A&P 1 Nervous System Lab Practical
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Main Regions of the brain
Cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum and brain stem
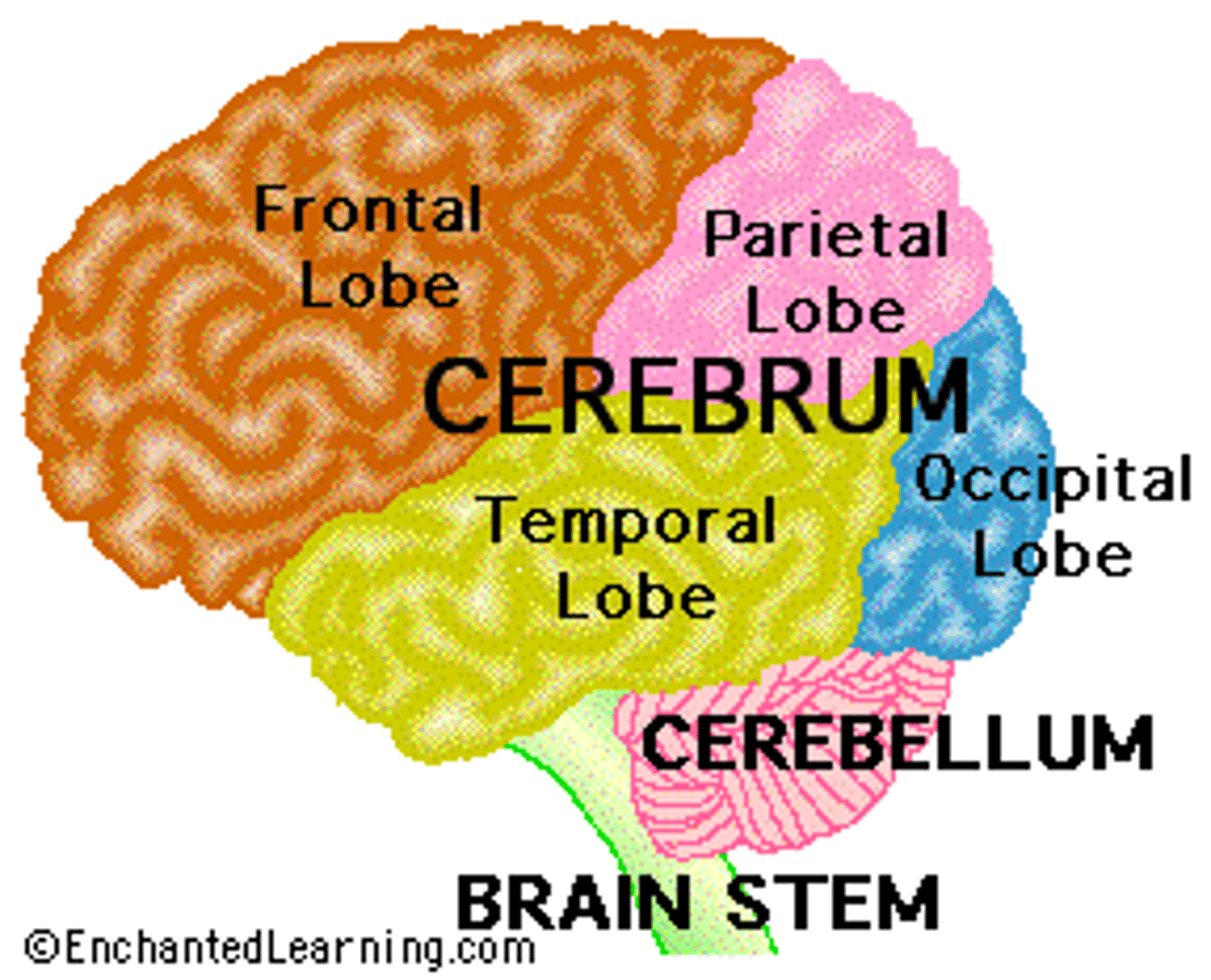
Cerebrum
top, biggest part, thinking
Cerebral Hemispheres
left and right halves of the brain
Corpus Callosum
Fibers connecting both halves of the brain, c shaped structure
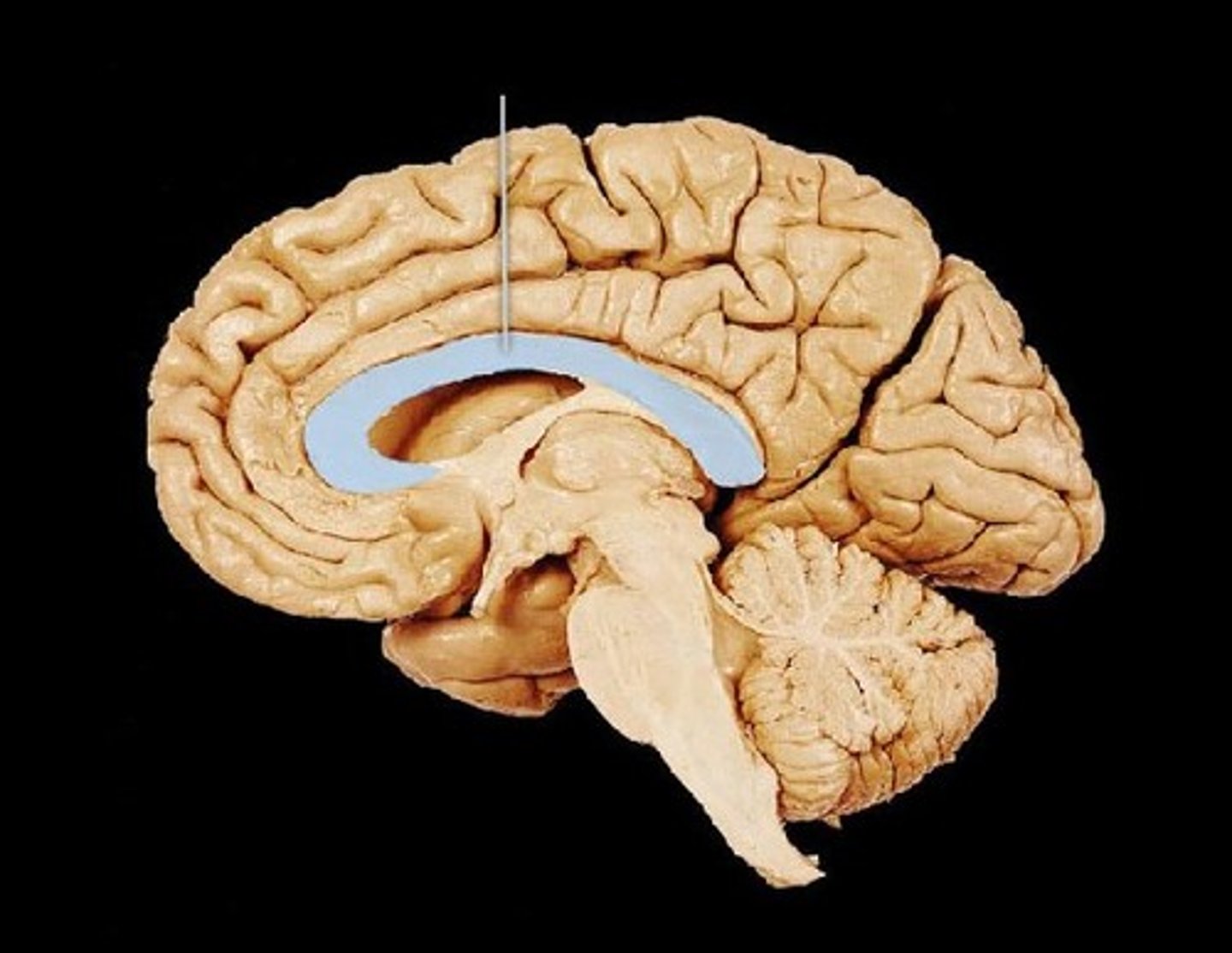
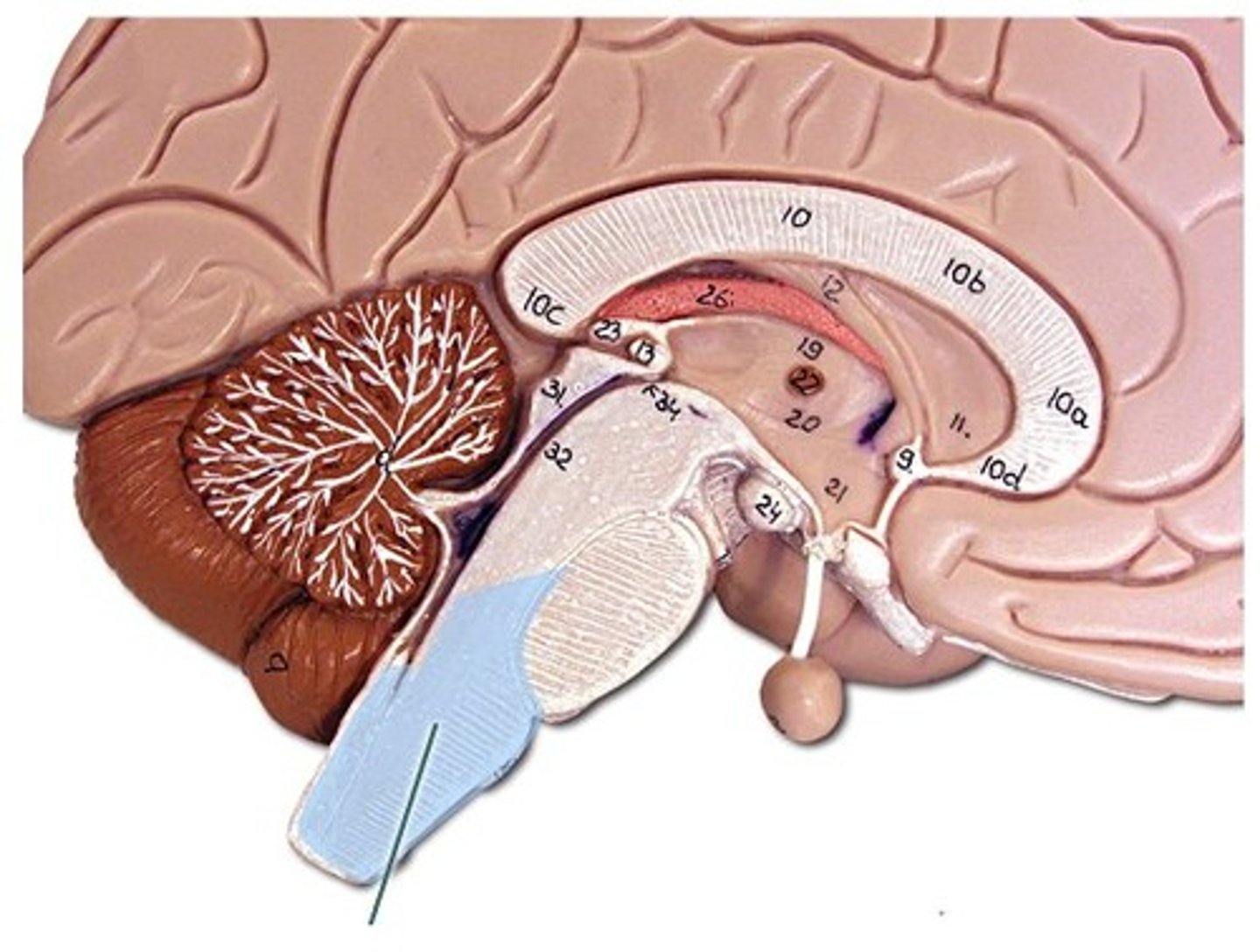
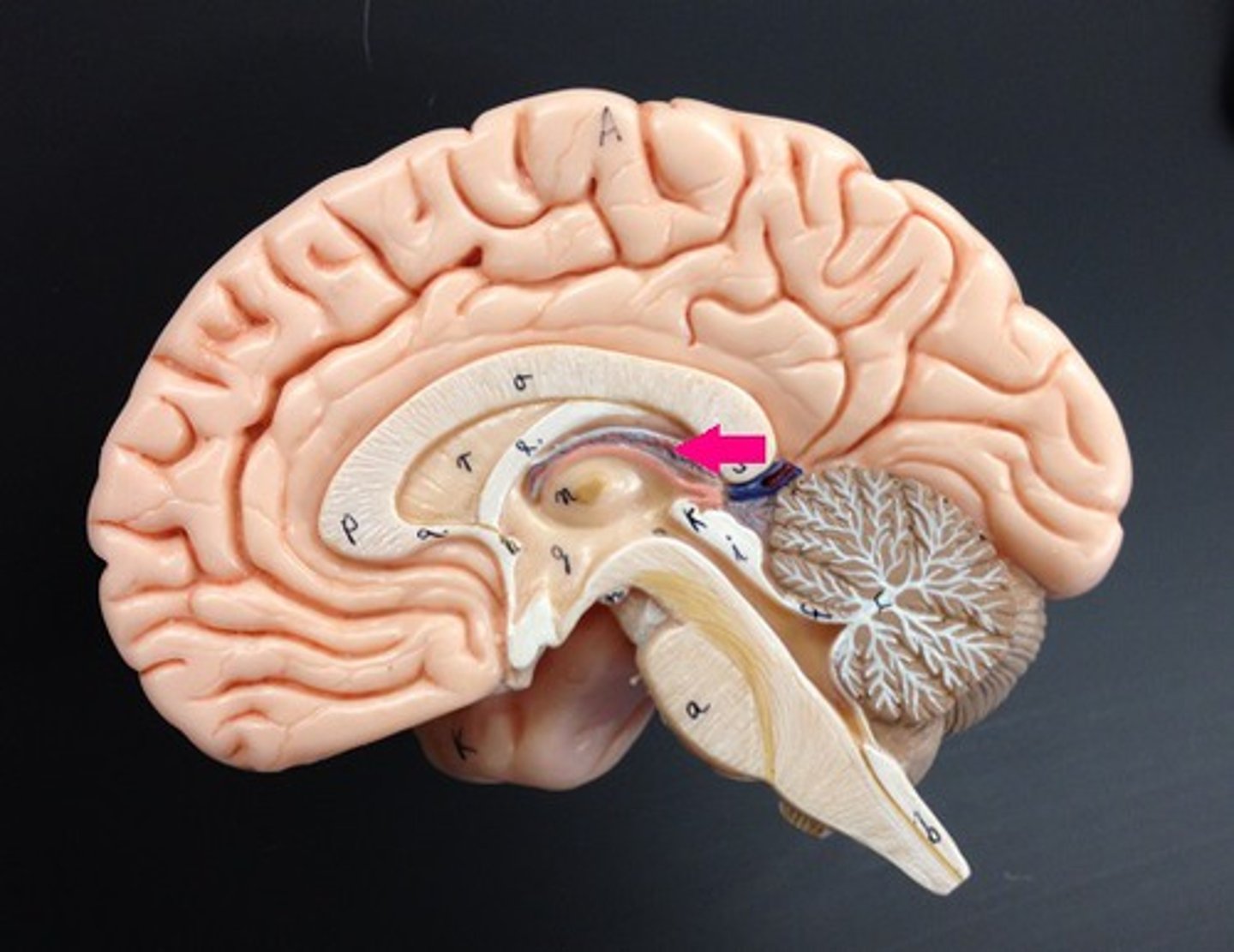
Fornix
fiber tract linking limbic system regions
