Ch17 - sound quality
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
where does sound quality matter?
Audio / HiFi
Concert halls
Noise annoyance
Speech intelligibility / Public address
Hearing aids / cochlear implants
Razors / Car engine sounds / Mechanical products
Musical instruments
sound quality is also important when making different technical choices (what effect will they have on quality)
quantity vs quality?
quantity - categorisedd by type or class of object where 2 ovbservations or entities cant be compared on same metric scale (1m vs 90.5kg)
quality - grade or rank objects on a subjective scale of preferability such as good – poor
how does sound quality relate to psychoacoustics?
Classical psychoacoustics sees human as simple metering device though basic results are of course very useful
In sound quality the expectations, mood, and other cognitive factors are important
Judged sound quality for devices or communication channels depends heavily on expectations
Basic psychoacoustic experimentation techniques may not be used
how is sound quality measured and evaluated?
sound quality → subjective but can be approximated by objective & computational criteria
Subjective quality → evaluated by listening experiments
compare to "perfect quality" reference to find out if any degradation can be noticed
compare two or more sounds and sort then by quality preference
give an overall quality rating on a numerical scale
Based on subjective experimentation, a computational (objective) measure and model → derived to simulate the perceived quality
Objective measures are less laborious and yield high repeatability
its important to check the validity range of a model
systemic framework for sound quality?
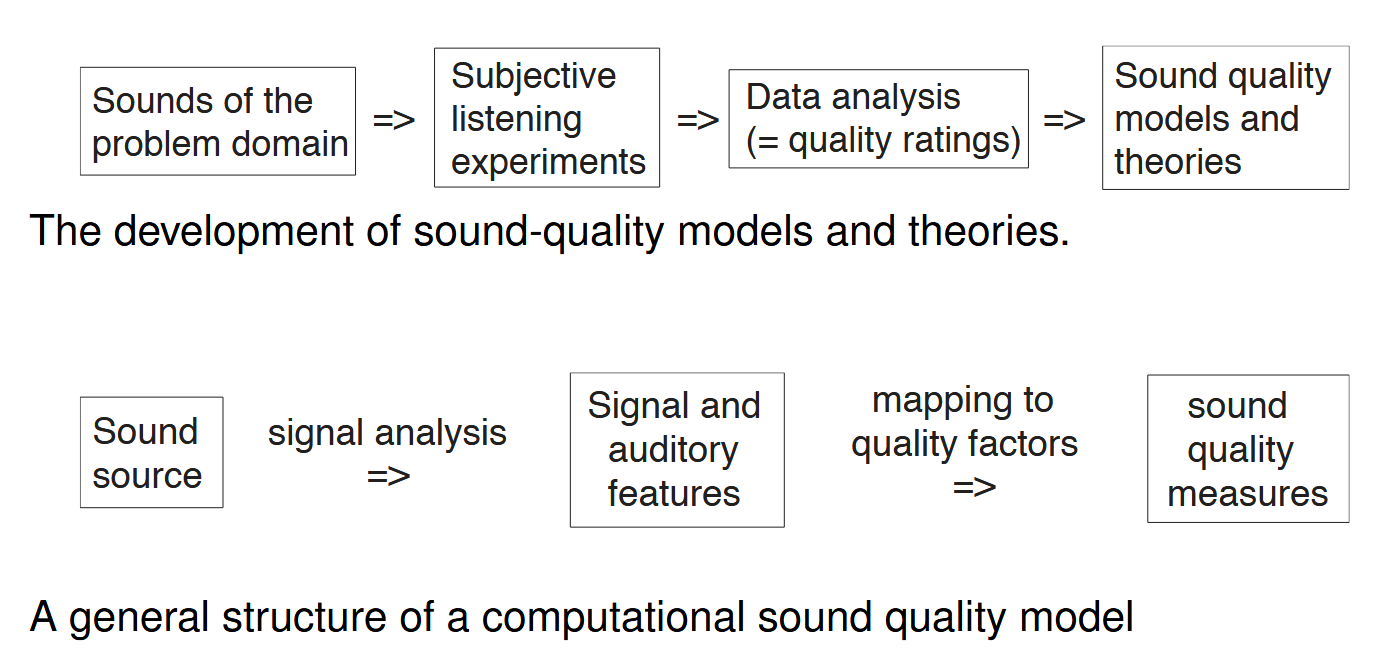
how to rate subjective sound quality
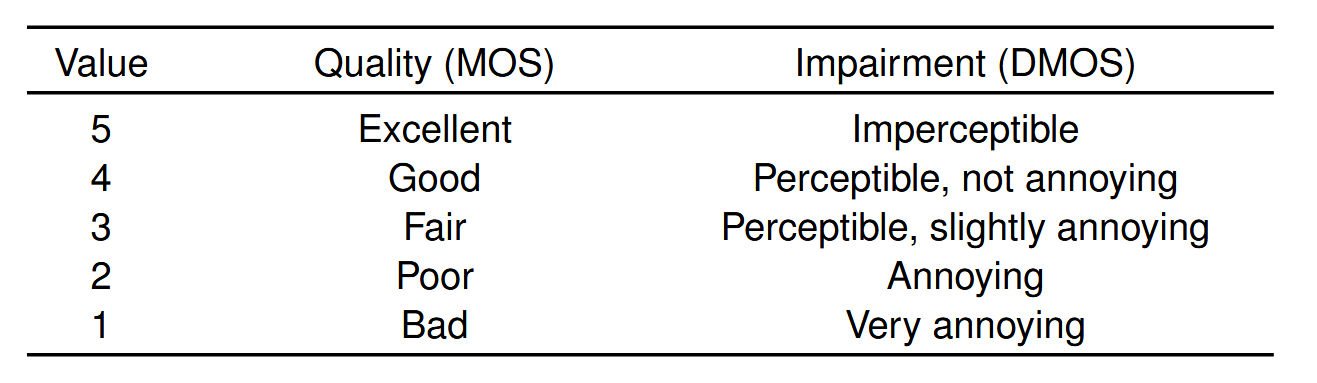
Mean opinion score (MOS)
Principle: ask opinion of some aspect of sound quality in numerical scale with anchors, take an average + other statistical measures
MOS scales have been also defined for measurement of improvement or degradation of quality
Multiple-stimulus hidden reference with anchors (MUSHRA) (group project core)
what is monaural audio quality?
Degradations of audio present by listening only one channel
(imagine audio engineer has mastered audio content as intended, and degradations in transmission channel are measured, not diffs in perceptions)
Deviations in:
Magnitude response
Phase and group delays
Non-linear distortions
Signal-to-noise ratio
how can we estimate perceived difference?
auditory models (wow)
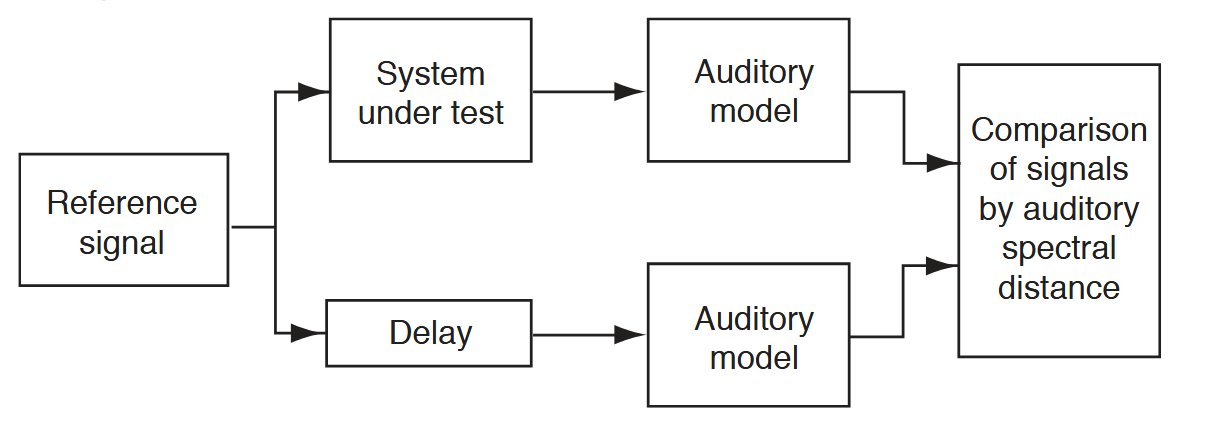
what is Perceptual audio quality measure (PAQM)?
