NURS 201: Final Exam Review (I made a mistake but CAM is more prevalent in DEVELOPING COUNTRIES, not DEVELOPED)
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
Health
- An ideal state of optimal well being toward which all individuals could strive to
- Applies to all persons, sick or well
- Broad in perspective
Global Health
- An area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving health equity in health for all people world wide
- The optimal well-being of all humans from an individual and collective perspective
Global health refers to the ____ not their ____
Scope, location
3 Factors that Global Health Encompasses
- Prevention
- Treatment
- Care
Global Burden of Disease
A metric that quantifies the health of the population at many levels
Communicable Diseases
Infectious diseases
Non-Communicable Diseases
Chronic diseases
Global Violence
Various forms of violence impacting health outcomes
Gender Equality
People of all genders enjoying the same rights and opportunities in all aspects of their lives
Intersectionality
The interconnected nature of social categorizations such as race, class, and gender as they apply to a given individual or group
Health Disparity
A statistically significant difference in health indicators that persists over time
Healthcare Disparity
A difference in access to healthcare by different groups
9 Indicators of Health Disparities
- Burden of disease
- Mortality rate
- Infant mortality rate
- Morbidity rate
- Life expectancy
- Birth rate
- Total fertility rate
- Disability
- Nutritional status
Burden of Disease
- The impact of a health problem in an area measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators
- Helps to measure the impact of health interventions
Mortality Rate
The number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population (expressed in units of death/1000 people)
Infant Mortality Rate
- The number of death of infants/1000 live births
- Indicator of a country's level of health/development
Morbidity Rate
- The number of individuals in poor health during a given time or number who currently have that disease, scaled to the size of that population
- Takes into account the state of poor health, degree/severity of a health condition, and total number of cases in a particular population and point in time, regardless of cause
Life Expectancy
- The average number of years of life remaining at a given age or average life span or average length of survival in a specific population
- The most important measure of health
Birth Rate
The number of childbirths/100 000 people/year
