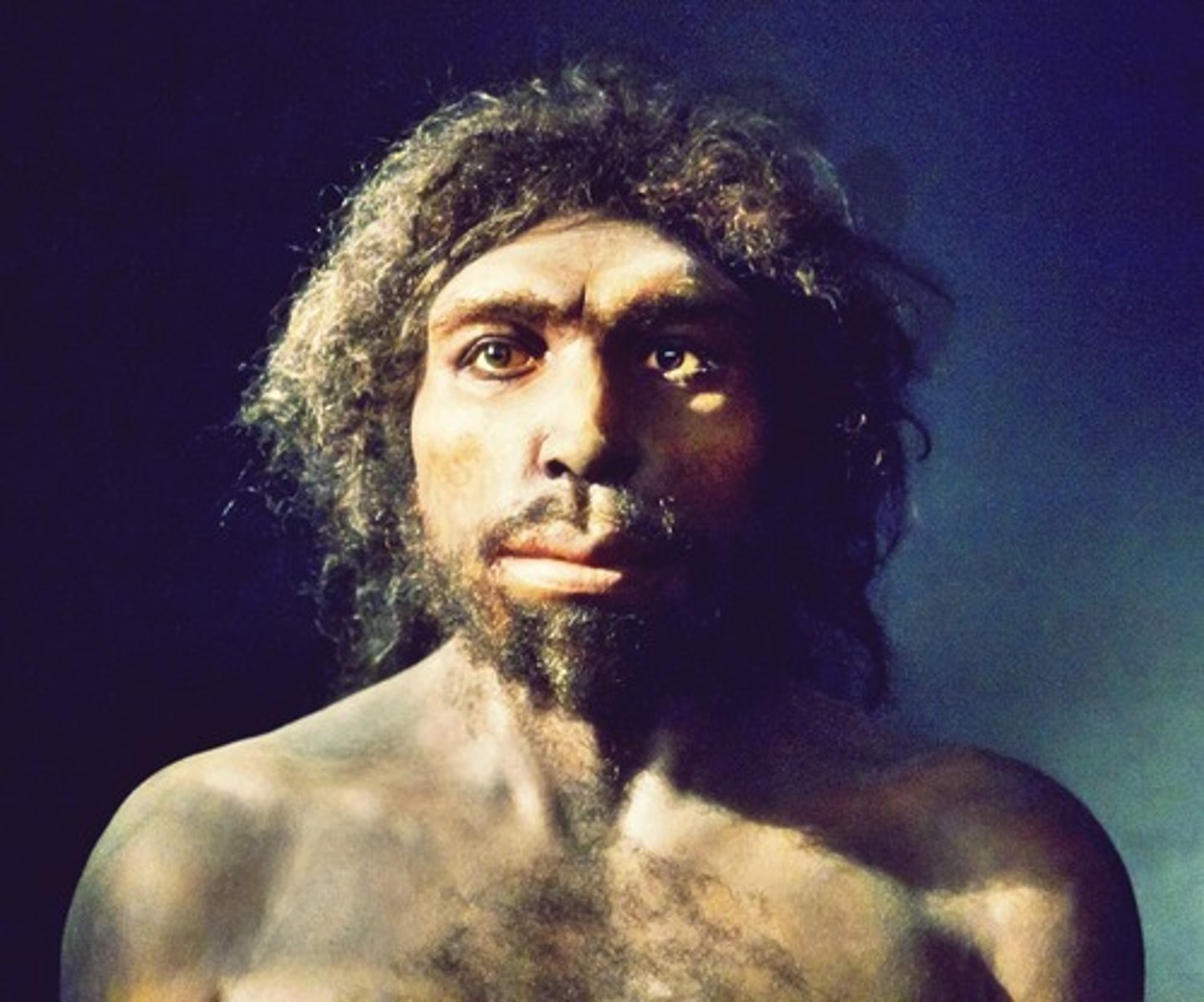

Homo neanderthalensis
Europe + Middle East, 300-35KYA, Bones marked with muscle, cotrical bones and large joints. Larger than modern humans, had tools
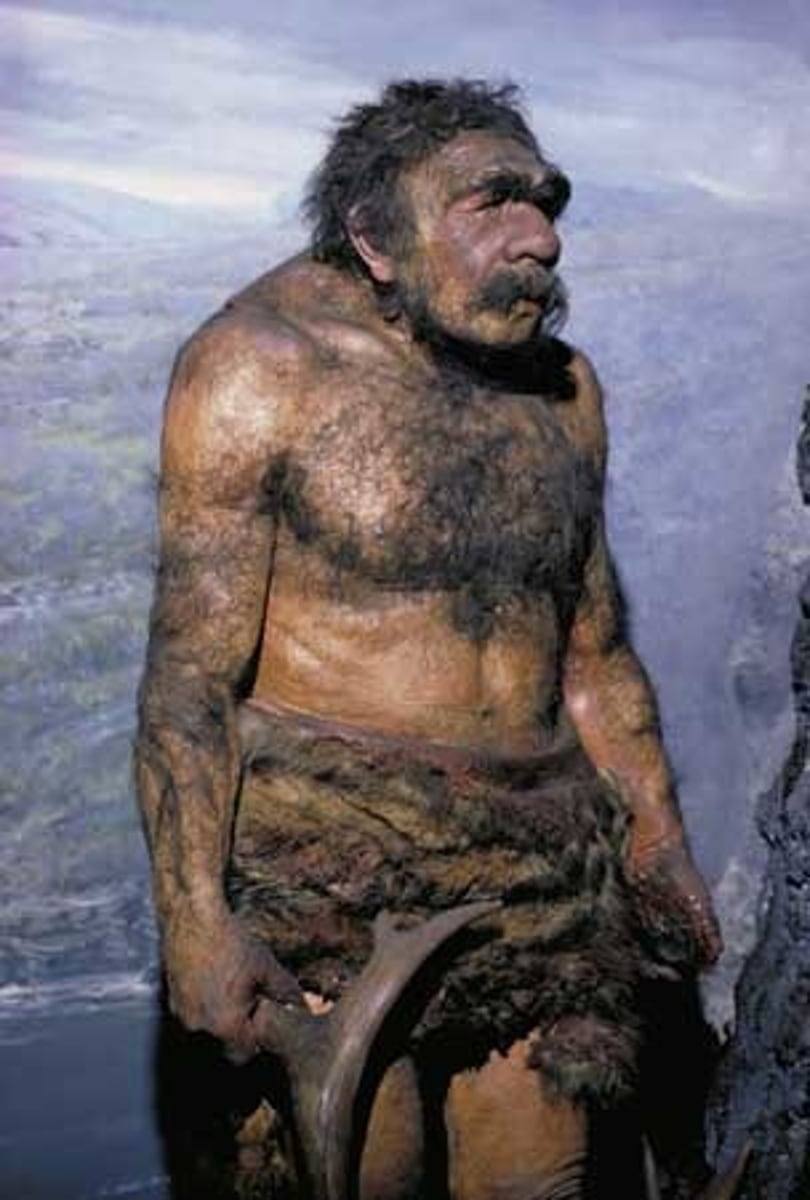

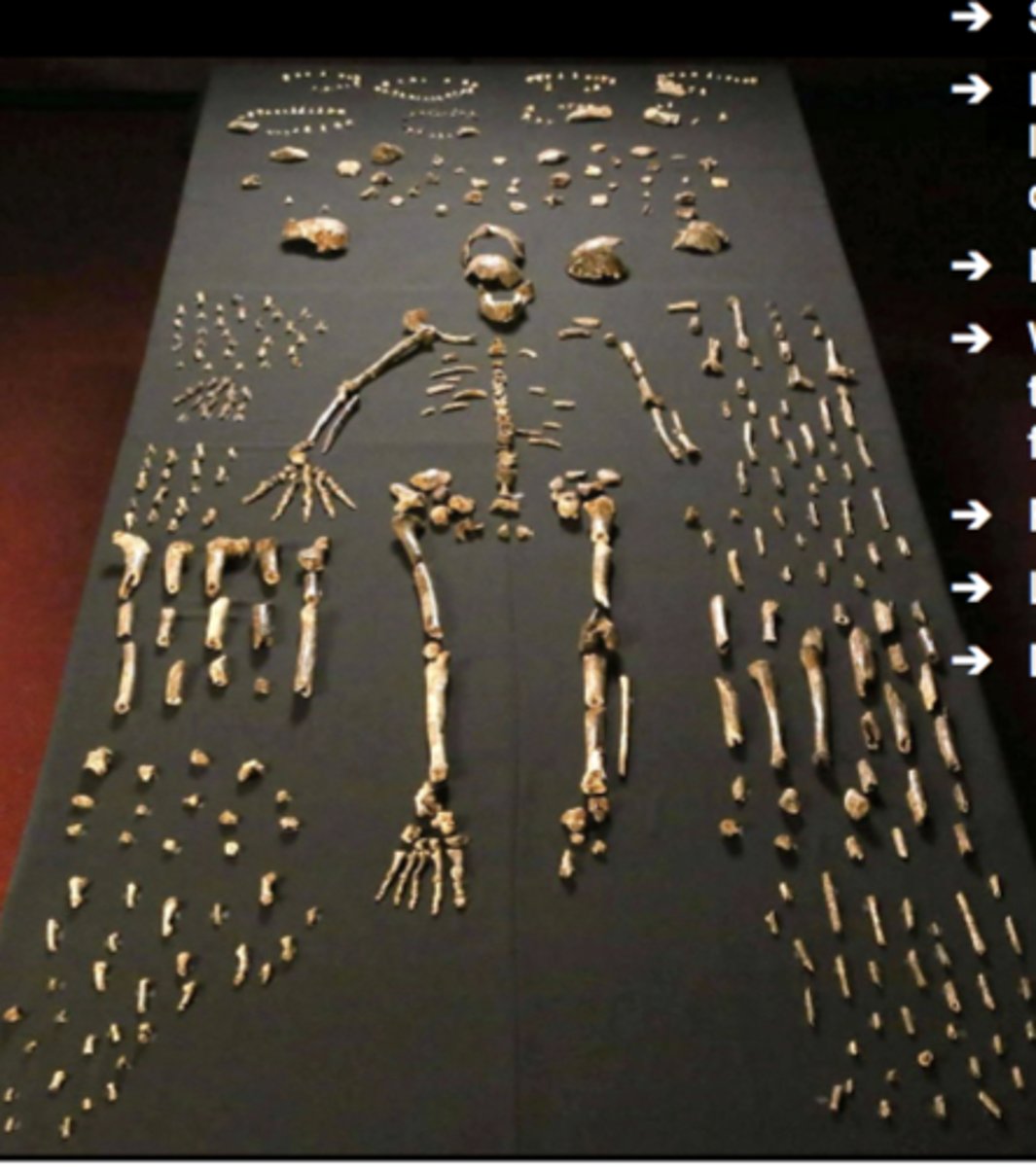
Homo Naledi
2013 South Africa, no date, body mass + stature = suggests small body

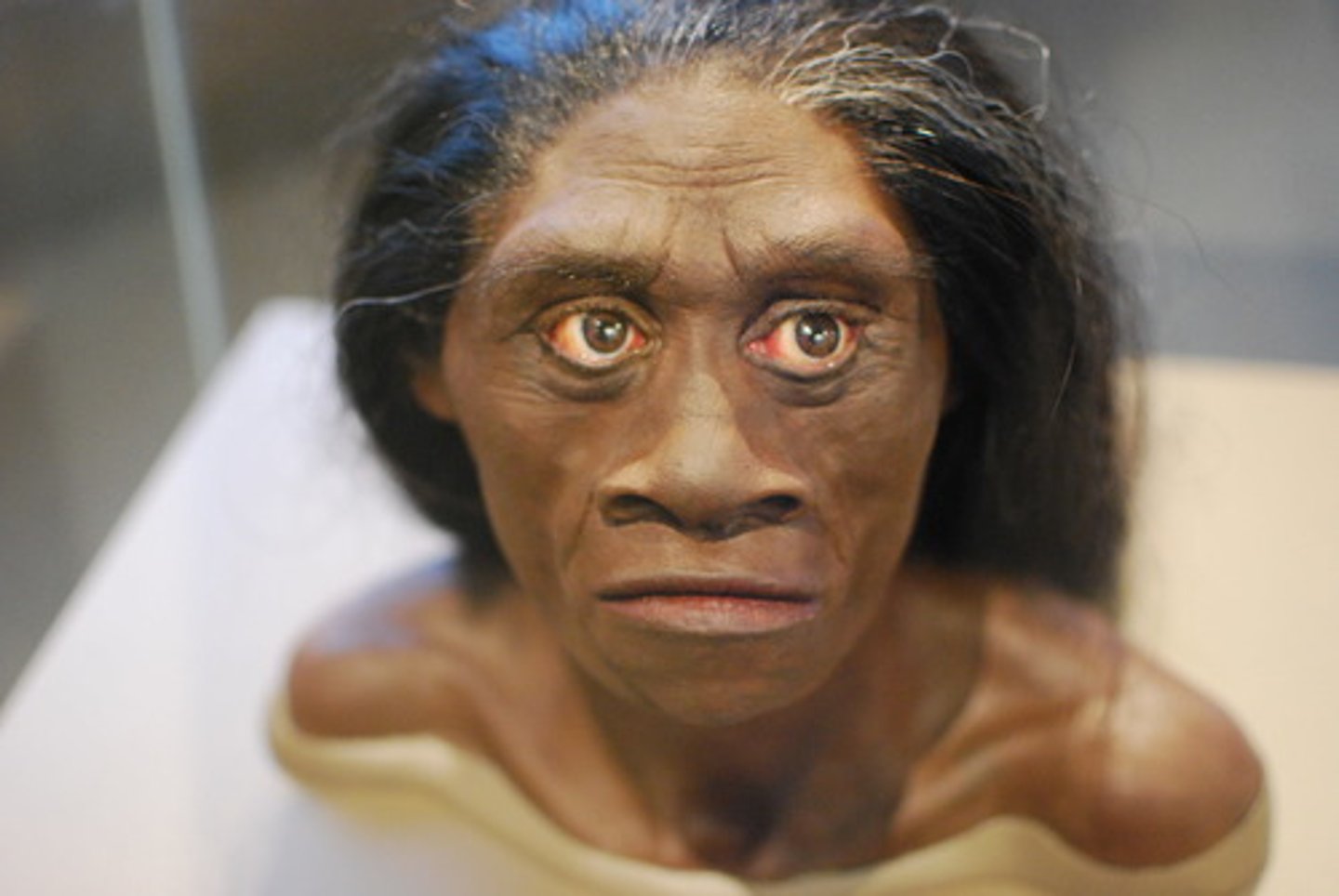
Homo Floresiensis
