Brain Bio Test
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Neurons and what connects to them
Neurons fire action potential
A brief electric charge that travels down the axon
Neurons have a cell body with dendrites
The axon connects the dendrite with the terminal axon branches
At the end of the terminal branches there are synapses
They are meeting points between neuron
These send signals to other neuron
Myelin Sheath covers the axon to increase the speed of signals
How are signals passed
Terminal axon branches connect to another dendrite and signals are continuing to pass
In between each terminal axon and a dendrite, neurotransmitters go through transporters and go to receptors on the dendrite
After, they reuptake and return to the axon
Nervous System
It is the body’s speedy electrochemical communication network
It holds all nerve cells in the peripheral and central nervous system
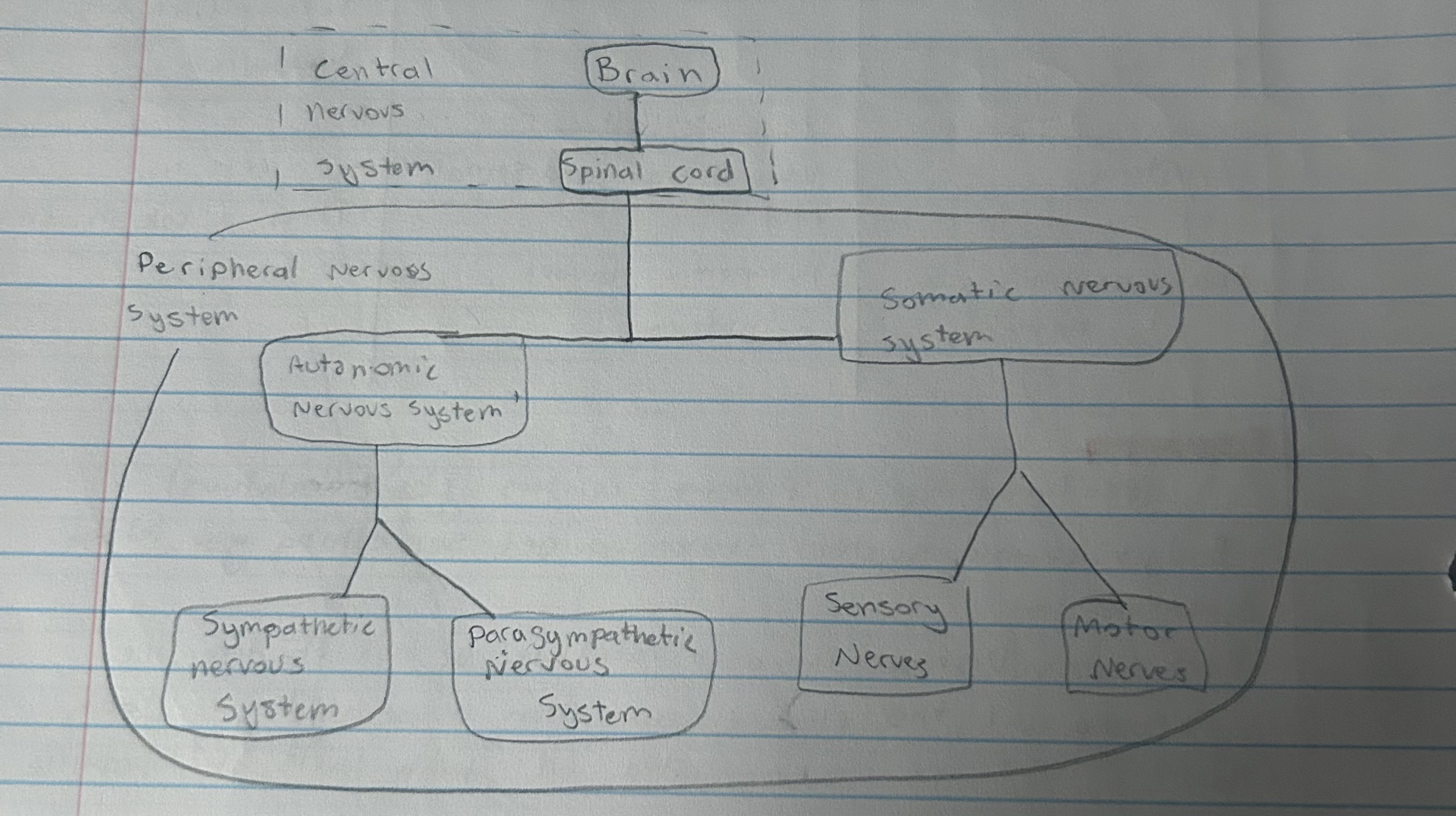
Nervous system: Central nervous system
what does it do
Where is it located
It is the body’s decision make
Located in the brain and spinal cord
Nervous system: Peripheral nervous system
It is responsible for gathering information and transferring it to other body parts
Somatic system
Enables voluntary control of our skeletal skin
Autonomic system
Controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs
In Autonomic there is the:
Sympathetic system
arouses and expands energy - ready for action
Parasympathetic system
Calm us down by decreasing heartbeat
In Somatic there is the:
Motor nerves
Sensory nerves
Endocrine System:
Purpose
What glands are in it?