Total Fertility Rate
The average number of children born to each woman over the course of her life
Disability
Lack of ability relative to a standard
Nutritional Status
A factor influenced by diet, levels of nutrients in the body, and ability to maintain normal metabolic integrity
Globalization
- A process resulting from a combination of forces that is increasing the flow of information, goods, capital, and people across political and geographical boundaries
- Relates to the increased interconnectedness and interdependence of people and countries
3 Ways that that Globalization Impacts Health
- Spread of disease
- New health problems
- Lifestyle influences
CNA's Position Statement Towards Health
- Health is a global issue
- Health is a human right
- Registered nurses have the responsibility and right to seek out inequalities
6 Roles in Global Health
- Governments
- Non-governmental and voluntary organizations
- Nursing organizations
- Registered nurses
- Communities
- Individuals
Role of Governments in Global Health
- Protect public interests
- Advocacy
- Policy
- Knowledge sharing
Role of Non-Governmental and Voluntary Organizations in Global Health
- Advocacy
- Advancement in research and policy
- Service providers
Role of Nursing Organizations in Global Health
- International partnerships
- Advocacy
- Education of members
- Response to international health issues
Role of Registered Nurses in Global Health
- Raising awareness
- Advocacy
- Educators
- Research
Role of Communities in Global Health
- Determining priorities
- Determining approaches to address health issues
Role of Individuals in Global Health
- Informing themselves
- Being responsible for others
4 Examples where Nurses may Experience the Impact of Global Health in their Work
- Clients
- Organizations
- Work colleagues
- Employment
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- A document adopted by world leaders that came into force on January 1, 2017, and outlines the 17 sustainable development goals
- Overall goal is to fight inequality, end all forms of poverty, and address climate change for all people of the world
17 Sustainable Development Goals
- No poverty
- Zero hunger and food security
- Healthy well-being for all ages
- Quality education
- Gender equality
- Access to water and sanitation
- Affordable and clean energy
- Decent work and economic growth
- Resilient infrastructure and sustainable industrialization
- Reduced inequality within/among countries
- Inclusive/safe/resilient/sustainable cities
- Sustainable consumption and production patterns
