VT 111 Lec. 6 Skeletal System: General & Axial Skeleton
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Divisions of the Skeleton
Axial skeleton:
Skull
Ribs
Vertebral column
Appendicular skeleton:
Pelvic girdle
Pectoral girdle
Appendages
About Bone
Osseous connective tissue
Most rigid type
Well vascularized
Haversian canal
Osteoblasts
Make bone by secreting matrix and then hardening it via ossification
Osteocytes
Osteoblasts that are trapped in ossified matrix
Can revert to osteoblasts if repair needed
Osteoclasts
Break down bone; reshape and remodel
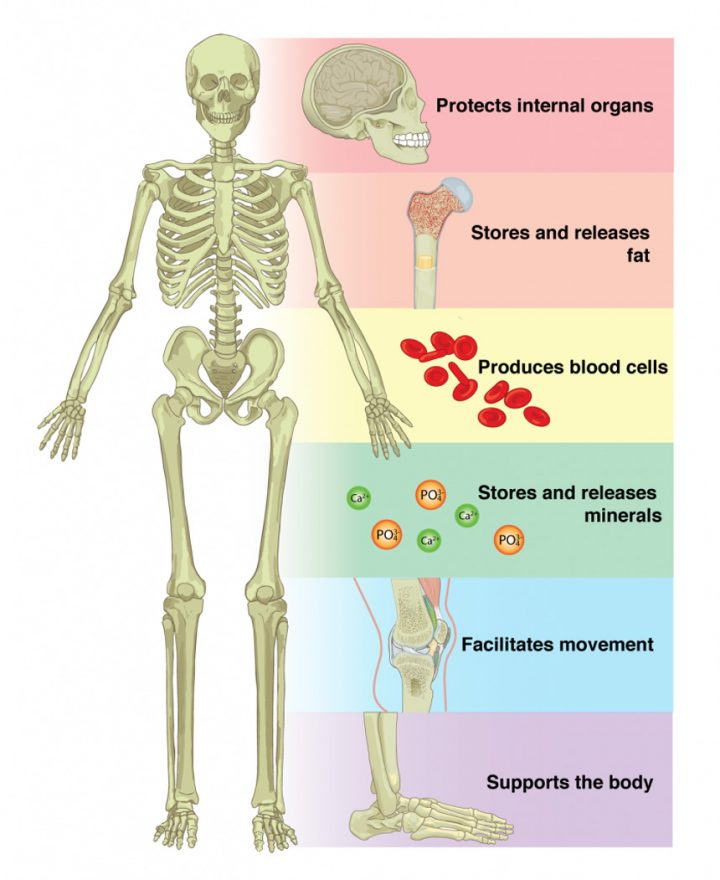
Bone: Functions
Support
Protection
Movement/leverage
Storage
Minerals (Ca++)
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell formation
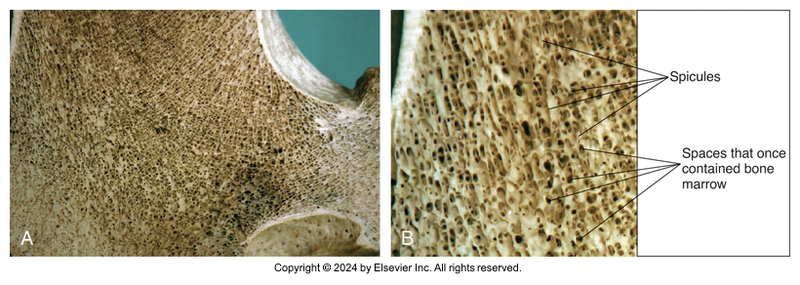
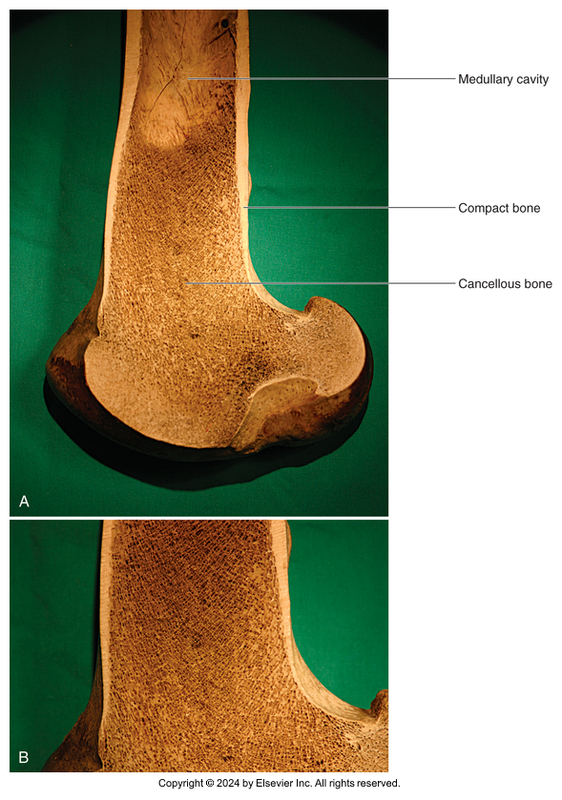
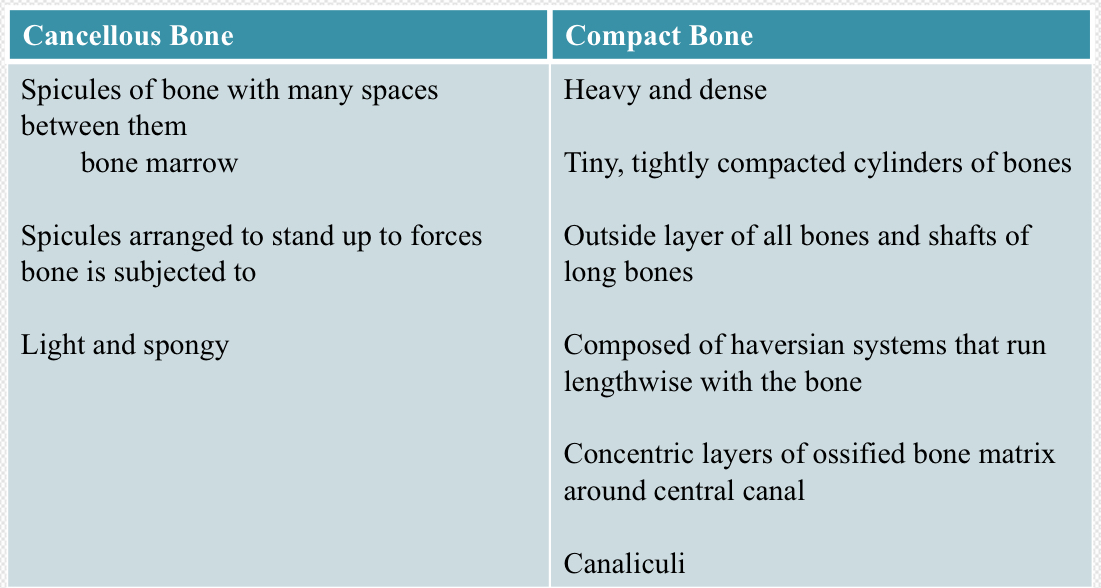
Bone Type Classification: Cancellous Bone
Light, spongy
Many spaces between spicules of bone
Occupied by bone marrow
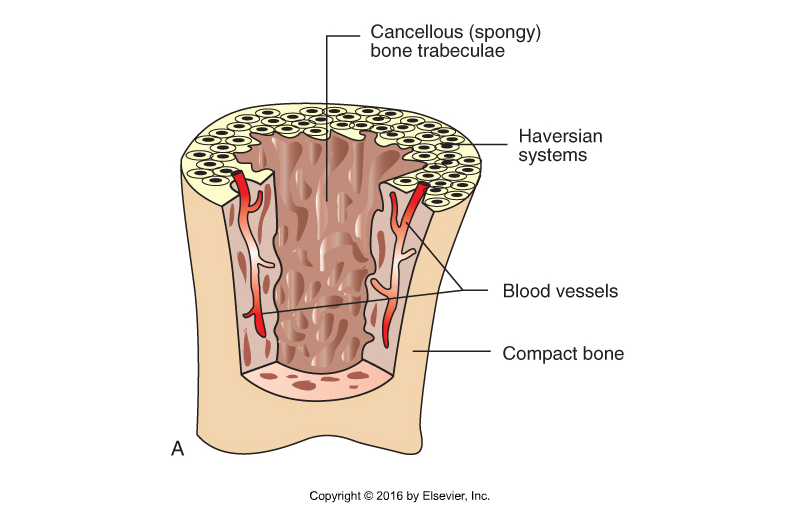
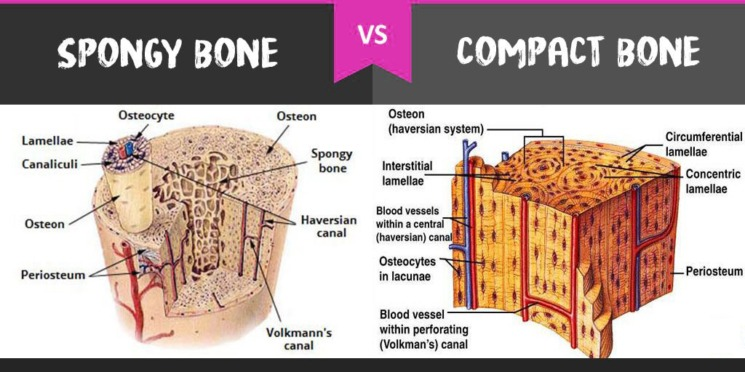
Bone Type Classification: Compact Bone
Heavy, dense
Shafts of long bones and outside layer of all bones
Haversian systems (osteon)
Tightly compacted cylinders of bone surrounding Haversian canal (where blood vessels run)
Run lengthwise to bone
Cancellous vs Compact
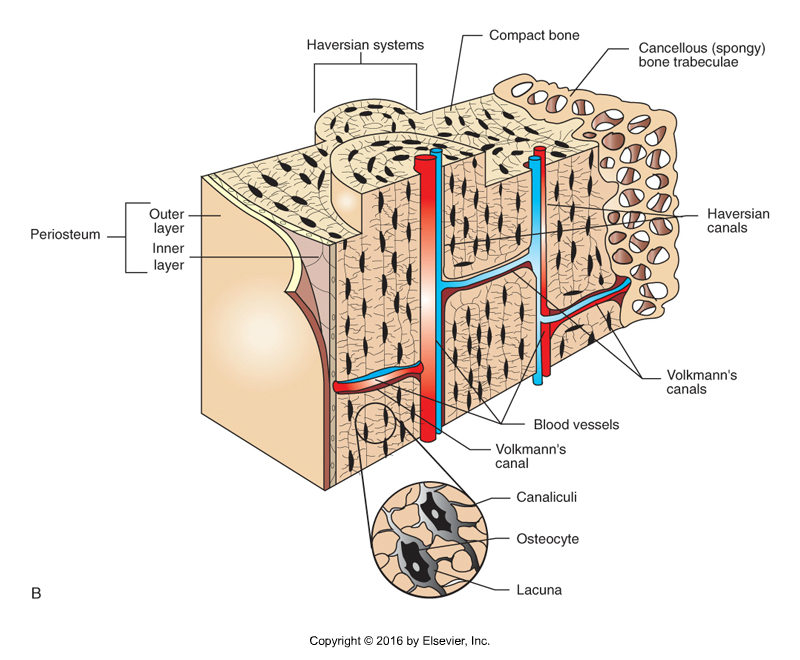
Bone Structure
Periosteum: membrane covers the outer surfaces of bones
Outer layer – fibrous tissue
Inner layer – osteoblasts
Endosteum: membrane lines hollow interior surfaces
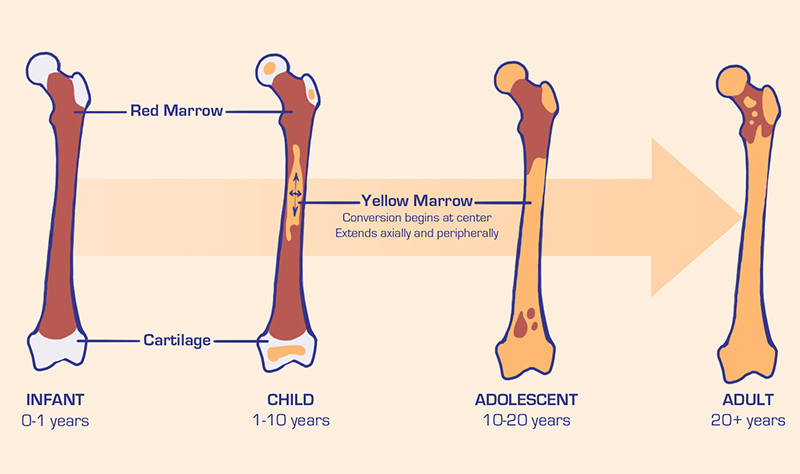
Bone Marrow
Red bone marrow
Hematopoietic
Forms blood cells
Large amounts in young animals
Yellow bone marrow
Adipose connective tissue
Large amount in adult marrow
