AP Biology: Cells
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
1
New cards
Two different types of cells
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
2
New cards
Prokaryotes traits
1) No membrane bound organelles
2) Unicellular
3) Domains: bacteria and archaea
2) Unicellular
3) Domains: bacteria and archaea
3
New cards
Eukaryotes Traits
1) Membrane-bound organelles
2) Uni- or multi-cellular
3) Domain: Eukaryota (animals, plants, fungi, protista)
2) Uni- or multi-cellular
3) Domain: Eukaryota (animals, plants, fungi, protista)
4
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
1)No membrane bound organelles**
2) DNA in a "nucleoid" region
4) Unicellular
5) Small
6) Domains: Bacteria and Archaea
2) DNA in a "nucleoid" region
4) Unicellular
5) Small
6) Domains: Bacteria and Archaea
5
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells
1) Has membrane bound organelles**
2) Nucleus contains DNA
3) Unicellular or Multicellular
4) Larger: 10x bigger than prokaryotes
5) Domain: Eukarya
2) Nucleus contains DNA
3) Unicellular or Multicellular
4) Larger: 10x bigger than prokaryotes
5) Domain: Eukarya
6
New cards
Nucleus
1) Contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes or chromatin
2) Has a nucleolus for ribosome production
3) Surrounded by a phospholipid nuclear membrane (envelope)
4) spherical shape
5) molecules pass in and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores
2) Has a nucleolus for ribosome production
3) Surrounded by a phospholipid nuclear membrane (envelope)
4) spherical shape
5) molecules pass in and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores
7
New cards
Cytoplasm
1) "Jelly goo" that is within the cell membrane
2) Has organelles/structures in it
3) Found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
2) Has organelles/structures in it
3) Found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
8
New cards
Ribosomes
1) Structures that build proteins during protein synthesis
2) Free-floating or attached to the rough ER
3) Found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
2) Free-floating or attached to the rough ER
3) Found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
9
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
1) Helps with protein production and shipping
2) Ribosomes attached make it "rough"
2) Ribosomes attached make it "rough"
10
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
1) Synthesis of lipids
2) Detoxification
3) Storage of calcium ions
2) Detoxification
3) Storage of calcium ions
11
New cards
Golgi Apparatus (body) - Gol-jee
"Warehouse" for receiving, sorting, and shipping of proteins
12
New cards
Vesicles
Small "containers" made from ER or golgi membrane that move products around the cell
13
New cards
Vacuoles
1) Large vesicles for storing products
2) Plant cells have a large central vacuole filled with water
2) Plant cells have a large central vacuole filled with water
14
New cards
Lysosomes
1) Digestive organelles where macromolecules are broken down
2) Contain hydrolytic enzymes
3) autophagy
2) Contain hydrolytic enzymes
3) autophagy
15
New cards
Mitochondria (mitochondrion)
1) Site of cell respiration
2) ATP is generated
3) Found in both plants and animals
2) ATP is generated
3) Found in both plants and animals
16
New cards
Chloroplast
1) Site of photosynthesis
2) Converts energy from the sun into sugar molecules
3) PLANTS AND ALGAE ONLY
2) Converts energy from the sun into sugar molecules
3) PLANTS AND ALGAE ONLY
17
New cards
Centrosomes
1) Helps with cell division (mitosis) in animals
2) Contains centrioles
2) Contains centrioles
18
New cards
Cytoskeleton
1) Reinforces cells shape
2) Helps with cell movement
3) Includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
2) Helps with cell movement
3) Includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
19
New cards
Cell (plasma) membrane
1) Found in plants, animals, and prokaryotes
2) surrounds cytoplasm
3) phospholipid semi-permeable bilayer
2) surrounds cytoplasm
3) phospholipid semi-permeable bilayer
20
New cards
cell wall
1) Protects, maintains shape, helps with structure
2) Made of cellulose
3) Found in plant cells and some prokaryotes
2) Made of cellulose
3) Found in plant cells and some prokaryotes
21
New cards
Cilia (Cilium)
1) Short appendages containing microtubules present on some eukaryotes
2) Used in locomotion
2) Used in locomotion
22
New cards
Flagella (Flagellum)
1) "Tail-like" appendage found on some eukaryotes
2) Used in locomotion
2) Used in locomotion
23
New cards
Plant Cell Traits
Shape: Square-ish
Eu or Prokaryote: Eukaryote
Border: Cell wall AND Cell membrane
Mitochondria for cell respiration: Yes
Chloroplast for photosynthesis: Yes
Vacuoles: Large, central, filled with water
Eu or Prokaryote: Eukaryote
Border: Cell wall AND Cell membrane
Mitochondria for cell respiration: Yes
Chloroplast for photosynthesis: Yes
Vacuoles: Large, central, filled with water
24
New cards
Animal Cell Traits
Shape: Varies
Eu or Prokaryote: Eukaryote
Border: Cell membrane
Mitochondria for cell respiration: Yes
Chloroplast for photosynthesis: No
Vacuoles: Small, stores various substances
Eu or Prokaryote: Eukaryote
Border: Cell membrane
Mitochondria for cell respiration: Yes
Chloroplast for photosynthesis: No
Vacuoles: Small, stores various substances
25
New cards
What Determines Cell Function?
