DP chem SL everything
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
mixture
a combination of pure substances that retain their individual properties
example of a heterogenous mixture
soil, blood, sand and water, oil and salt etc
example of a homogenous mixture
rain, air, saltwater, steel, brass, coffee etc.
crystallisation
used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution, when the solid is more soluble in hot solvent than in cold (e.g. copper sulphate from a solution of copper (II) sulphate in water)
based on their ease of evaporation
recrystallisation
used to purify impure solids
simple distillation
used to separate a liquid and soluble solid from a solution (e.g. water from a solution of saltwater) or a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids
fractional distillation
separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another (e.g. ethanol and water from a mixture of the two)
paper chromotography
separate substances that have different solubilities in a given solvent
solids
fixed volume and shape
they have a high density
atoms vibrate in position but can’t change location
particles are packed very closely together in a fixed and regular pattern
liquids
fixed volume but adopt the shape of the container
generally less dense than solids, but much denser than gases
particles move and slide past each other which is why liquids adopt the shape of the container and also why they are able to flow freely
gases
do not have a fixed volume
take up the shape of the container (fill the whole container)
very low density
can be compressed into a much smaller volume
particles are far apart and move randomly and quickly in all directions
particles collide with each other and with the sides of the container
change of states graph
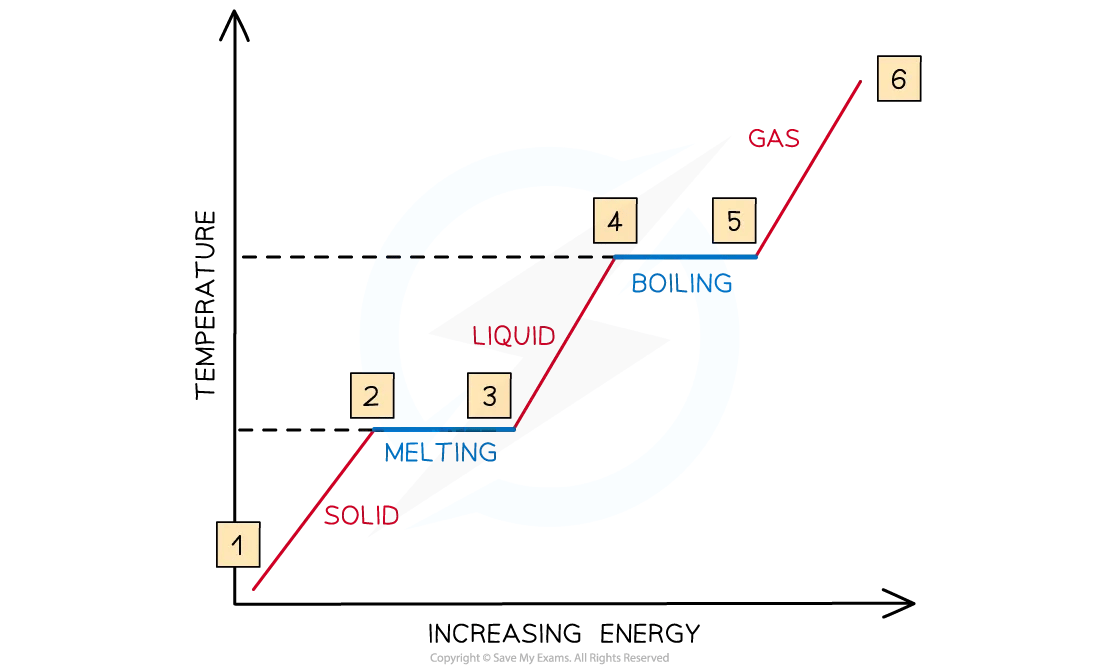
1&2 = particles are vibrating and gaining kinetic energy + temperature rises
2&3 = all the energy goes into breaking bonds; no increase in kinetic energy or temperature
3&4 = particles are moving around and gaining kinetic energy
4&5 = substance is boiling; bonds are breaking; there is no increase in kinetic energy or temperature
5&6 = particles are moving around rapidly and increasing in kinetic energy