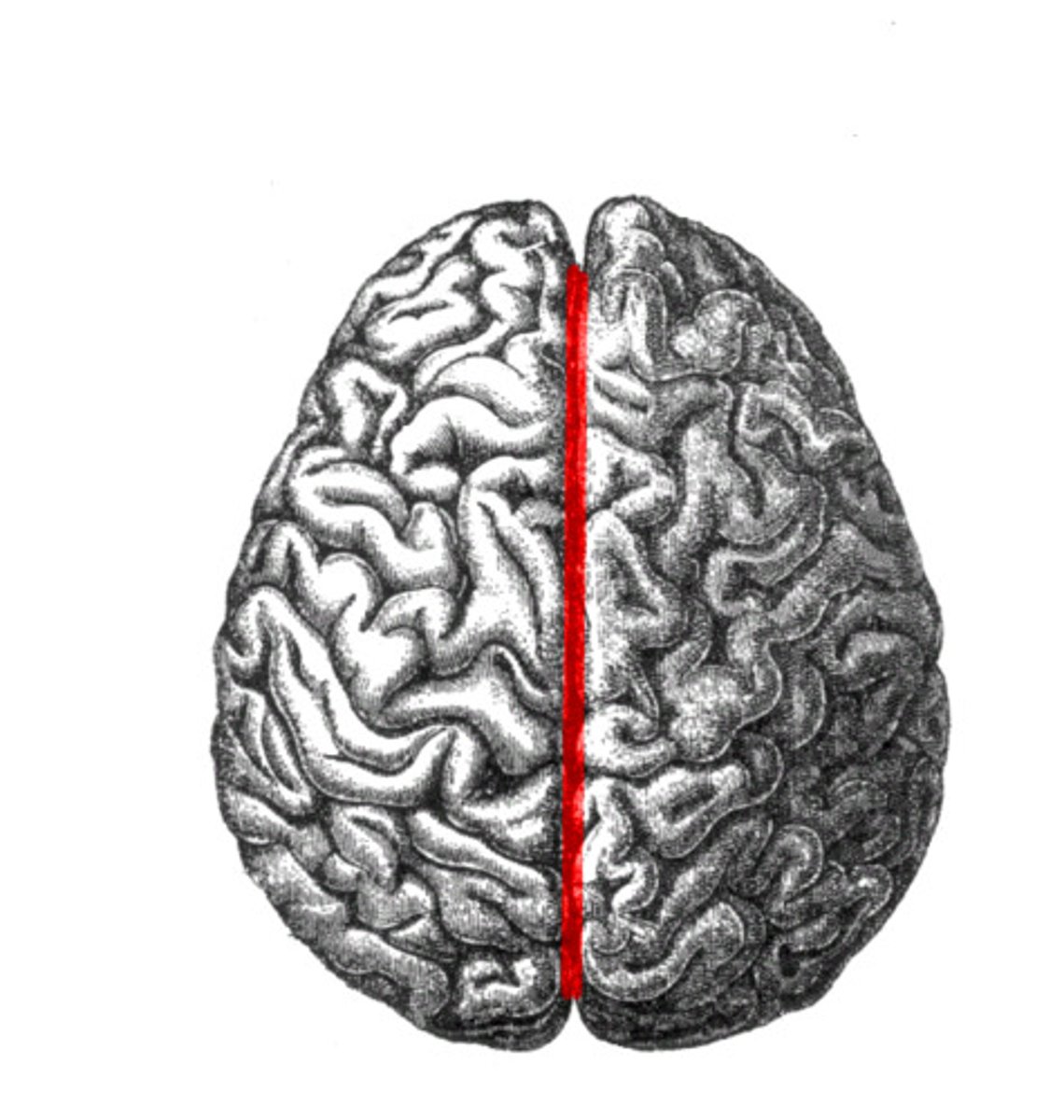
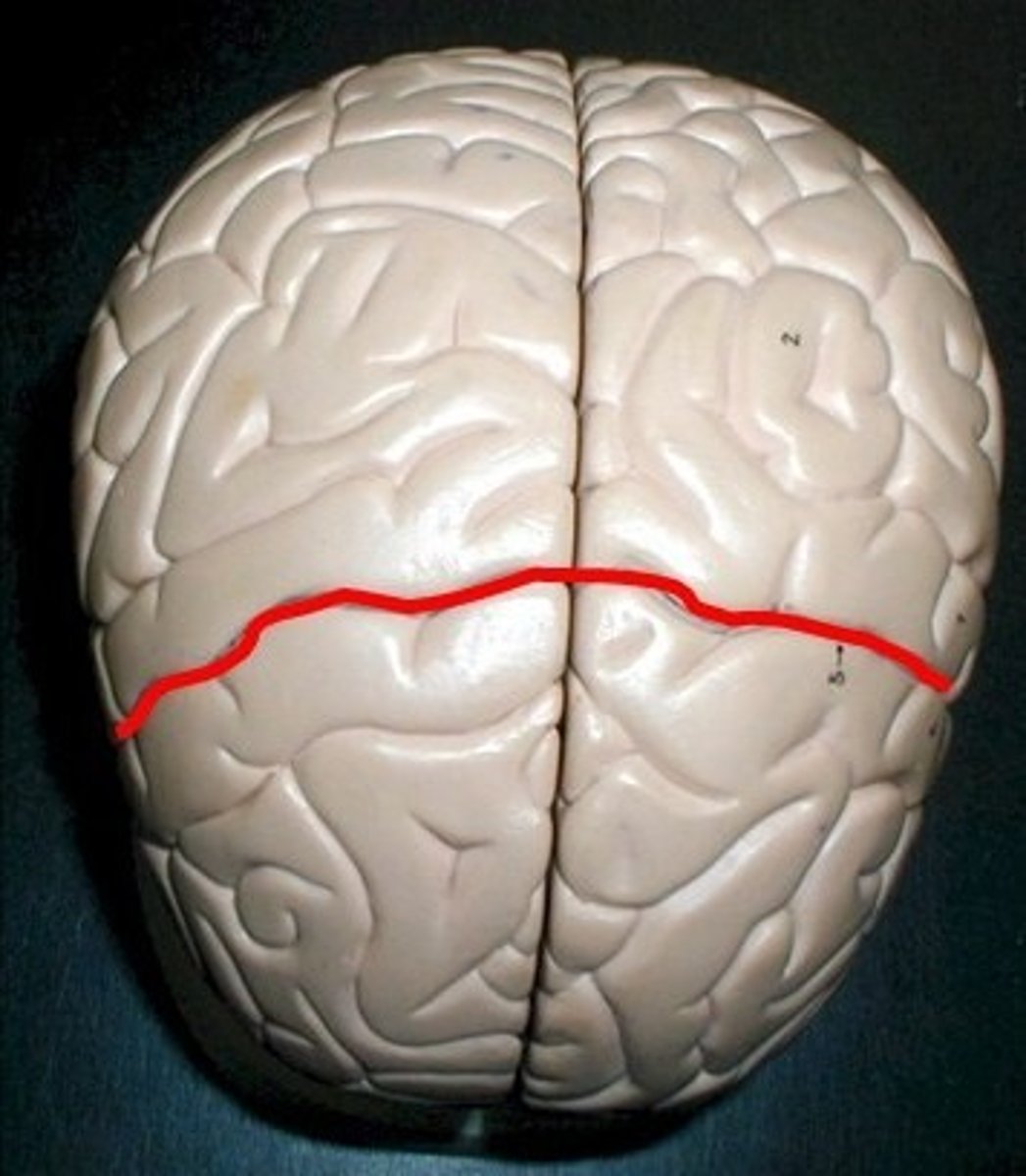
Longitudinal Fissure
big divide of cerebral hemispheres
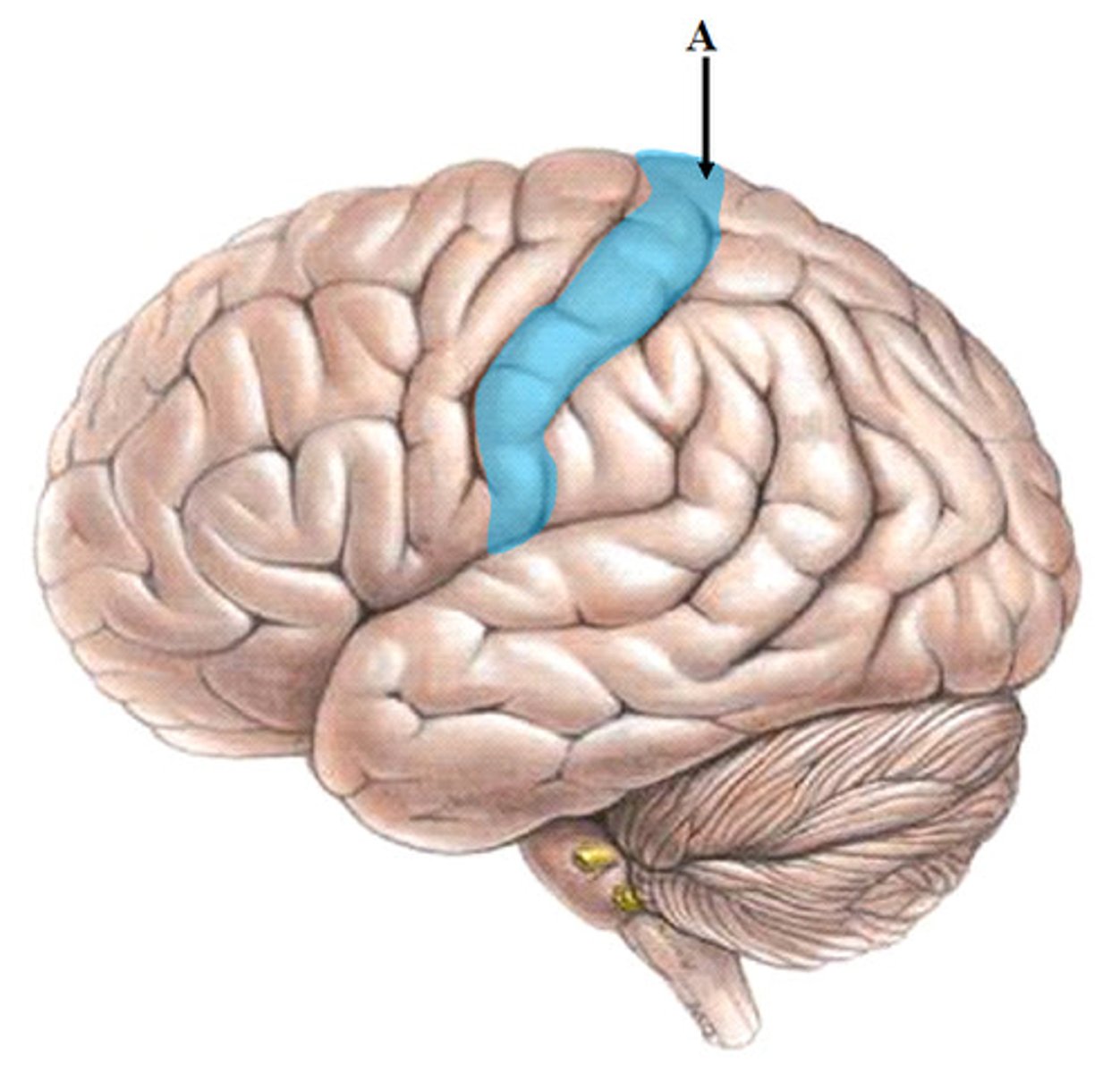
Gyrus
raised bumpy grooves of cerebrum
Sulcus
lower pit of cerebrum
Diencephalon
made up of epithalamus, thalamus and hypothalamus
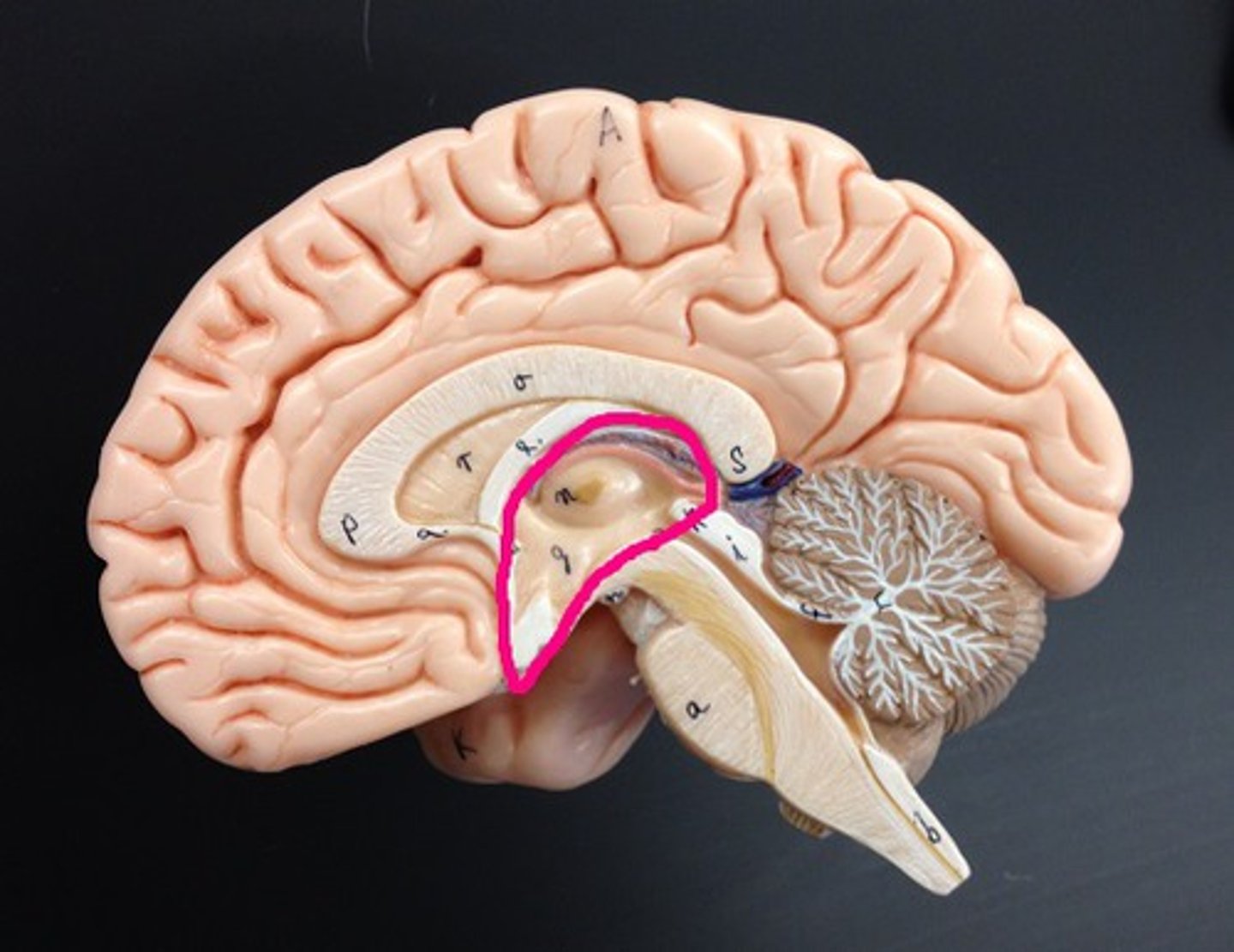
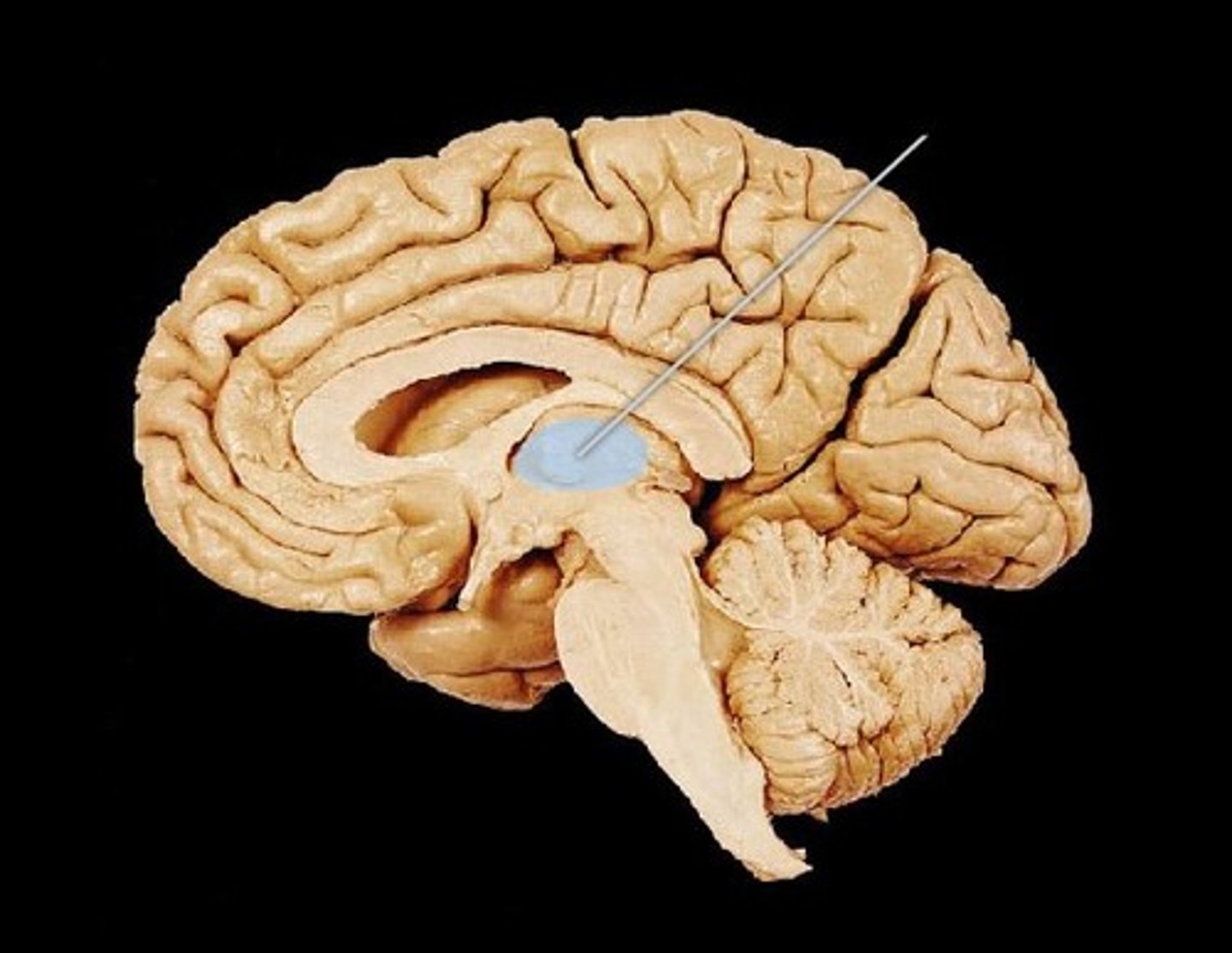
Thalamus
bilateral egg shaped nuclei connected by interthalamic adhesion and forming superior wall of 3rd ventricle. relay station for info coming from cortex.