Flores Island Indonesia. 95-13KYA. Small body/brain. Primative and derived traits

Homo Sapiens
300KYA in Africa, 150KYA Asia/Middle East. 50KYA in Europe, used fire, cultural remains, complex tools
Multiregional Hypothesis
No wave of sapiens replacement. Erectus is most recent, neanderthal contributed to the gene pool
vs. Replacement Hypothesis
When erectus was here, humans were not
Denisova Hominin
Cave in Russia, found a tooth + finger not fossilized, not human nor neanderthal, 390KYA. lived and interbred in asia
Denisovan finger
13 year old girl would had a neanderthal mother and a denisovan father. Gene flow could have led to immunity against pathogens
White bundle
pale skin, straight/wavy hair, thin nose, medium/tall stature
Black bundle
black/brown skin, wirey hair, thick nose, medium stature
Methods of Forensic Anthropologists
Measure AGE, STATURE, SEX, PATHOLOGY(TRUAMA)
Forensic Method of Age
Ossification of bone
Forensic Method of Sex
Pelvis size/angle
Forensic Method of Stature
Long bones and humorous length, males have longer humorous
Forensic Method of Trauma (Pathology)
Pre-mortem: Some disease affect your bones (syphillis)
Peri-mortem: location, size, and weapon
Post mortem: contaminated scene, decomposers