isotopes
different atoms of the same element with the same number of protons + electrons but a different number of neutrons
relative atomic mass
average mass of one atom of an element compared to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
total mass of 100 atoms = (% abundanceA x massA) + (% abundanceB x massB)
electromagnetic spectrum
range of frequencies that covers all electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and energy
shows the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy
frequency = how many waves pass per second
wavelength = distance between two consecutive peaks on the wave
frequency is … to wavelength
inversely proportional
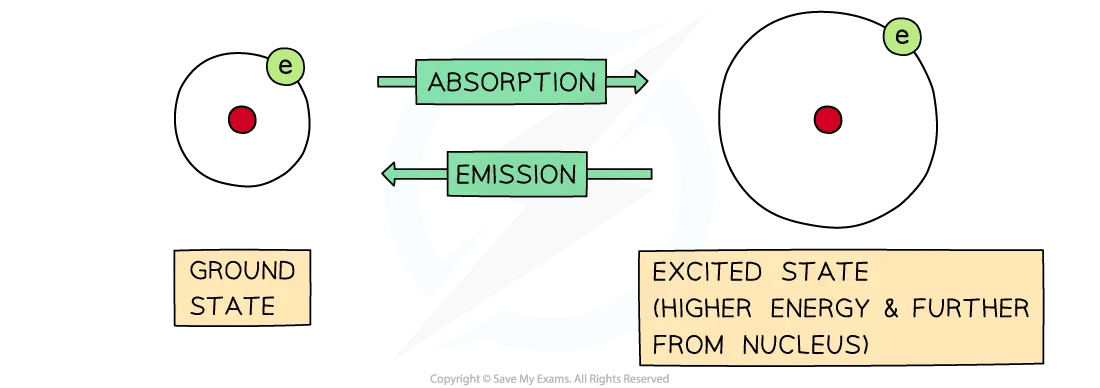
emission spectra
produced when an atom moves from a higher to a lower energy level
energy emitted is a mixture of different frequencies
principal quantum numbers (n)
used to number the energy levels or quantum shells
the lower the principal quantum number, the closer the shell is to the nucleus
mathematical relationship between the number of electrons and the principal energy level is 2n2
ground state
most stable electronic configuration of an atom which has the lowest amount of energy
achieved by filling the subshells of energy with the lowest energy first
atomic orbital
region around an atomic nucleus where there is a 90% chance of finding the electron
shape depends on electron’s energy
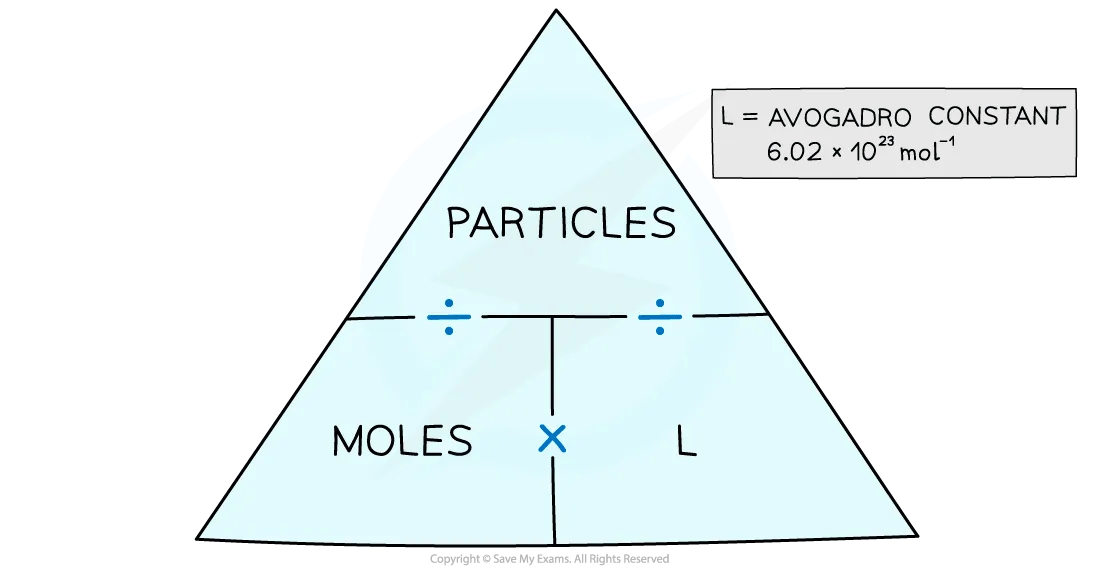
avogadro constant
6.02 x 1023 mol-1
mole (mol)
SI unit of amount of substance
moles/particles triangle

