Origin and Evolution of Life on Earth
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
Earth Formation
Earth formed 4.6 billion years ago from cosmic materials.
Prokaryotic Life
First life forms, including Archaebacteria and Eubacteria.
Anaerobic Environments
Habitats lacking oxygen where early life thrived.
Oxygen Revolution
Cyanobacteria produced oxygen through photosynthesis.
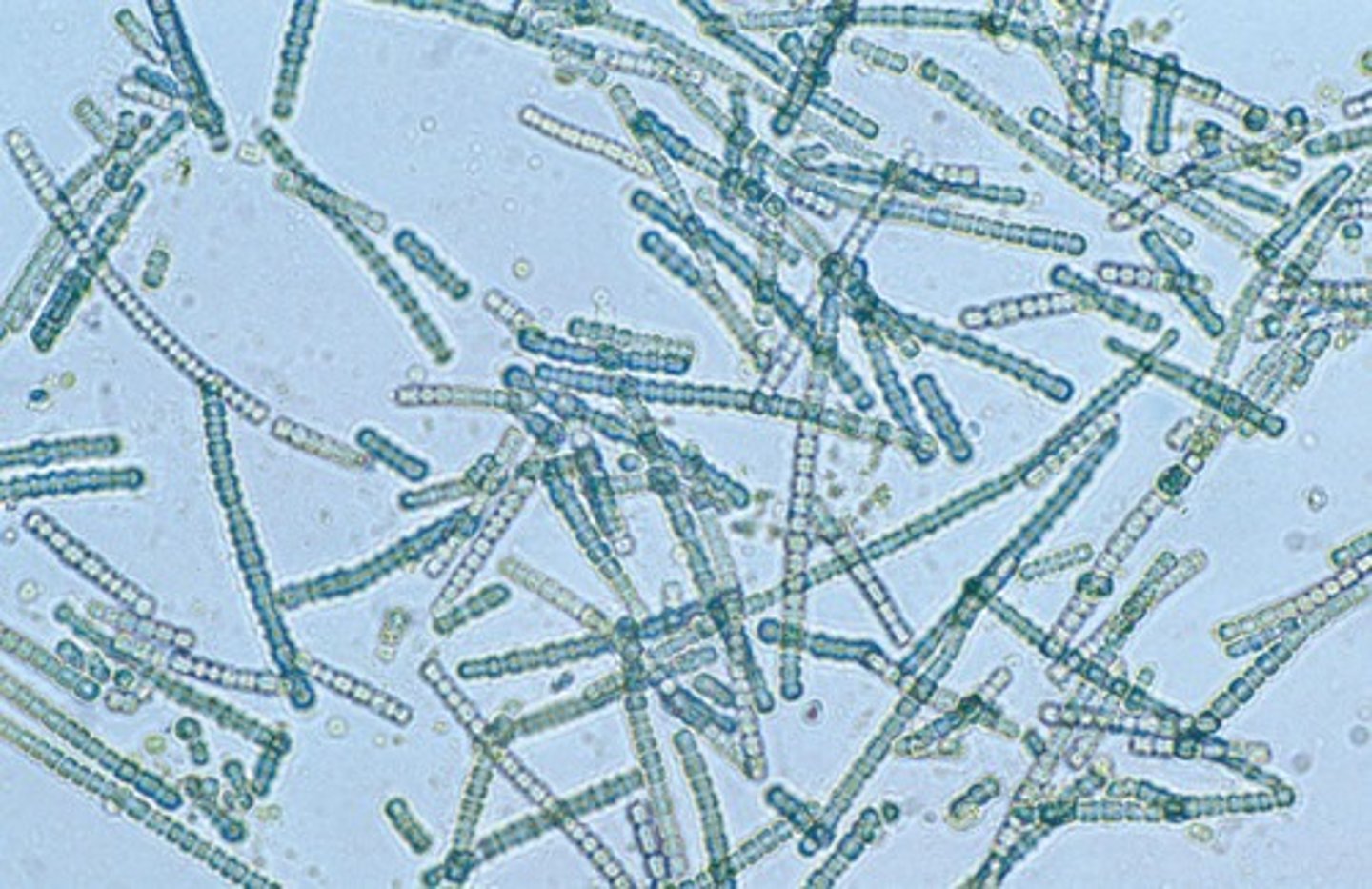

Eukaryotic Life
Complex cells emerged 2 billion years ago.