Hypothalamus
forms floor of 3rd ventricle , cap over brain dtem and 3rd ventricle. Visceral control center, 3 fs
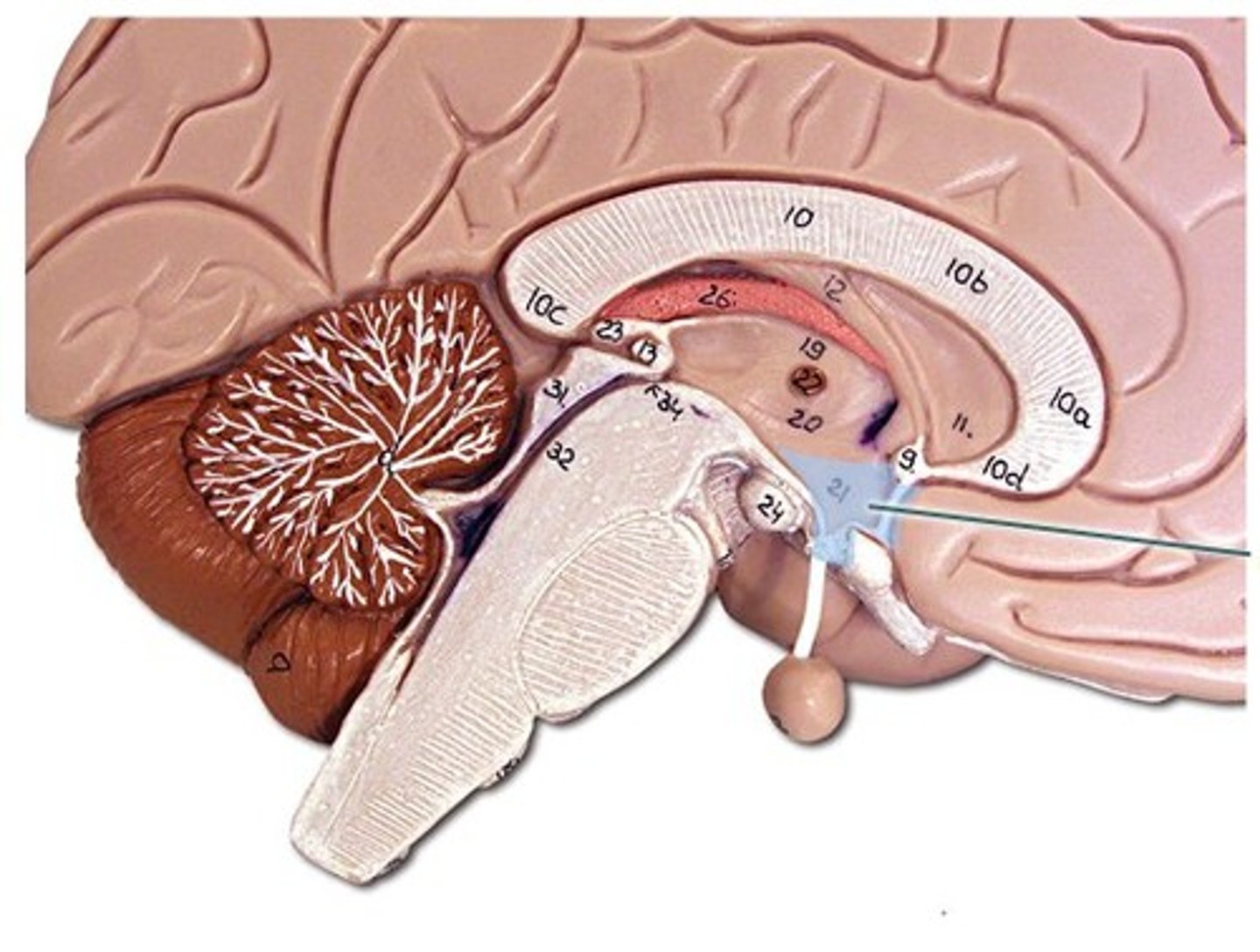
Pineal Gland
a pea-sized conical mass of tissue behind the third ventricle of the brain, secreting a hormone like substance in some mammals.
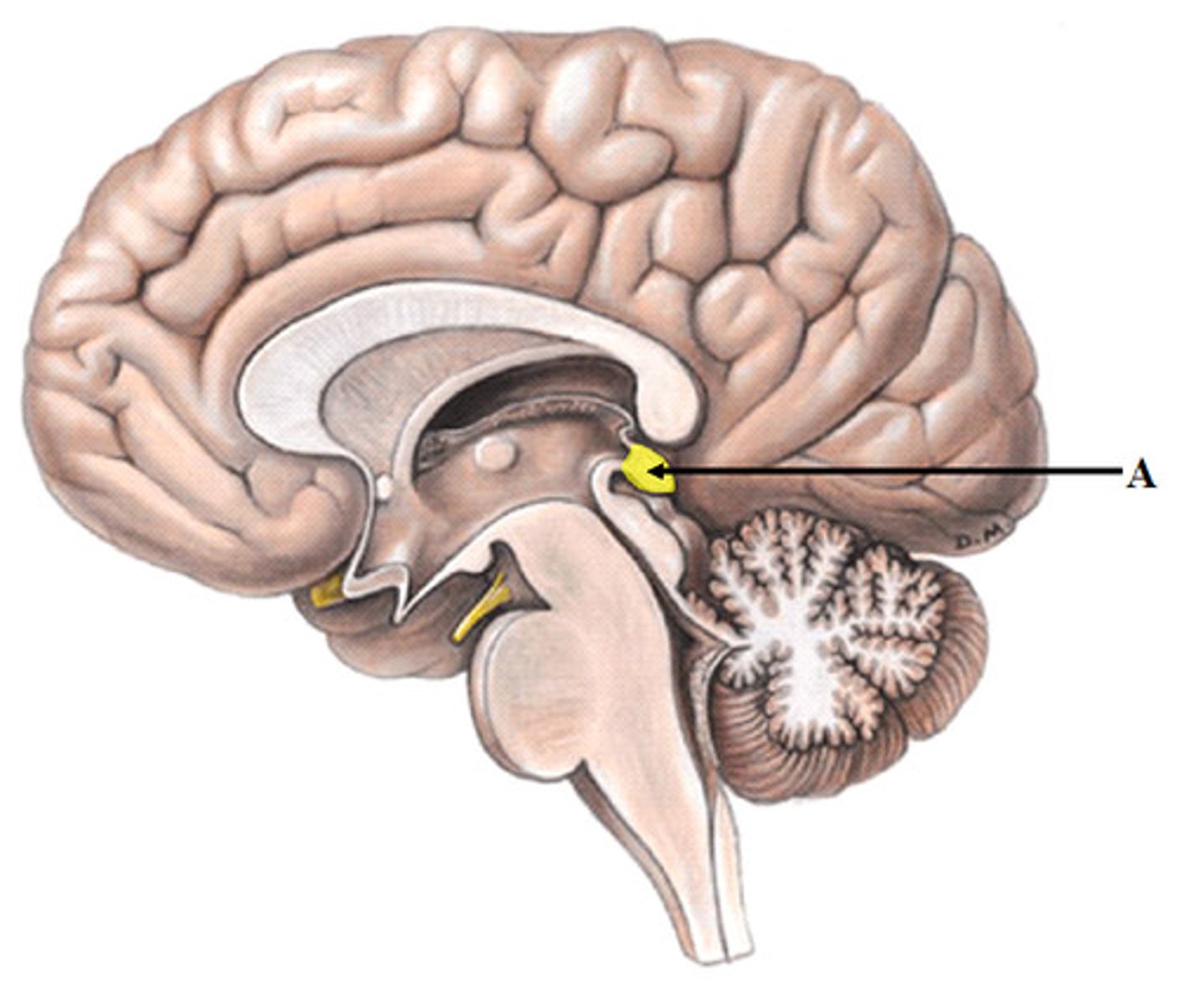
Infundibulum
the hollow stalk that connects the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary gland.
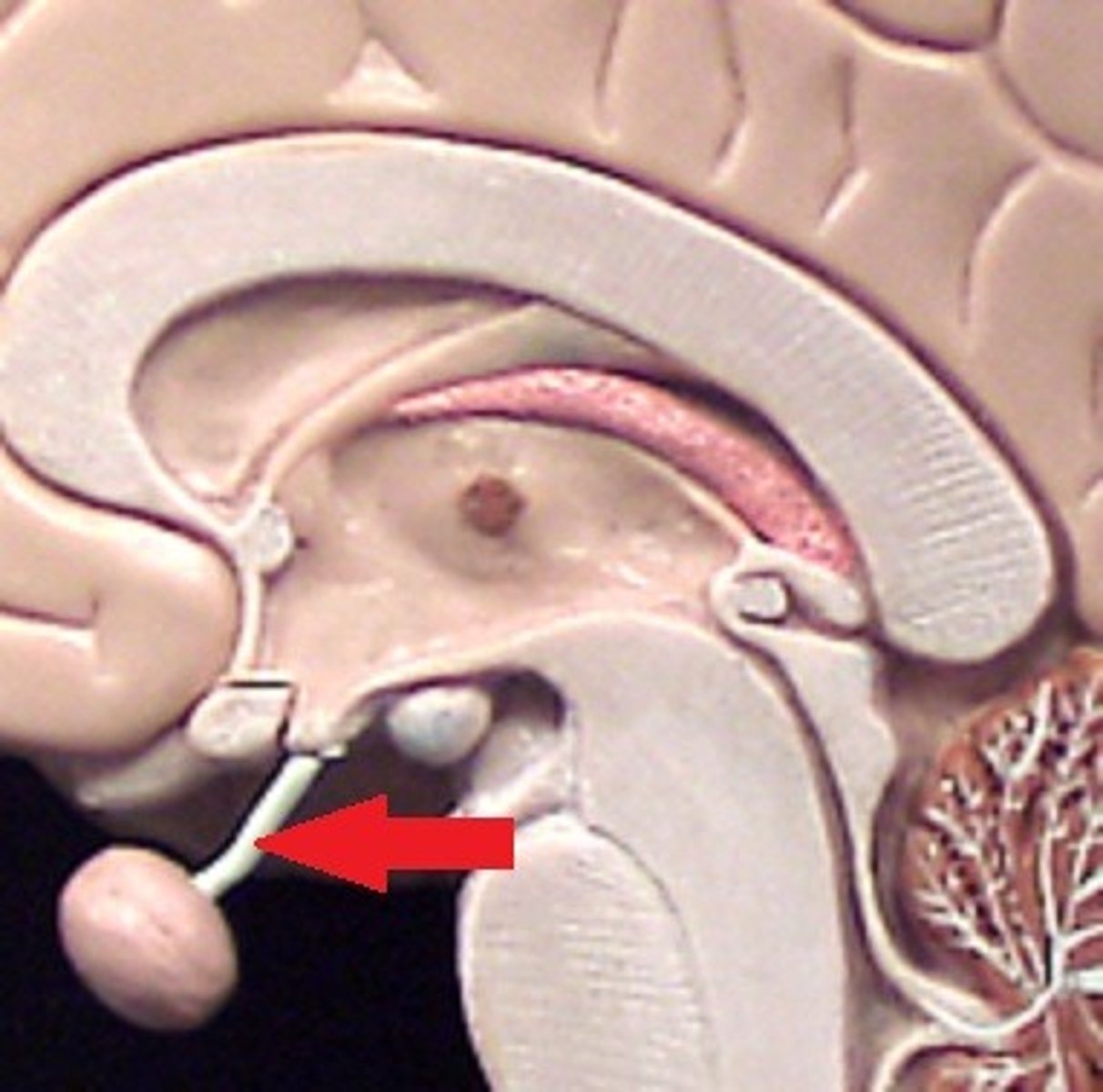
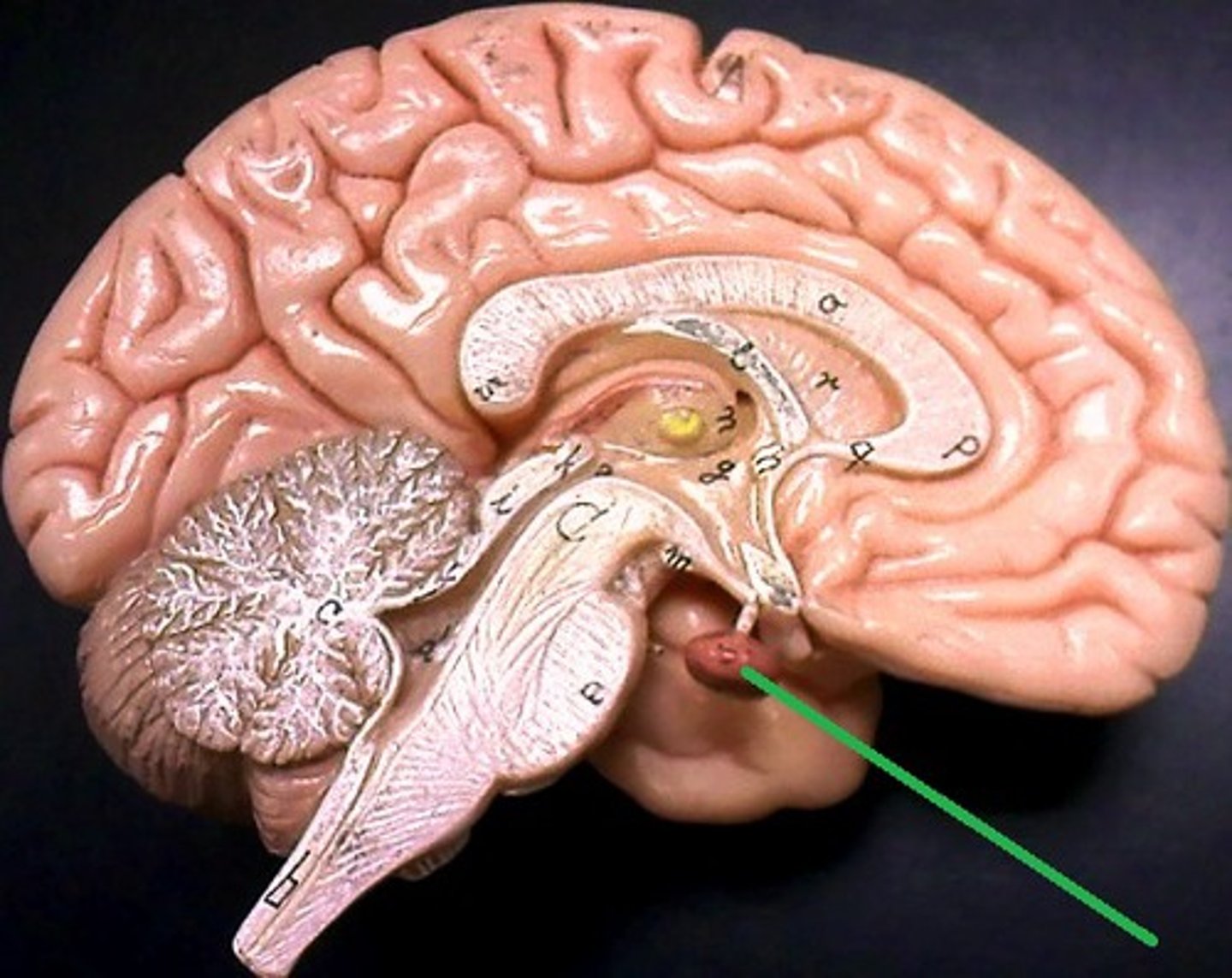
Pituitary Gland
the major endocrine gland. A pea-sized body attached to the base of the brain, the pituitary is important in controlling growth and development and the functioning of the other endocrine glands.
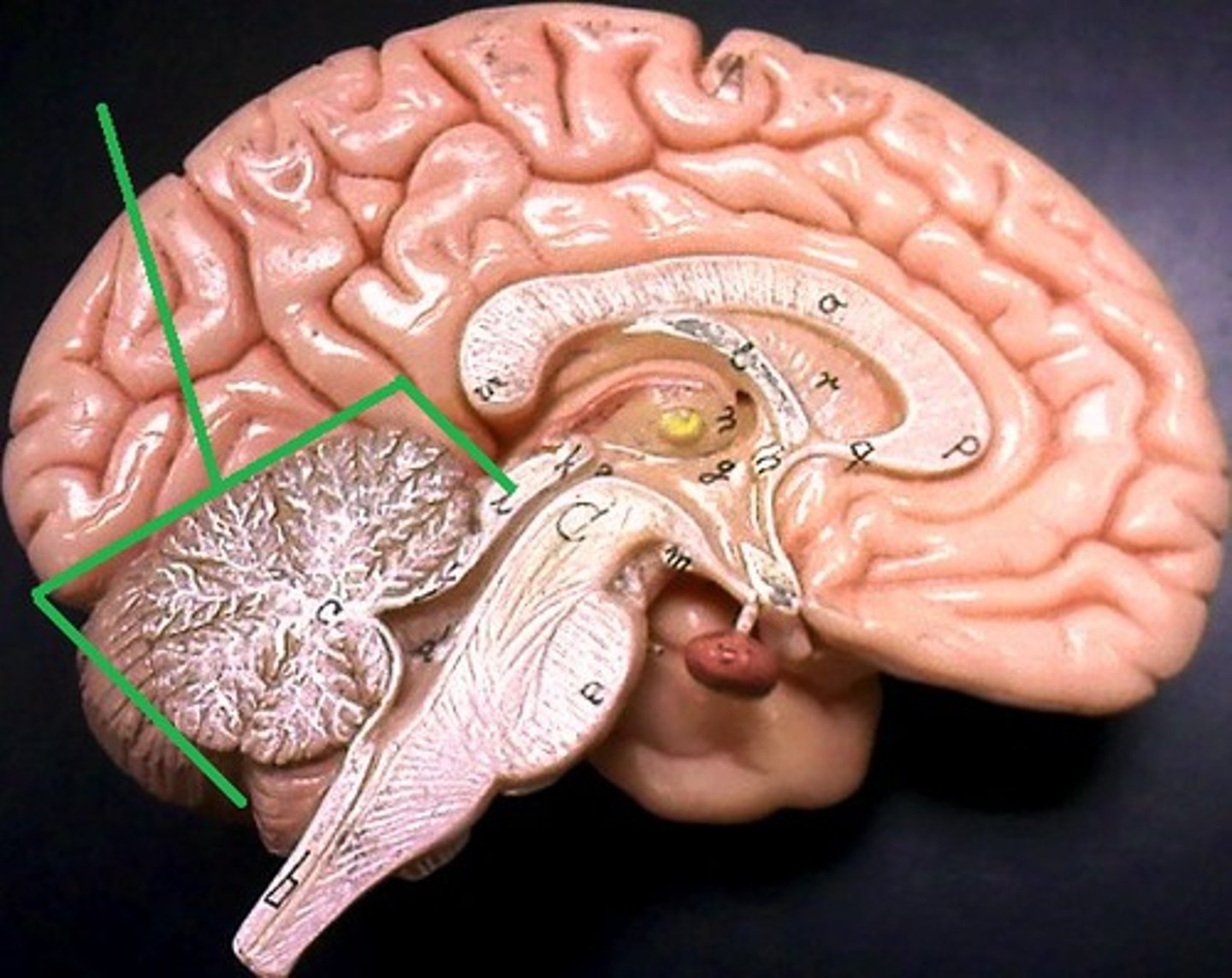
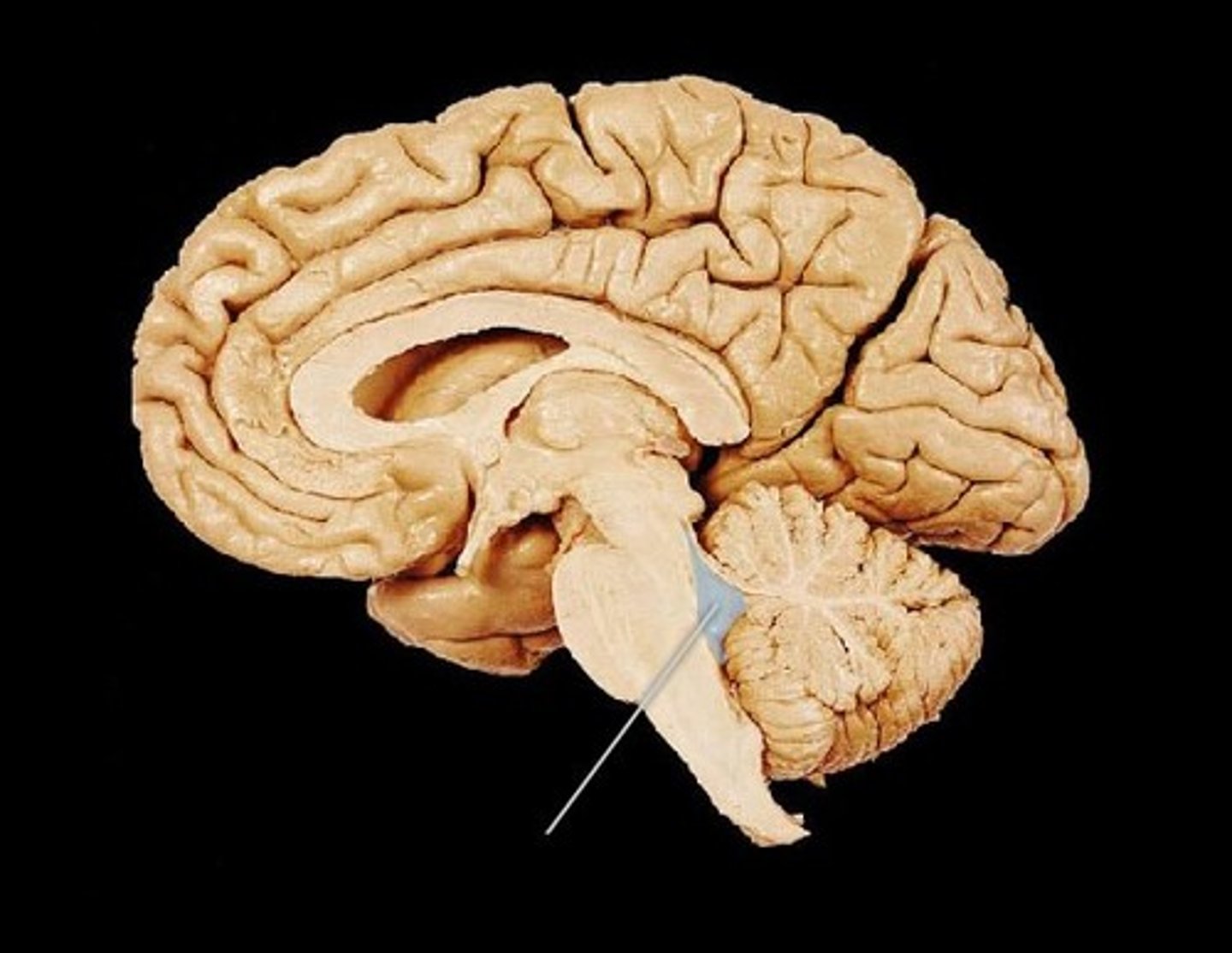
Cerebellum
"little brain" attach to the top of the brain stem. Components include vermis, arbor vitale, cortex, peduncles
Brain Stem
Continuation of spinal cord. Contains medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain
Midbrain
a small central part of the brainstem, developing from the middle of the primitive or embryonic brain.