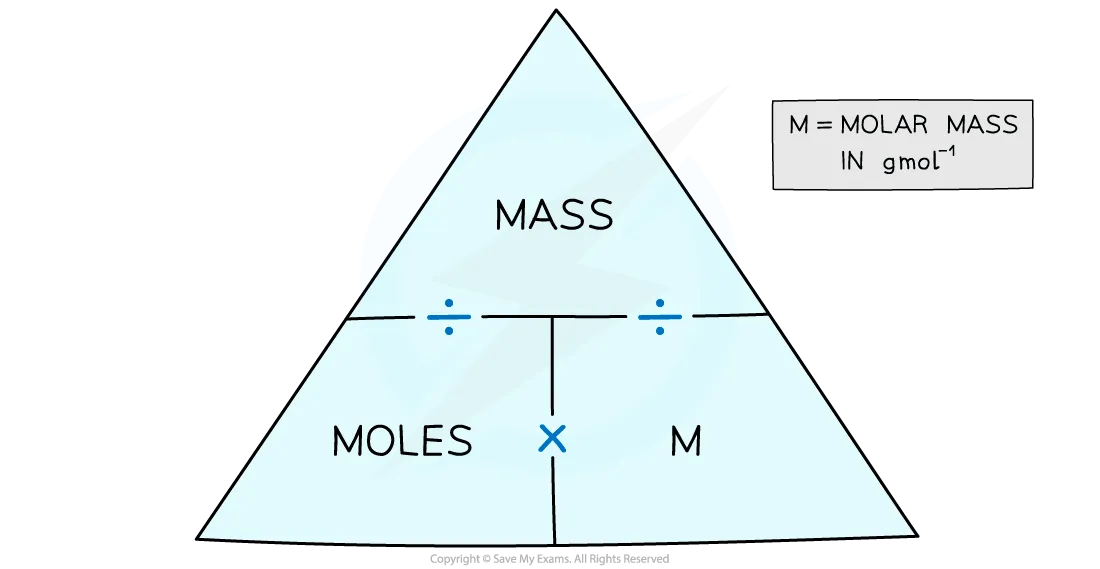
moles/mass triangle

molecular formula
shows the actual number and type of each atom in a molecule
(mass of empirical formula)x
empirical formula
simplest whole number ratio of the elements in a compound
molar concentration
amount of solute per volume, given in mol dm-3
moles/concentration triangle
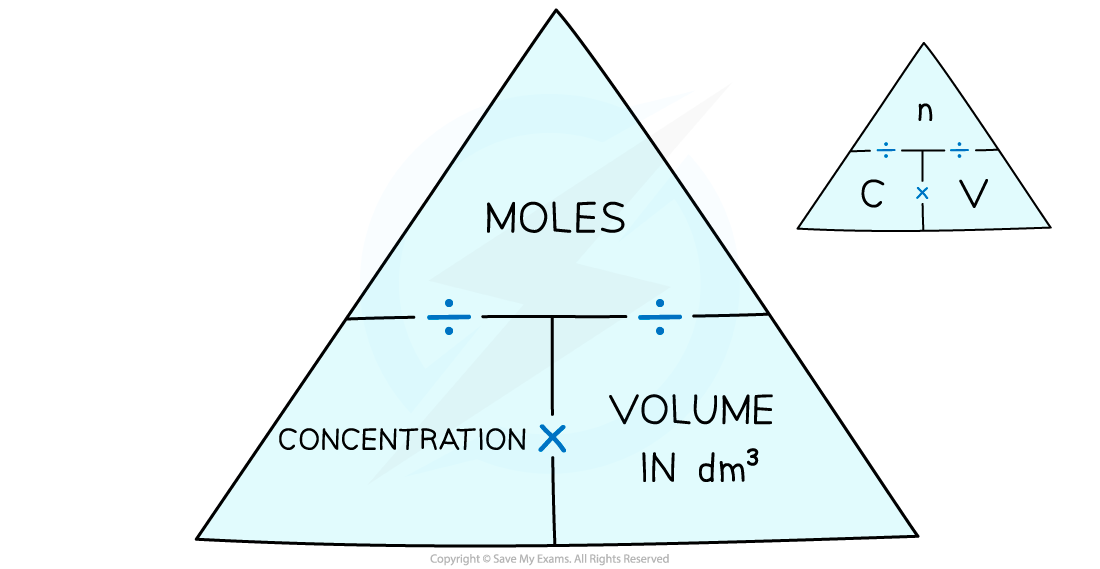
standard solution
solution of known concentration
ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy
uses direct relationship between concentration of solution and its absorbance
absorbance is measured → results plotted in a calibration curve
avogadro’s law
equal volumes of all gases, when measured at the same temperature and pressure, contain an equal number of particles
ideal gases
negligible volume
no intermolecular forces between particles
gas particles have range of speeds and move randomly; average kinetic energy is proportional to temperature
collisions are elastic; kinetic energy is conserved
gases in a container exert … as the gas molecules are constantly … with the walls of the container
pressure … colliding
pressure is … to volume
inversely proportional