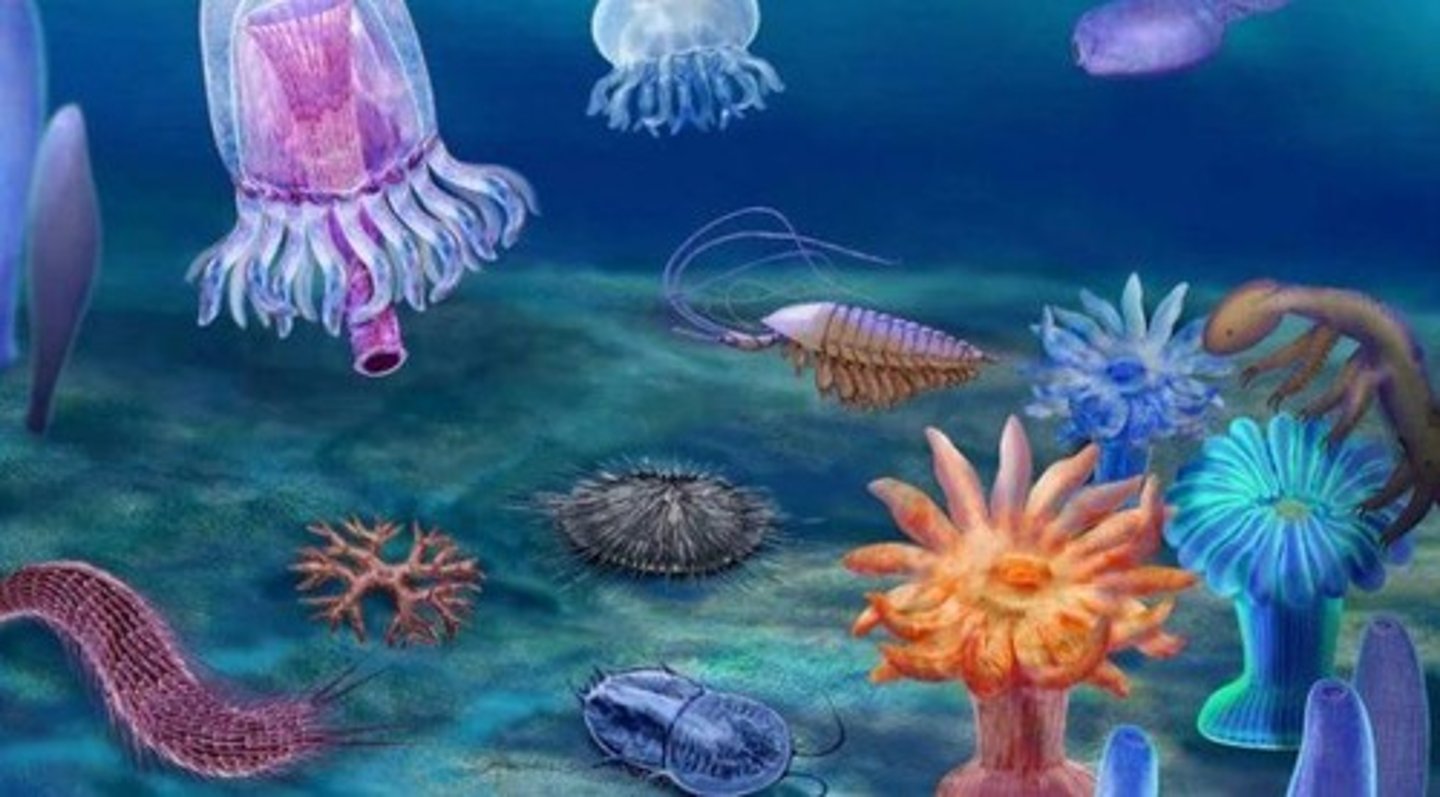
Cambrian Explosion
Major animal groups appeared 541 million years ago.