Can revert to red bone marrow if animal becomes anemic
Brown Growth (Osteogenesis)
Bone formation starts in utero
Bone development continues throughout adulthood
Repair
Remodeling
Two types of ossification:
Intramembranous—forms from fibrous tissue membranes that cover brain in developing fetus
Endochondral—grows from a cartilage template
Endochondral Bone Formation
New bone develops along epiphyseal plates of cartilage located between shaft and ends of bones
Allows long bones to lengthen
Cartilage cells create new cartilage on epiphyseal surface of the plate
Osteoblasts replace cartilage with bone on diaphyseal surface
When bone is full size the epiphyseal plates ossify
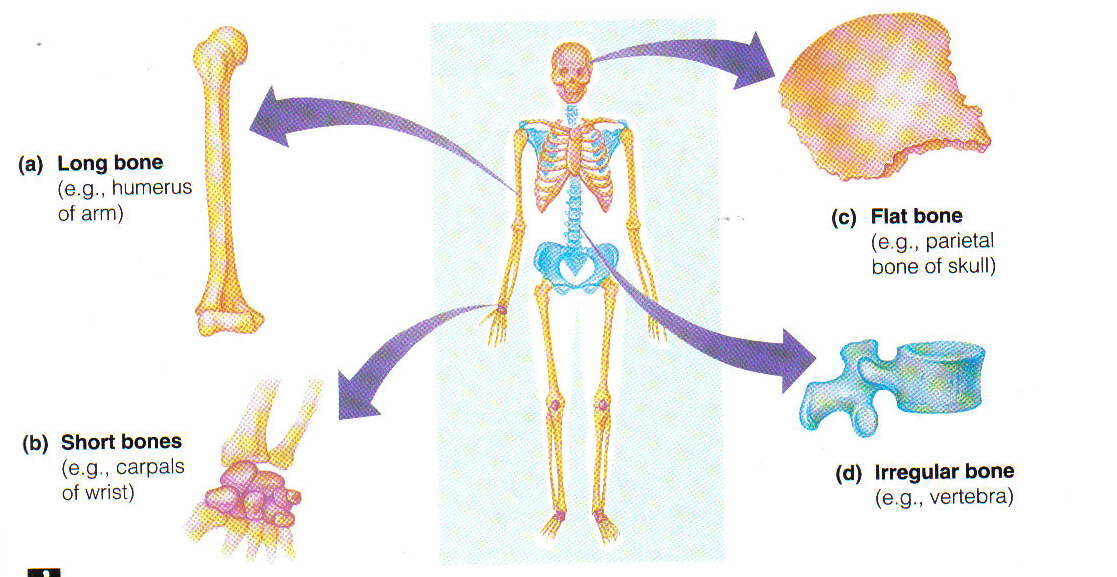
Bone Shapes
Long
Longer than they are wide
Most limb bones
Have Diaphysis is the main part of long bones
Short
Shaped like small cubes
Examples include carpal and tarsal bones
Flat
Relatively thin and flat
Many skull bones, scapulae, and pelvic bones are flat
Irregular
Miscellaneous category
All bones that don’t fit other categories
Examples include vertebrae, some skull bones, and sesamoid bones

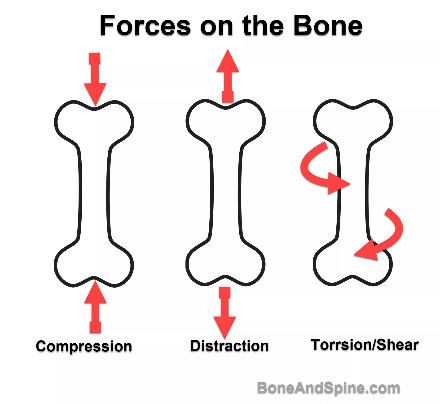
Forces Placed Upon Bones
Compression: force placed on bone along the long axis of the shaft toward an object
Tension/distraction: force that tends to pull the ends of bone apart along the long axis
Torsion: twisting force on bone
Shearing: parallel forces in opposite direction, usually perpendicular to the long axis of a bone
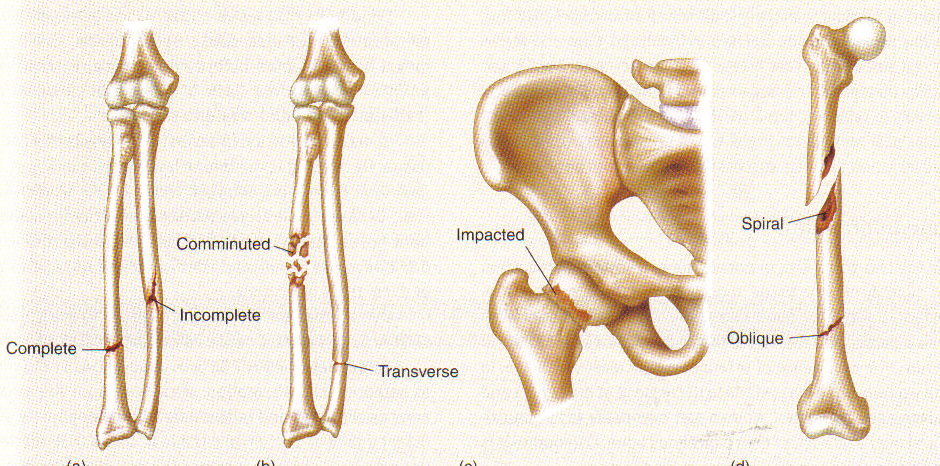
Fracture Types: Complete Fracture
Transverse: fracture line transverse to long axis
Oblique: fracture line oblique to long axis
Spiral: torsional forces fracture bone; spirals along long axis; edges of fracture are very sharp