- Maintain the environment
- Promote peace, justice, and strong institutions
- Revitalize global partnerships for sustainable development
Equality
The state of being equal

Equity
The state of being fair

Health Inequity
Differences in health that are unfair, unjust, avoidable, and are often a result of a power dynamic
Downstream Thinking
A way of thinking that blames the individual as the source of the problem
Upstream Thinking
A broader way of thinking that acknowledges that their are SDOHs that affects a person's overall well-being
LaLonde Report 1974
An important report that emphasized the importance of a biopscychosocial model over a biological model of health (Ex. SDOHs)
Determinants of Health
The broad range of personal, social, economic, and environmental factors that determine individual and population health
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH/SDH)
- The conditions in which people are born, grow,
live, work and age
- Shaped by the distribution of money,
power and resources at global, national and local levels
- Determines what resources a person has to achieve their goals
- Determines health or lack thereof
- Impacts individual choice
12 Main Determinants of Health
- Income and social status
- Social supports and coping skills
- Education and literacy
- Employment and working conditions
- Childhood experiences
- Physical environment
- Healthy behaviours
- Biology and genetic endowment
- Access to health services
- Gender
- Culture
- Race/racism
Food Security
The access to adequate quality and quantities of food
Food Insecurity
A state of being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable and nutritious food
3 Types of Food Insecurity
- Marginal
- Moderate
- Severe
Marginal Food Insecurity
Type of food insecurity in which people have limited choice in food items or worry about running out of food
Moderate Food Insecurity
Type of food insecurity in which people have uncertain access to food impacting the quality and or quantity of food
Severe Food Insecurity
Type of food insecurity in which people run out of food, with 1 or more days without food
Neoliberalism
A concept relating to how some nations are wealthier, and therefore, healthier than others
Institutional Racism
Differential access to goods, services, and opportunities of society by race
Systematic Racism
Racism that is embedded in the laws, regulations, policies, and practices of a society or an organization
Colonization is _____ and not ______
Contemporary, historical
1 multiple choice option
3 Main Types of Social Determinants of Indigenous People's Health