volume is … to temperature
directly proportional
temperature is … to pressure
directly proportional
constant relationships in gases
PV = a constant
V / T = a constant
P / T = a constant
ideal gas equations
PV = nRT
P = pressure (pascals, Pa)
V = volume (m3)
n = number of moles of gas (mol)
R = gas constant (8.31 J K-1 mol-1)
T = temperature (Kelvin, K)
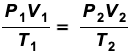
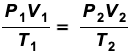
real gases
volume is not negligible
collisions more frequent than predicted
pressure is greater
forces between particles are present
reduces speed of colliding particles
pressure is lower
density
mass/volume
if volume of gas particles is not negligible…
PV/nRT > 1
if attractive forces between particles are present…
PV/nRT < 1
ionic bonds
transfer of electrons (between metal + non metal)
pulled together by electrostatic attraction
attraction is very strong and requires a lot of energy to overcome
metals have … ionization energies
low; positive ions
non-metals have … ionization energies
high; negative ions
polyatomic ions
more than one ion which together lost or gained an electron
covalent bonding
eg. NH4+
why are noble gases unreactive?
high ionization energies
stable electron shells (full)
lattice enthalpy
strength of ionic bond
the … the ionic charge, the … the attraction between ions, the … the lattice enthalpy
higher … higher … higher
the … the ionic radius, the … the attraction between ions, the … the lattice enthalpy
higher … lower … lower
ionic compounds
high MP
high BP
low volatility
solid at room temperature
soluble in water, insoluble in non-polar
conduct electricity only when molten
generally brittle
% ionic character
difference in electronegativity/3.2
covalent bond
sharing of electrons
electrostatic attraction between shared pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei
forms a molecule
… and … are exceptions to the octet rule
Boron and Beryllium
(to Be or not to B)
the … the atomic radius, the … the bond length
larger … longer
the … the bond length, the … the bonds
shorter … stronger
coordination bond
covalent bond in which both shared electrons originate from the same atom
eg. CO
VESPR model
valense shell electron pair repulsion
electron domains
electron pair
double/triple bonds are 1 ED
EDG vs MG
electron domain geometry = positions of all EDs
molecular geometry = positions of bonded EDs
2 EDs
180˚
linear shape
3 EDs
EDG
120˚
triangular planar
MG
2 bonded, 1 lone = 117˚, bent/v-shaped
4 EDs
EDG
109.5˚
tetrahedral
MG
3 bonded, 1 lone = 107˚, trigonal pyramidal
2 bonded, 2 lone = 104.5˚, bent/v-shaped
electronegativity
measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
the … the electronegativity, the … the pull on electrons
higher … higher = polar
bond dipole
bond with 2 partially separated electric charges
more electronegative = delta -
less electronegative = delta +
the … the electronegativity, the … the bond polarity
higher … higher
net dipole
dipoles do not cancel each other out
carbon allotropes
diamond; C bonded to 4 other Cs
graphite; C bonded to 3 other Cs, layers held by weak london forces
graphene; single layer of graphite
C60; fullerene, sphere of 60 Cs
SiO2
silica or SAND!!!!!!!!!
london dispersion forces
opposite ends of temporary dipoles
weakest forces of attraction
increased strength with increased molecular size
only forces between non-polar
dipole-dipole
opposite ends of permanent dipoles
stronger than london
dipole-induced dipole
permanent dipole creates a temporary dipole
hydrogen bonding
strongest type of bonding
only when H bonds to F, N, or O
large electronegativity difference
Rf
distance moved by component / distance moved by solvent
metallic character
loss of control over outer shell electrons
metallic bond
electrostatic attraction between a lattice of cations and delocalized electrons
metal properties
good electrical conductivity
good thermal conductivity
malleable
ductile
high MP
shiny, lustrous appearance
alloys
homogenous mixtures containing at least one metal, and held together by metallic bonding
presence of atoms of different sizes disrupts regular structure + prevents atoms from slipping across each other
atom economy
molar mass of desired product/molar mass of all reactants x 100%
effective nuclear charge
attraction of nucleus to outer electrons
the … the effective nuclear charge, the … the attraction between outer electrons + nucleus
higher … higher
ionic radii … down a group as the number of electron energy levels …
increase … increases
first ionization energy
measure of attraction between nucleus and outer electrons
energy required to remove 1 mole of gaseous atoms in the ground state
electron affinity
energy change when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mole of gaseous atoms)
chemical properties are determined by …
the number of valence electrons in their outer energy level
different types of oxides
oxides of metals = ionic + basic
oxides of non-metals = covalent + acidic (ACID RAIN!)
amphoteric oxides = both acidic + basic
SO2 acid rain