Comminuted: fragmented into 3 or more pieces; fracture lines interconnect
Multiple: 3 or more fracture fragments, but the lines do not connect
Impacted: bone ends are forced into each other
Compression: cancellous bone (vertebrae) is crushed
Fracture Types: Incomplete Fracture
Greenstick: incomplete break
Fissure: crack on long or flat bone as a result of direct pressure
Depression: bone is depressed inward; multiple fissures lines intersect
Fracture Type: Simple/Closed
No skin penetration of bone
Fracture Type: Compound/Open
Bone broken ends protrude through skin
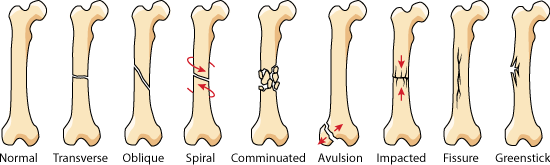
Epiphyseal Plate Fractures
Immature animals
Salter-Harris classification
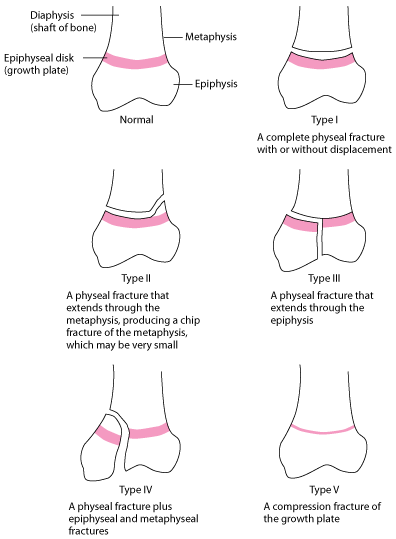
Fracture Repair
Osteoblasts gradually bridge fracture gap
Mineralization
To return bone to original size and shape
Axial & Appendicular Skeletons
Bone Terminology
Holes
Foramen
Plural foramina
Sunken area
Fossa
Groove
sulcus
Flat articular surface
Facet
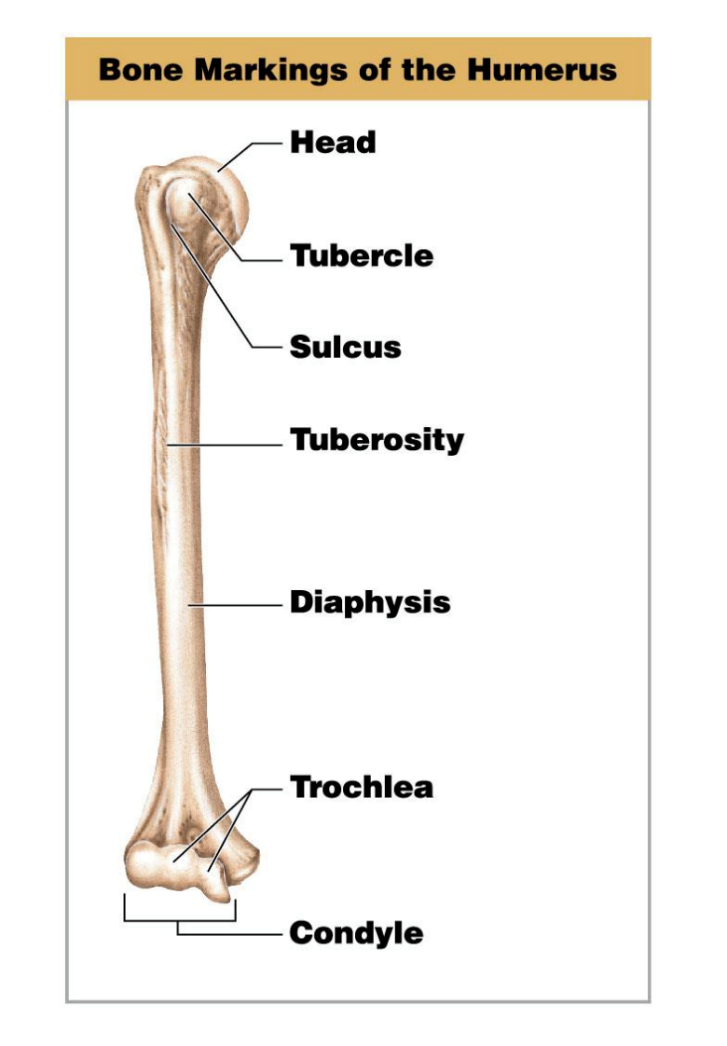
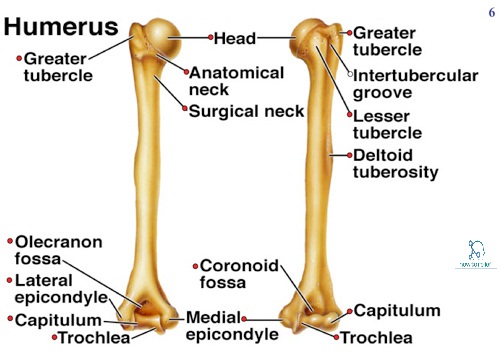
Bone Processes
Any and all projections on bones
Head
Condyle
Epicondyle
Process
Trochanter
Spine
Crest
Wing
Trochlea
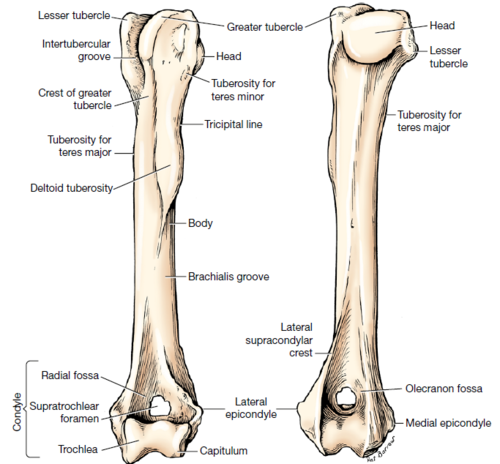
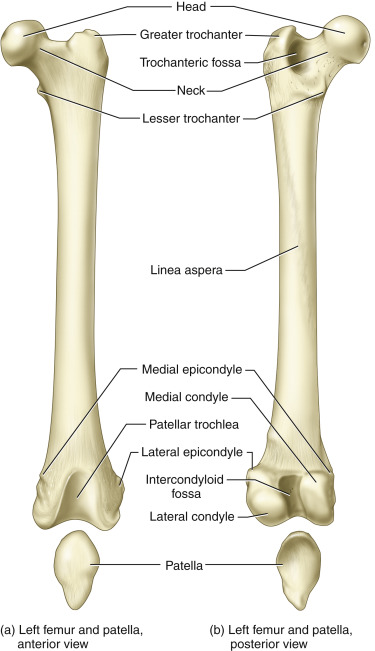
Condyle vs Epicondyle
Condyle:
a rounded protuberance at the end of some bones
forms an articulation with another bone
smooth surface
Epicondyle:
a protuberance above or on the condyle of a long bone
site for attachment of muscles
rough surface
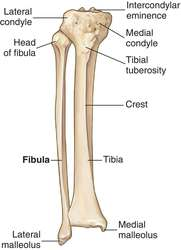
Tuberosity vs Tubercle
Tuberosity: a large prominence on a bone usually serving for the attachment of muscles or ligaments
Tubercle: a small rounded projection or protuberance, especially on a bone
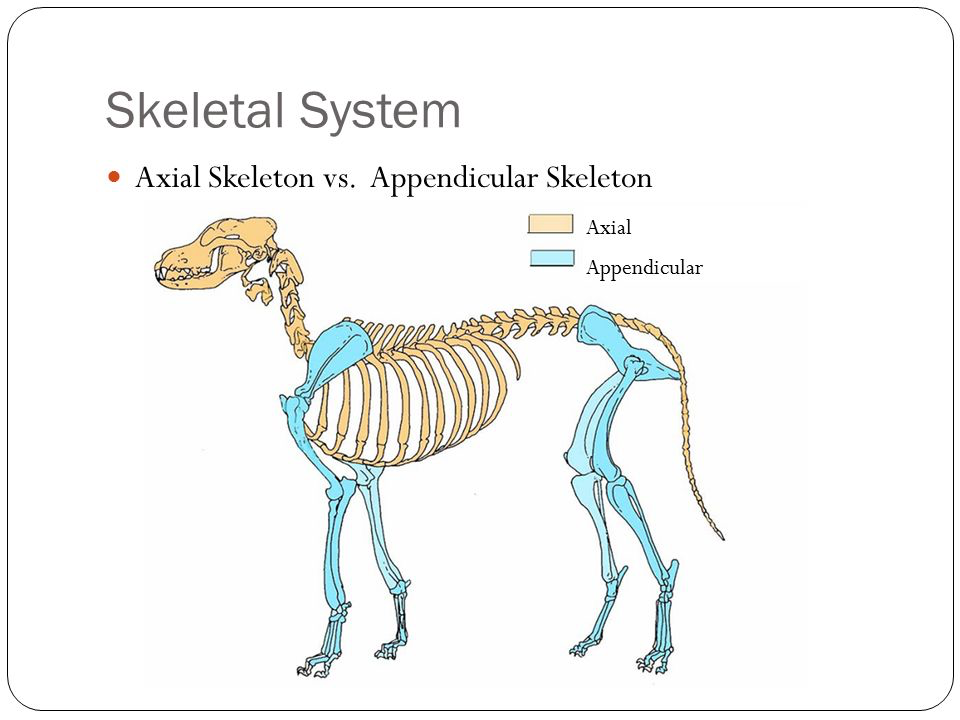