1) Size, shape, and surface area
2) Organelles present or absent
3) Quantity of different organelles
2) Organelles present or absent
3) Quantity of different organelles
26
New cards
Examples of size, shape, and surface area affecting cell functions
1) Neurons (nerve cells) - spread out; electrical signals
2) Adipose (fat cells) - packed together; only stores fat
2) Adipose (fat cells) - packed together; only stores fat
27
New cards
Examples of Organelles present or absent affecting cell functions
1) Red blood cells (moves oxygen/waste) - no nucleus
2) Lung cells w/ cilia (hairs) - diffusion of oxygen from lungs to blood stream
2) Lung cells w/ cilia (hairs) - diffusion of oxygen from lungs to blood stream
28
New cards
Examples of the quantity of different organelles affecting cell functions
Smooth ER: detoxify, liver cells have a lot
muscle cells have extra mitochondria
Endosymbiotic theory
muscle cells have extra mitochondria
Endosymbiotic theory
29
New cards
Endosymbiotic theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms (mitochondria and chloroplasts)
30
New cards
Evidence for Endosymbiosis
1. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have a double membrane
2. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own circular DNA (but no nucleus)
3. Mitochondria and chloroplasts divide like bacteria
4. About the same size as bacteria
5. own ribosomes
2. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own circular DNA (but no nucleus)
3. Mitochondria and chloroplasts divide like bacteria
4. About the same size as bacteria
5. own ribosomes
31
New cards
Why are Cells small?
Cells are small so their surface area to volume ratio is large, allowing the entrance of oxygen and food to the whole cell and the release of CO2 and wastes from the whole cell. If the cell is too big, it wouldn't be able to release waste properly/fully.