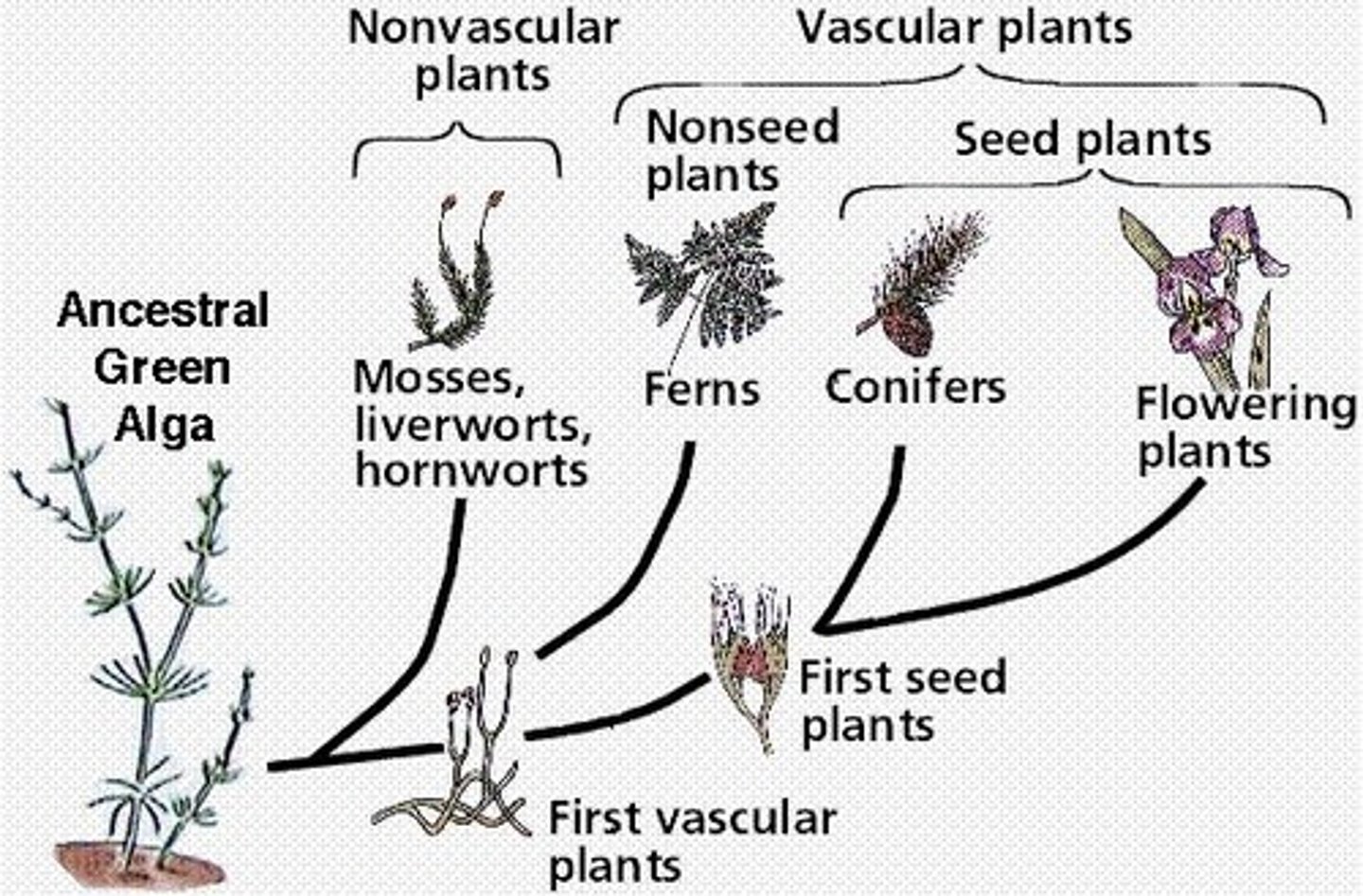
Vascular Plants
Plants adapted to land, enabling terrestrial ecosystems.
Arthropods
Invertebrates that adapted to land environments.
Tetrapods
Four-limbed vertebrates transitioning from sea to land.
Dinosaurs Emergence
Dinosaurs appeared around 230 million years ago.
Early Mammals
Mammals began to rise 66 million years ago.
Hominid Development
Evolution of human ancestors 4 to 2 million years ago.
Anthropocene Epoch
Current geological epoch marked by human impact.
Geologic Time Scale
Calendar of Earth's history events and periods.
