Chapter 12: Statement of Cash Flows
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/61
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
statement of cash flows
The ________ is able to show business activities that make the company’s cash increase or decrease.
2
New cards
cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash
Cash in the statement of cash flows includes:
3
New cards
Cash equivalents
________ are short term, liquid investments purchased within three months of maturity.
4
New cards
does not change near maturity
Cash equivalents are convertible to amounts of cash and the value of them ________.
5
New cards
Restricted cash
________ must legally be set aside and is not used for day to day operations.
6
New cards
operating, investing, and financing
Cash inflows and outflows correlate to ________ activities.
7
New cards
positive
Cash inflows will be a _________ number.
8
New cards
negative
Cash outflows will be a ________ number.
9
New cards
Revenues and expenses
_________ on the income statement are the result of operating activities.
10
New cards
Operating activities
_________ are day to day activities related to running a business.
11
New cards
examples of operating activities
Collecting money, receiving dividends, and receiving interest are ________.
12
New cards
Net Cash Provided by (used for) Operating Activities
The difference between inflows and outflows are the subtotal of the financial statement (operating) , which is called ________.
13
New cards
current assets and liabilities
Operating activities cause changes in ________.
14
New cards
investments
The purchase and disposal of investments and long lived assets are the result of cash flows from ________.
15
New cards
examples of investing activities
The sale/disposal of equipment and sale/maturity of investments in securities are ________.
16
New cards
Net Cash Provided by (used by) Investing Activities
The difference between inflows and outflows is the subtotal of the financial statement (investing), which is called ________.
17
New cards
financing activities
The exchange of cash with stockholders and cash exchanges with lenders results in cash flows from ________.
18
New cards
examples of financing activities
Borrowing from lenders through formal debt contracts and issuing stock to owners are both ________.
19
New cards
Net Cash Provided by (used in) Financing Activities
The difference between inflows and outflows is the subtotal of the financial statement (financing).
20
New cards
non-current liabilities or stockholders’ equity
Financing activities cause changes in ________ accounts.
21
New cards
comparative balance sheets
The statement of cash flows use _________, which uses the beginning and ending balances to calculate the cash flows from activities.
22
New cards
complete income statements
The statement of cash flows uses ________ to help calculate cash flows for operating activities.
23
New cards
Additional data
________ is used in the statement of cash flows to show the affects of investing and financing activities.
24
New cards
non-cash
Assets are split into cash and ________ assets.
25
New cards
Change in cash = Change in (Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity - Non cash Assets)
In this statement, the basic accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity) is split to create the equation _______. The change in cash between the beginning and end of the year must be equal to the right side.
26
New cards

\
Equation to calculate the change in balance sheet accounts:
27
New cards
determine the change in each balance sheet account
The first step to the create the statement is to ________.
28
New cards
identify the cash flows category to which each account relates
The second step to create the statement is to ________.
29
New cards
summarize operating, investing, and financing activities
The last step to creating the statement is to make schedules that ________.
30
New cards
Direct method and Indirect method
The two types of reports for operating cash flows:
31
New cards
direct method
The ________ reports the total cash inflow or outflows from each major transaction.
32
New cards
indirect method
The ________ eliminates the effects of items that don’t involve cash and includes items that do have cash effects.
33
New cards
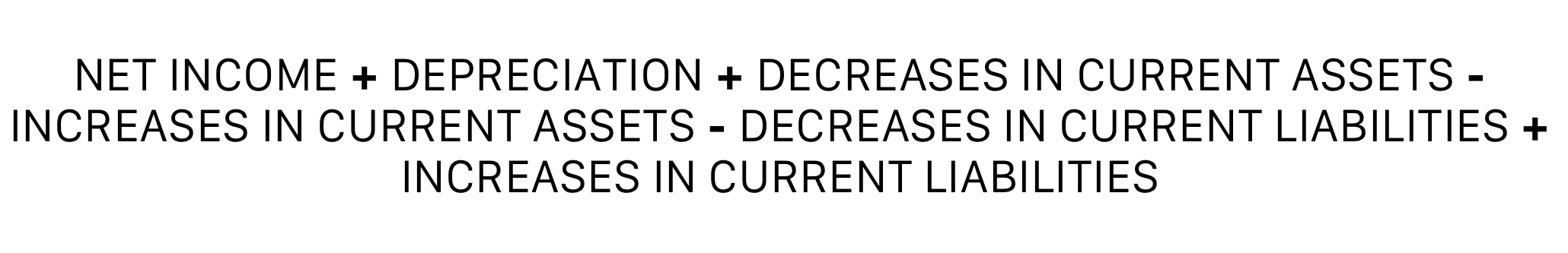
\
Equation to calculate net cash flow provided (used in) operating activities:
34
New cards
Cash
________ is found at the bottom of the Statement of Cash Flows.
35
New cards
Net income
________ is changed into operating cash flows.
36
New cards
Accounts Receivable
An increase in ________ indicates sales on accounts were less than the collection of cash from customers while a decrease means sales on account were more than the collection of cash.
37
New cards
Cash prepayments
________ increase prepaid expenses.
38
New cards
expenses
Recording ________ decreases prepaid expenses.
39
New cards
on account
Accounts Payable is increased by purchases _______.
40
New cards
suppliers
Accounts Payable is decreased when payments are made to the _______.
41
New cards
Accrued expenses
________ increases Accrued Liabilities.
42
New cards
Payment of expenses
________ decreases Accrued Liabilities.
43
New cards
long lived tangible and intangible assets
The investing activities section of this statement correlates to ________.
44
New cards
Purchases
________ for property or equipment are considered increases.
45
New cards
\
Disposals
Disposals
________ of property or equipment are considered decreases.
46
New cards
net cash from investing activities
Add together the purchases of tangible assets to calculate ________.
47
New cards
Intangible assets
________ are effected by disposals, impairments, and amortization.
48
New cards
owners
Dividends Payable goes to ________.
49
New cards
financial institutions
Notes Payable goes to ________.
50
New cards
financing activity section
Notes Payable, Bonds Payable, Common Stock, Retained Earnings, and Treasury Stock are examples of accounts found in the ________.
51
New cards
reported separately
Cash inflows and outflows are ________.
52
New cards
Net change
________ is combined with the initial cash balance to get the ending cash balance.
53
New cards
balance sheet
The ending cash balance must be the same as the amount found on the ________.
54
New cards
Non-cash investing and financing activities
_________ include material investing and financing transaction that didn’t have an effect on cash flows.
55
New cards
introductory phase
During the __________, a company is in the process of being established. The company has negative net operating cash flows and negative investing cash flows.
56
New cards
growth phase
The ________ indicates the evolution of the company. It has positive operating cash flows.
57
New cards
maturity phase
At the _________, the company stabilizes. It has positive operating cash flows and is no longer expanding.
58
New cards
decline phase
In the _________ (last phase), the company falls out. It has negative operating and financing cash flows, but positive investing cash flows.
59
New cards
Seasonality
_________ means sales are occurring more during specific points of the years. It is one cause of deviation.
60
New cards
corporate life cycle
The _________ (aka growth in sales), is the rapid sales of new companies. This is a cause of deviation and results in negative operating cash flows.
61
New cards
change in revenues and expenses recognition
The __________ says that revenues must be recorded before providing a service and expense reports are delayed. They both increase net income and there is no affect on operating activities.
62
New cards
Changes in working capital management
_________ measures to see if current assets exceed current liabilities. If current assets grow, operating cash flows are reduced.