- Root
- Core
- Stem
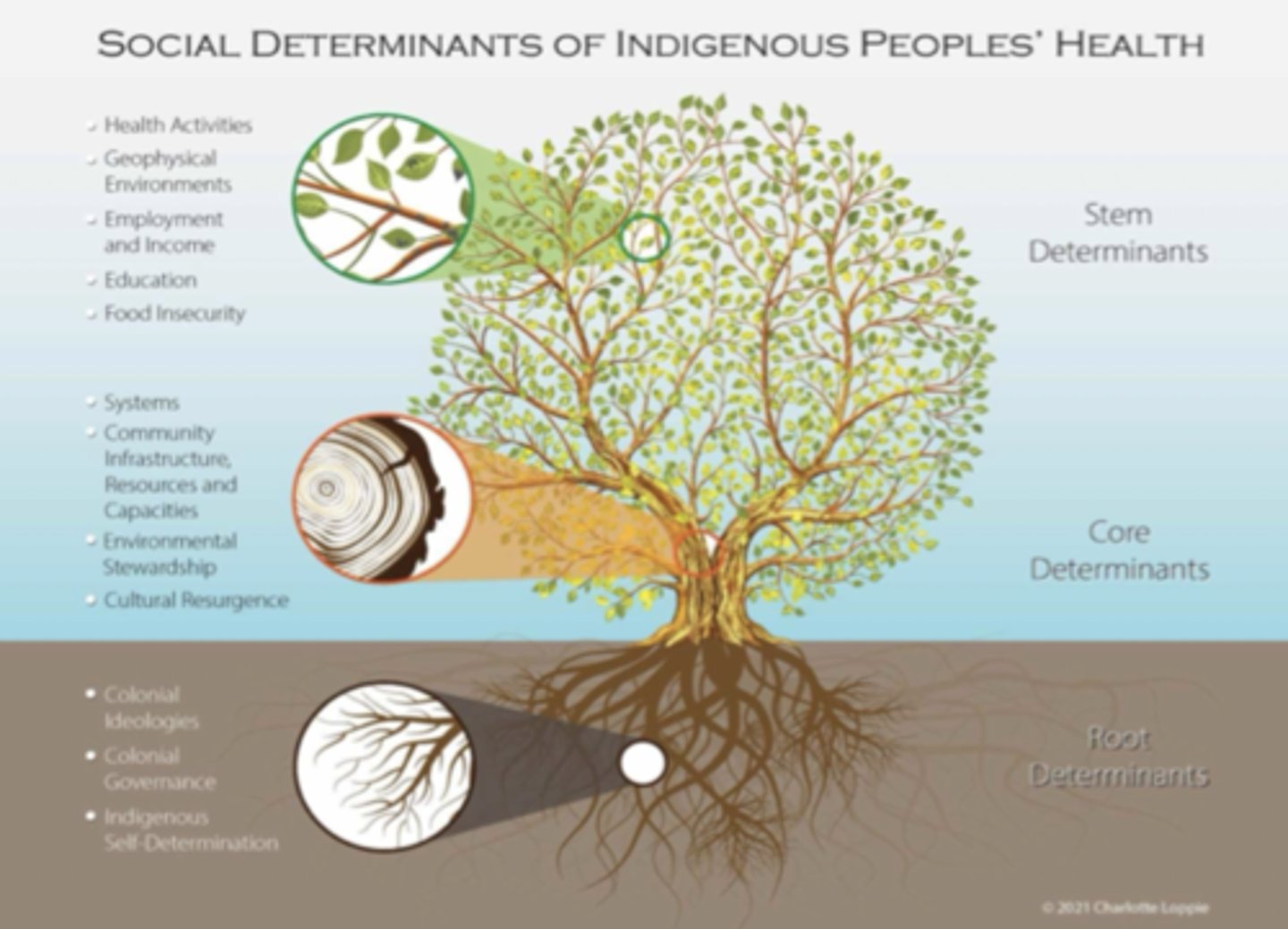
Root (Structural) Determinants
- Determinants that are deeply embedded ideological and political foundations that shape all other determinants
- Has the most profound influence
- Ex.) Colonialism

Core Determinants
- Determinants that represent infrastructure and systems responsible for the allocation of resources, supports, and engagement of individuals and communities
- Ex.) Education, health, justice, social welfare

Stem Determinants
- Determinants that have a more direct impact on the health of individuals
- Often the primary focus
- Ex.) Education/training, employment, social supports, resources

3 Areas of Focus in Addressing Indigenous Health Inequities
- Adopt a structural approach
- Community strength-based approach
- Acknowledge the positive determinants of health Indigenous people hold
Community
- A group of people who live, learn, work, and play in an environment at a given time
- May be defined by geopolitical boundaries, common interests, goals, beliefs, and cultures
Health Literacy
The skills that enable individuals to obtain, understand, and use information to make decisions, and take actions that will have an impact on health status
Primary Healthcare (PHC)
- The approach of the whole-of-society to health
- Aims at highest possible level of health and well-being
- Works towards an equitable distribution of health by focusing on people's needs and preferences
- Works along the continuum of heath from health promotion all the way to palliative care
- Should be as close to people's everyday environment
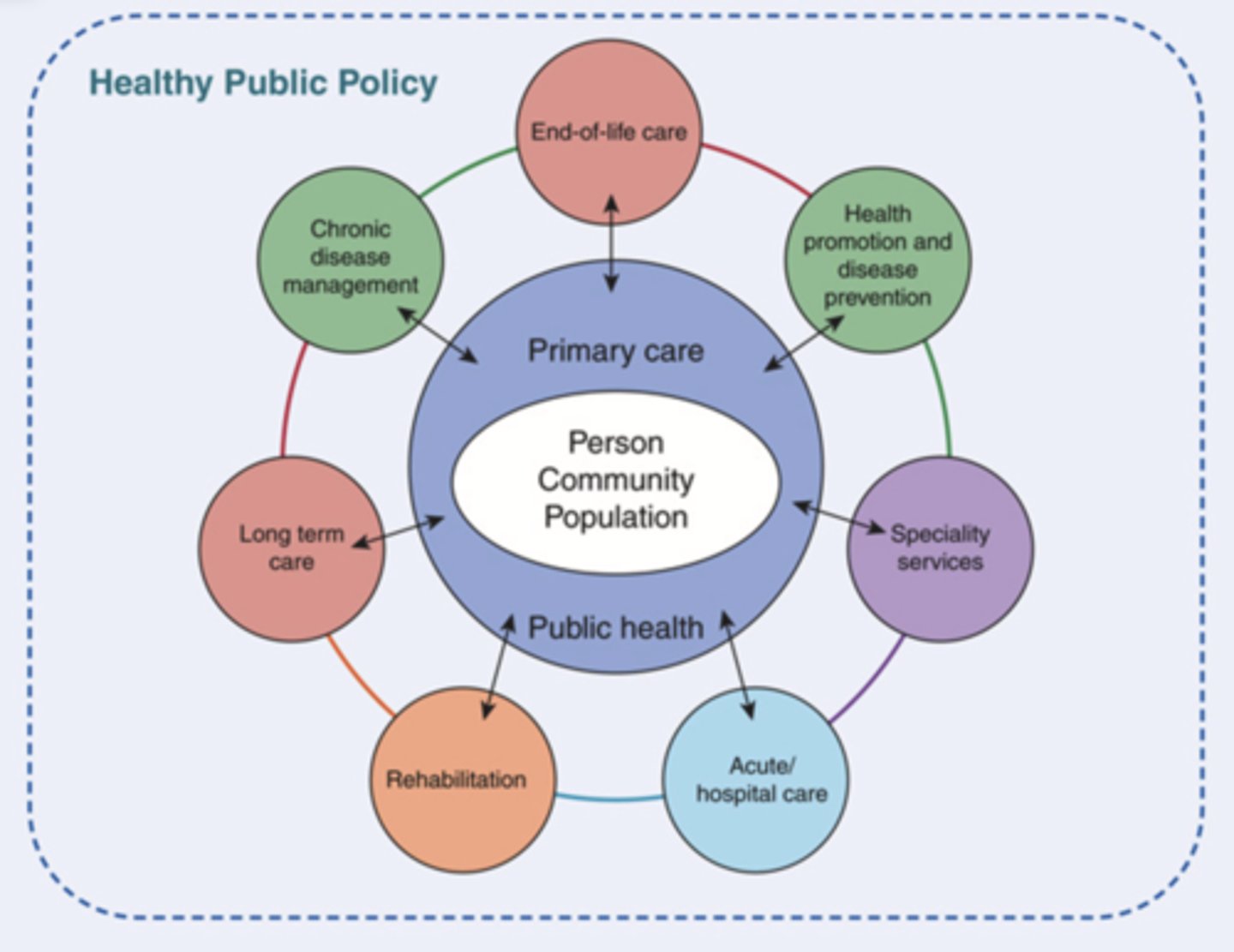
Main Differentiating Characteristics of Primary Health Care
- Whole-of society approach
- Principle-based
- Comprehensive
- Improves the health of populations along a continuum
- Works across the lifespan
- Focuses on population, community, and individual level health strategies
- Acknowledges the broader conditions that influence health
- Values/principles are included into policy and implemented into programs and practice
Main Differentiating Characteristics of Primary Care
- Focus is on personal health services
- Refers to the delivery of community-based clinical health services
- Provides coordinated care
- Enables equitable and timely access to other services and providers
- Focuses on preventing, diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions
- Also promotes health
1978-Alma Ata Declaration-I
A document that emphasized the importance of PHC in achieving health for all
PHC is both a . . .