Corpora Quadrigemina
largest mid brain nuclei, made up of superior colliculus and inferior colliculi
Pons
bulging brain stem region between midbrain and medulla.
Medulla Oblongata
most inferior part of brain stem, eventually becomes spinal cord. Autonomic reflex center.
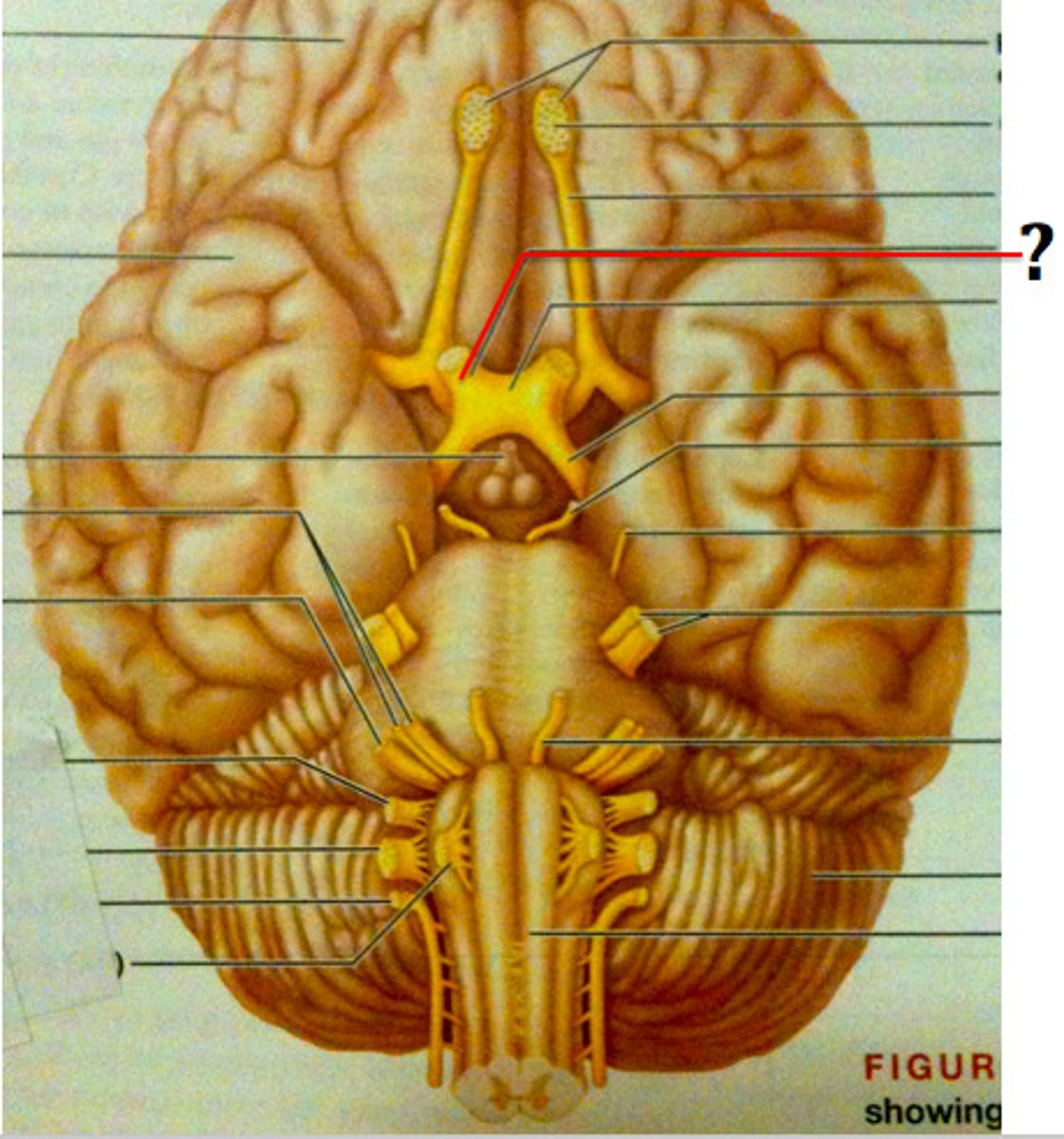
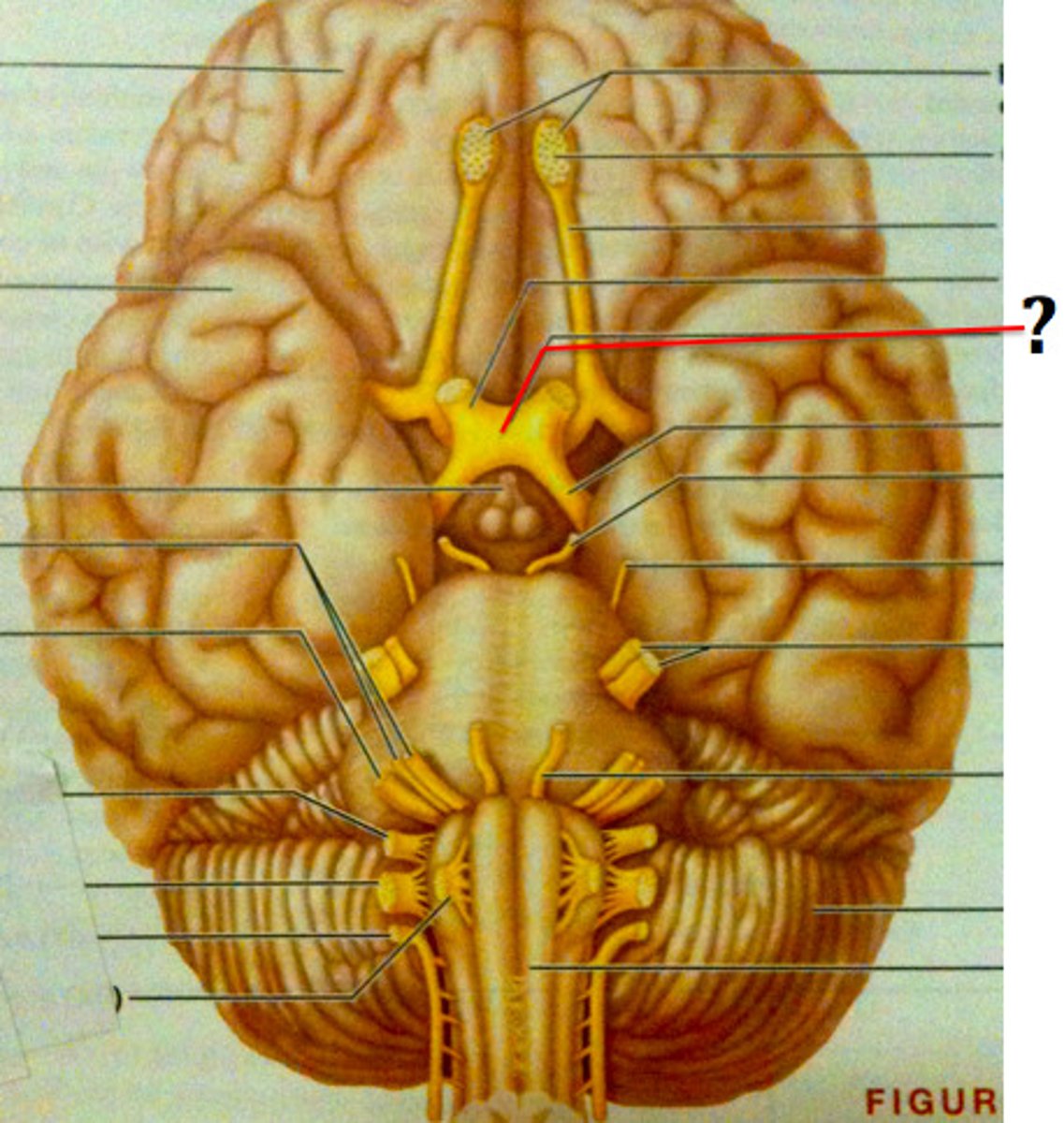
Cranial Nerves
Olfactory (S) smell
Optic (S) vision
Oculomotor (M): pupil dilation
Trochlear(M) eye movement
Trigeminal (B) sensory and motor control of face
Abducens (M): eye movement
Facial (B) facial movement
Vestibulocochlear (S) hearing and balance
Glossopharyngeal (B): control of muscles used for swallowing
Vagus (B): stimulation of the diaphragm
Accessory spinal (M): control muscle movement of head
Hypoglossal (M): control of the tongue
Cranial Nerve 1 or olfactory bulb
neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, or the sense of smell. Flow of olfactory information from receptors to glomeruli layer
Cranial Nerve 2 or optic nerve
each of the second pair of cranial nerves, transmitting impulses to the brain from the retina at the back of the eye.
Optic Chiasma
