Reintroducing Inferential Statistics
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
p: Assume Dr. Null is correct and there was zero
relationship between our variables in the
population, p is the probability we would obtain a
random sample with a relationship between
variables that’s at least as strong as the relationship
we found in the current sample.
More concisely: If there is zero effect in the
population, we would find the observed effect (or a
larger effect) in [p*100]% of random samples.
What’s the ppint of inferential stats?
To use sample data to make a conclusion (an inference) about the entire population
To get research published, the p values for you effect needs to be?
p < .05
ONE-SAMPLE T-TEST
When do we use it?
Is the sample mean significantly different from a set, pre-determined number?
Examples…
1. Is the mean NU-psych IQ significantly higher than the population mean IQ of 100?
Is the mean high school GPA of NU students significantly different from the nationwide (population mean) high school GPA of 2.8?
Can the average person hold their breath for more than 30 seconds?
INDEPENDENT-SAMPLES T-TEST
When to use it?
For some numeric variable, is the mean among Group 1 significantly different from the mean Group 2?
Examples…
When it’s time for a meal, who takes longer to decide to what to eat, men or women?
Is the importance of your favorite musicians’ authenticity (1=NOT-IMPORTANT to 7= EXTREMELY-IMPORTANT) significantly different between hardcore Drake fans and hardcore Kendrick Lamar fans?
3. Is the mean number of Instagram followers significantly different between people over 50 and people under 25?
Paired-samples t-test aka DEPENDENT-MEASURES, REPEATED MEASURES,WITHIN GROUPS
Paired, they depend, you need to repeat, groupies
When to use it?
Scenario 1: is a “before” score significantly different from an “after”?
Examples…
When people have a headache, will they report reduced pain symptoms 30 minutes after (vs before) taking an ibuprofen?
Do people average more car accidents during the year before (vs during the year after) they complete a defensive-driving course?
Do people with ADHD perform better on an attention test after they take adderall, compared to on a day when they haven’t taken addreall?
Paired-samples t-test aka DEPENDENT-MEASURES, WITHIN-GROUPS
Scenario 2: Test for differences between two similarly-scored variables
Examples…
Do NU students score significantly higher on the ACT math section, compared to the ACT reading section? (Both scored out of 36 total)
All else equal (eg. looks, income, etc) is the perceived attractiveness of a flat-earther significantly different than the perceived attractiveness of a STEM major? (both scored on a scale from 1=unattractive to 5= attractive)
Bivariate Correlation & Line Regression Analyses
When to use it?
As numeric variable #1 increases, deos numeric variable #2 tend to increase or decrease?
Examples…
As people get older do they tend to become more conscientious?
As people exercise more hours per week, do they tend to have fewer depressive symptoms?
As people give more high fives per day, do they tend to report higher levels of life satisfaction?
Context non-specific definition of p…
If the null hypothesis were true, we would find the effect we found - or a larger effect in p of random samples from the population
Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error
Chi-sqaure (χ²) test for independence
When to use it?
Given categorical variable A-vs-B and categorical variable X-vs-Y… When people are members of category A (vs B), is it more likely that they’re also members of category Y (vs X)?
Examples…
If you prefer dogs (vs cats), are you more likely to be an extravert (vs introvert)?
If you are a STEM major (vs not) are you more likely to be a frequent video gamer (vs not)?
If you enjoy cooking (vs don’t) are you more likely to have a BMI <30 (vs BMI>30)?
One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
When to use it?
For numeric variable, is the mean among Group 1 significantly different from the mean among Group 2 (vs Group 3, vs Group 4, etc.)?
ANY situation where you can use independent-samples t-test, you can also use one-way ANOVA
→If testing between 3 or more groups, you can use one-way ANOVA but NOT independent-samples t-test
Examples…
Is the average IQ different between Democrats, Republicans, or Independents?
Is GPA different between psych, BNS, or engineering majors?
Alcohol consumption different between 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th years?
2×2 Factorial ANOVA
When to use it?
Assessing how a numeric variable differs between two different 2-level categorical variables
Examples…
Factor 1: ADHD (yes vs no)
Factor 2: Adderall (20mg vs placebo)
Outcome variable: Attention Test score
Above, did ADHD (present vs not) influence attention scores?
Or, did Adderall (20mg vs not) influence attention scores?
Factor 1: pre-bed screentime (yes vs no)
Factor 2: pre-6pm cardio exercise (20 min vs none)
Outcome variable: time elapsed between sleep attempt and sleep onset
Factor 1: alcohol drinker vs not
Factor 2: male vs female
Outcome variable: Autobiographical History of Violence Score
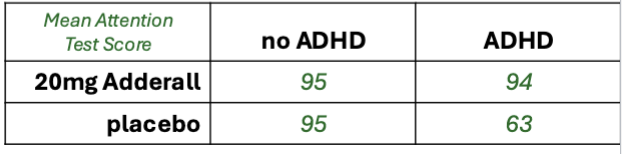
What can 2×2 Factorial ANOVA tell you?
Whether there was an INTERACTION EFFECT
aka MODERATION
INTERACTION EFFECT: When the effect of one independent variable on a dependent variable changes depending on the value of another independent variable