32
New cards
Diffusion
1) Movement of molecules in a fluid (gas or liquid) from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated
2) movement DOWN its concentration gradient
3) Does not require energy
2) movement DOWN its concentration gradient
3) Does not require energy
33
New cards
Protein Production Steps (17)
1) DNA in nucleus
2) Specific chunk/segment of ATCGs = gene
3) mRNA built from gene (transcription)
4) mRNA comes out from nucleus via nuclear pore
5) Ribosomes clamps onto mRNA, reads in 3 letter sequences
6) Assembles primary structure of protein (translation)
7) Could be a free ribosome (protein free in cytoplasm), done
8) Or could be a bound ribosome
9) Sticks to rough ER, release protein inside, ribosome free again
10) Protein modified in the ER (folding, addition of carbohydrate side chains)
11) Goes to Golgi apparatus via transport vesicle (little pouch of membrane)
12) Vesicle gets "pulled" along via motor proteins on cytoskeletal fibers
13) Vesicle fuses w/ Golgi membrane, releases proteins
14) Golgi modifies and packages proteins
15) Repackaged in other vesicle
16) Motor proteins take to another organelle, cell membrane, or out of cell
17) If exits our of the cell, vesicle fuses to membrane and releases via exocytosis
2) Specific chunk/segment of ATCGs = gene
3) mRNA built from gene (transcription)
4) mRNA comes out from nucleus via nuclear pore
5) Ribosomes clamps onto mRNA, reads in 3 letter sequences
6) Assembles primary structure of protein (translation)
7) Could be a free ribosome (protein free in cytoplasm), done
8) Or could be a bound ribosome
9) Sticks to rough ER, release protein inside, ribosome free again
10) Protein modified in the ER (folding, addition of carbohydrate side chains)
11) Goes to Golgi apparatus via transport vesicle (little pouch of membrane)
12) Vesicle gets "pulled" along via motor proteins on cytoskeletal fibers
13) Vesicle fuses w/ Golgi membrane, releases proteins
14) Golgi modifies and packages proteins
15) Repackaged in other vesicle
16) Motor proteins take to another organelle, cell membrane, or out of cell
17) If exits our of the cell, vesicle fuses to membrane and releases via exocytosis
34
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
35
New cards
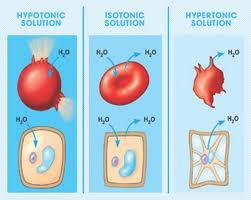
Water balance in cells
Cells can be placed in different solutions
1) Hypotonic: less solute; more water
2) Hypertonic: more solute, less water
3) Isotonic: same solute and water
1) Hypotonic: less solute; more water
2) Hypertonic: more solute, less water
3) Isotonic: same solute and water
36
New cards
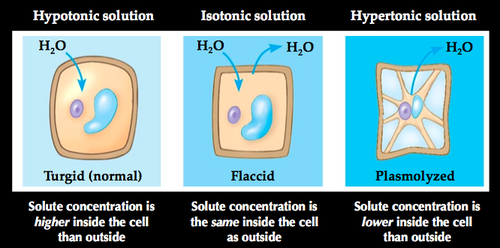
Osmosis Terms
1) Lysed (burst) (hypotonic)
2) Turgid (normal) (hypotonic)
3) Flaccid (isotonic)
4) Plasmolyzed (hypertonic)
2) Turgid (normal) (hypotonic)
3) Flaccid (isotonic)
4) Plasmolyzed (hypertonic)
