2.4-2.9 AP HuGe
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms

demographic balancing equation
a simple equation used to describe the future population of a region of any scale
immigrants
people moving into a country
emigrants
people moving out of a country
crude birth rate
number of live births per year for every 1000 people
total fertility rate
average number of children born per woman in childbearing years in a country
(number) the replacement rate for a stable population
2.1
life expectancy
the average number of years people live
infant mortality rate
number of children, born alive, die before their first birthday per 1,000 births
crude death rate
deaths a year per 1,000 people
rate of natural increase
the percentage at which a country’s population is growing or declining, without the impact of migration
population doubling time
the time it takes for a population to double in size, estimated with an equation known as the rule of 70
rule of 70 (sometimes 72)
70/growth rate per year (sometimes 72)
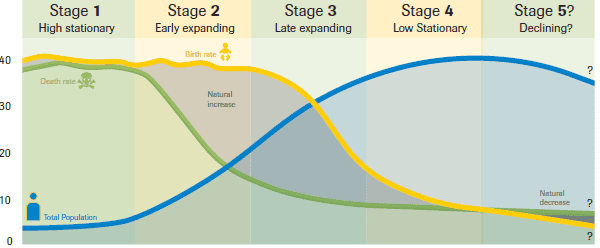
demographic transition model
a model showing 5 typical stages of population change that countries experience as they modernize
demographic momentum
even though fertility has declined, people are living longer, resulting in population growth for the next 20-40 years
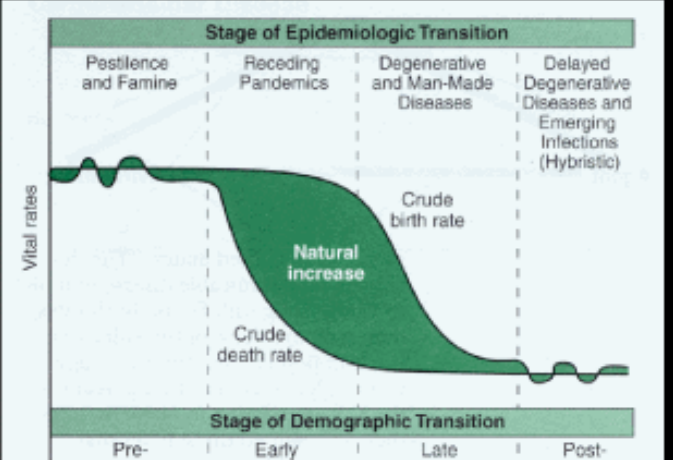
epidemiological transition model
an extension of the demographic transition model showing death rates and common causes of death within societies.

Malthusian theory
the theory that population will outgrow natural resources, specifically food, leading to widespread starvation.

Boserup theory
the theory that the more people there are, the more hands there are to work, rather than the more mouths to feed.
neo-Malthusians
modern believers of the Malthusian theory who argue that population growth is a great threat.
antinatalist policies
policies aiming to decrease the number of births in a country
pronatalist policies
policies aiming to increase the number of births in a country
dependency ratio
compares the amount of people in the nonworking parts of the population to the amount of people in the working parts
dependent population
people in society under 15 or over 64, who don’t tend to participate in the labor force