Philosophy and an approach
3 multiple choice options
5 Principles of PHC
- Accessibility
- Active public participation
- Health promotion and chronic disease prevention and management
- Use of appropriate technology and innovation
- Intersectoral collaboration
2 Types of Accessibility
- Tangible
- Intangible
Arnstein's Ladder
Model illustrating levels of citizen participation
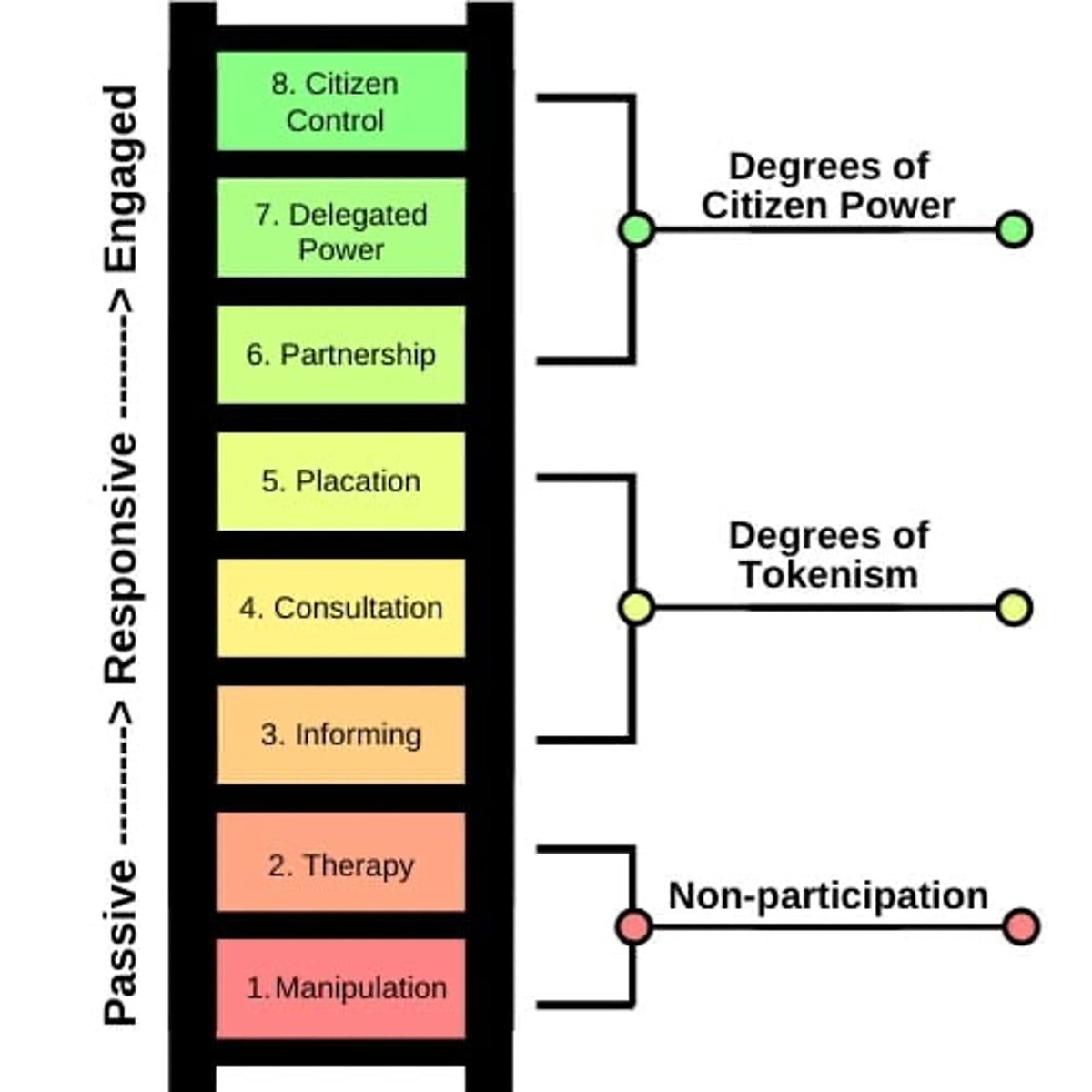
Main Goal of Health Promotion
To enable individuals, families, and communities to live healthier lives
3 multiple choice options
3 Approaches of PHC
- Primary care and essential public health
- Multi-sector policy and action
- Empowered people and communities
Characteristic of Quality Primary Care
- Evidence-informed
- Community-delivered
- Person-centered
- Provides first point of contact
- Continuous
- Comprehensive
- Coordinated
5 Main Population-Based Services
- Health protection
- Health promotion
- Disease prevention
- Surveillance and response
- Emergency preparedness
Health Protection
Risk assessment and supervision of enforcement and control of activities for minimizing exposure to health hazards in order to protect the population, by ensuring environmental, toxicological, road and food safety
Health Promotion
The process of enabling people to increase control over, and improve their health
Disease Prevention
Action that is taken to avoid or forestall illness/disease
Surveillance and Response
A combination of monitoring and prevention of diseases
Emergency Preparedness
An aim to address unforeseen and catastrophic circumstances that create a surge of demand for health services and strain resources and infrastructure (Ex. Covid)
4 Categories of Multisectoral Interventions for PHC
- Fiscal measures
- Laws and regulations
- Changes in the built environment
- Information, education, and communication campaigns