objective metric for assessing audio quality that uses a model of the human auditory system to predict how a person would perceive the sound
what is PEAQ (Perceptual audio quality)?
standardized algorithm for objectively measuring perceived audio quality (improved PAQM)
spatial audio quality?
accounts for 30% of total quality
loses quality if sound degraded by colourations
how to measure subjectively?
compare with reference, if exists and can be brought to listening room (no simple solution exists tho)
how to measure objectively?
binaural auditory models under research, tho standardisation has failed
what determines quality of speech communication?
Speech intelligibility
Speaker recognizability
Speech naturalness
Subjective and objective measurement
what determines quality of speech communication (subjectively)?
Articulation tests and articulation score (/CV/ or /CVC/ sequences used to measure recognition percentage)
Intelligibility test and intelligibility score (recognition percentage using meaningful words or sentences)
Rhyme tests (RT)
Diagnostic rhyme tests (DRT) (modifying single distinctive feature at a time (nasality, voicing, etc.) in RT)
Speech interference tests (find a disturbing noise level of 50% articulation)
Quality comparison method, including pairwise comparison methods
Other methods
Communicability tests (communicate a drawing task, measure the difficulty)
Task recall tests (memorizing ability)
Noise suppression test
what determines quality of speech communication (objectively)?
Articulation index (AI) (for measuring a (linear) speech transmission channel with additive noise articulation loss is assumed to be additive from 20 frequency bands)
Percentage articulation loss of consonants (%ALcons) (measure of speech intelligibitly, estimated from room acoustic parameters)
Room acoustical indices
Speech transmission index (STI, STIPA) (based on modulation transfer function)
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) (ratio of speech vs. noise (power) level (in dB))
Spectral distance measures
Auditory sound quality measures (based on auditory modeling)
what is modulation transfer function?
each critical band in auditory system is analysed by signal level (modulation envelope)
More important than the exact transfer function is modulation transfer function, i.e., how signal modulations in each critical band are transmitted
modulation transfer degraded by
reverberation (lowpass of modulation) → depth of modulation changes due to reverberation and noise
background noise (reduction of relative modulation)
these effects are multiplicative (cascaded)
Reverberation reduces the modulation depth more at high modulation frequencies than at low modulation frequencies. Noise, in turn, reduces the modulation depth equally at all modulation frequencies. The rightmost plots show the corresponding modulation transfer functions for cases A and B. In case A, the reverberation clearly acts as a low-pass filter in the transfer function, while the noise in case B reduces the modulation evenly at all modulation frequencies.
what is Speech Transmission Index STI
Measure m with many carrier frequencies and modulation frequencies, take logarithm-like-measure and take a weighted average
optimally reflects the intelligibility of speech over measured channel
STI measurement requires presentation of all carrier-frequency-pairs at separate times – slow
measure of speech transmission quality
STI measures some physical characteristics of transmission channel (a room, electro-acoustic equipment, telephone line, etc.), and expresses ability of channel to carry across characteristics of speech signal
Objective speech quality measurement for telecommunication?