37
New cards
Water Potential
1) Determined by solute and pressure potential
2) Water moves from regions of high water potential to regions of low water potential
2) Water moves from regions of high water potential to regions of low water potential
38
New cards
Water potential equation
Ψ = Ψs + Ψp
39
New cards
Solute potential
1) Also called osmotic potential
2) Ψs is pressure from membranes/walls as water moves in or out
3) Can be positive or negative
4) Unit = bars ("in an open beaker" = 0 bars)
2) Ψs is pressure from membranes/walls as water moves in or out
3) Can be positive or negative
4) Unit = bars ("in an open beaker" = 0 bars)
40
New cards
Solute potential equation
Ψs = -iCRT
i - ionization constant (NaCl = 2, Sucrose/glucose = 1)
C - molar concentration
R - Pressure constant (.0831 Liter*Bar/Mol*Kelvin)
T - Temperature (in Kelvin)
i - ionization constant (NaCl = 2, Sucrose/glucose = 1)
C - molar concentration
R - Pressure constant (.0831 Liter*Bar/Mol*Kelvin)
T - Temperature (in Kelvin)
41
New cards
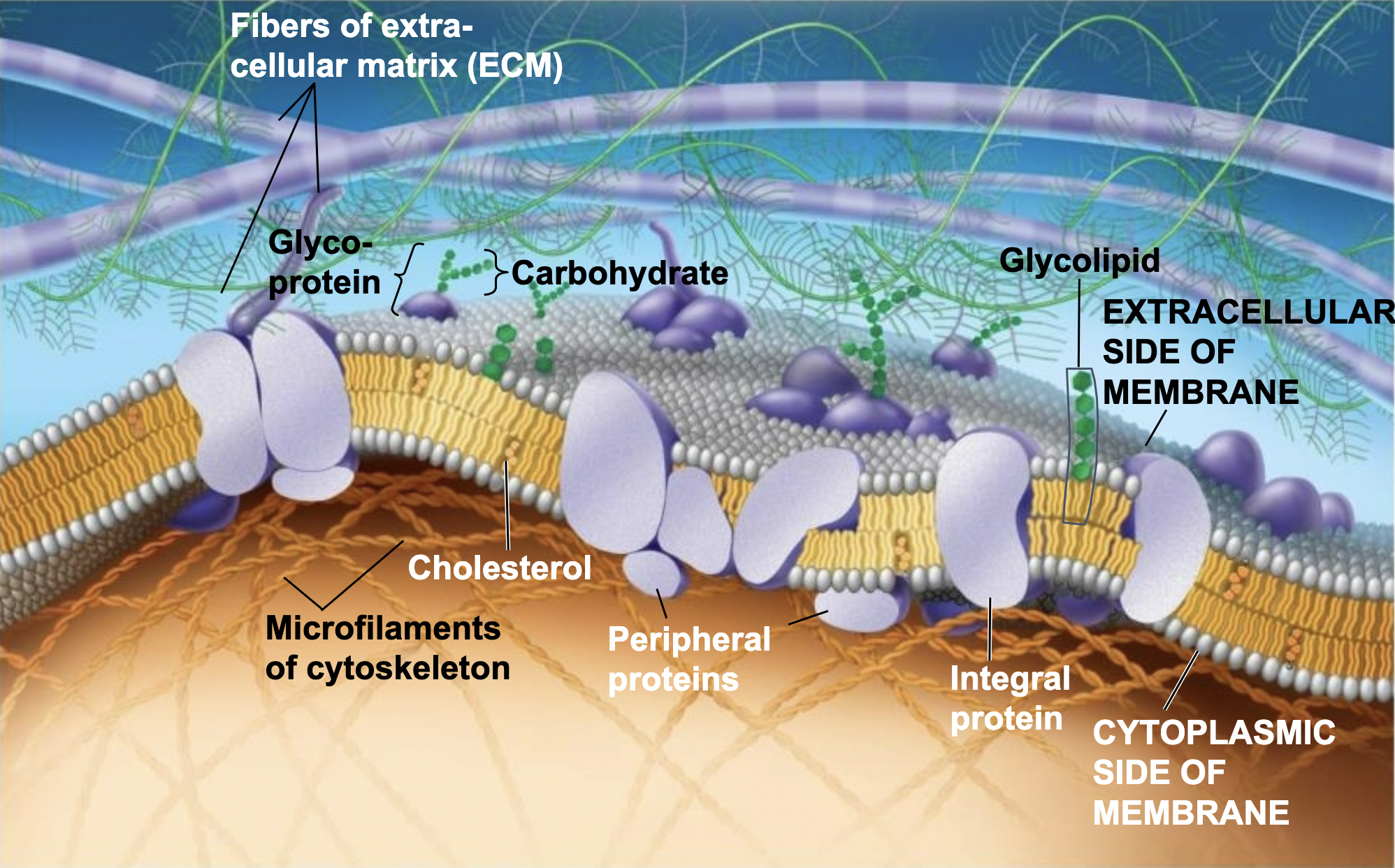
Components of the Cell (plasma) membrane
1) Phospholipids
2) Proteins
3) Carbohydrates
4) Steroids
2) Proteins
3) Carbohydrates
4) Steroids
42
New cards
Phospholipid Bilayer
1) Hydrophilic head
2) Hydrophobic tails
3) Amphipathic (has hydrophobic and philic parts)
2) Hydrophobic tails
3) Amphipathic (has hydrophobic and philic parts)
43
New cards
Membrane Proteins
1) Peripheral proteins: bound to the membrane surface
2) Integral proteins: penetrate the hydrophobic core
2a) transmembrane protein: spans entire membrane
2) Integral proteins: penetrate the hydrophobic core
2a) transmembrane protein: spans entire membrane
44
New cards
Carbohydrate
1) Glycoproteins: oligosaccharides bonded to proteins
2) Glycolipids: oligosaccharides bonded to lipids
Both help with cell to cell recognition
2) Glycolipids: oligosaccharides bonded to lipids
Both help with cell to cell recognition
45
New cards
Steroids
Cholesterol: regulates cell membrane fluidity
46
New cards
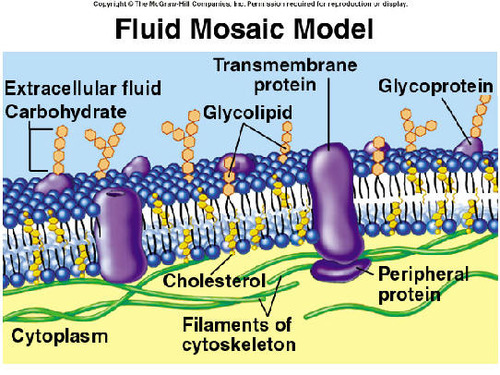
Fluid Mosaic Model
1) Membrane is a "mosaic" of protein molecules in a semi-fluid bilayer of phospholipids
2) Selectively permeable
3) semi-permeable
2) Selectively permeable
3) semi-permeable
47
New cards
Six functions of membrane proteins
1. Transport
2. Enzymatic activity
3. Signal transduction
4. Cell-cell recognition
5. Intercellular joining
6. Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
2. Enzymatic activity
3. Signal transduction
4. Cell-cell recognition
5. Intercellular joining
6. Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
48
New cards
Passive transport
1) No energy required
2) diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer of small, nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules like O2 and CO2
2) diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer of small, nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules like O2 and CO2
49
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion through transport proteins
Can move larger, polar molecules
50
New cards
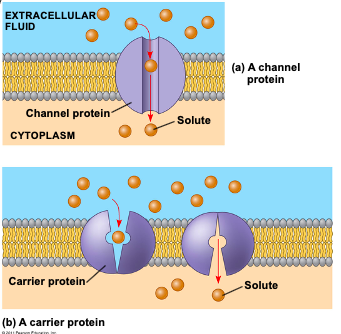
Two types of transport proteins
1) Channel proteins
2) Carrier proteins
2) Carrier proteins
51
New cards
Active Transport
1) Energy required (ATP)
2) Moves substances AGAINST their concentration gradients through transmembrane proteins
2) Moves substances AGAINST their concentration gradients through transmembrane proteins
52
New cards
Bulk Transport
1) Requires energy
2) Moves larger molecules across cell membrane
3) Molecules packaged in transport vesicles
2) Moves larger molecules across cell membrane
3) Molecules packaged in transport vesicles
53
New cards
Exocytosis
1) Moving molecules from inside to outside the cell membrane
2) Vesicle fuses with cell membrane and releases contents outside
2) Vesicle fuses with cell membrane and releases contents outside
54
New cards
Endocytosis
1) Moving molecules form outside to inside the cell membrane
2) New vesicle formed from cell membrane containing molecules to be moved inside membrane
2) New vesicle formed from cell membrane containing molecules to be moved inside membrane
55
New cards
Endocytosis types
1. Phagocytosis
2. Pinocytosis
3. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
2. Pinocytosis
3. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
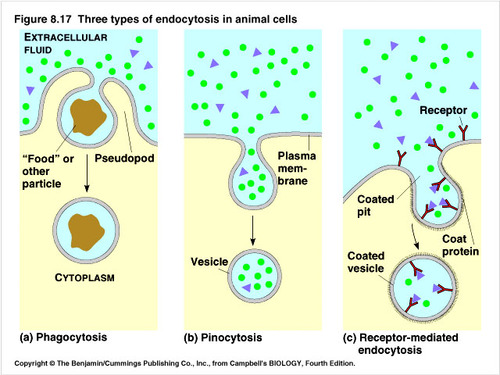
56
New cards
Structures Present in Prokaryotic Cells
1) DNA localized in nucleoid
2) Ribosomes
3) Cell (plasma) membrane
4) cell wall
5) cytoplasm
6) capsule
2) Ribosomes
3) Cell (plasma) membrane
4) cell wall
5) cytoplasm
6) capsule
57
New cards
Difference between nucleoid region and nucleus
Nucleus:
1) Found in eukaryotic cells
2) Stores genetic material
3) Contains several chromosomes
4) Spherically shaped
5) surrounded by double layer membrane
Nucleoid:
1) Found in prokaryotes
2) Stores genetic materials
3) Only one chromosome
4) Irregular shape
5) Doesn't contain any surrounding membrane
1) Found in eukaryotic cells
2) Stores genetic material
3) Contains several chromosomes
4) Spherically shaped
5) surrounded by double layer membrane
Nucleoid:
1) Found in prokaryotes
2) Stores genetic materials
3) Only one chromosome
4) Irregular shape
5) Doesn't contain any surrounding membrane
58
New cards
Proteins synthesized by free ribosomes
Usually stay in cell
59
New cards
Proteins Synthesized by Bound Ribosomes
Usually travel out of cell
60
New cards
Plant vs. Animal Cells
Shape:
Plant - Square-ish
Animal - Varies
Eukaryote or Prokaryote:
Both Eukaryotes
Border:
Plant - Cell Wall and Membrane
Animal - Cell membrane
Mitochondria:
Plant - Yes