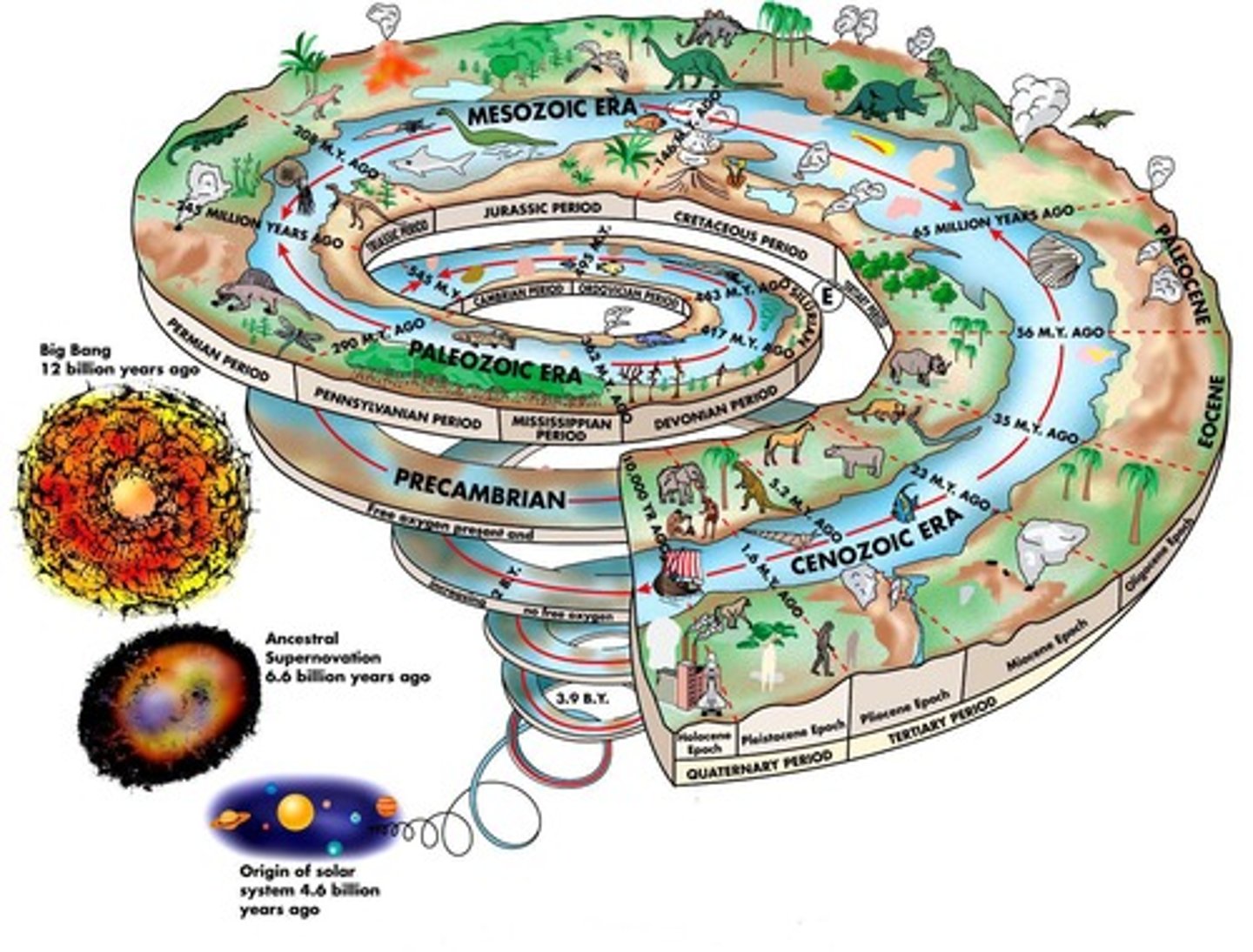
Pre-Cambrian Eons
Longest eon, covering most of Earth's history.
Phanerozoic Eon
Recent eon divided into Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic.