STI doesnt estimate naturalness of speech
Mobile telecommunication codecs may make speaker unidentifiable, although intelligibility is good
more methods needed
Models for general speech quality are expected to give a high MOS value only for natural-sounding and intelligible speech
Methods for measuring the perceptual effect of background noise suppression
Measures for echo suppression
if a mobile device enters market, sound quality should be tested but listenin tests would be tedious (Basic quality, Effects of network problems delays, echos, background noise, background noise suppression), so standerdised auditory model based evaluation tool is used instead (3GPP - global standards organization that develops technical specifications for mobile communication, including detailed acoustic testing standards for mobile devices)
Techniques for objective speech quality evaluation?
Perceptual speech quality measure (PSQM)
Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)
Telecommunications objective speech quality assessment (TOSQA)
Perceptual objective listening quality assessment) POLQA
Hearing-aid speech quality index (HASQI)
devices entering markets need to produce a high enough score with one of those metrics
Techniques for evaluation of the effect of background noise?
mobile phones often involve algorithms to suppress background noise using non-linear DSP methods with time-variant processing
Non-linear noise-suppression algorithms try to reduce noise
How much does the algorithm reduce the problem
Standardized MOS scales for listening tests
Similar techniques exist also for measurement of the effect of echoes in two-way communication channel
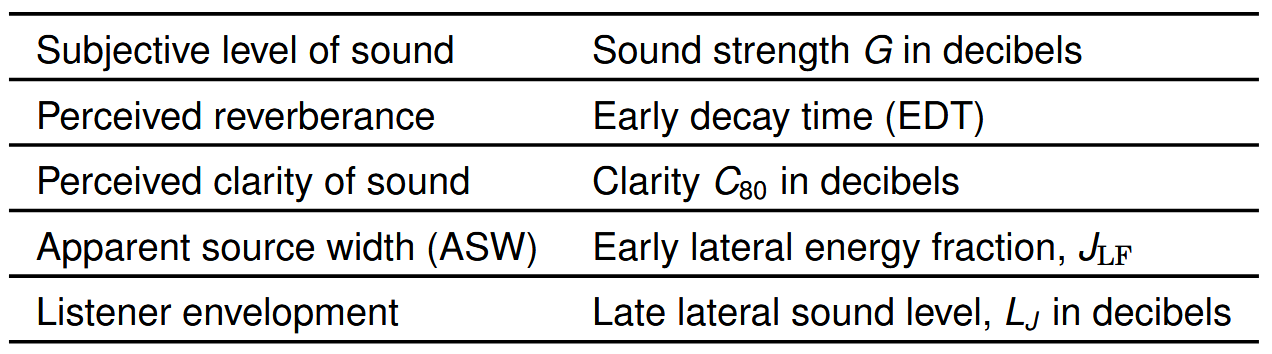
what are some perceptual attributes of concert halls?
Defined by Beranek by personal listening,
Intimacy or presence / Reverberation or liveness / Spaciousness: Apparent source width(ASW) / Spaciousness: Listener envelopment (LEV) / Clarity / Warmth / Loudness / Acoustic glare / Brilliance / Balance / Blend / Ensemble / Immediacy of response / Texture / Freedom from echo / Dynamic range and background noise level / Extraneous effects on tonal quality / Uniformity of sound
List is subject to debate and further studies
Objective measures of concert hall acoustics?
Measure few impulse responses in the hall
Compute the values from the responses
Subject to criticism, correspondence to actual perceptual quality is questionable
Noise quality?
Sound that is disturbing or annoying → purely subjective measure
Annoyance → depends on signal and on context (speech and laughter are disturbing in open-plan office, ventilation humming is ok)
Disturbance (Speech intelligibility over distance is not desired in open-plan office opposite to theatres and auditoria)
product sound quality?
Minimize negative effects and maximize positive effects of product sound
Mechanic devices communicate their functioning to to the user
Electronic devices may have loudspeakers to do the same (car turn
signal earlier relay, nowadays loudspeaker)
Examples:
Cars and work machines
Home appliances
Office equipment
Personal devices