the X-shaped structure formed at the point below the brain where the two optic nerves cross over each other
Septum Pellucidum
separates lateral ventricles
choroid plexus
network of capillaries in ventricle walls
lateral ventricle
2 lateral ventricles. one in each cerebral hemisphere.
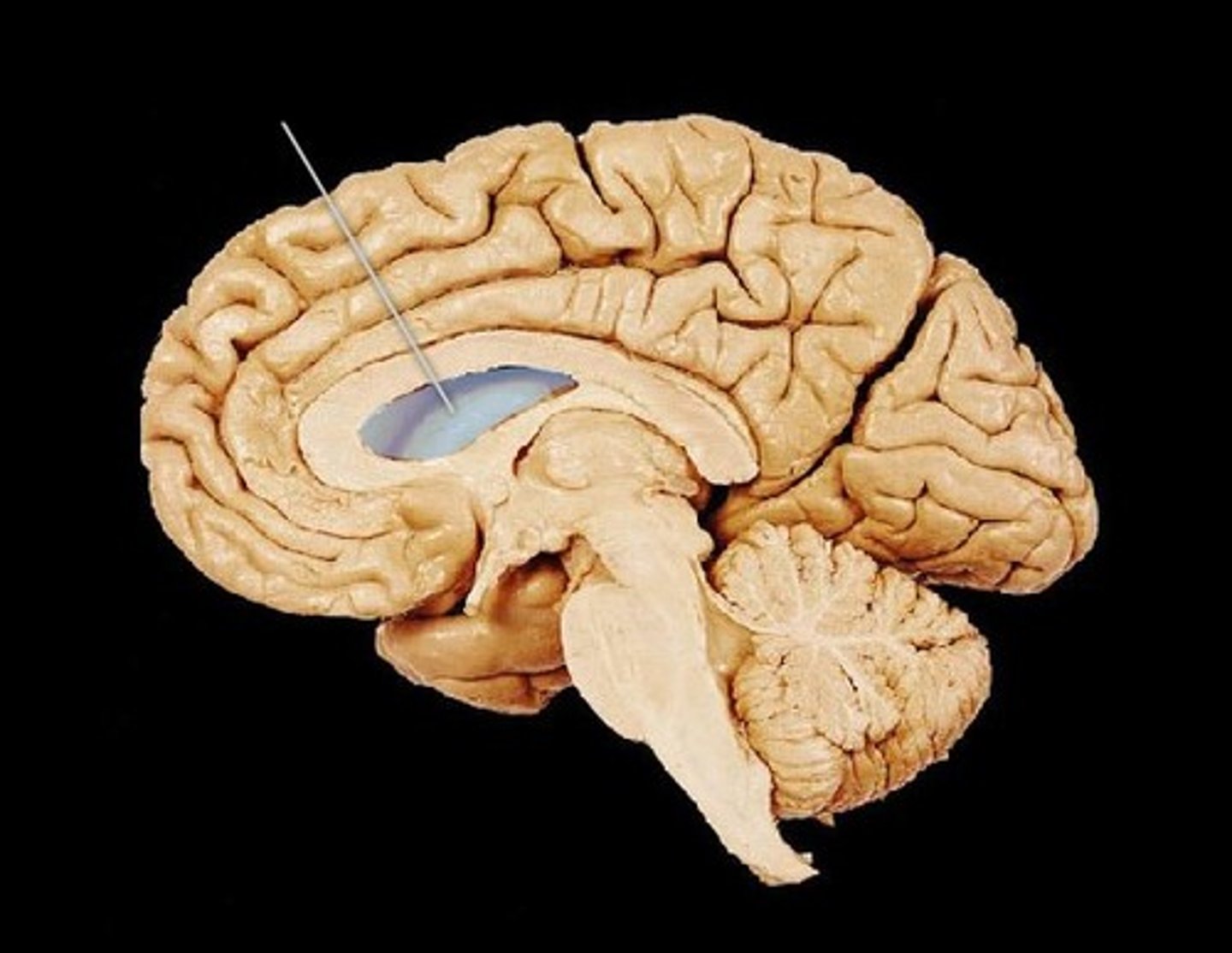
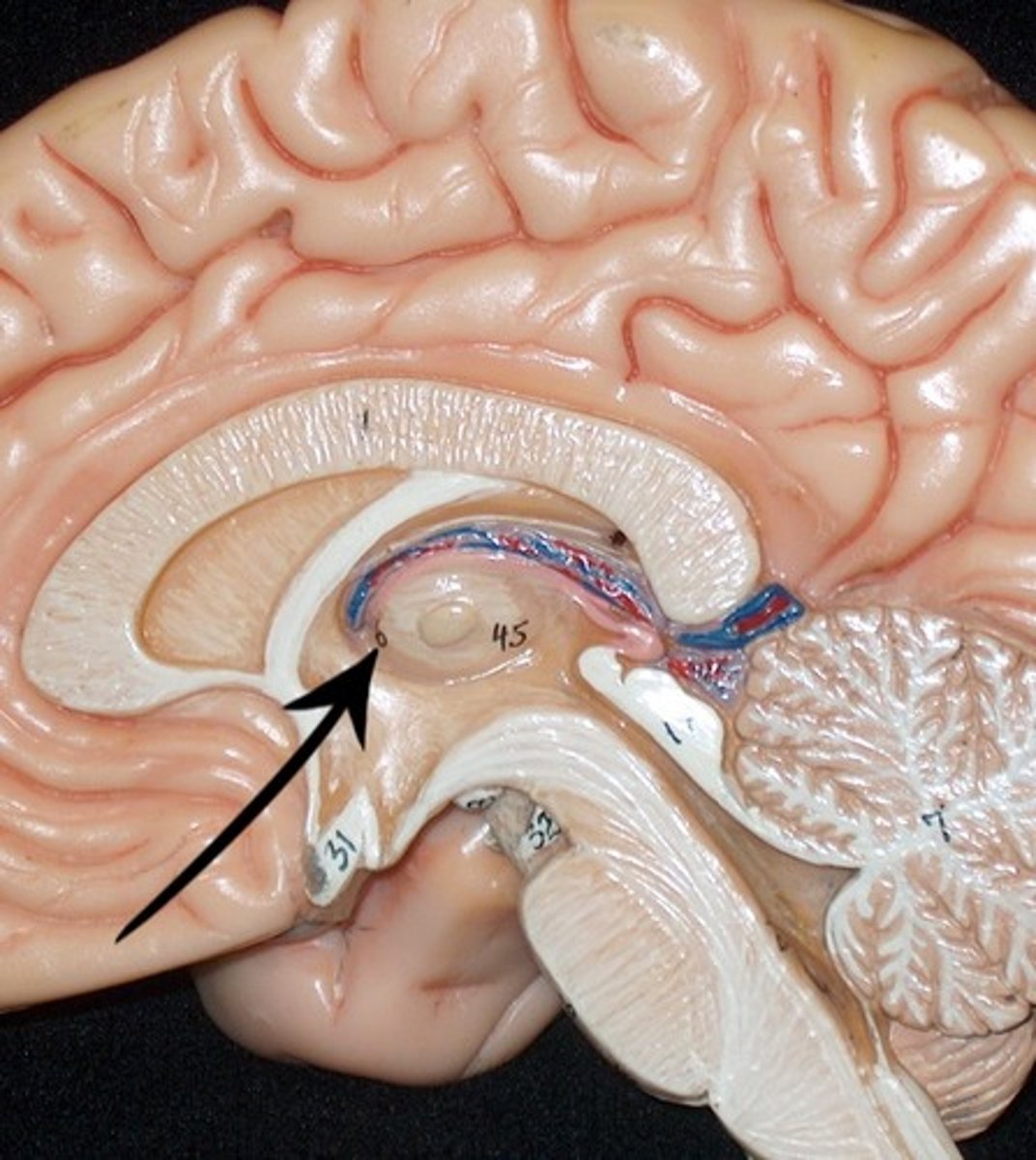
third ventricle
formed from diencephalon. Superior to hypothalamus; lies between right/left halves of thalamus
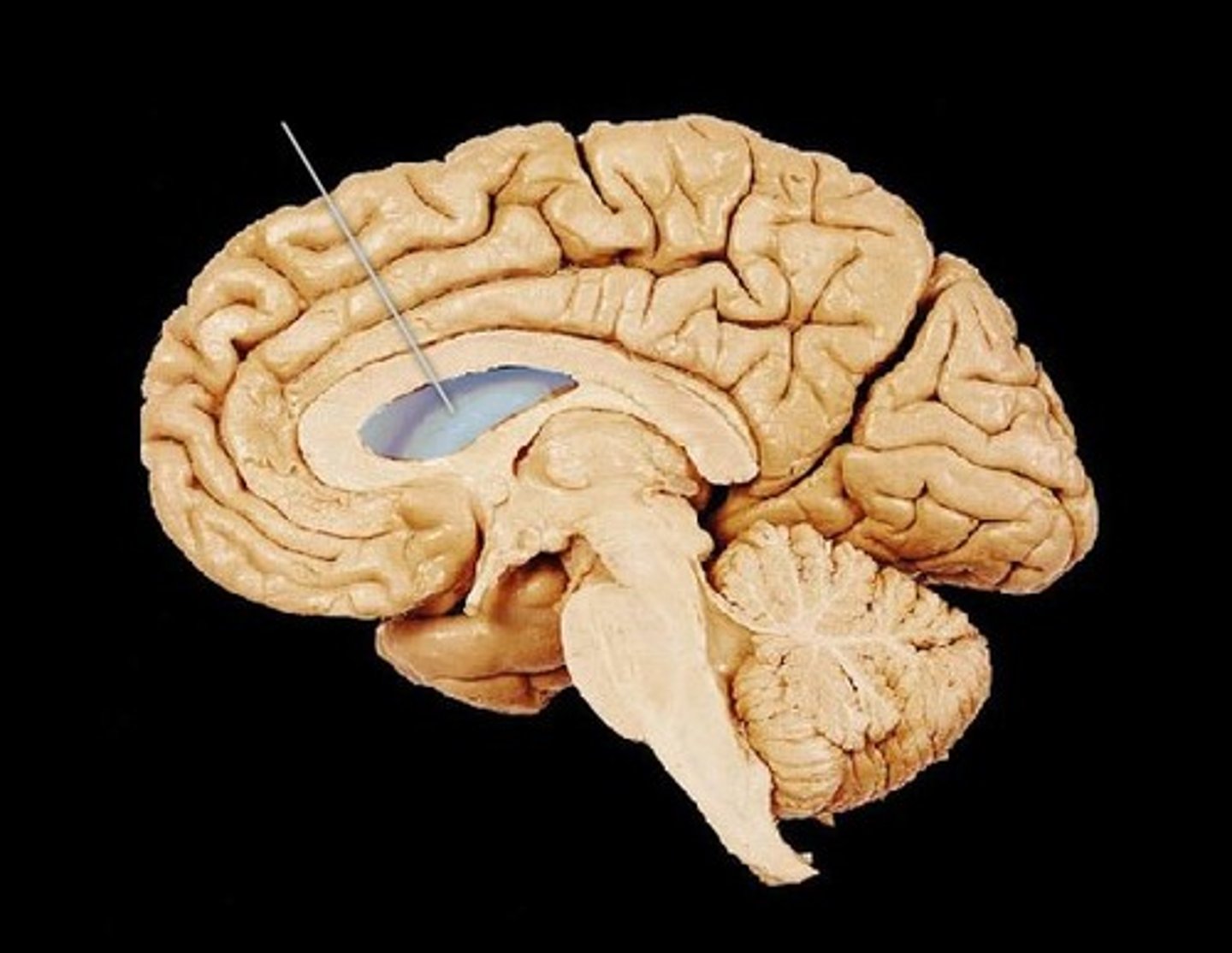
cerebral aqueduct
connects 3rd and 4th ventricle
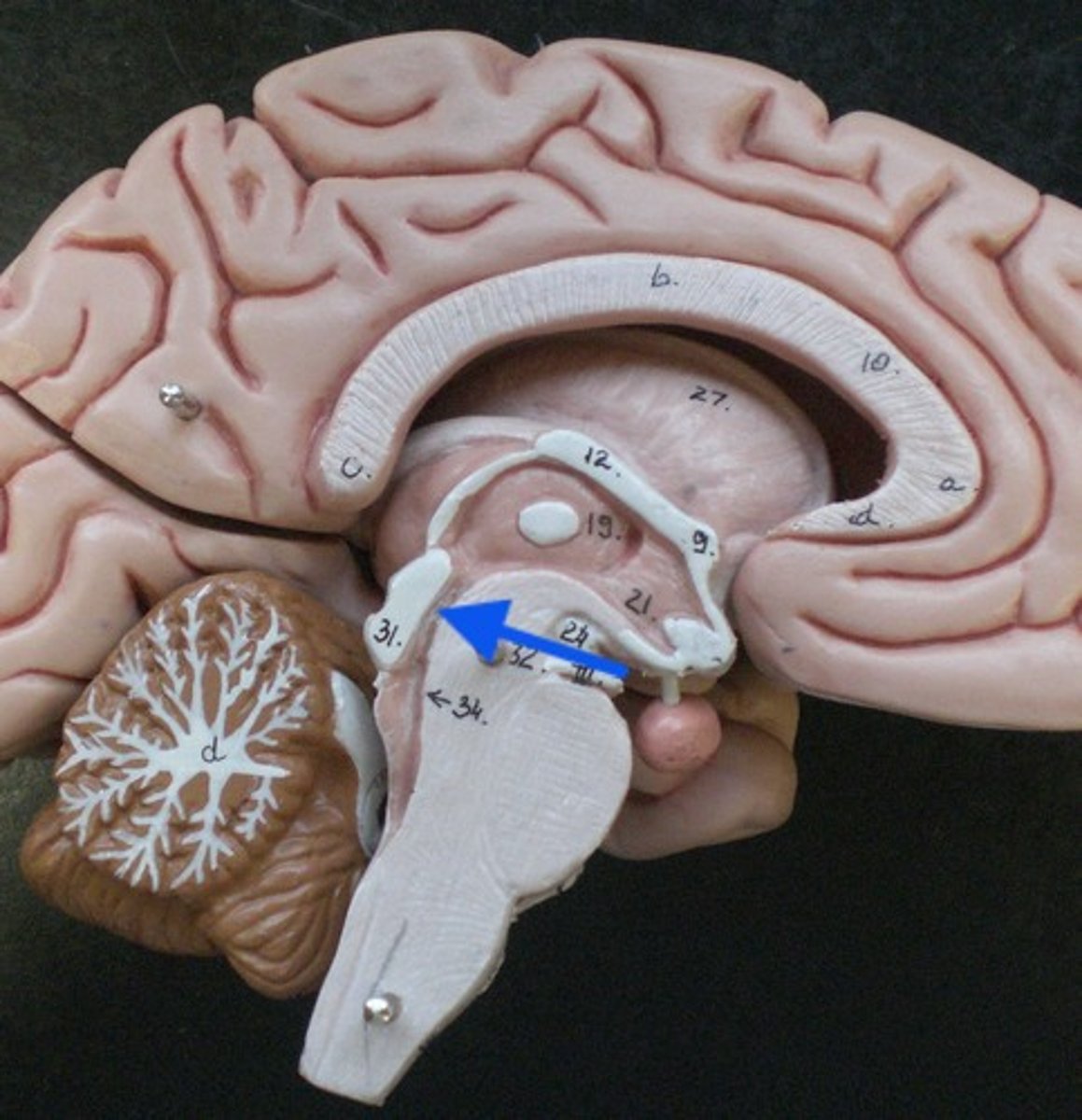
fourth ventricle
runs through brain stem (midbrain) and becomes the central canal of the spinal cord.
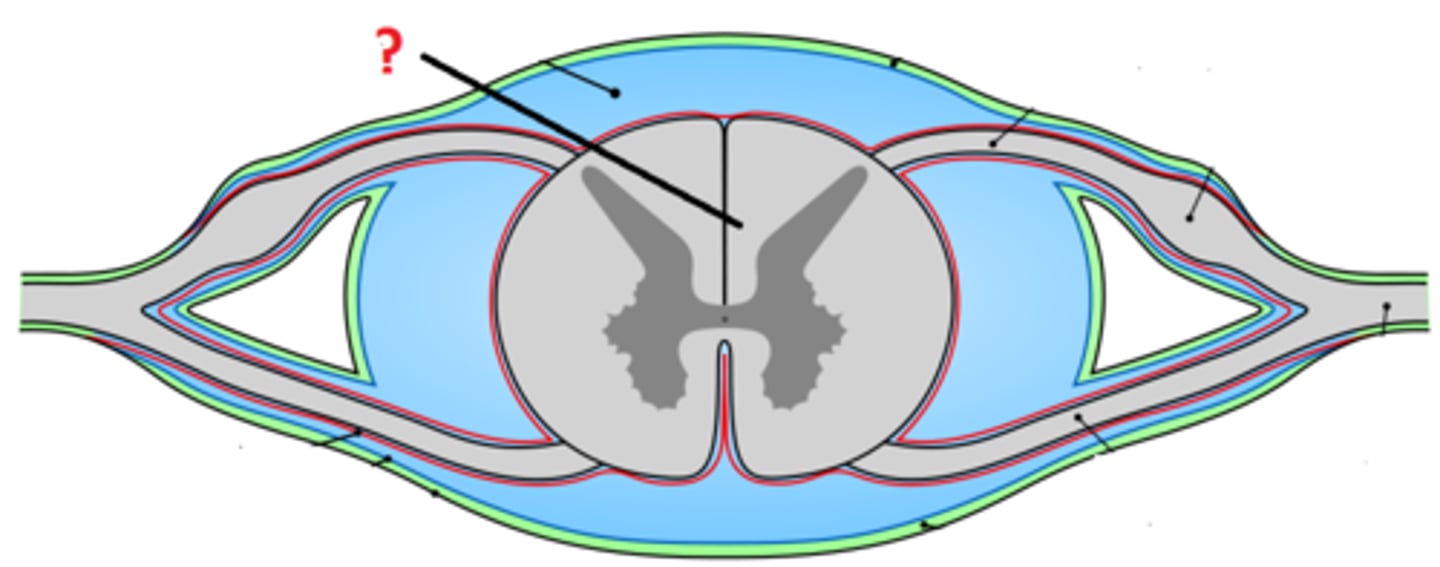
white matter
made up of myelinated axons found largerly in CNS. Cerebral cortex, outer surface of spinal chord
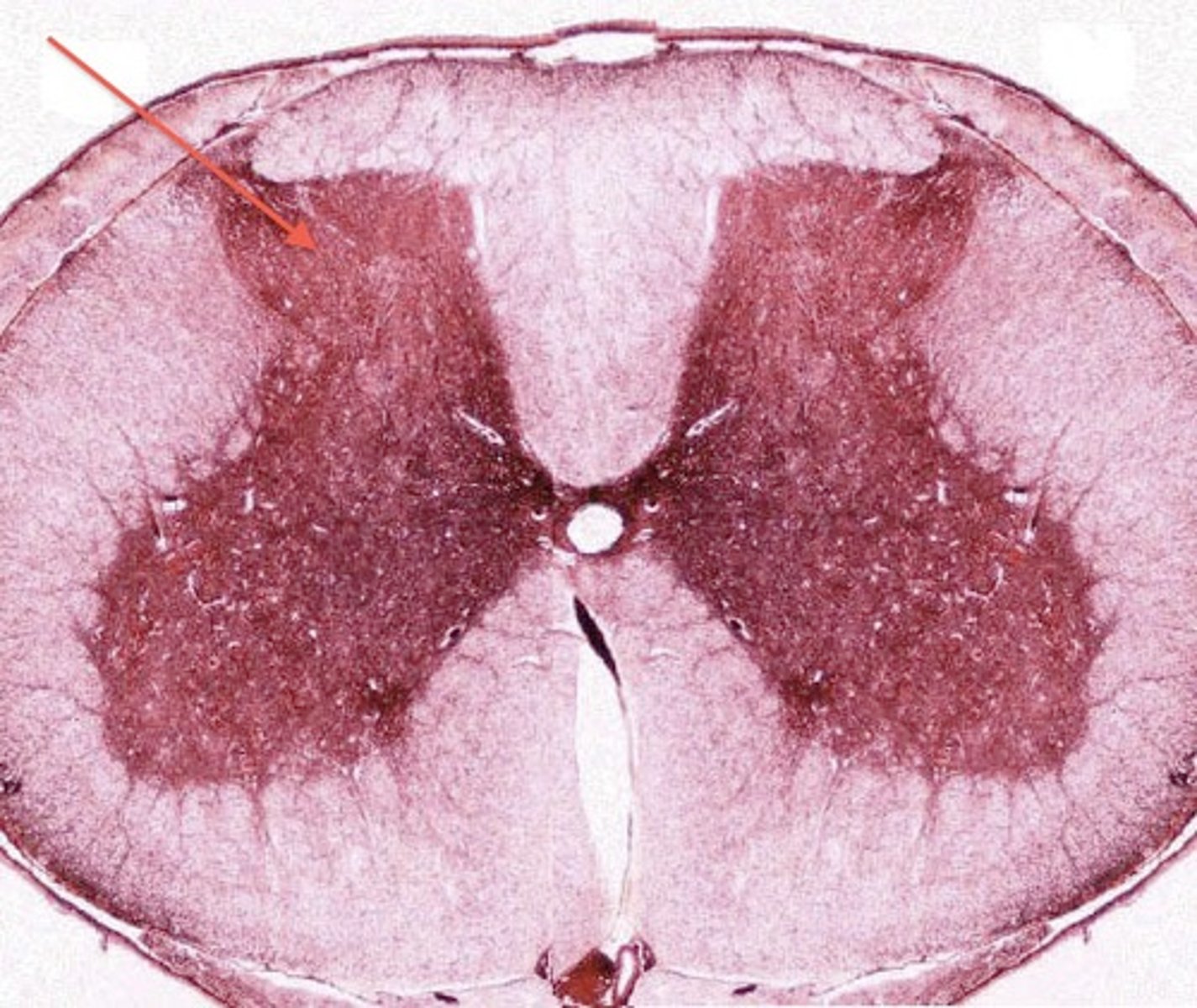
grey matter
made up of unmyelinated axons and cell bodies. Slower signal transmission. inner layer of spinal cord.
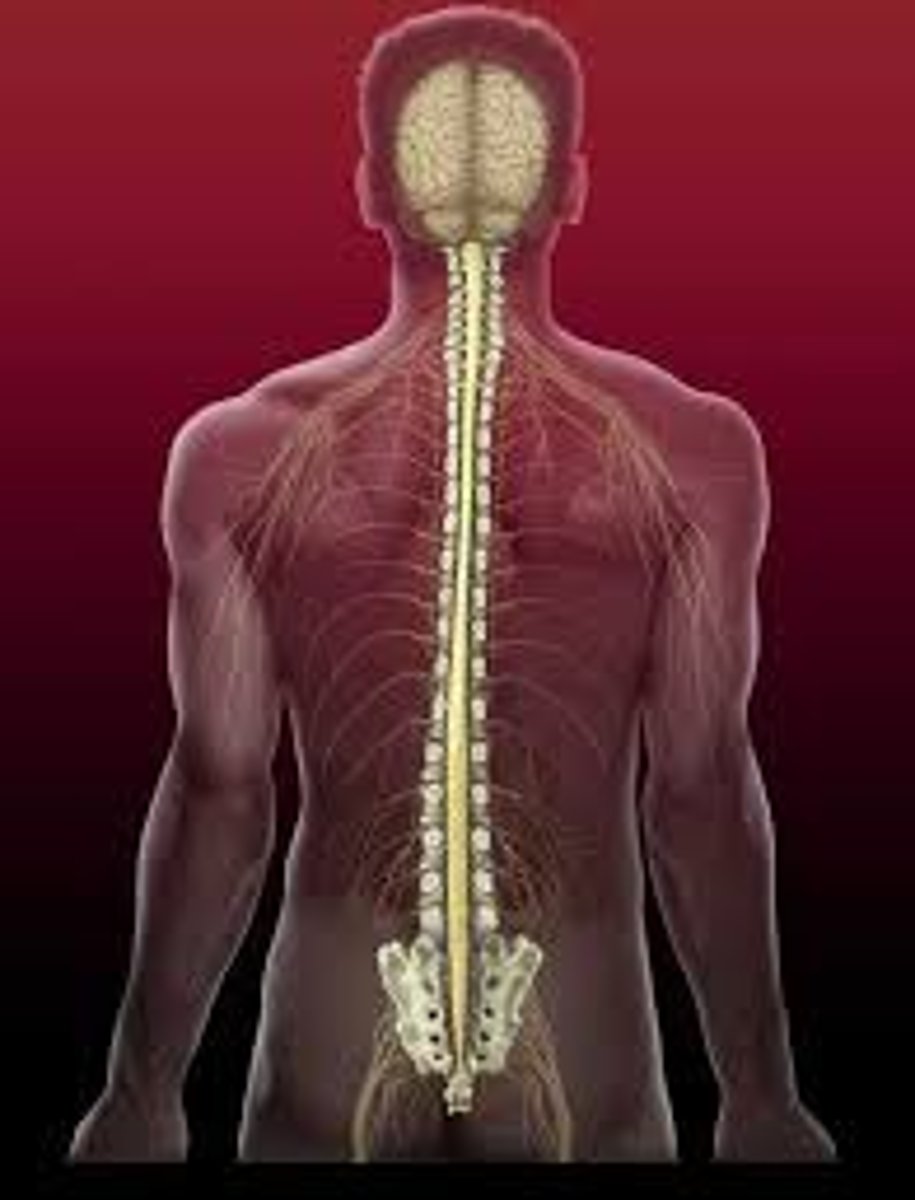
spinal cord
attaches to the brain via brain stem. extends to lumbar vertebra. Housed in vertebral column, CSF runs through central canal.