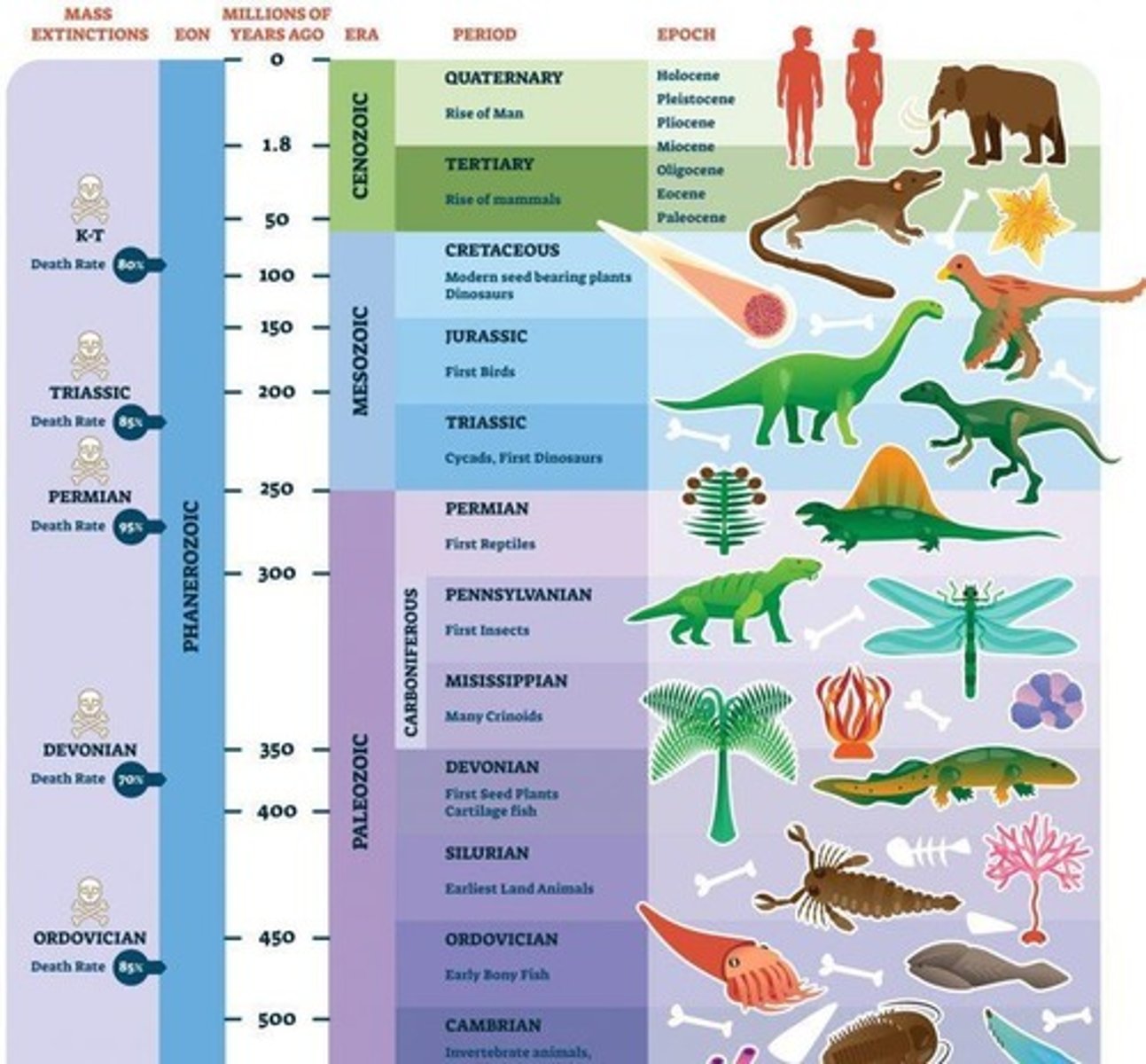
Paleozoic Era
Era of ancient life, 541 to 252 million years ago.
Mesozoic Era
Era of middle life, 252 to 66 million years ago.
Cenozoic Era
Era of recent life, 66 million years ago to present.
Cambrian Period
Known for the Cambrian Explosion of life.
Ordovician Period
Diverse marine life and first vertebrates evolved.
Devonian Period
Age of Fish; first amphibians and trees appeared.
Permian Period
Evolution of reptiles; ended with largest extinction.
Triassic Period
Early dinosaurs and first mammals appeared.
Jurassic Period
Dominance of dinosaurs and first birds evolved.
Cretaceous Period
Diversification of dinosaurs; ended with mass extinction.