Components of the Axial Skeleton
Axial: bones of head and trunk
Skull
Cranial and Facial
Mandible
Spinal column
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacrum
Caudal
Ribs
Sternum
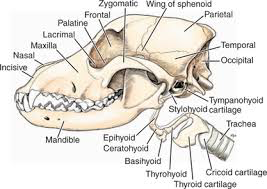
Skull
~38 bones united by sutures which are immovable, fibrous joints
The mandible is connected to the skull by a freely movable synovial joint
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Skull is divided into regions: cranial, facial, ear
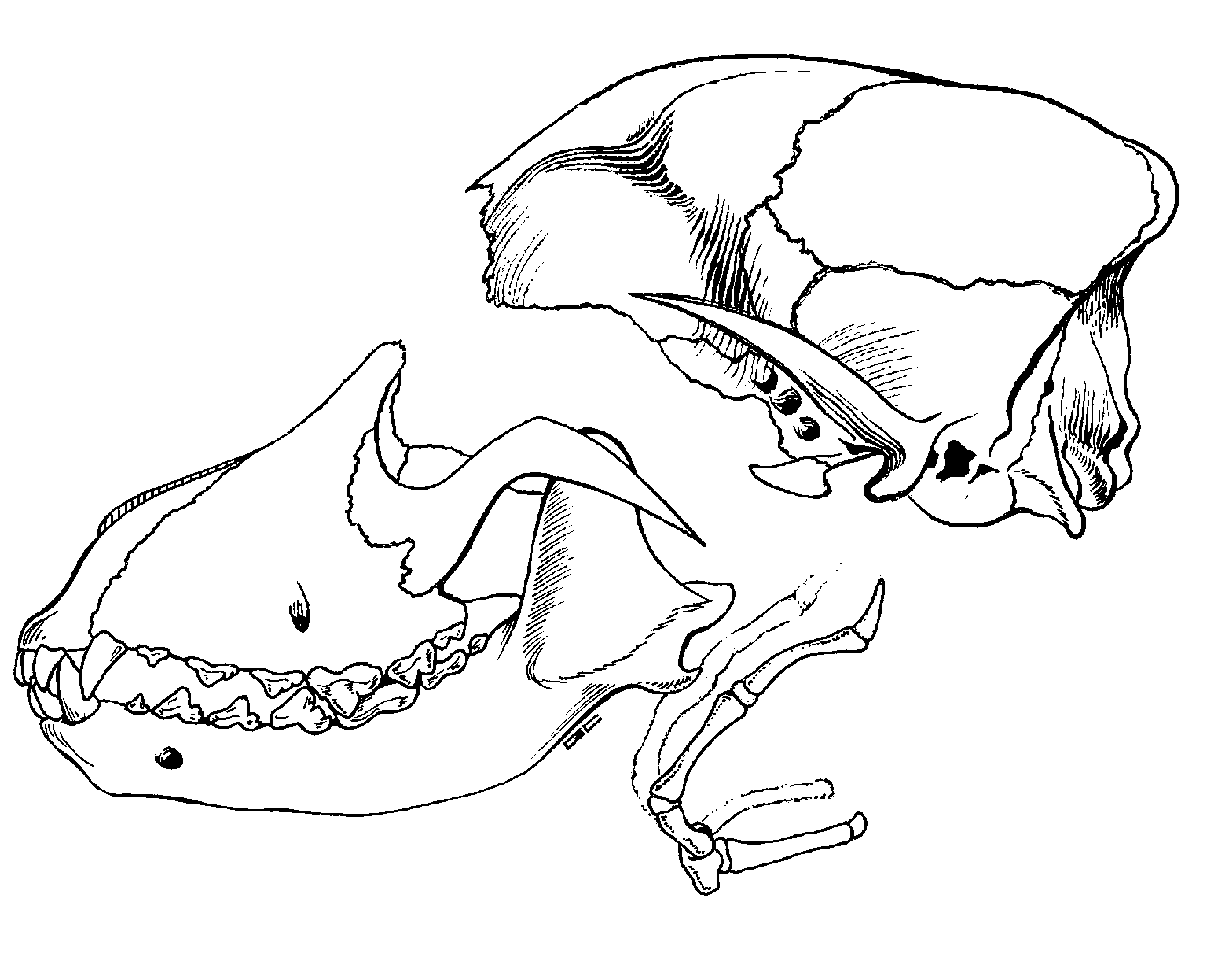
Cranial Bones: External
Occipital (1)
Interparietal (2)
Parietal (2)
Temporal (2)
Frontal (2)
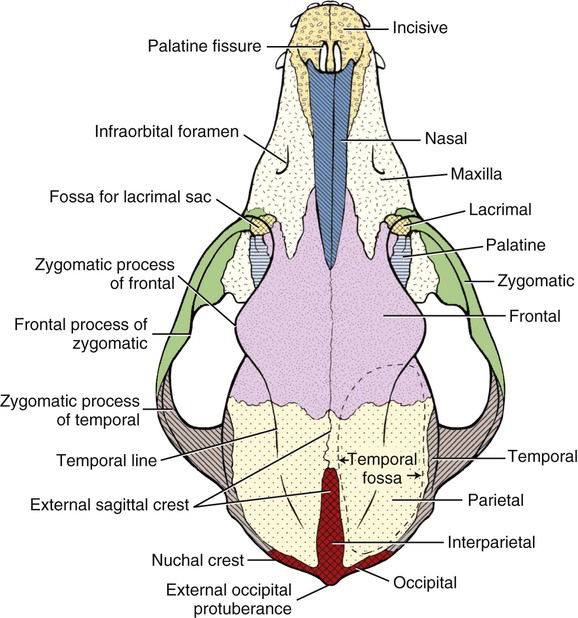
External Skull
Occipital
Base of skull
Most caudal
Where spinal cord exits
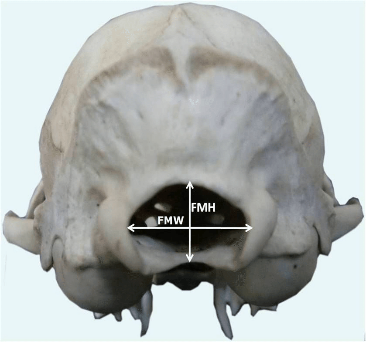
Foramen magnum
Forms a joint with C1
Occipital condyles articulate with atlas(C1)
Interparietal
Dorsal midline between occipital and parietal
May fuse with age
Parietal
Forms dorsolateral walls of cranium
Small in horses/cattle
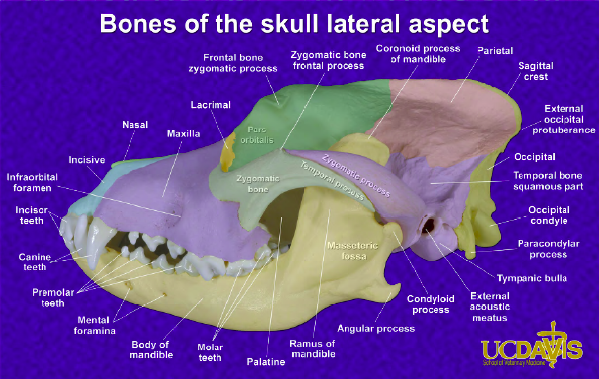
External Skull Continued…
Temporal
Form lateral walls of cranium
Contain middle and inner ear structures
External acoustic meatus
Forms temporomandibular joint (TMJ) with mandible
Frontal
Forehead region
In front of parietal bones
Concave portion of orbit
Contain frontal sinus
Horned animals – cornual process
Horn core; communicates with frontal sinus
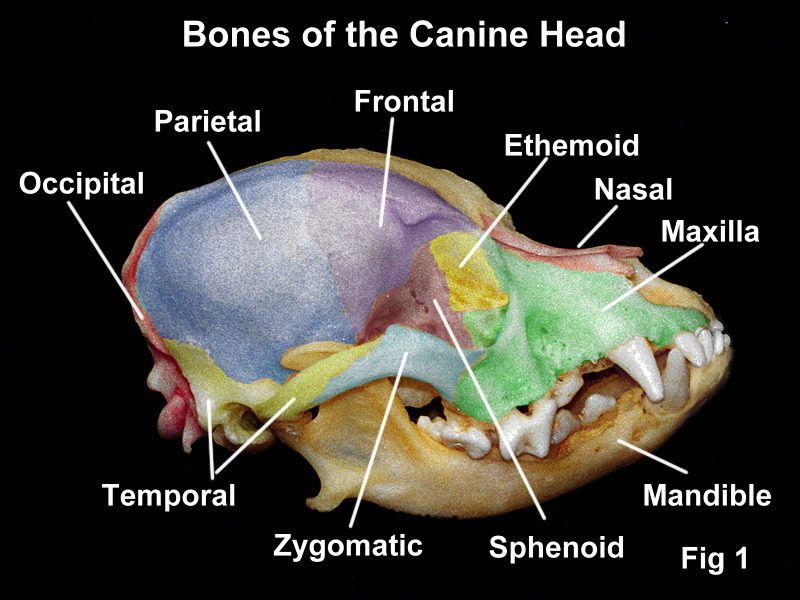
Skull: Internal View
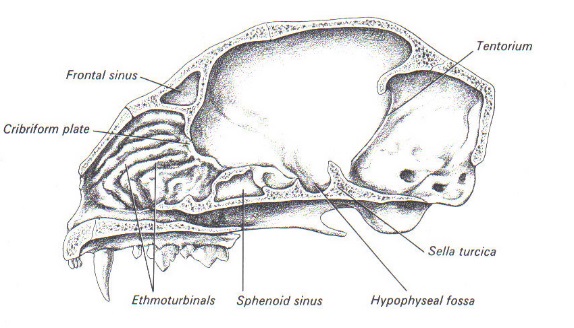
Ethmoid (1)
Separates nasal cavity from brain
Forms part of medial orbit wall
Cribriform plate
Passage of olfactory nerve branches
Sphenoid (1)
Bottom of cranium rostral to occipital bone
Bat shaped
Has pituitary fossa
Sella turcica
What lives here???
