AP Psychology Unit 1 - Nervous System, Neurons, & Hormones
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System
Contains all other nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, connecting the central nervous system to limbs and organs.
Follows instructions from the brain and controls our body
Central Nervous System
Contains the brain and the spinal cord and is responsible for processing information and coordinating responses.
Somatic Nervous System
A part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary actions
Autonomic Nervous System
A part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the automatic actions or bodily functions of the body
Example: heart rate, digestion, breathing, etc
Sympathetic Nervous System
A part of the autonomic nervous system that triggers the fight or flight response in stressful situations. It increases heart rate, breathing, and dilates pupils, preparing the body for action.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
A part of the autonomic nervous system that triggers the rest and digest system that happens when the body is in a relaxed or peaceful state. It increases digestion and calms the heart rate, promoting conservation of energy.
Neurons
Cells that receive and transmit information through electrical and chemical signals throughout the nervous system. They play a crucial role between the brain and the body
Glial Cells
Cells that support and protect neurons, providing structural and functional support in the nervous system. They help maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and aid in the transmission of electrical impulses.
Afferent Neurons (Sensory)
Neurons with sensory information that travel to the brain to process it
Efferent Neurons (Motor)
After the brain processes sensory information, efferent neurons carry signals away from the brain to initiate responses (actions) in muscles or glands.
Neural Firing Process
Neuron fires, sending an electrical signal (action potential) along its axon to communicate with other neurons.
Action potential reaches the axon terminal, where specific neurotransmitters are triggered to release
Neurotransmitters float to the synapse to bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, influencing its potential to fire.
Signals continue from neuron to neuron in a process called synaptic transmission, enabling communication throughout the nervous system.
Depolarization
The process during the action potential when the neuron's membrane potential becomes more positive, allowing Na+ ions to enter the cell, which is crucial for the transmission of signals in neurons.
This change in membrane potential occurs after the threshold is reached, leading to an excitatory phase of the action potential.
Reuptake
Happens after a signal is transmitted, when neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron from the synapse, terminating their action on the postsynaptic neuron.
Action Potential
The electrical impulse that travels down an axon, triggering the release of neurotransmitters.
Refractory Period
The brief phase after an action potential during which a neuron cannot fire again, ensuring that impulses travel in one direction.
All or Nothing Principle
The principle that a neuron either fires fully or not at all when the threshold is reached, ensuring consistent signal strength.
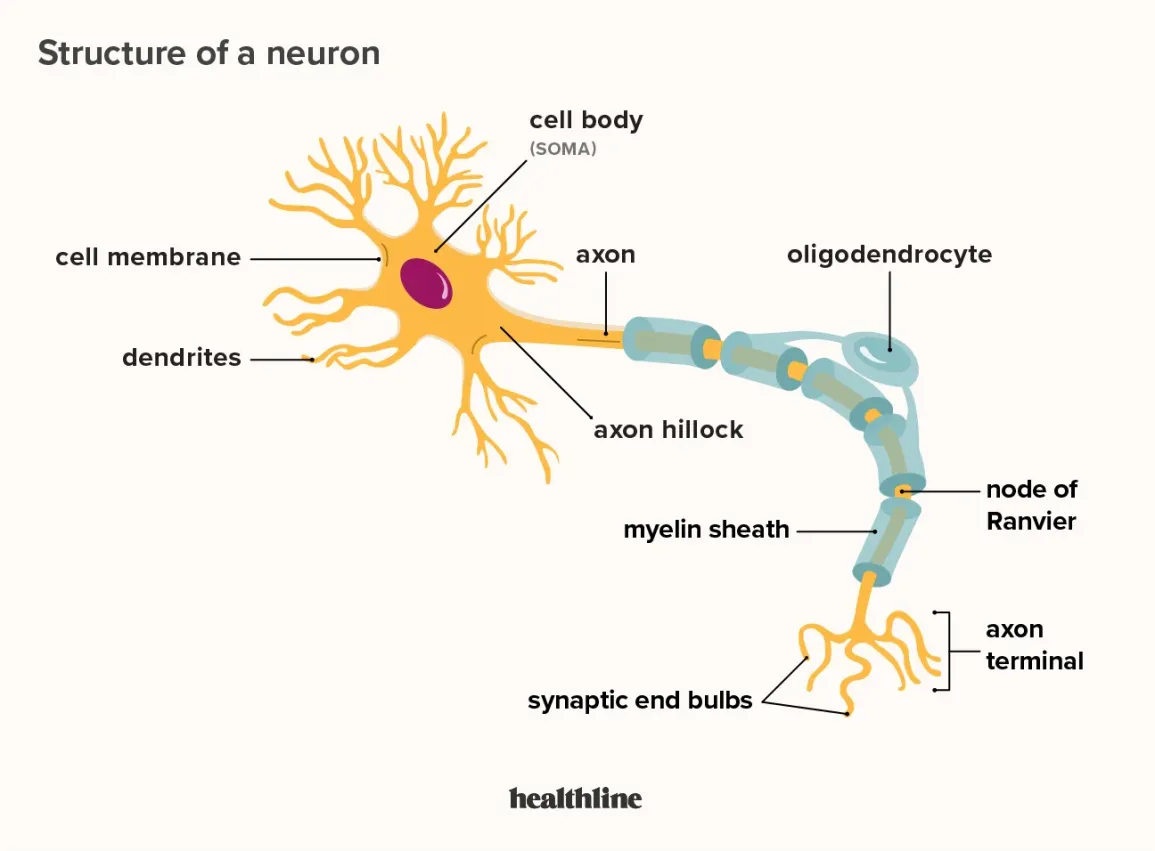
Structure of Neuron
Soma (Cell body): Maintains cell and keeps neuron functioning efficiently
Dendrite: Receives information
Axon: Transmits information to other neurons
Axon Terminal: The endpoint of an axon where neurotransmitters are released. Transports action potentials away from the soma and into other neurons
Myelin Sheath: Insulation that encases axons
Interneurons
Carry information between other neurons that process information within the central nervous system and facilitate communication between sensory and motor neurons.