Health in All Policies (HiAP)
A whole-of-government approach to multisectoral policy and action at the national, subnational and regional levels
3 Expressions of Empowerment and Engagement for People through PHC
- Advocates
- Co-developers of health and social services
- Self-carers and givers
4 Pillars of PHC
- Teams
- Access
- Information
- Healthy living
Reasons for the Slow Progression of PHC in Canada
- Not the focus of the Canadian health system
- Many Canadians view the healthcare system as providing curative care
- Many Canadians value expensive technology and "quick fixes"
Reasons Why Canada Should Adopt a PHC Approach
- Continues calls for healthcare reforms
- Health indicators are below international comparisons
- An aging population
- Rising costs of hospital-based care
- Ensures health equity
Differentiating Characteristics of Health Promotion
- Increases health and well-being
- Includes variety of activities from health education, advocacy, illness prevention, strong community participation, public policy
- Emphasizes empowerment, participation, and equity
- Broader approach
- Often political
Differentiating Characteristics of Disease Prevention
- Specific to avoiding an illness or disease
- Focused on physical health
- Limited to the health sector
Levels of Disease Prevention
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
Primary Prevention
Activities that protect against a disease before signs and symptoms occur (Ex. Vaccines, exercise, nutrition, etc.)
Secondary Prevention
Activities that promote early detection and limit or minimize the effect(s) (Ex. Health screenings)
Tertiary Prevention
Activities that minimize disease impacts and disability and help people live productively with limitations (Ex. Rehab, therapy, dialysis, etc.)
Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion
- The first International Conference on Health Promotion