Difference Among Species
Horse
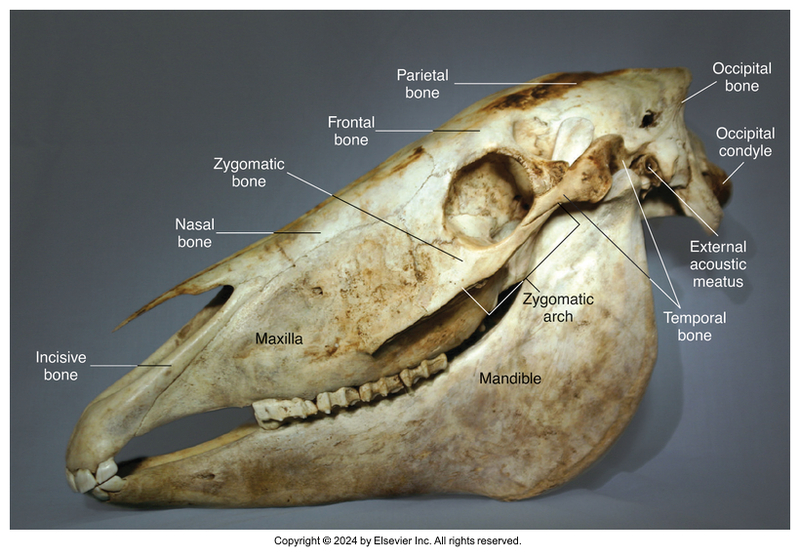
Facial Bones: External
Incisive (2)
Nasal (2)
Maxillary (2)
Lacrimal (2)
Zygomatic (2)
Mandible (1)
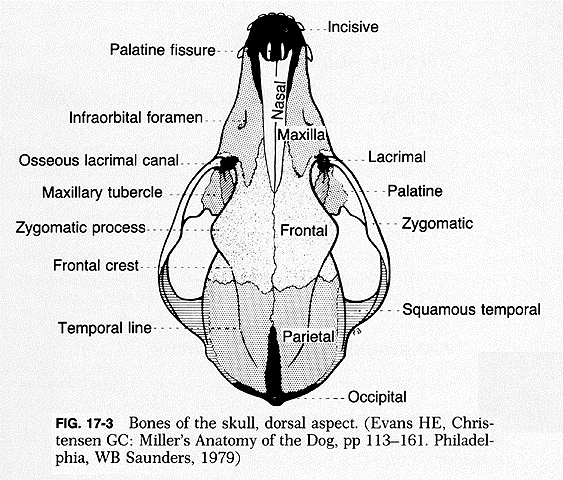
External Facial Bones
Incisive
AKA premaxillary
Most rostral
House upper teeth
Exceptions → ruminants
Nasal
Bridge of nose (dorsal nasal cavity)
Shape depends upon length of face
Dolichocephalic vs. brachycephalic
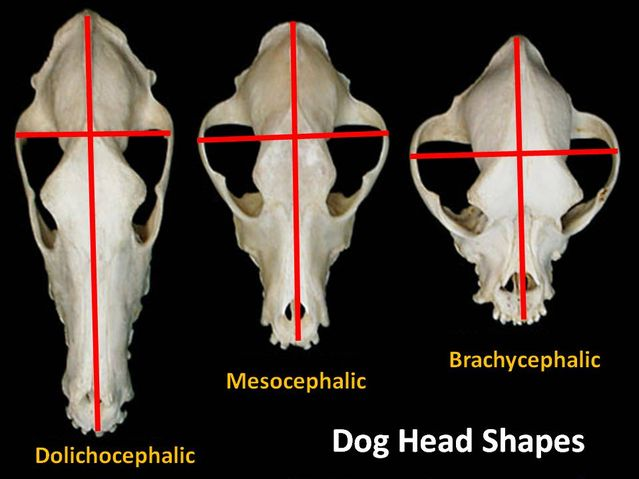
External Facial Bones Continued…
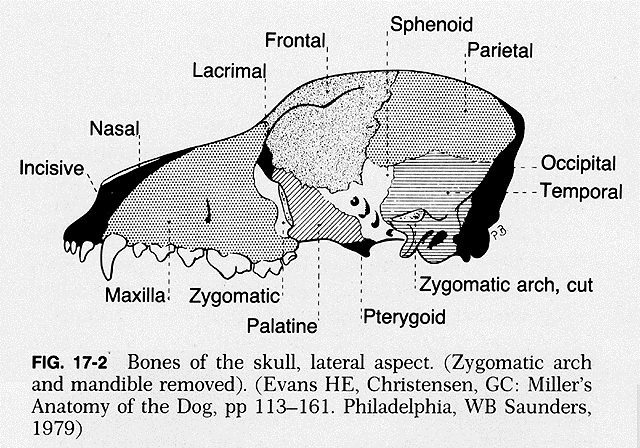
Maxillary
Upper jaw (with incisive)
Upper canines, PM’s and M’s
Maxillary sinuses
Hard palate (separates mouth and nasal cavity)
Infraorbital foramen
Lacrimal
Medial portion of orbit
Zygomatic
Forms portion of orbit
Join with portion of temporal bone process to make zygomatic arch
Internal Facial Bones
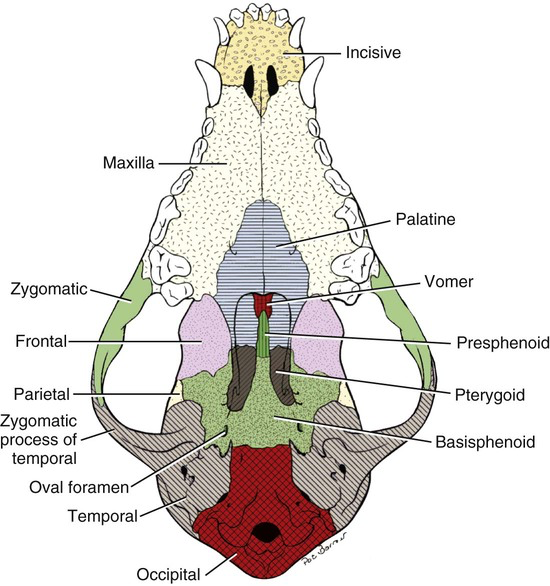
Palatine (2)
Caudal portion of hard palate
Pterygoid (2)
Support lateral pharynx
Vomer (1)
Midline
Forms part of nasal septum