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that increase the likelihood a neuron will fire an action potential
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that decrease the likelihood a neuron will fire an action potential
Modulatory Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that can send messages to many neurons at the same time
Disruptions of Neural Firing
Refers to conditions or factors that hinder the proper transmission of electrical signals in neurons, potentially leading to neurological disorders.
Disorders include…
Multiple Sclerosis: When myelin sheath is damaged, disrupting transmission signals, it lead sto muscle weakness, coordination problems, and fatigue
Myasthenia Gravis: Autoimmune disorder that affects communication between nerves and muscles, causing muscle fatigue and weakness
Threshold
The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse or action potential in a neuron.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons, influencing various physiological and psychological functions.
They play an important role in influencing mental state and behavior, including mood, sleep, and cognition.
Acetylcholine
An excitatory neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning, and memory
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter that has both inhibitory and excitatory properties and plays a key role in pleasure, motivation, and reward.
Serotonin
An inhibitory neurotransmitter that plays a key role in mood, happiness, and feelings of well-being.
GABA
A excitatory neurotransmitter that plays a key role in inhibiting neural activity, calming down, and reducing anxiety.
Glutamate
An excitatory neurotransmitter that plays a key role in long term learning, and memory.
Endorphins
An inhibitory neurotransmitter that plays a key role in pain relief and pleasure. They are often released in response to stress or pain, promoting feelings of euphoria.
Substance P
An excitatory neurotransmitter that plays a key role in transmitting pain signals and the perception of pain. It is involved in inflammatory responses and can contribute to the sensation of discomfort.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter that has both excitatory and inhibitory properties and is involved in arousal, alertness, and stress responses. It plays a role in the body's fight or flight response and is linked to mood regulation.
Hormones
Chemical messengers released into the bloodstream that regulate various physiological processes, including growth, metabolism, and mood. They are produced by glands in the endocrine system and can have widespread effects on the body.
They’re different from neurotransmitters in that they travel through the bloodstream and act on distant target organs, whereas neurotransmitters act locally across synapses.
Adrenaline
A hormone and neurotransmitter produced by the adrenal glands, also known as epinephrine. It plays a crucial role in the body's fight or flight response by increasing heart rate, blood flow, and energy availability.
Leptin
A hormone produced by fat cells that helps regulate energy balance and inhibits hunger by signaling to the brain that hunger is satiated
Ghrelin
A hormone produced by the stomach that stimulates appetite and increases food intake by sending signals to the brain.
Melatonin
A hormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates sleep-wake cycles and helps control circadian rhythms.
Oxytocin
A hormone that plays a role in social bonding, sexual reproduction, love, and during and after childbirth.
Psychoactive drugs
Substances that alter brain function, affecting mood, perception, and behavior. They can be used medicinally or recreationally and include categories such as stimulants, depressants, and hallucinogens.
Agonist Drugs
Drugs that enhance the action of neurotransmitters by mimicking their effects at receptor sites.
Antagonist Drugs
Drugs that blocks discourages the function of a neurotransmitter in the brain
Stimulant Drugs
Drugs that increase heart rate, energy, and alertness by enhancing the effects of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. Examples include caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines.
Depressant Drugs
Drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions, often leading to relaxation and sedation. Common examples include alcohol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines.
Hallucinogen Drugs
Drugs that alter perception, thoughts, and feelings, often causing visual or auditory hallucinations. Common examples include LSD, psilocybin (magic mushrooms), and mescaline.
Opiod Drugs
Drugs that cause pain relief and produce euphoria by binding to opioid receptors in the brain. Common examples include morphine, codeine, and heroin.
Tolerance
The condition when a body gets used to a medicine, where it is no longer as effective
Addiction
Psychological and physical dependence on a substance, characterized by compulsive use despite harmful consequences.
Withdrawal
The symptoms experienced when a person stops taking a substance they are dependent on, often including anxiety, nausea, and cravings.
Dependence
A state in which an individual requires a substance to function normally, leading to withdrawal symptoms without it.