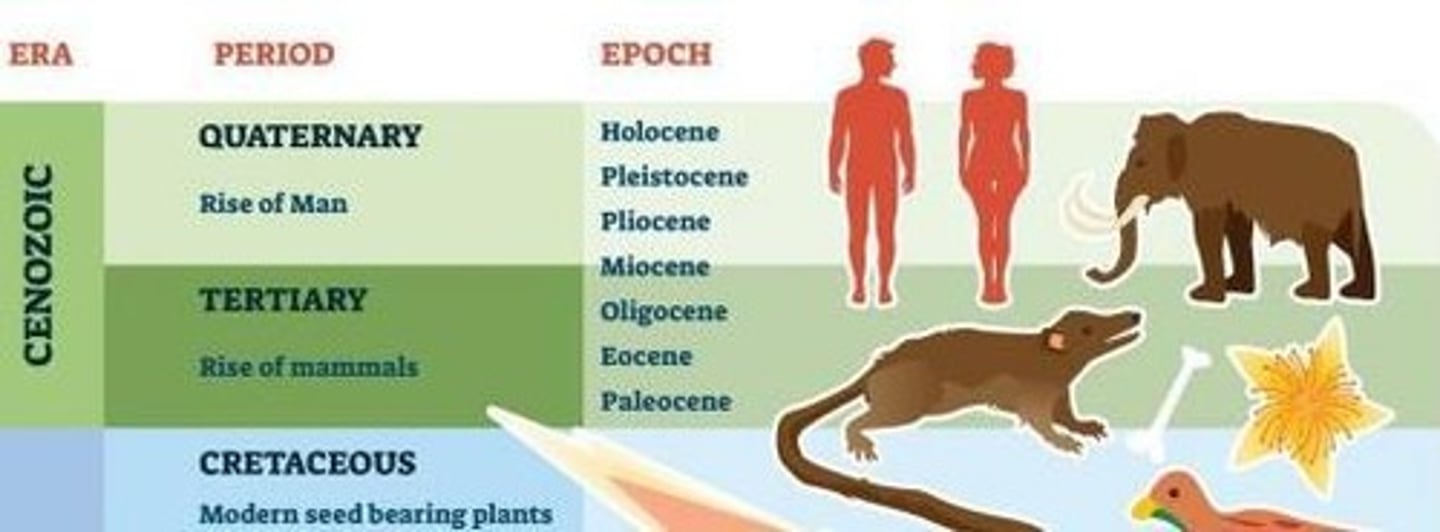
Paleogene Period
Mammals diversified; early primates set stage for humans.
Neogene Period
Evolution of hominids and grazing mammals.
Quaternary Period
Lasts from 2.58 million years ago to present.
Homo sapiens
Modern humans, dominant species on Earth.
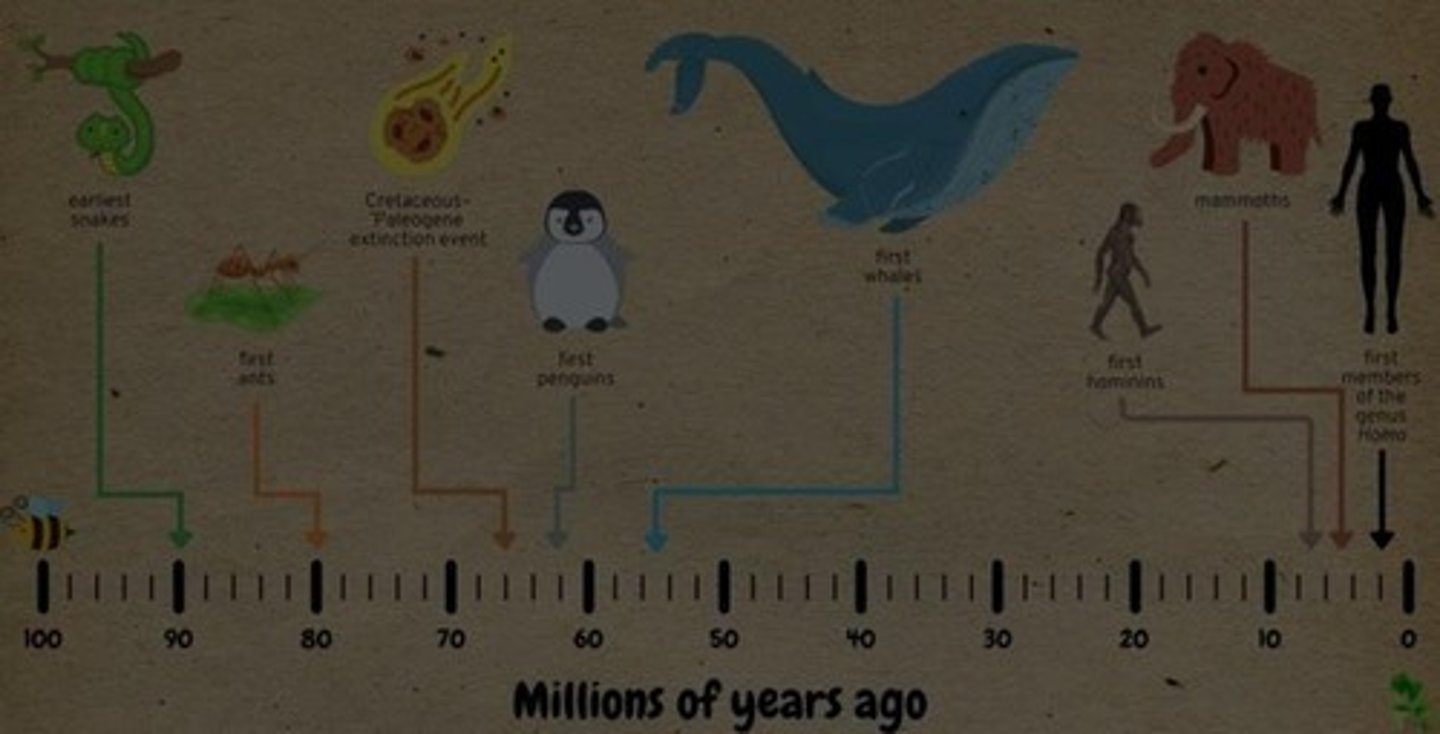

Continental Drift
Movement of continents affecting climate and species.