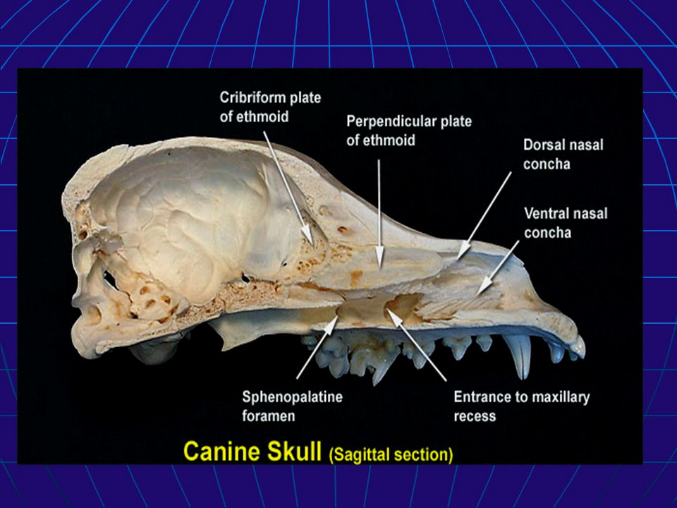
(Ethmo)turbinates (4)
AKA nasal turbinate or conchae
Thin, scroll-like bones that fill nasal cavity
Covered in nasal epithelium
Cleans, humidifies and warms air before lungs
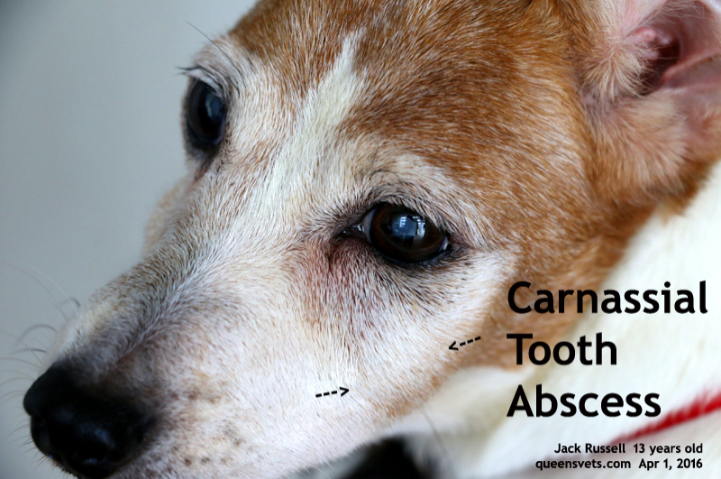
Clinically Important Areas of the Face
Carnassial tooth abscesses
Zygomatic arch fractures
Fractured maxillae
Fractured mandibles
Separation of mandibular symphysis
Mandibular symphysial fracture
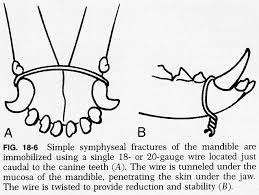
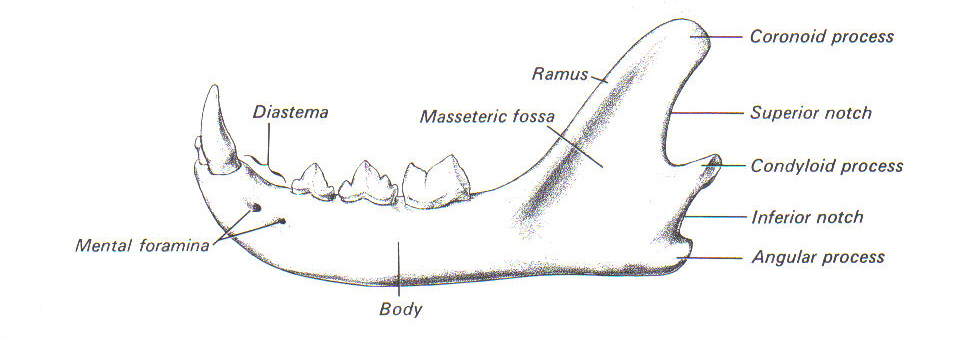
Mandible
Houses all lower teeth
Only movable skull bone
Forms TMJ with temporal bone on each side
2 sides fused at mandibular symphysis at rostral end
Joint is cartilaginous: amphiarthrosis
Dogs, cats, cattle
Ramus is site of jaw muscle attachment
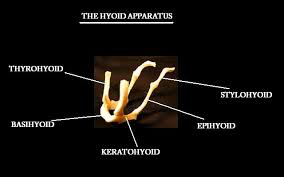
Hyped Bone
AKA hyoid apparatus
Located just above larynx
Made up of several small bones untied by cartilage
Supports base of tongue, pharynx and larynx
Aids in swallowing
Attached to temporal bone