Animal - Yes
Chloroplast:
Plant - Yes
Animal - No
Vacuoles
Plant - Large, central, filled with water
Animal - Small, stores various substances
Plant - Square-ish
Animal - Varies
Eukaryote or Prokaryote:
Both Eukaryotes
Border:
Plant - Cell Wall and Membrane
Animal - Cell membrane
Mitochondria:
Plant - Yes
Animal - Yes
Chloroplast:
Plant - Yes
Animal - No
Vacuoles
Plant - Large, central, filled with water
Animal - Small, stores various substances
61
New cards
Organelles only present in plants
1) Chloroplasts
2) Cell Wall
3) central vacuole
2) Cell Wall
3) central vacuole
62
New cards
Organelles only present in animal cells
centriole
63
New cards
Organelles present in both animal and plant cells
1) Nucleus
2) mitochondrion
3) cell (plasma) membrane
4) endoplasmic reticulum
5) golgi apparatus
6) cytoskeleton
2) mitochondrion
3) cell (plasma) membrane
4) endoplasmic reticulum
5) golgi apparatus
6) cytoskeleton
64
New cards
Organelles involved in endosymbiotic theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts
65
New cards
Cell Membrane Components
Phospholipids
Proteins
Glycolipids
Glycoproteins
cholesterol
Proteins
Glycolipids
Glycoproteins
cholesterol
66
New cards
semi-permeable
membranes that allow some substances through but not others
67
New cards
How do molecules move through the membrane
Passive Transport
Active Transport
Active Transport
68
New cards
concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
69
New cards
Nonpolar molecules crossing cell membrane
1)Hydrophobic
2) Can cross easily
3) No transport protein required
2) Can cross easily
3) No transport protein required
70
New cards
Polar Molecules crossing cell membrane
1) Hydrophilic
2) Have difficulty crossing hydrophobic portion of lipid bilayer
3) transport protein required
2) Have difficulty crossing hydrophobic portion of lipid bilayer
3) transport protein required
71
New cards
Ions crossing cell membrane
1) Hydrophilic
2) Have difficulty crossing hydrophobic portion of lipid bilayer
3) transport protein required
2) Have difficulty crossing hydrophobic portion of lipid bilayer
3) transport protein required
72
New cards
exocytosis steps
1) molecules to be secreted rest in a secretory vesicle
2) vesicle fuses with cell membrane
3) contents released outside
2) vesicle fuses with cell membrane
3) contents released outside
73
New cards
endocytosis steps
1) molecules to be moved inside cell membrane travel into a new vesicle formed from the cell membrane
2) vesicle detaches from the cell membrane and brings contents inside
2) vesicle detaches from the cell membrane and brings contents inside
74
New cards
Peroxisomes
1) Break down fatty acids and produce hydrogen peroxide
2) located in the cytoplasm
2) located in the cytoplasm
75
New cards
Motor proteins
moves vesicles to other organelles, cell membranes, or out of the cell