It is humans other communication system
It is carried by blood
It is a set of glands that secrete hormones in the bloodstream
It is the slow system - takes a long time for thing to leave and enter
Endocrine System: Adrenal glands
Sit above the kidneys and arouse during times of stress
Endocrine System: Pituitary gland
It is the most important and influential gland
It regulates and growth and controls other glands
Endocrine System: Pineal gland
It is related to the sleep cycle
Brainstem
It is the oldest and innermost region, starting where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull
Controls basic functions like breathing
The swelling is the medulla
Brainstem: Medulla
Controls heartbeat and breathing
Brainstem: Pons
These are above the medulla and they help coordinate movement
Brainstem: Thalamus
Thalamus is on the top of the brainstem and it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas and in the cortex
Transmit replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Brainstem: Reticular formation
It helps control arousal
Brainstem: Cerebellum
It is the “little brain”
Function include nonverbal learning and processing sensory inout, and coordinating movement and balance
An injured cerebellum can hurt someone’s movement
Limbic system
Has a role is memories, emotions, and behavior
Limbic system: Hippocampus
Processes memories
Specifically, episodic memories
Biographical events (anything that has happened to you)
Limbic system: Amygdala
Two lime-bean sized neural clusters
Its role is in rage and fear
It is linked to emotions
It helps the perception of emotions and processing emotional memories
Limbic system: Hypothalamus
Linked to bodily maintenance
It influences hunger, regulates thirst, body temp, and sexual behavior
Reward center
Cerebral Cortex
Interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres
Control and information processing center
It has 85% of the brains weight
Cerebral Cortex: Frontal lobe
Directly behind the forehead
Involves speaking and muscle movements/making plans and judgements
Cerebral Cortex: Parietal lobe
Is at the top of the head, toward the rear
Receives sensory inout for touch and body position
Cerebral Cortex: Occipital lobe
Is at the back of the head
Includes areas that receives information from visual fields
Cerebral Cortex: Temporal lobe
Is above the ears
It includes auditory areas
Each receiving information from the opposite ear
Cerebral Cortex: Somato-Sensory Cortex
It is at the front of the parietal lobe
Processes input for touch feelings of movement
These inputs come from any part of the body
Cerebral Cortex: Motor cortex
It is at the rear of the frontal lobe
It controls voluntary movements
Left hemisphere controls right side of body
Right hemisphere controls left side of body
Cerebral Cortex: Corpus callosum
Large band of neural fibers connecting the two hemispheres
It carries messages between the two hemispheres
If this is removed, the two hemispheres work independently now
Cerebral Cortex: Broca’s area
Controls language expression
It direct muscle movements in speech
Cerebral Cortex: Wernicke’s area
Controls language reception
Language comprehension
Cerebral Cortex: Angular gyrus
It is involved with reading out loud
It is from visual areas and turns into auditory form
If it is damaged, a person is unable to read
Aphasia
It is an impairment of language caused by left-hemisphere damage either to the Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area
Plasticity
The ability to modify itself after some types of damages
Neurogensis
The formation of new neurons
Split brain
The surgery when the fibers are cut between the two hemispheres and they are now isolated
Agonist
Mimics a neurotransmitter
Antiagonist
Blocks receptors sites for cellular activit
What does the left brain do?
Logic
Reason
Purpose
Speech production
Analytical thinking
Problem-solving
Word-recognition
Rationalizing reactions
What does the right brain do?
Playful
group oriented
Visual
Creativity
Music and arts
Spatial relations
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine (ACH)
It is released on the brain and autonomic nervous system
Its actions include physical activities
Issue
Lock jaw - restrictive muscle movement
Bachalism - get it from canned good
Hormone: Epinephrine
Or named adrenaline
It is released in areas of the brain and spinal cord
Autonomic nervous system
Plays a role in emotions
Released by adrenal glands
Neurotransmitter: Dopamine
Located in pleasure centers
Body’s reward system - when you get something you want you release dopamine
Parkinson’s disease is related to a lack of dopamine
Schizophrenia is associated with high levels of dopamine
Neurotransmitter: Endorphins
Our internal pain killer
When endorphins stop there is physical pain
Neurotransmitter: Serotonin
Associated with depression and anxiety disorders
Happens in the gut, the stomach has a lot of serotnin
Studying the brain: Lesion
tissue destruction
Studying the brain: EEG
amplified recording of the waves across the brains surface
Studying the brain: PET Scan
is a visual display of the brains activity that detects where radioactive form of glucose goes
Studying the brain: MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce generated images soft tissue
Studying the brain: fMRI
Reveals blood flow
Autonomic nervous system
Controls heartbeat, digestion, and other self-regulating functions
Somatic nervous system
Involved with voluntary movements
Association areas
Brain areas involved in higher mental functions
integrates information from different receptors/ sensory areas that relay information to past experiences
If damaged - process of information slows down