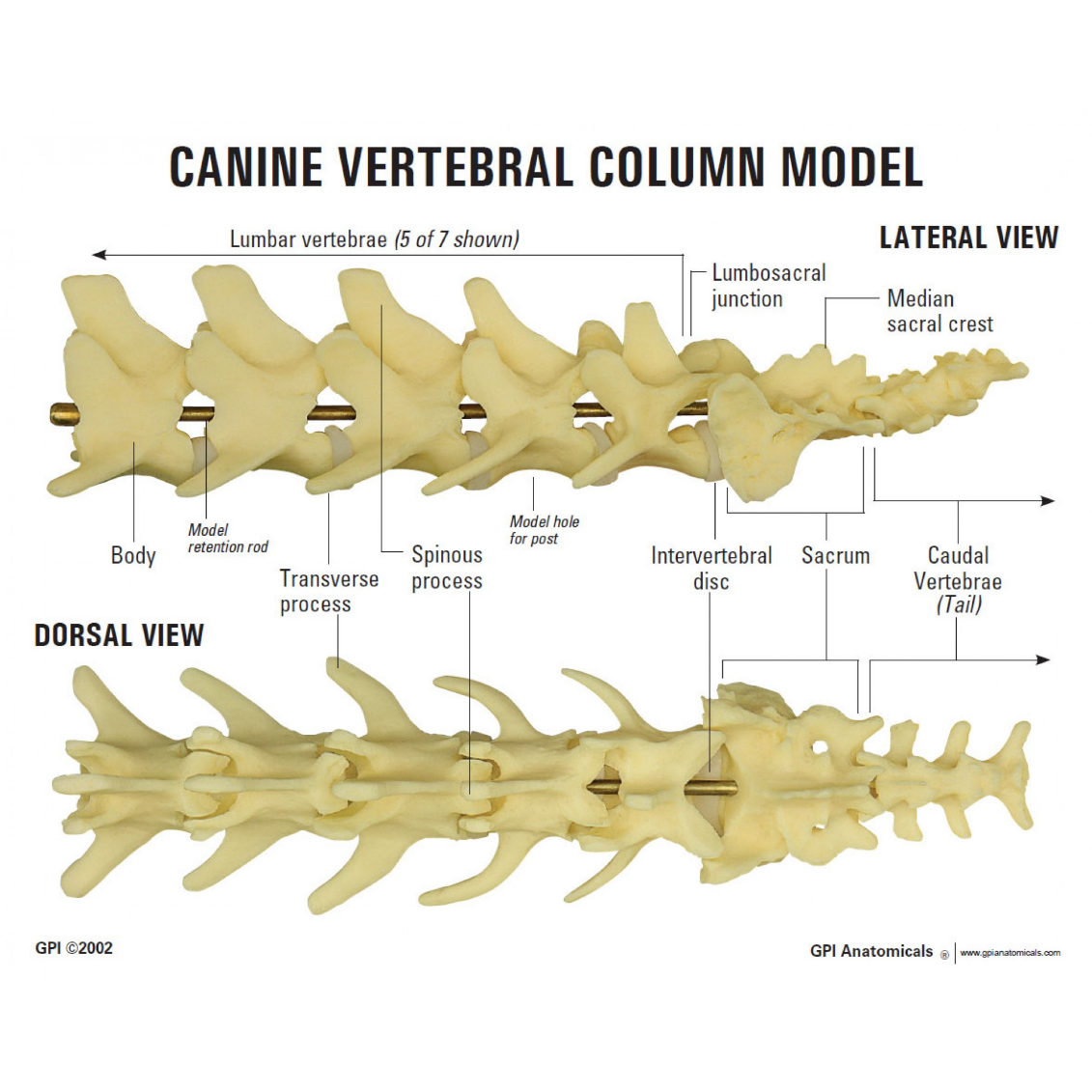
Spinal Cord: Vertebrae
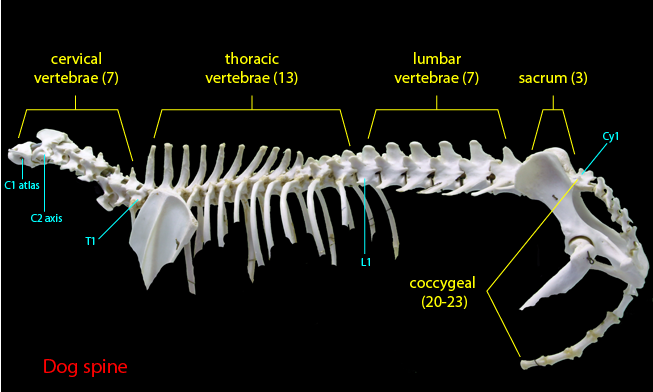
Vertebral formulae of dog
Cervical 7
Thoracic 13
Lumbar 7
Sacral 3
Coccygeal - varies; tail length
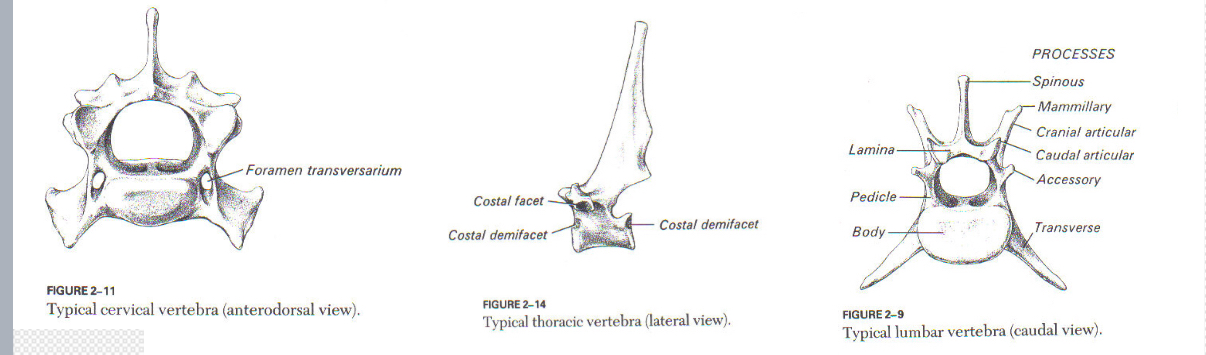
Cervical, Thoracic & Lumbar
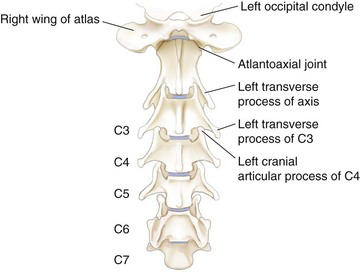
Cervical
Constant number among mammalian species (7)
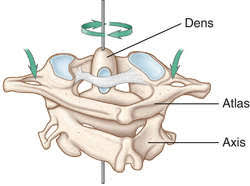
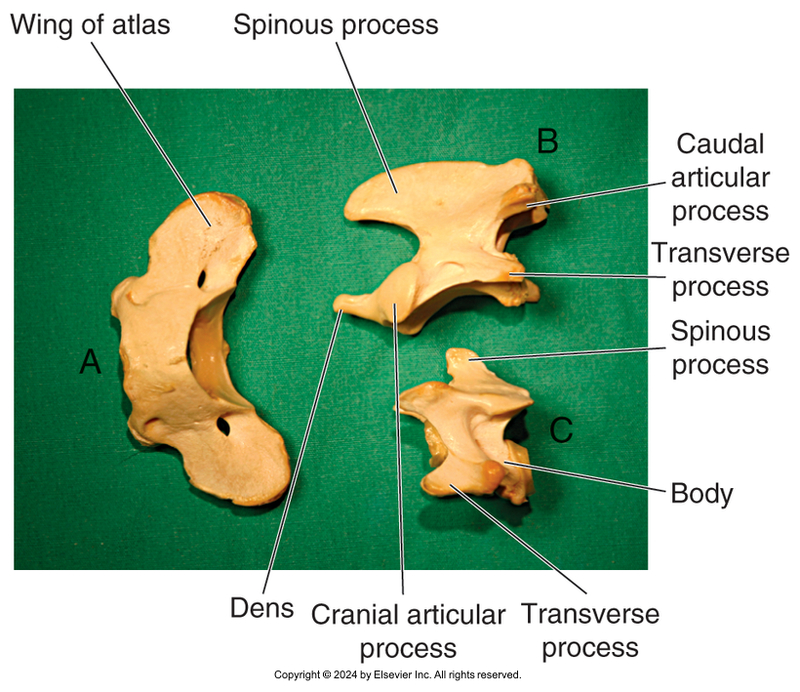
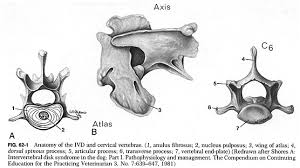
C1 = atlas
articulates with occipital condyles
wings, but no vertebral body
C2 = axis
dens
Cervical Continued…
Thoracic
Tall spinous processes
Lateral articular facets
Form joints with head of ribs
Number varies among species
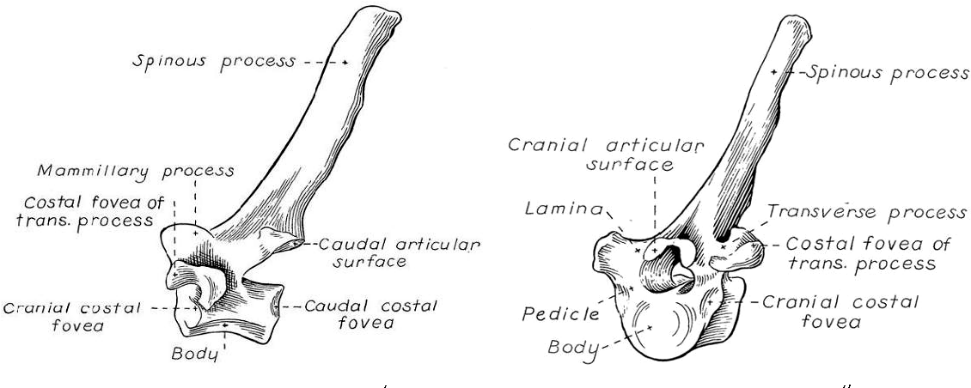
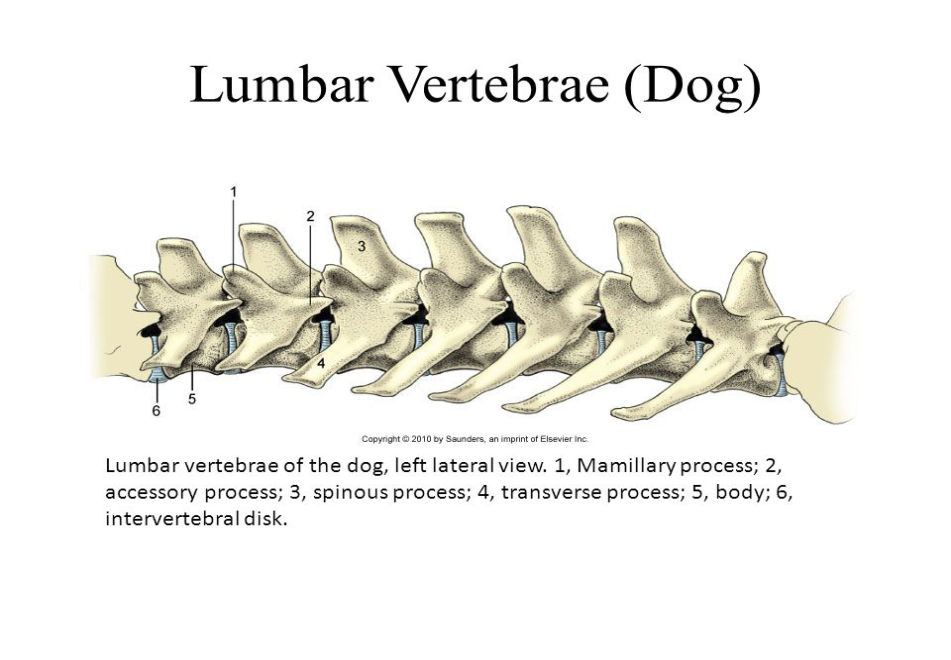
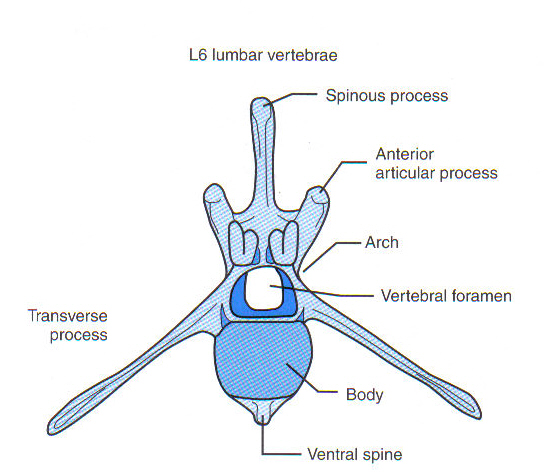
Lumbar
Large and bulky
Support weight of abdominal organs and structures
Number varies by species
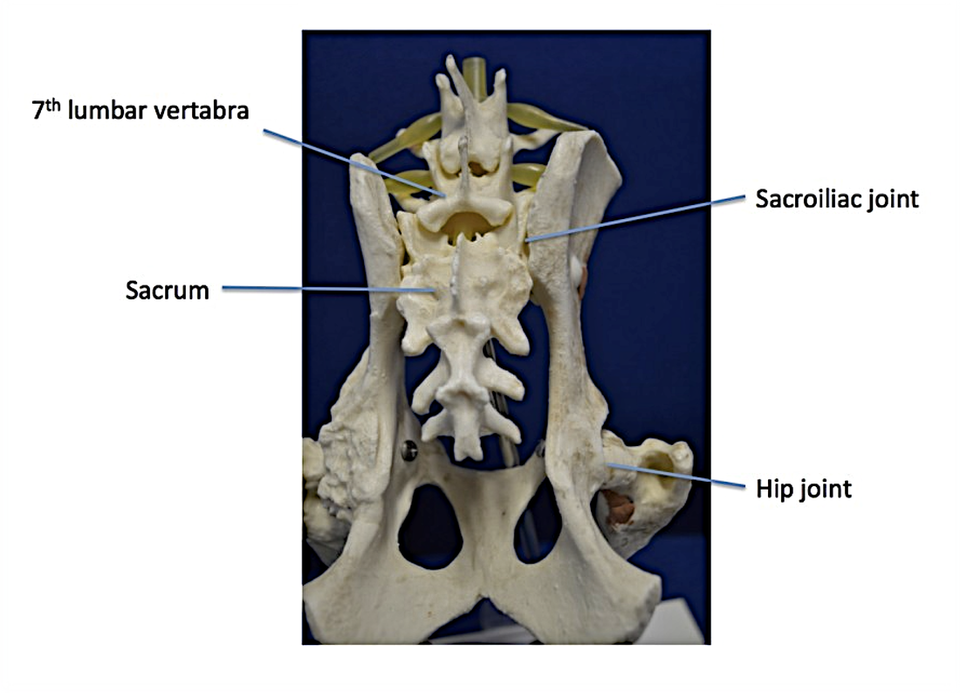
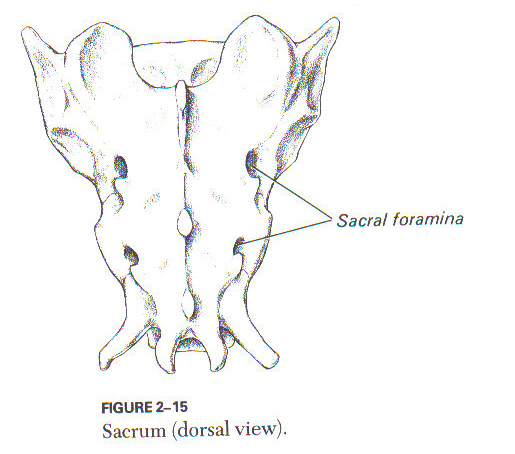