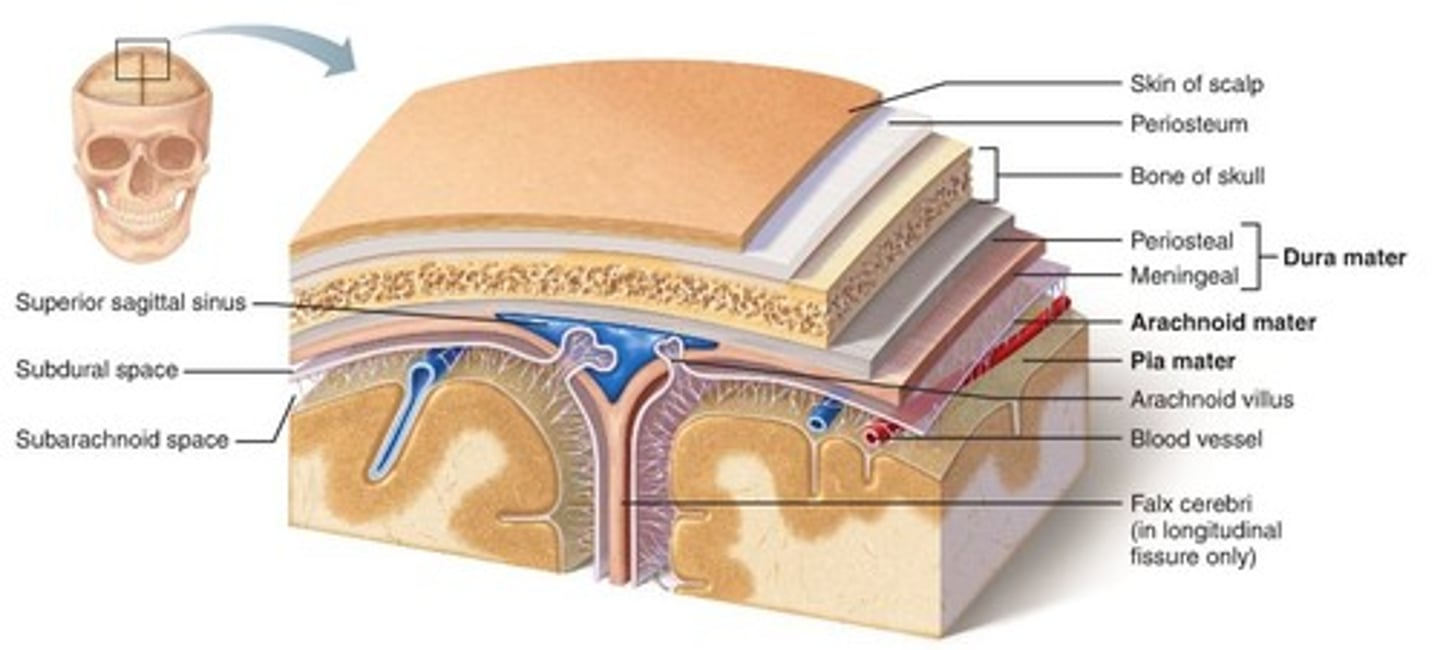
meninges
dura, arachnoid and pia mater
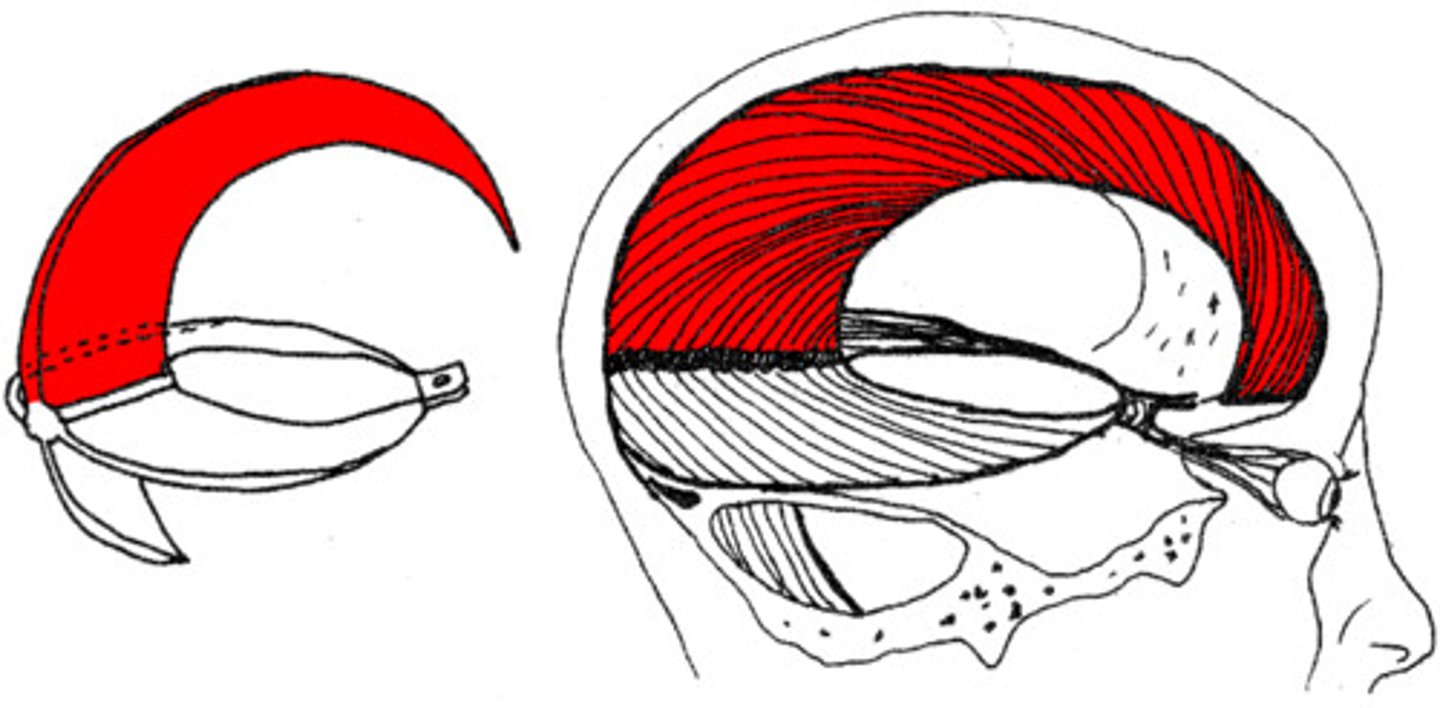
falx cerebri
crescent-shaped fold of meningeal layer of dura mater that descends vertically in the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres.
cervical/lumbar enlargement
2 enlargements where nerves serving upper and lower limbs arise
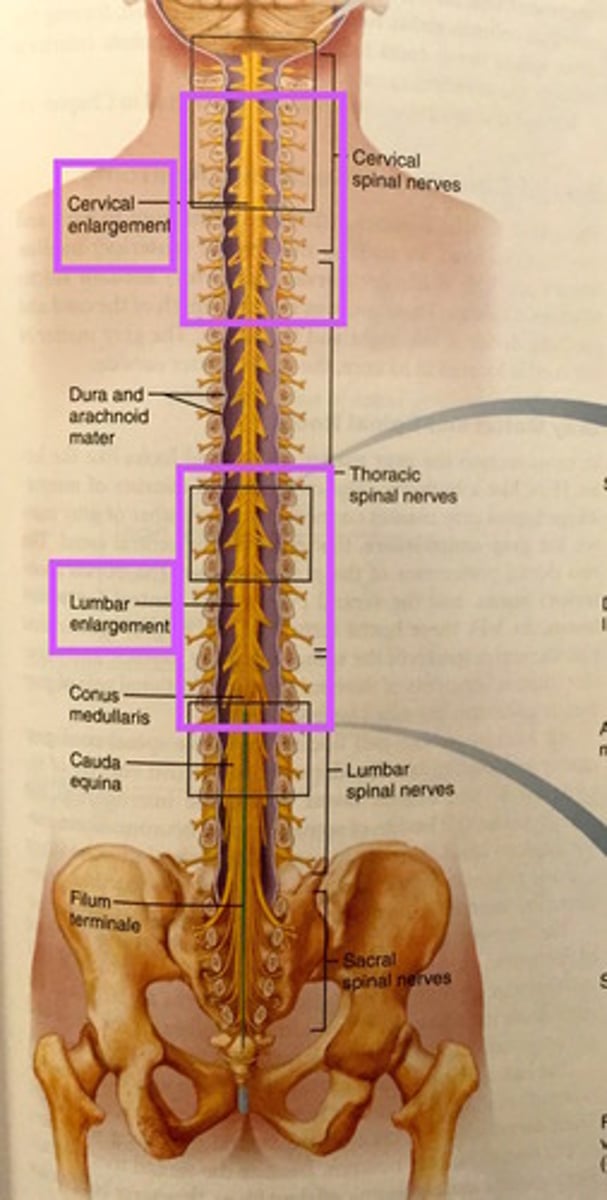
conus medullaris
tappered cone shaped end of spinal column found between L1 and L2
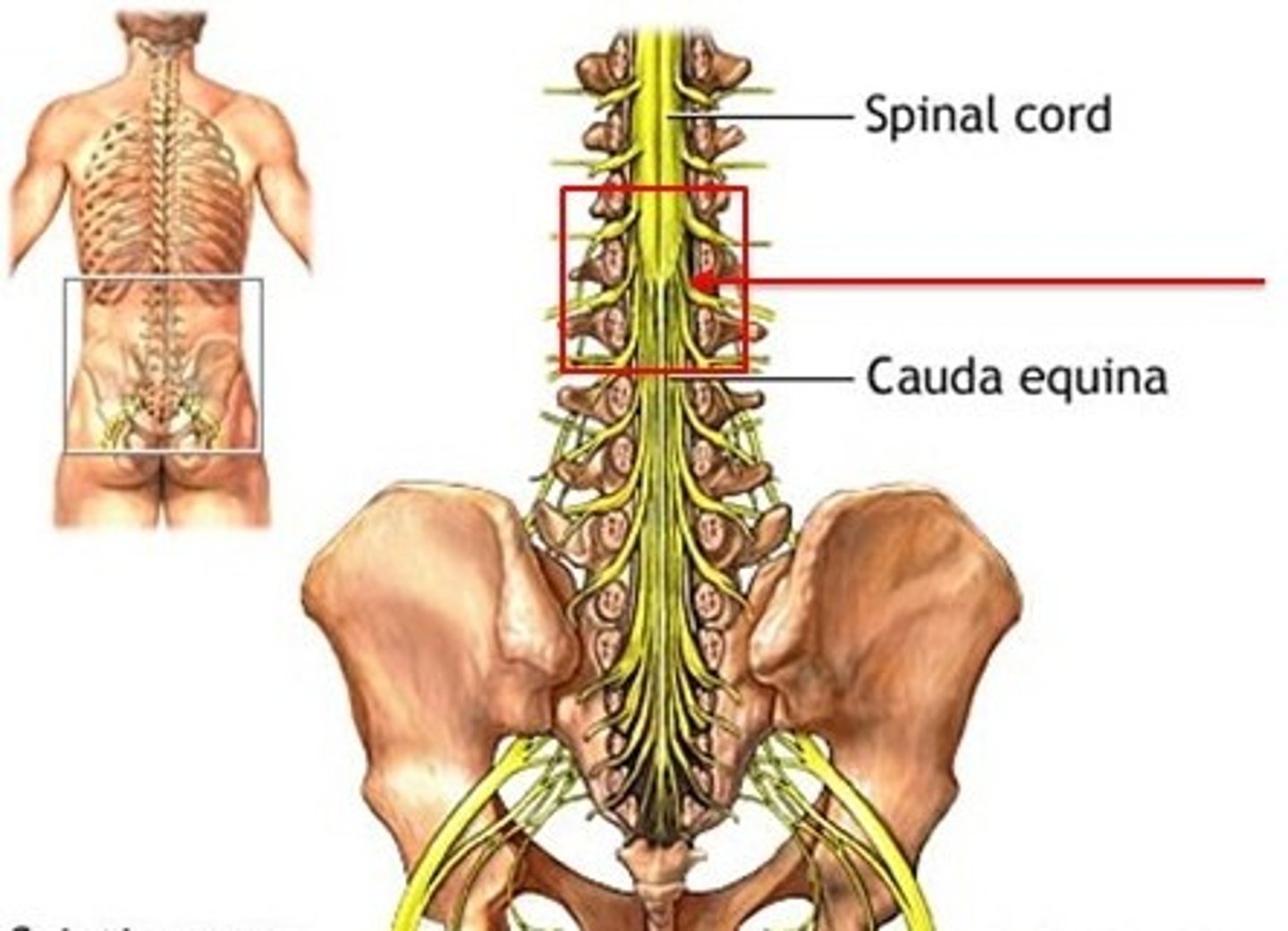
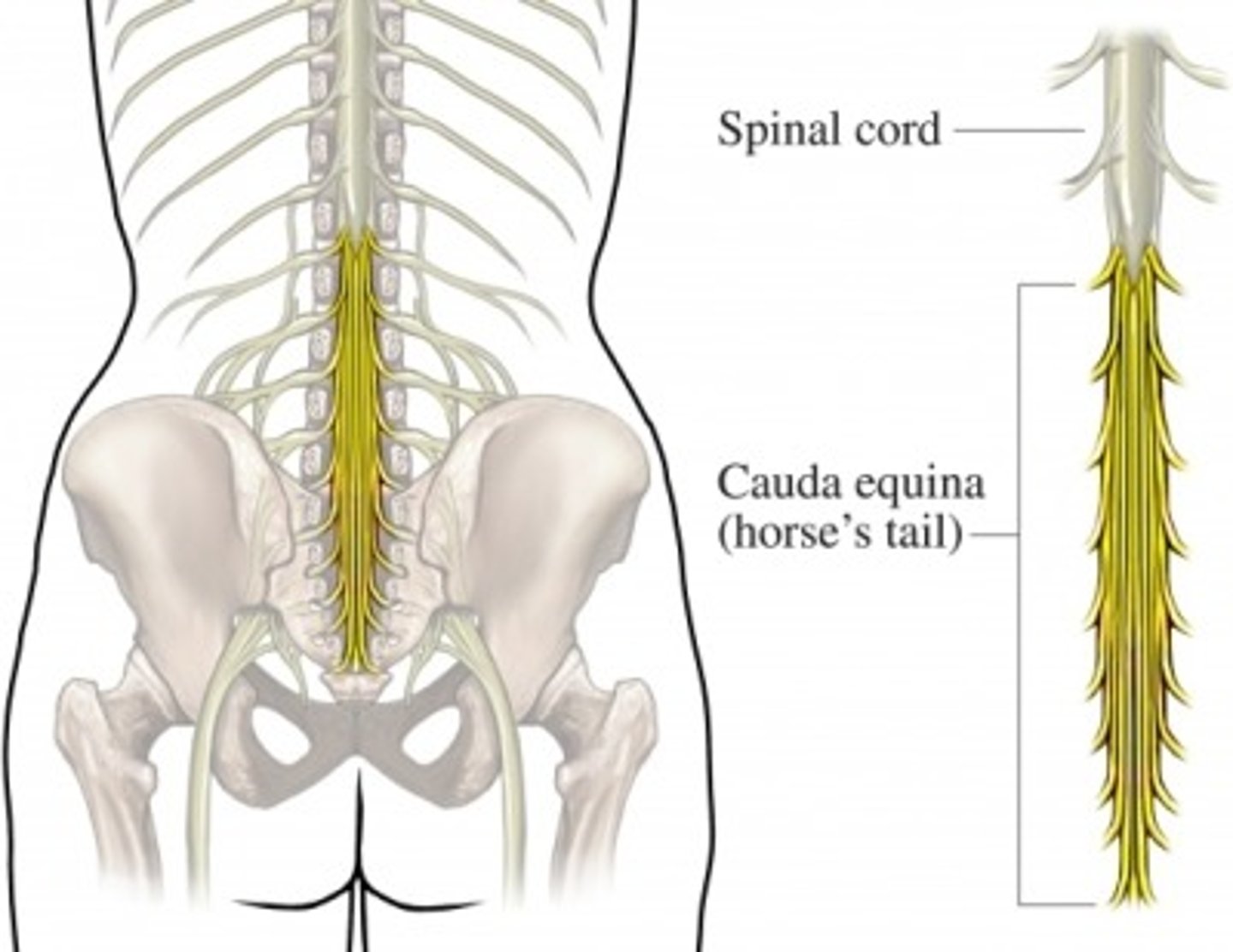
