Profit Maximization and Market Structures in Economics (L1)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Profit
Total Revenue (TR) - Total Cost (TC).
Total Revenue
Price Quantity = PQ.
Total Cost
Total Cost is a function of Quantity [C(Q)].
Marginal Cost
The additional cost incurred by producing an additional unit of output. = ∆TC/∆Q.
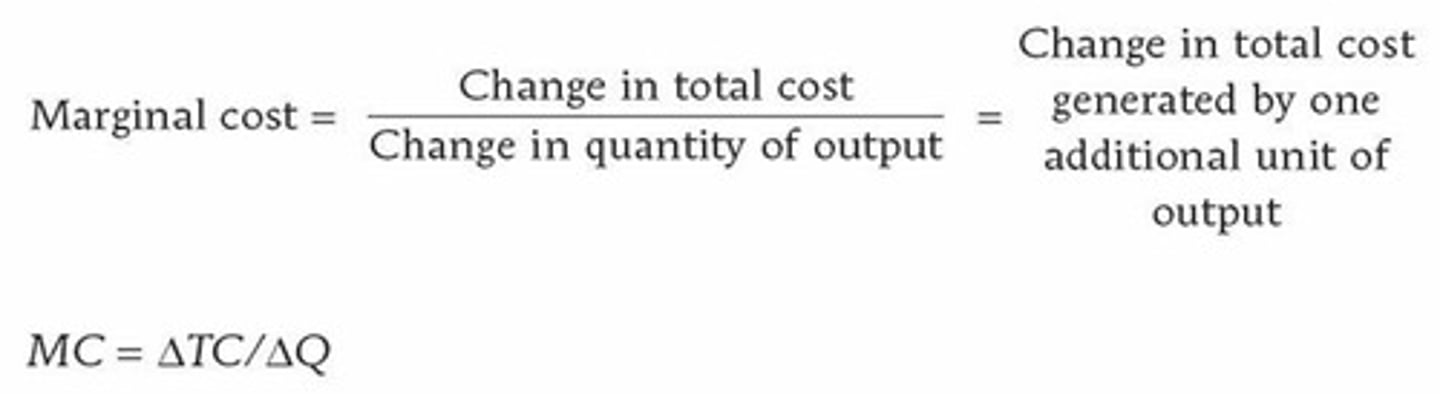
Marginal Revenue
Change in Total Revenue (TR) generated by selling an additional unit of output.
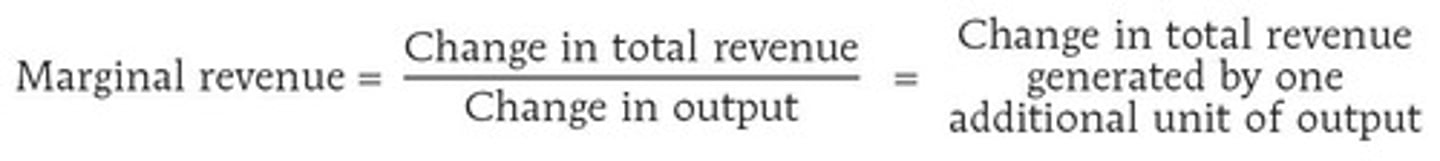
Marginal Revenue Formula
MR = ∆TR/∆Q.
Profit Maximizing Condition
Continue producing until MR = MC.
Profitable Firm Condition
If TR > TC, the firm is profitable.
Break Even Condition
If TR = TC, the firm breaks even.
Loss Condition
If TR < TC, the firm incurs a loss.
Shutdown Decision
A firm should only decide to produce a good or service if the revenue it would receive is at least enough to cover the avoidable cost.
Long-Run Shutdown Condition
Firm should shutdown if TR < TC.
Short-Run Shutdown Condition
Firm should shutdown if TR < VC.
Market Structure
Perfect Competition (many firms), Imperfect Competition, Monopoly (one firm)
Perfect Competition
A perfectly competitive industry is an industry in which all producers are price-takers.
Price Takers
Takes market price as given. Has no individual impact on market price.
Necessary Conditions for Perfect Competition
For an industry to be perfectly competitive, it must contain many producers, none of whom have a large market share.
Producer's Market Share
The fraction of the total industry output accounted for by that producer's output.
Perfectly Competitive Industry
An industry can be perfectly competitive only if consumers regard the products of all producers as equivalent.
Homogeneous Product
Consumers regard the products of different producers as the same good.
Free Entry and Exit
There is free entry and exit into and out of an industry when new producers can easily enter into or leave that industry.
Barriers to Entry or Exit
There are no barriers to entry or exit in the long-run.
Short-Run Limitations
Free entry and exit does not exist in the short-run because some inputs are fixed and cannot be altered.
MR in Perfect Competition
Under perfect competition: MR = Price.
Average Revenue (AR)
Revenue per unit of output, calculated as AR = TR/Q = (P*Q)/Q = P.
AR in Perfect Competition
Under Perfect Competition: AR = MR = Price.
Profit-Maximizing Quantity of Output
The profit-maximizing point is where MC crosses the MR curve (horizontal line at the market price).
Production Decision
Produce quantity where Price (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC).
Profit Maximizing Condition
For a perfectly competitive firm: P = MC.
Shutdown Decision
Shutdown if Price < Average Variable Cost (P < AVC).
Total Cost (TC)
TC = Variable Cost (VC) + Fixed Cost (FC).
Profit Calculation
= TR - VC - FC.
Shutdown Condition
A firm should produce only if: Profit(from producing) ≥ Profit (not producing).
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Should only produce if average revenue (P) is greater than or equal to the average variable cost (AVC).
Short-Run Supply Curve
The short-run supply curve for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market is the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve.
Production Decision for Perfectly Competitive Firms
Produce quantity where Price (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC)
Profit maximizing condition for a perfectly competitive firm
P = MC
Shutdown Decision in the long-run
Shutdown and exit the industry if Price < Average Total Cost
Zero Economic Profit in the Long-Run
Perfectly competitive firms earn zero economic profit due to free entry and exit
Long-run Market Equilibrium condition
P = MC = ATC
Long-run profits condition
(P - ATC)*Q = 0
Firm profitability conditions
If P > ATC, the firm is profitable; If P = ATC, the firm breaks even; If P < ATC, the firm incurs a loss
Shutdown condition in the short-run
P < AVC
Shutdown condition in the long-run
P < ATC
Profit Maximizing Level of Output condition
If produce, maximize profits where MR = P = MC
Profits
= P*Q-C(Q)