- Goal is to achieve a health for all
- Views health as a resource for living
- Holistic view of health
- Goes beyond the individual to include groups
Principles of Health Promotion
- Considers the context of the health issue
- Holistic approach
- Long-term perspective
- Multisectoral
- Draws on the knowledge of various disciplines
Foundations Required for Health
- Shelter
- Education
- Equity
- Income
- Food
- Peace
- Stable ecosystem
- Sustainable resources
- Social justice
(SEE IF PSSS)
5 Strategies for Health Promotion
- Building healthy public policy
- Creating supportive environments
- Reorienting health services
- Developing personal skills
- Strengthening community action
2 Objectives of Health System Reform
- Shift emphasis from treating disease to improving health
- Make healthcare system more efficient and effective
Population Health
- Health of the population
- Measured by health status indicators
- Influenced by determinants of health
Population Health Approach
- An approach to health that improves the health of the entire population and reduce health inequities
- Addresses determinants of health
- Invests in upstream thinking
- Evidence-based
Population Health Promotion Model
A model that combines population health and health promotion through four major questions
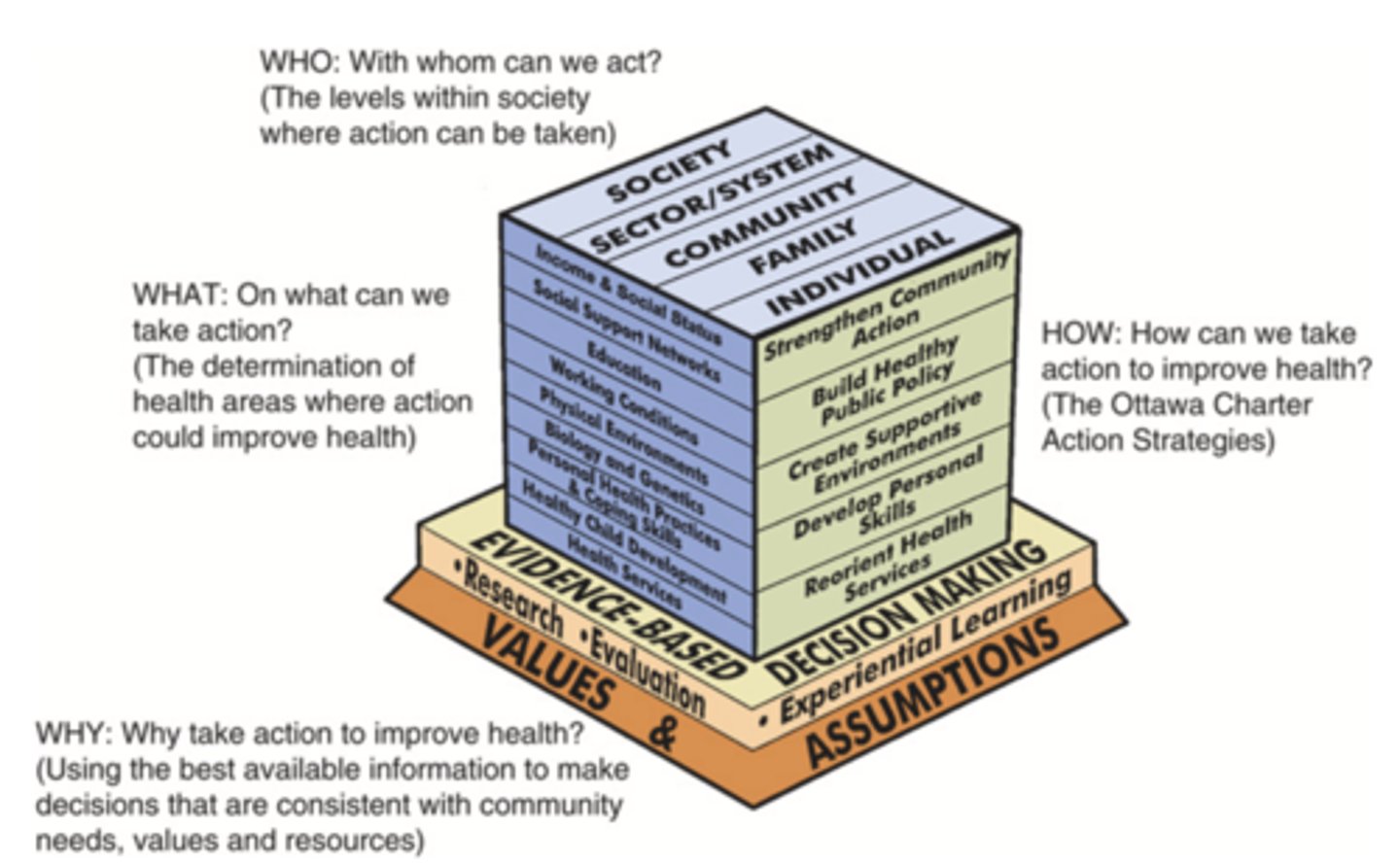
4 Major Questions of the Population Health Promotion Model
- On what can we take action? (levels of society)
- How can we take action? (determinants of health)
- With whom can we act? (5 Ottawa Charter strategies)
- Why take action? (evidence-based)
Differentiating Characteristics of Health Disparities
- Statistically significant differences in health indicators
- Persists over time
- Obscures fundamental causes embedded in societal structures
- Hides ethical principles of social justice
- Deficit-based connotation