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves that extend like wisps of hair
filum terminale
fibrous extension of the conus covered by pia mater
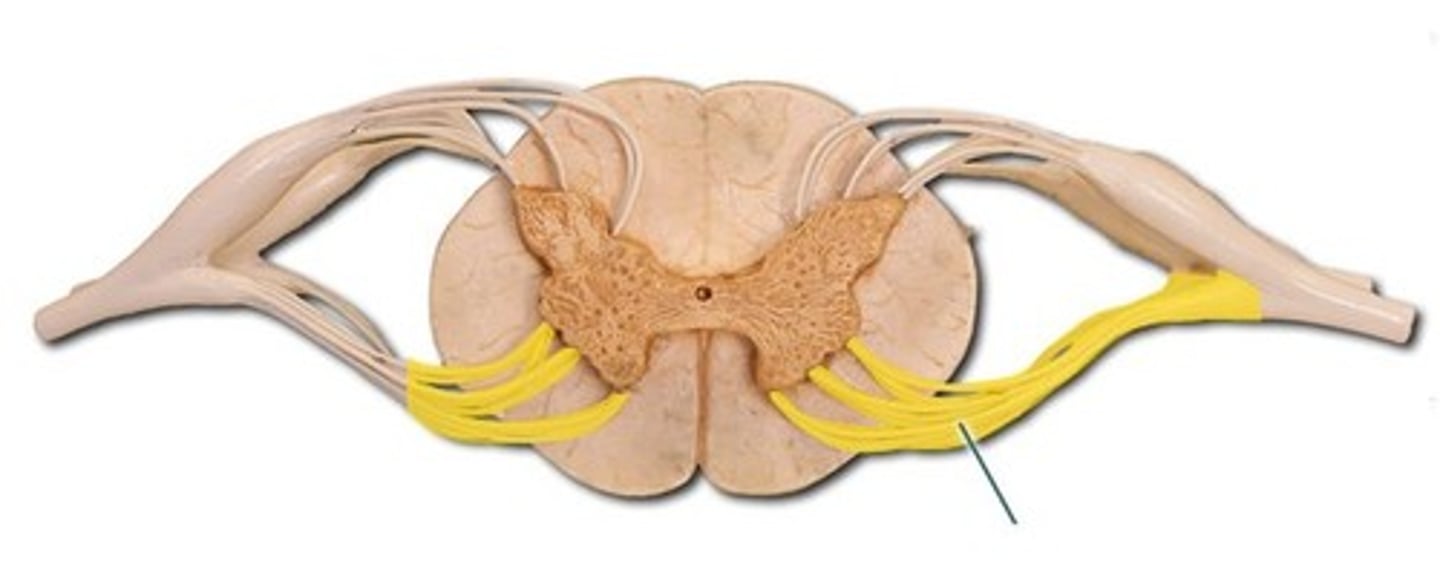
Ventral horn
multipolar motor nerve cell bodies
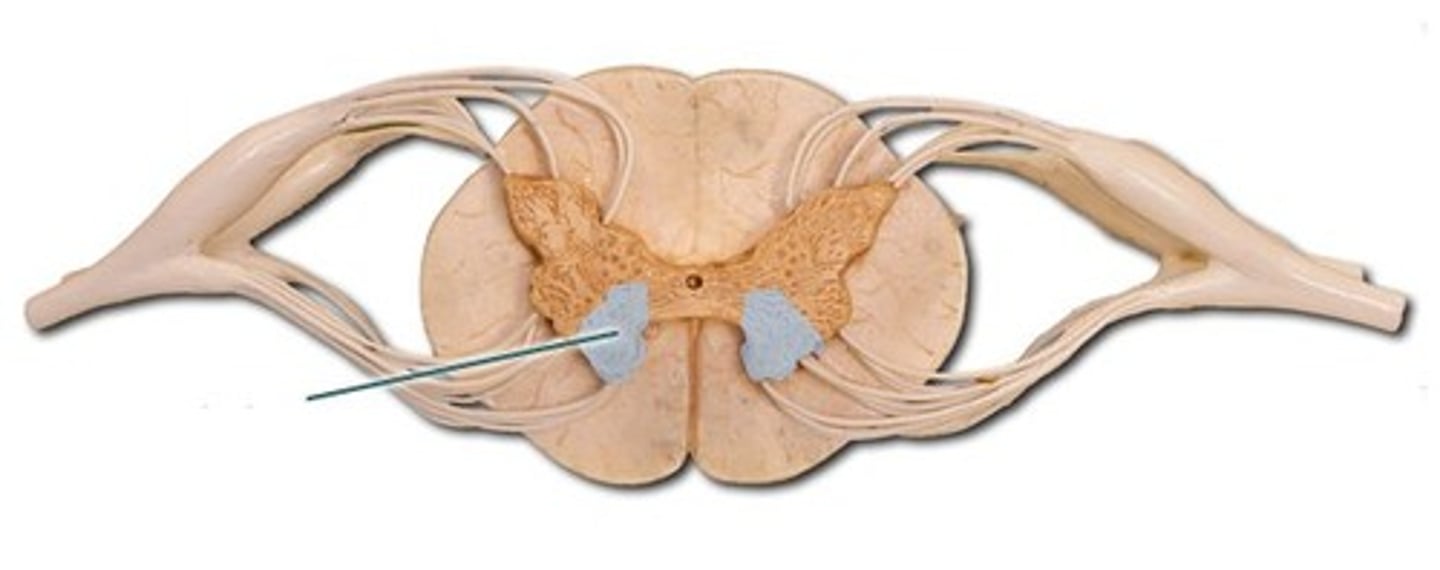
lateral horn
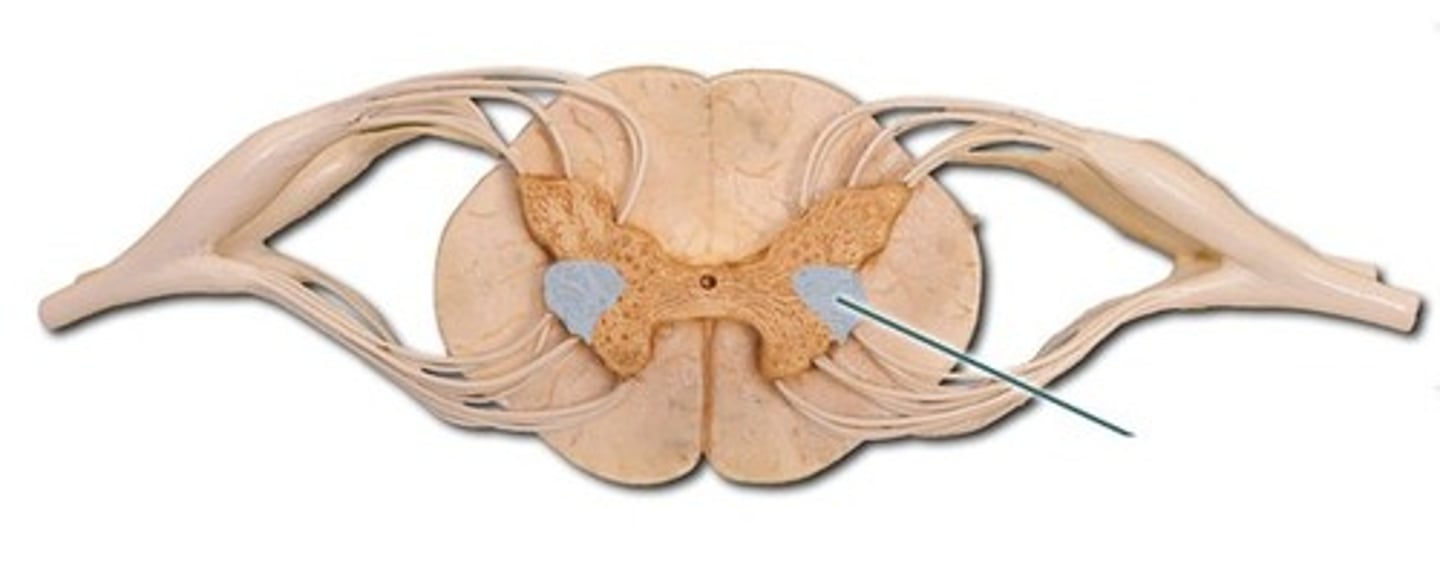
Dorsal horn
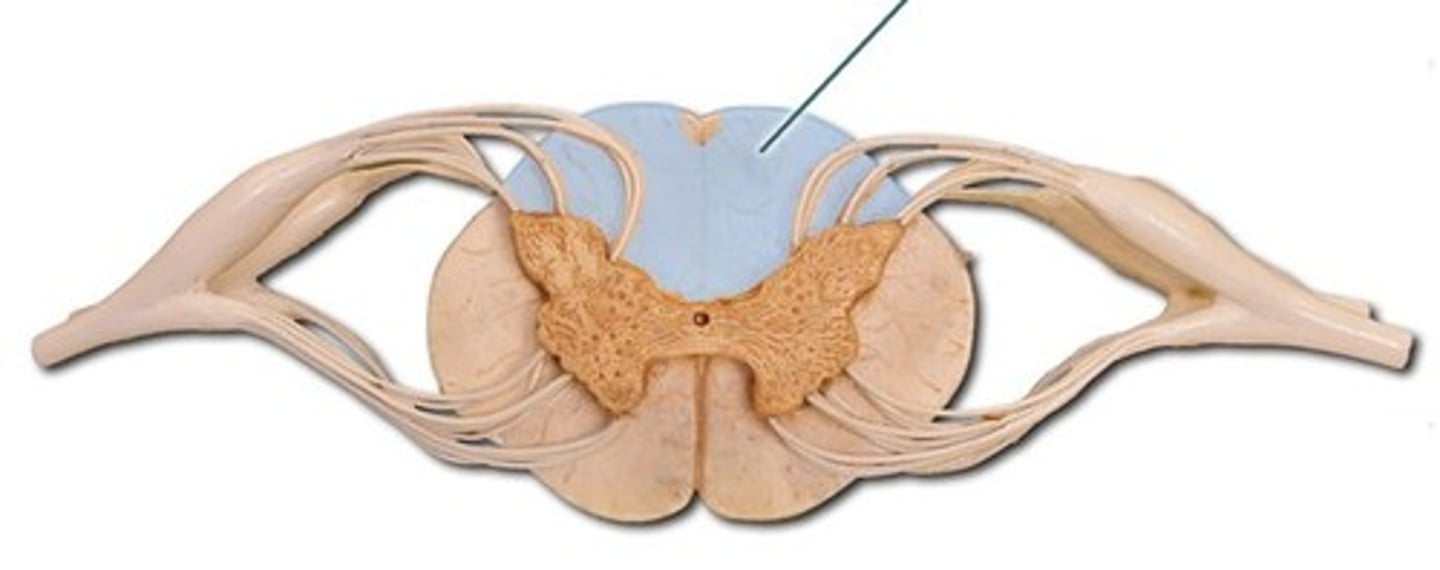
dorsal funiculus
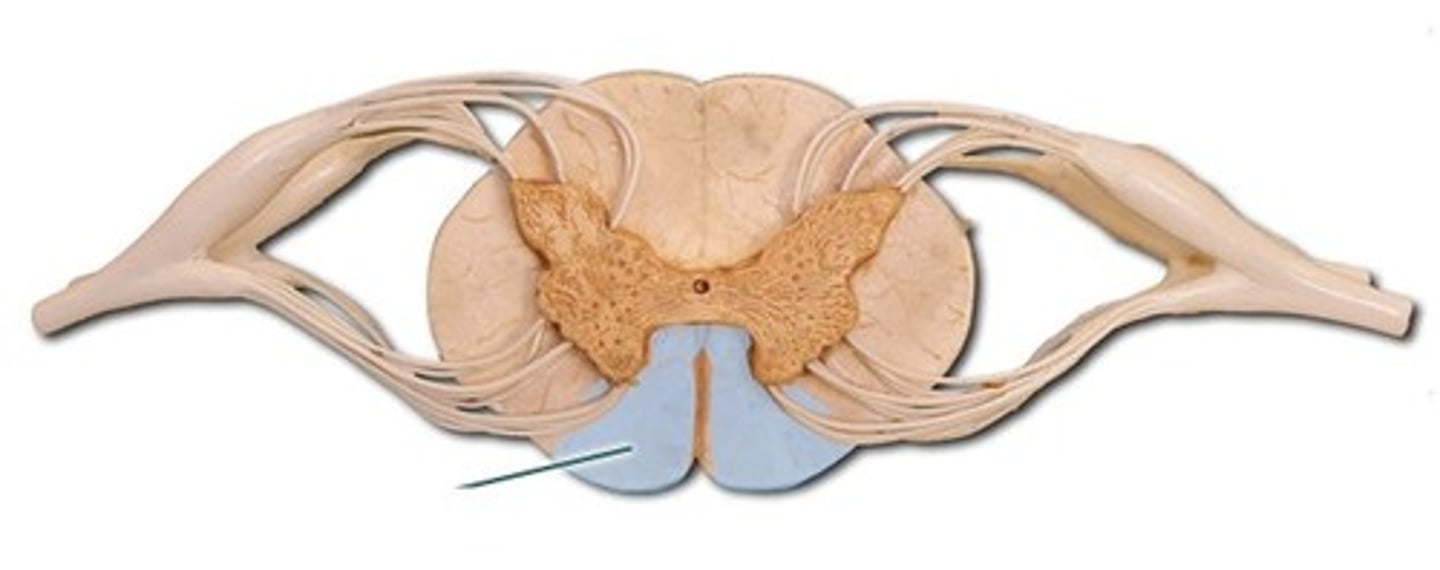
ventral funiculus
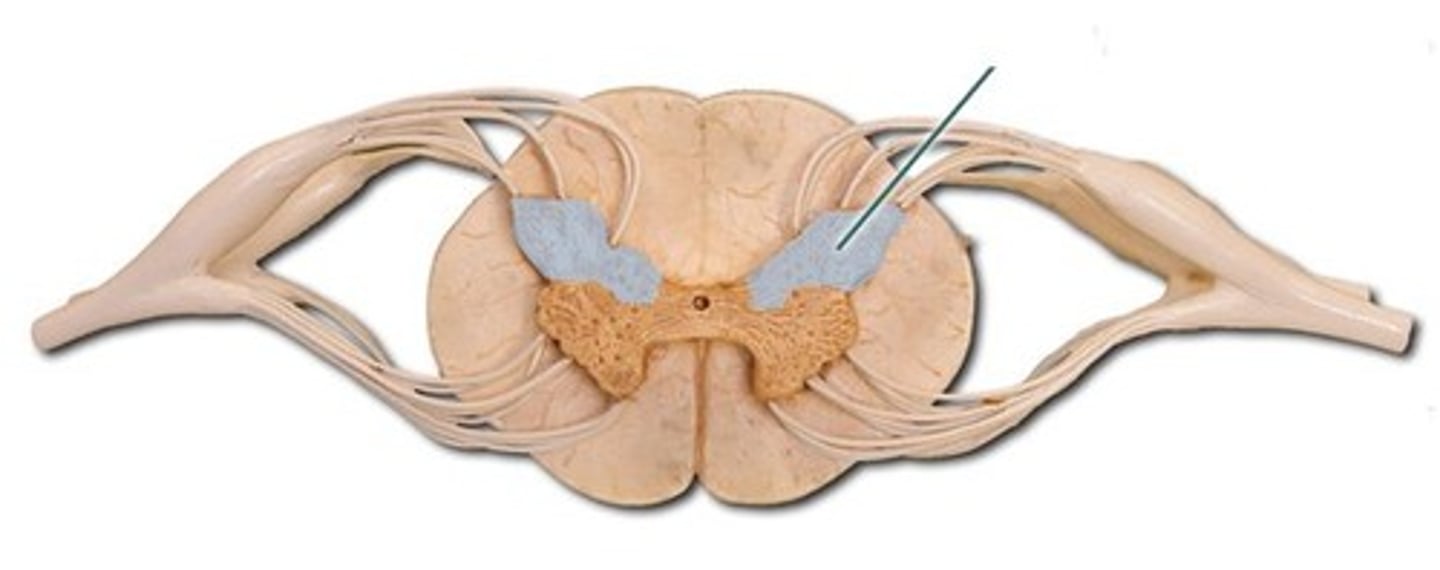
lateral funiculus
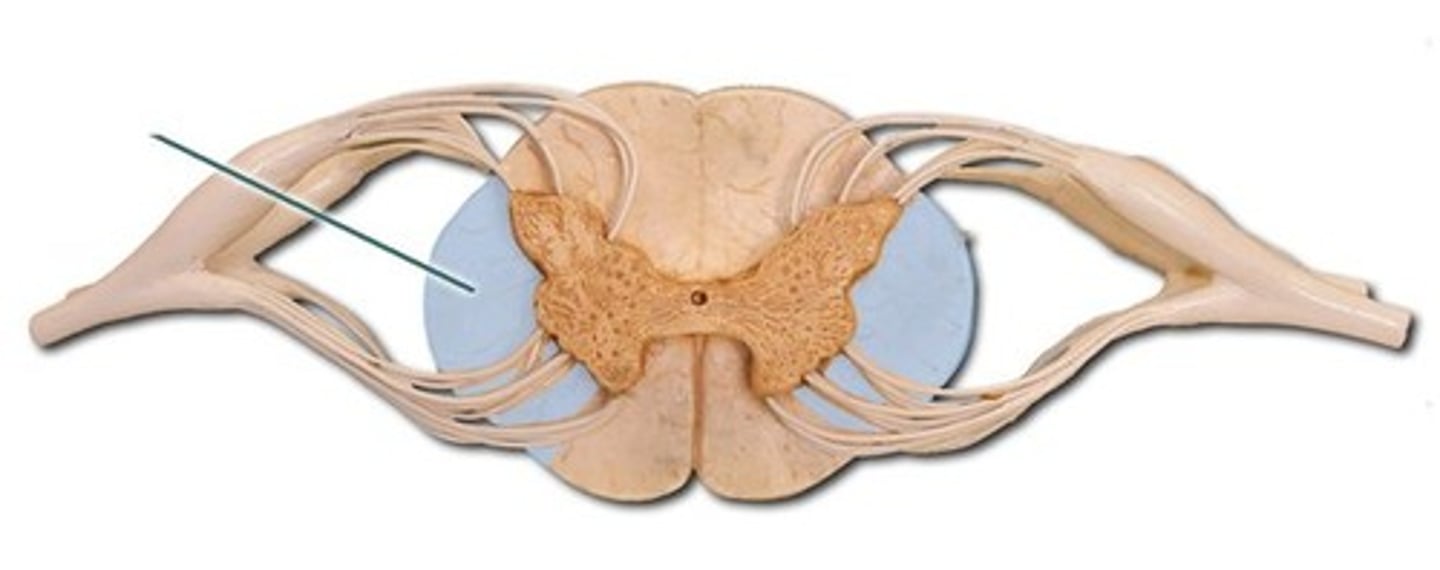
central canal
filled with cerebral spinal fluid