NO acid rain
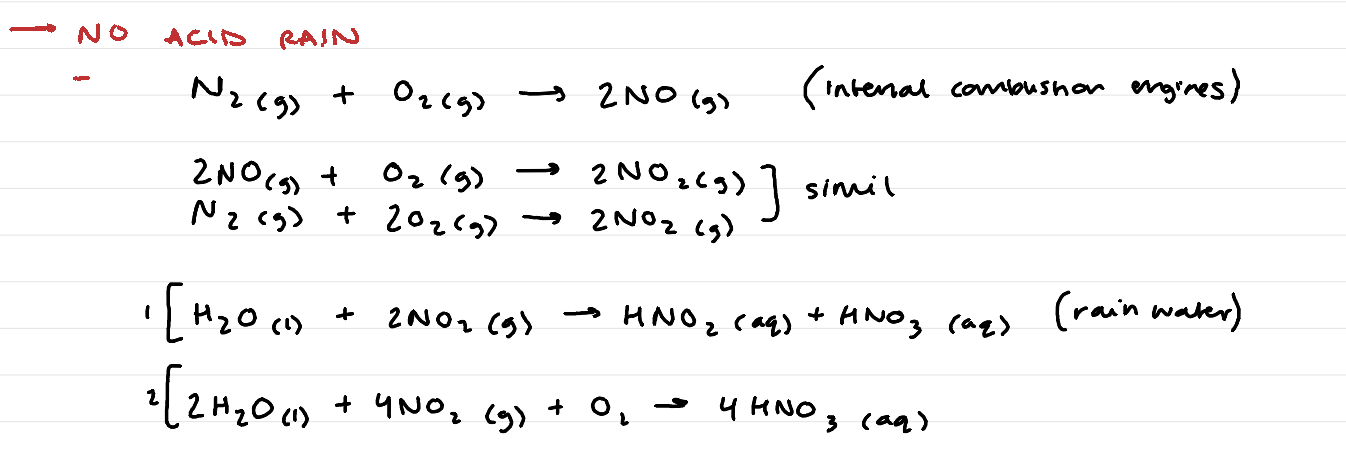
ocean acidification

oxidation state
the charge the atom would have if the compound was composed of ions
functional groups
atoms/groups of atoms present in organic compounds responsible for a compounds physical properties and chemical reactivity
same functional group = same …
class
alkane
-ane
alkene
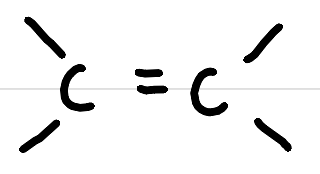
alkenyl
-ene
alkyne

alkynyl
-yne
alcohol
-OH
hydroxyl
-anol
ether

alkoxy
-oxyalkane
aldehyde
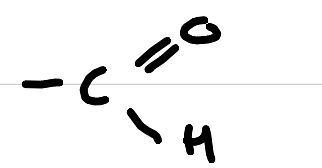
carbonyl (aldehyde)
-anal
ketone

carbonyl (ketone)
-anone
carboxylic acid
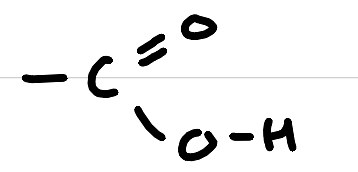
carboxyl (acid)
-anoic acid