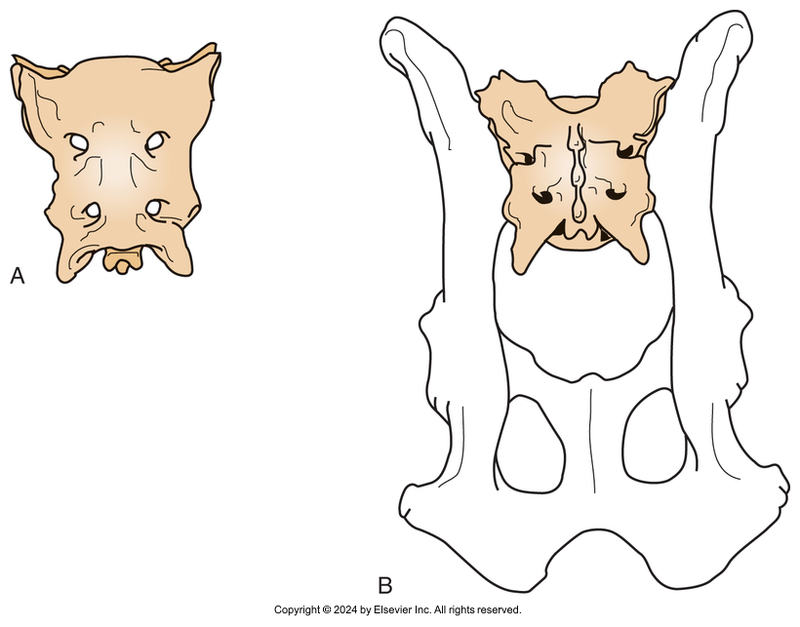
Sacrum
Fused vertebrae
Solid platform to connect to ilium
Sacral foramina
passage of nerves
Sacroiliac joint
articulation between sacrum and pelvis
Fibrocartilaginous
Most species number 3-5 (fused vertebrae)
Sacroiliac Joint
Coccygeal/Caudal
Tail
Number varies among and within species
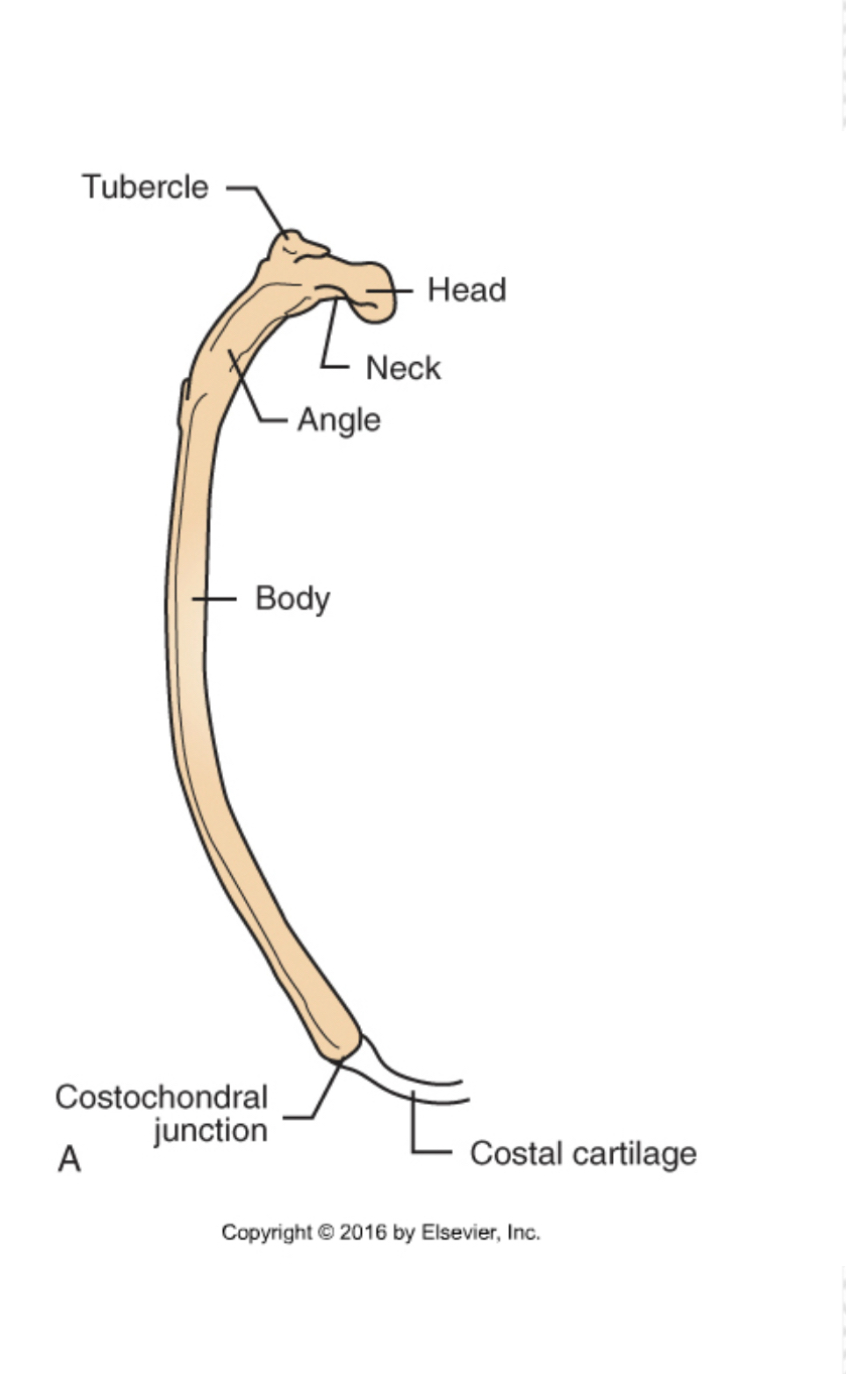
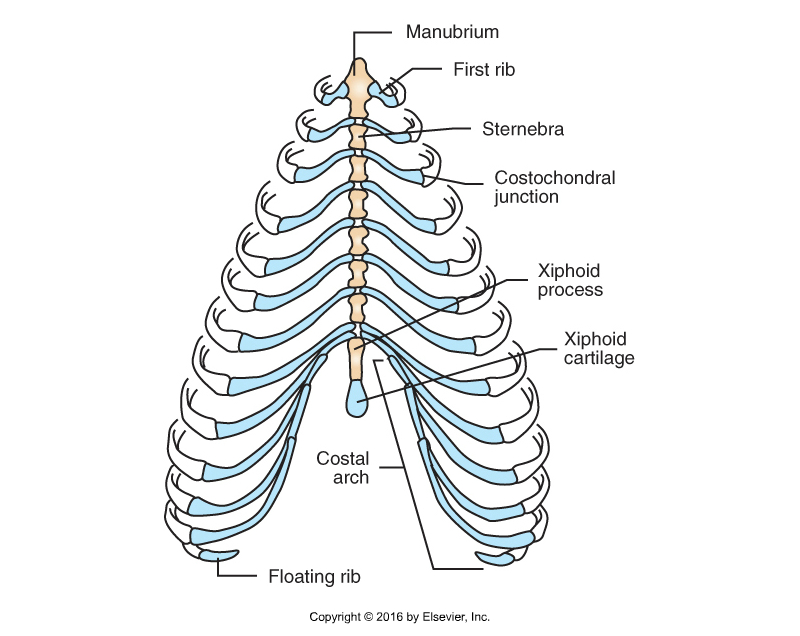
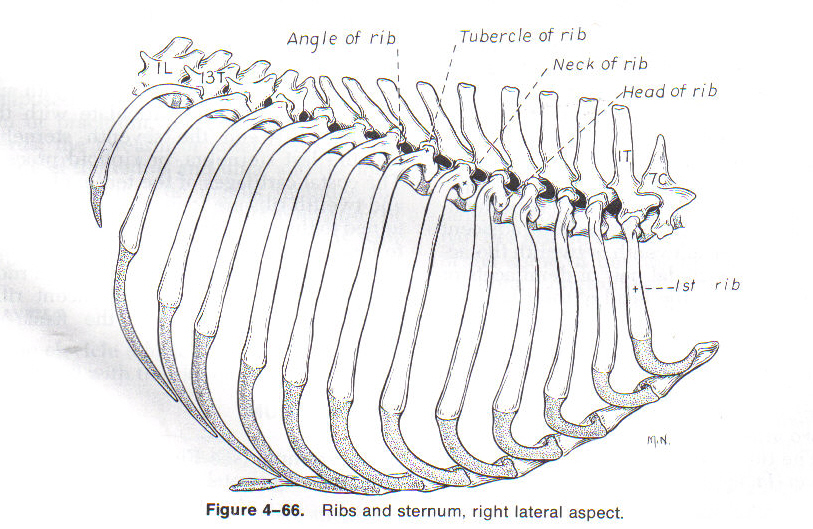
Ribs (Costals)
13 ribs in dog
13th rib is floating
Form walls of thorax
Heads form joints with thoracic vertebrae
Freely movable – allow expansion of chest wall
Dorsal part
Bone
Ventral part
Costal cartilage
Dorsal and ventral part joined by costochondral junctions
Ends of costal cartilage attach to sternum, adjacent costal cartilage (asternal ribs) or nothing (floating ribs)
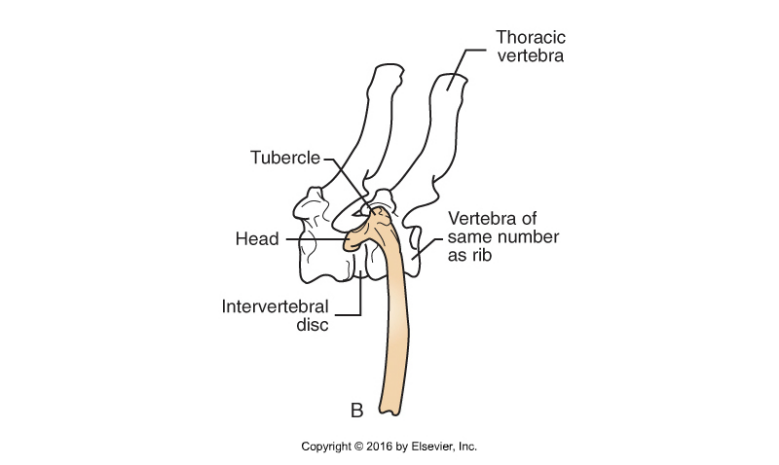
Ribs
Sternum
AKA breastbone
Forms floor of thorax
Formed of sternebrae
1st: manubrium
Last: xiphoid process
Has extension of cartilage - xiphoid cartilage