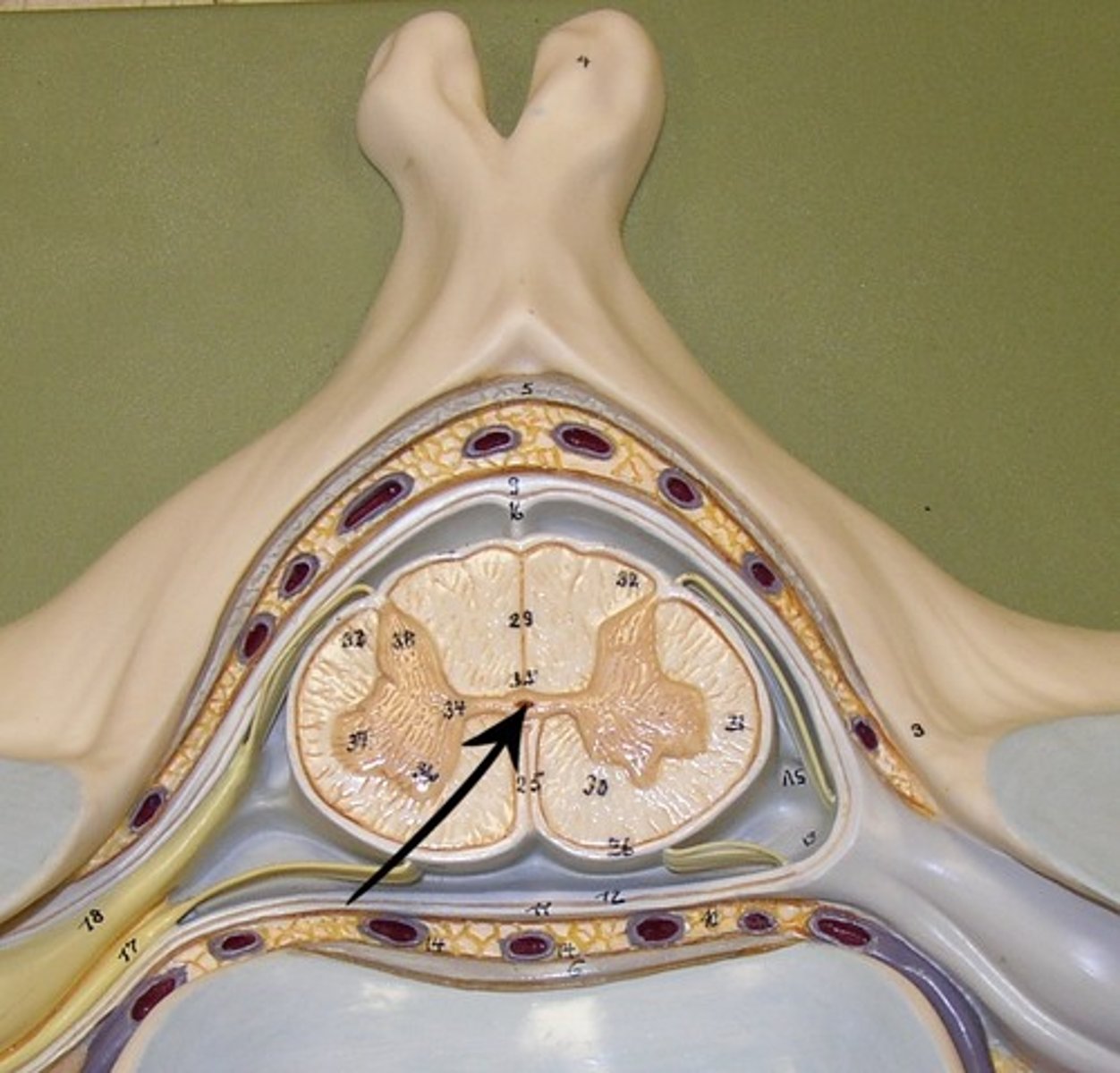
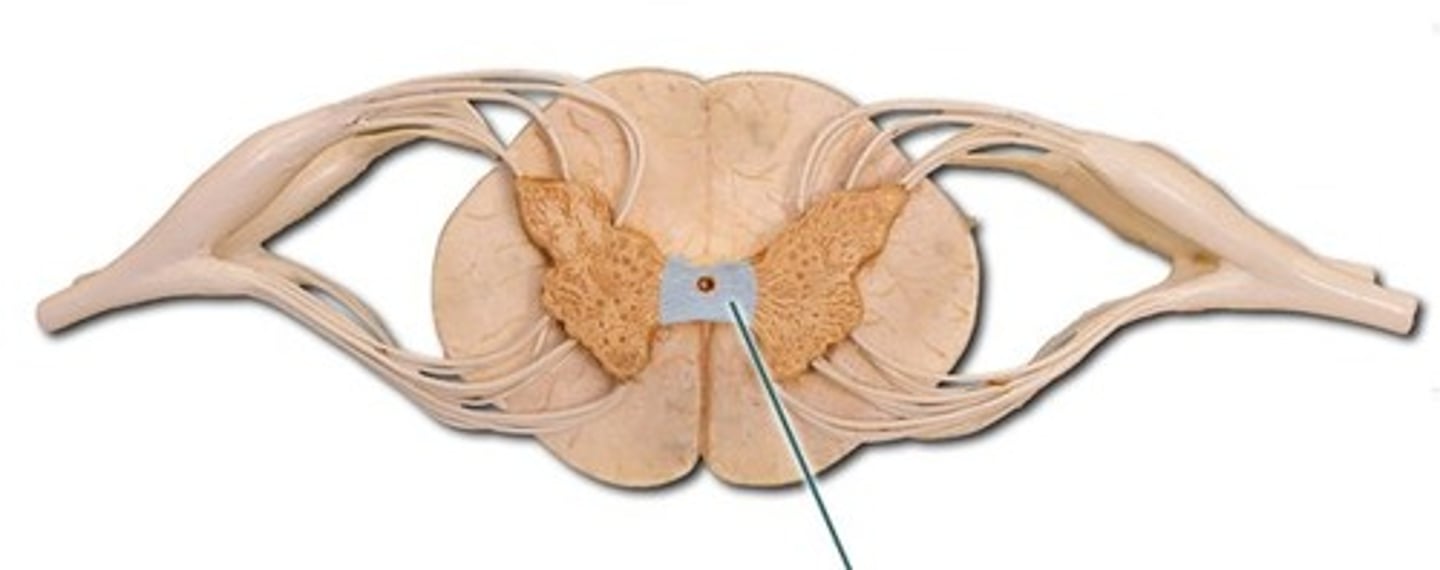
gray commissure
cross bar of butterfly
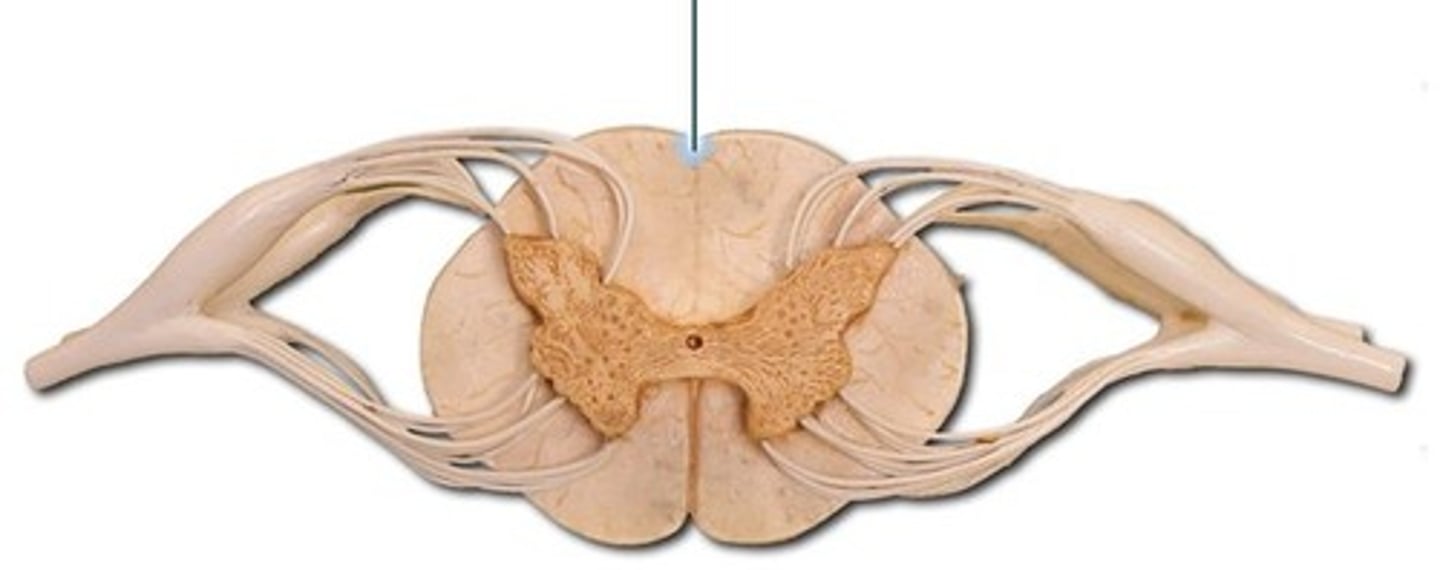
posterior median sulcus
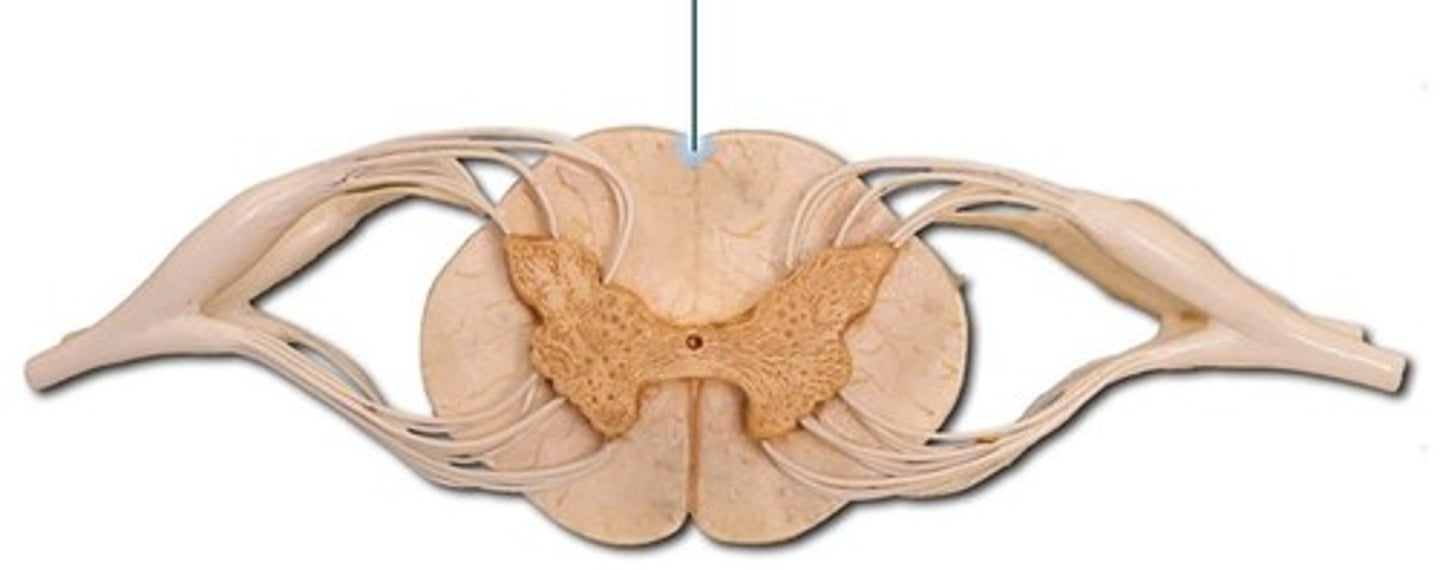
anterior median sulcus
dorsal root
attach to the dorsal horn of the root ganglia on the spinal cord
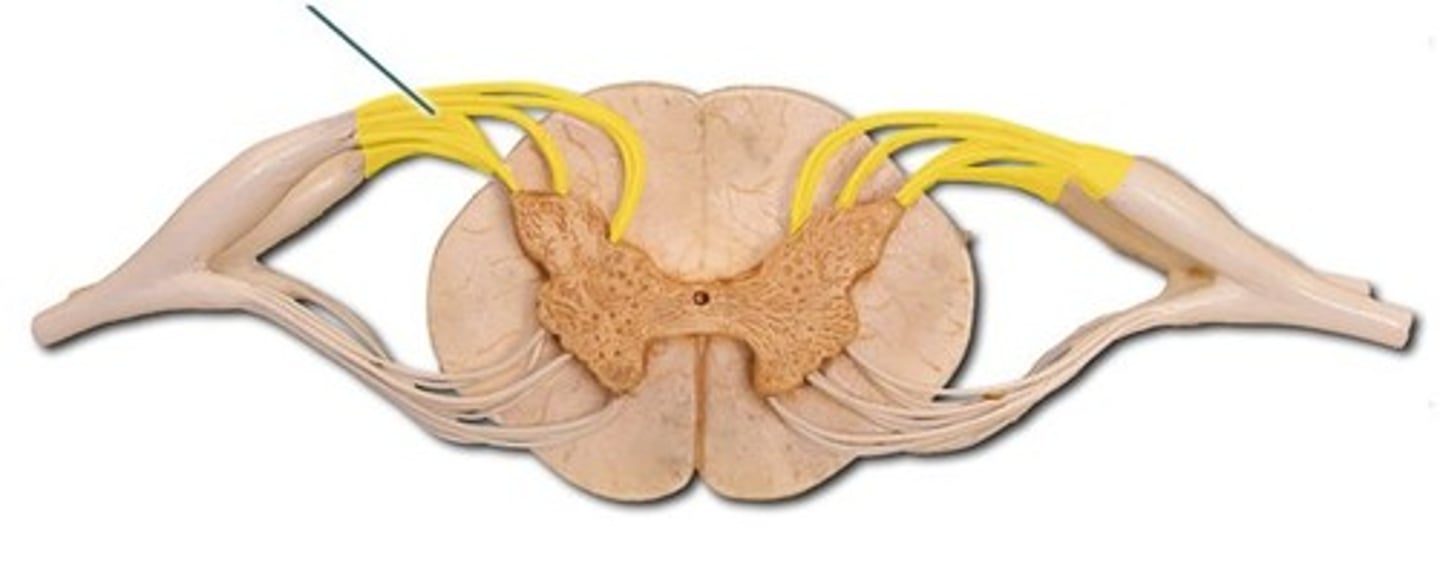
dorsal root ganglion
cell body of sensory neurons attached to dorsal horn of spinal cord
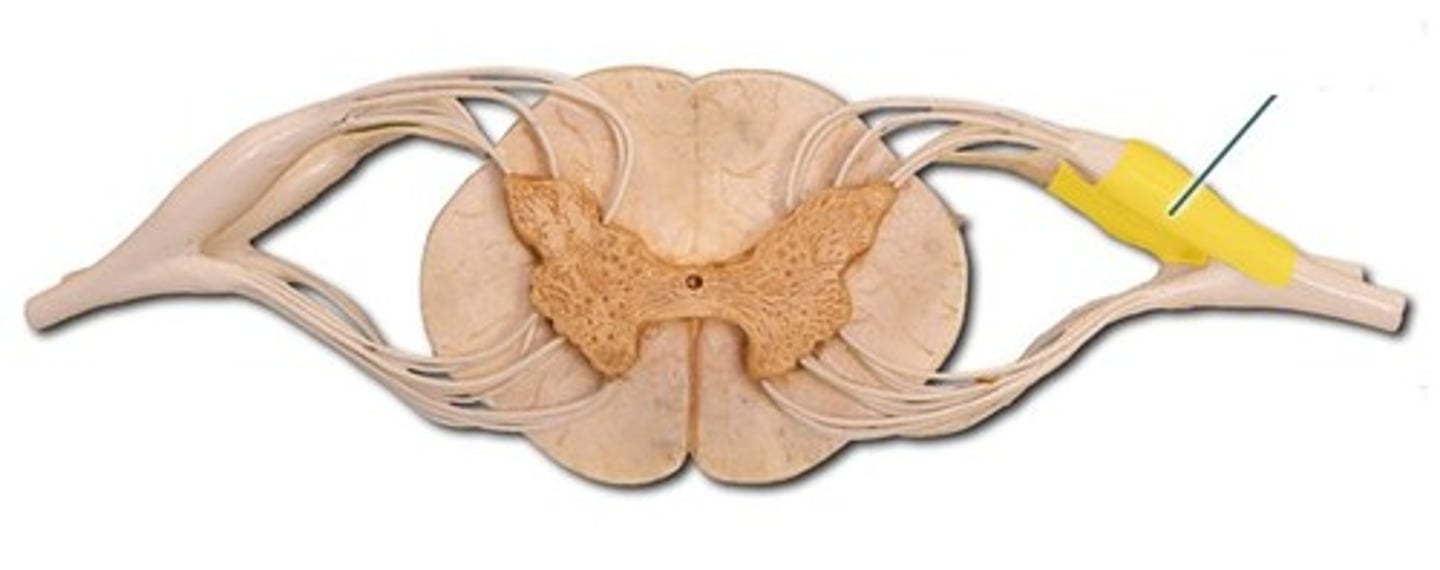
ventral root
origin of motor neurons attached to ventral horn on the spinal cord