Abiogenesis
Life emerged from non-living matter through reactions.
RNA World Hypothesis
Replicating RNA crucial for early life stages.
Panspermia
Life may have originated from outside Earth.
Photosynthetic Autotrophs
Organisms producing energy through photosynthesis.
Plant Characteristics
Multicellular eukaryotes with cellulose cell walls.
Mosses
Small, non-vascular plants reproducing via spores.
Ferns
Large, vascular plants with feathery leaves.
Gymnosperms
Seeds exposed on cone scales, not fruits.
Angiosperms
Produce flowers and seeds within fruits.
Animal Characteristics
Multicellular eukaryotes, heterotrophic, lacking cell walls.
Porifera
Simple, porous animals like sponges.
Cnidaria
Radially symmetrical animals like jellyfish.
Platyhelminthes
Flatworms, often parasitic or free-living.
Nematoda
Roundworms, diverse in habitats.
Annelida
Segmented worms like earthworms.
Arthropoda
Invertebrates with exoskeletons, jointed limbs.
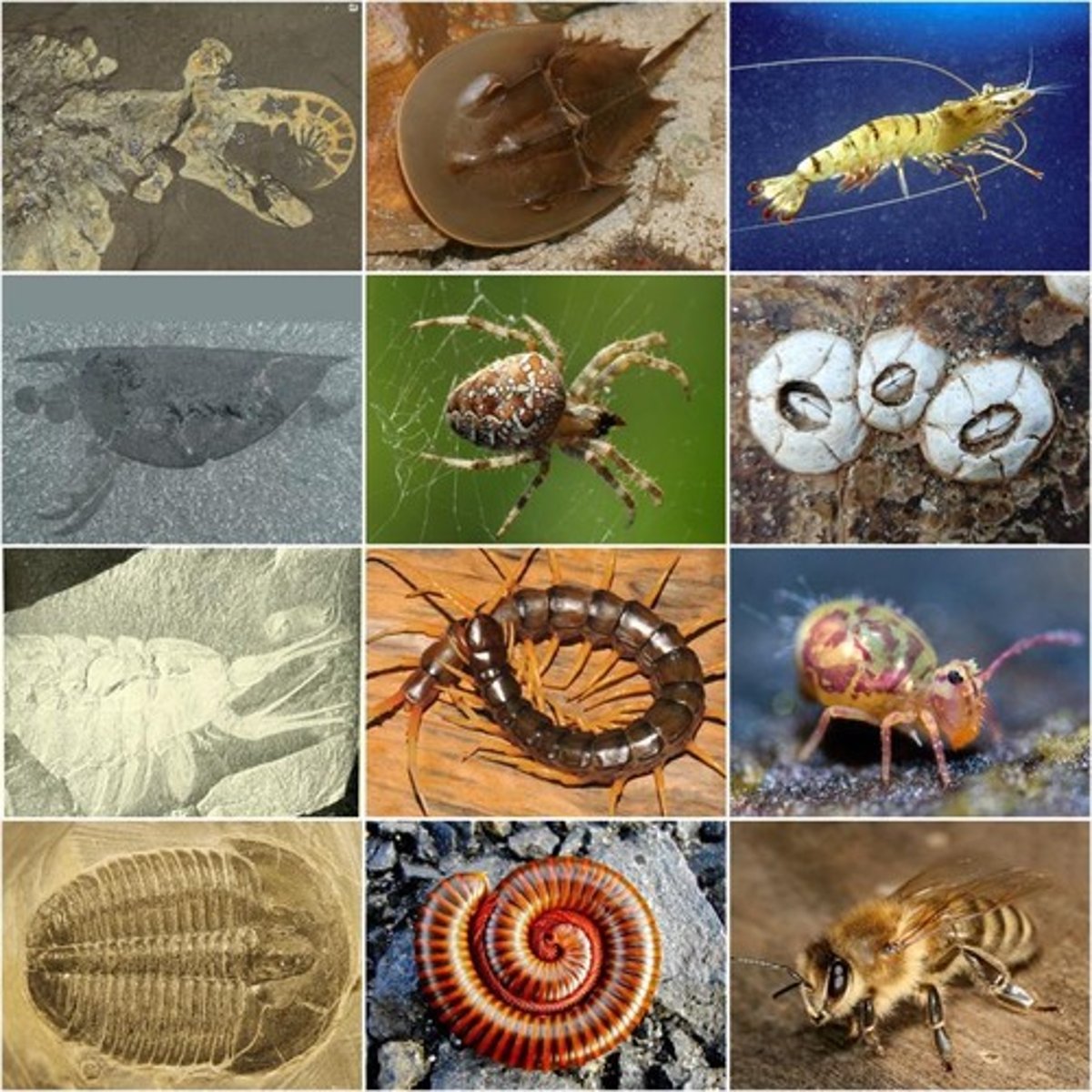

Mollusca
Soft-bodied animals, often with shells.
Echinodermata
Marine animals with radial symmetry, like starfish.
Chordata
Animals with a notochord, including vertebrates.
Microorganism Characteristics
Unicellular or simple multicellular organisms.
Bacteria
Prokaryotic cells crucial for nutrient cycling.
Fungi
Eukaryotic decomposers forming symbiotic relationships.
Viruses
Non-living entities requiring host cells for reproduction.
Protists
Eukaryotic, mostly unicellular organisms like algae.
Natural Selection
Survival of traits enhancing fitness in populations.
Artificial Selection
Humans breed individuals for desired traits.
Giraffe Neck Length
Longer necks favored for accessing food.
Peppered Moths
Dark moths favored for camouflage during Industrial Revolution.
Natural Selection
Process where organisms better adapted survive.
Peppered Moths
Dark moths thrived due to soot camouflage.
Selective Breeding
Intentional mating for specific characteristics.
Dog Breeds
Humans select traits like size and color.
Genetic Drift
Random allele frequency changes in populations.
Founder Effect
New population starts from a small group.
Bottleneck Events
Population size drastically reduced by catastrophe.
Mutation
Heritable DNA sequence change in organisms.
Antibiotic Resistance
Bacterial mutations confer survival against antibiotics.
Evolutionary Relationships
Patterns of ancestry among different species.
Molecular Data
Information from DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Protein Sequences
Reflect genetic changes over evolutionary time.
Homologous Structures
Anatomical features from a common ancestor.
Analogous Structures
Similar functions without common evolutionary origin.
Fossils
Preserved remains providing evidence of ancient life.
Developmental Characteristics
Traits used for categorizing organisms in taxonomy.
Embryonic Development
Early vertebrate embryos share similar appearances.
Metamorphosis
Life cycle changes in butterflies and moths.
Mendelian Genetics
Study of inheritance patterns in traits.
Sex-Linked Traits
Traits associated with genes on sex chromosomes.
Pedigree Analysis
Charting family traits to understand inheritance.
Colorblindness
X-linked recessive trait affecting vision.
Carrier
Individual with one recessive allele, not expressed.
Hemophilia
X-linked recessive disorder affecting blood clotting.
Hypophosphatemic Rickets
X-linked dominant condition causing phosphate deficiency.
Webbed Toes
Recessive trait causing webbing in frog toes.
Genotypic Ratio
Proportion of different genotypes in offspring.
Phenotypic Ratio
Proportion of different phenotypes in offspring.
Dominant Trait
Trait that masks the expression of another.
Recessive Trait
Trait that is masked by a dominant trait.
P Generation
Parental generation in Mendelian experiments.
F1 Generation
First generation of offspring from P generation.
F2 Generation
Second generation from self-pollination of F1.
Self-Pollination
Process where a plant fertilizes itself.
True Breeding
Plants that consistently produce the same trait.
Mendel's Law of Dominance
Dominant traits mask recessive traits in offspring.
Tongue Rolling
Dominant trait for rolling the tongue.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait.
Autosomal Trait
Trait not linked to sex chromosomes.
X-linked Trait
Trait associated with genes on the X chromosome.
Probability of Offspring
Likelihood of specific traits in offspring.