(5.3.2) Key processes of ecosystems at different scales
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Tropical rainforest + Savannah
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is a tropical rainforest?
Warm, wet ecosystem with high biodiversity and little seasonal variation located within the Tropics.
Describe the rainfall in ranforests.
extremely high rainfall
exceeds 2000mm annually
usually seasonal with distinct wet seasons
very humid
Describe the temperature in rainforests.
high 26-27 degrees C
little seasonal variation
due to Sun’s direct shine all year
Describe the soil characteristics in rainforests.
infertile, iron-rich, nutrient deprived soil- latosol
due to rapid leaching by rainfall
plants get nutrients from decomposing organic matter on top of soil
nutrients from decomposing matter rapidly absorbed by roots
From top to bottom, state and describe the layers of the rainforest.
Emergent/Upper canopy
birds + flowers
trees are tall + relatively branchless
reach max sunlight
Canopy
monkeys + sloths
shade the forest floor below with leaves
Understory
smaller trees + vines
receives less light
Forest floor
decomposers + decaying organic matter
darkest + most humid layer
What are buttress roots?
large, ridge-like, above ground roots
an adaptation to the nutrient deprived soil
ensure tall trees remain stable
How have leaves adapted to the rainforest?
drip tips- tapered ends of leaves
allows rain to drip off
ensuring leaves don’t remain wet,
which could cause rotting
flexible stems to move to light
What are lianas?
Plants that have roots on the ground
but grow into canopy by wrapping around trees
gets them sunlight from canopy and nutrients from forest floor
How have animals adapted to protect against being eaten in the rainsforest?
developed poisons or carry venoms
How have animals adapted physically to the rainforest?
long limbs + strong tails
swing around
strong claws
climbing trees
sticky pads
help climbing
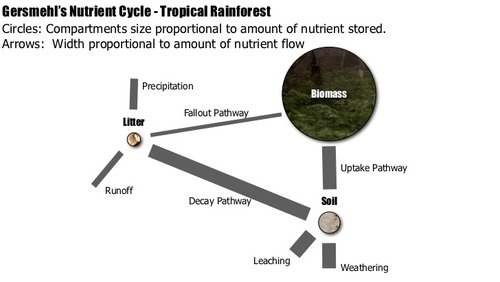
Outline the nutrient cycle in the tropical rainforest.
quick process
continuous fallout from biomass
litter decomposes quickly due to warmth + damp conditions
nutrient uptake by roots from soil
loss from leaching
consumers eat plants
consumers die and nutrients back in soil by decomposers
Outline the carbon cycle in the tropical rainforest.
trees take carbon from atmosphere into biomass during photosynthesis
carbon transferred back to soil and atmosphere during decomposition
carbon released during respiration
carbon sink- photosynthesis
when forests are cleared, 30-60% of carbon is lost to atmosphere
Outline the water cycle in the tropical rainforest.
roots take up water from ground
rain is intercepted as it falls
as forest heats up, water evaporates and, with transpiration, forms clouds
forest is a store of water
rainfall feeds rivers
What services does the rainforest perform?
carbon store
water supply
provides goods- food, fuel
sustaining culture
climate regulation
What are some threats to the tropical rainforest?
deforestation
increased access- roads + mining
farming
large scale machinery → compacts soil
logging
tourism
What is the savanna biome?
hot semi-arid grasslands found between the Tropics
(between high rainfall of tropical rainforests and dry desert lands)
Describe the climate in the savanna.
2 distinct wet and dry seasons
consistently high temperatures
Describe the soil in the savanna.
high temperatures (20-30) lead to evaporation
water moves up soil in dry season
carrying minerals
depositing it in the upper layers of the soil
mineral rich upper soil
heavy rains in wet season = leaching
faster decomposition in wet than dry season
Describe vegetation in the savanna.
tall continuous grass understory
tree canopy are dotted around- showing areas of higher water
What are the challenges for plants and animals in the savanna?
adapting to a wet and dry season
adapting to a dry climate with fire risk
What are some adaptations plants have undergone to survive in the savanna biome?
xerophytic- drought resistant
pyrophytic- fire resistant
trees have small waxy leaves/lose leaves to reduce transpiration and grow leaves just before rainy season
long roots to reach underground water stores
some trees- baobab- store water in trunk’s spongy layer
How have animals adapted to the savanna?
migration for water during dry season
hibernation through dry season
nocturnal to avoid the heat of the day
increased SA- reduces heat
Describe the water cycle in the savanna glassland.
recurrent drought lasting 4-6 months
dry xeropause, plant activities continue but at reduced rates
diverting water for tourists is exploiting local water reserves
Describe the carbon cycle in the savanna grassland.
cover 20% of Earth so their extent rather than their density makes them significant
regular bush fires → release of CO2
fires are becoming more common
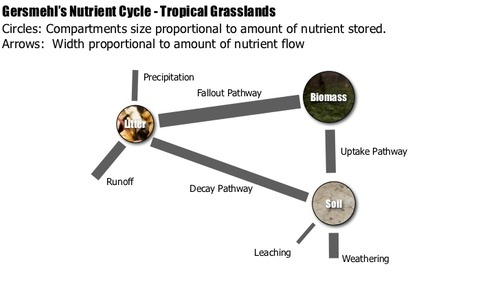
Describe the nutrient cycle in the savanna.
Stores relatively even
biomass much smaller than rainforest due to shorter growing season
start of dry season: biomass→litter is high
leaves fall
grasses die
litter is small due to fires
slow transfer litter→soil in dry season
larger soil store than rainforest as:
less vegetation demand
uptake mainly in wet season
less leaching overall
What services does the savanna provide?
natural medicines
food
regulate water + carbon cycle
tourism
cultural importance
What are the main threats to the savanna ecosystem?
logging
hunting
over-grazing
global warming
desertification
What are the effects of desertification on the savanna?
overgrazing + farming
extracts nutrients
removes vegetation
little coverage exposes soil
exposed soil breaks and cracks
infertile soil
exacerbated cycle due to little coverage
higher rates of erosion + further decline
What is biodiversity?
the variety of plant and animal life in the world or in a particular habitat
What are supporting services? Give examples.
services necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services
primary production
photosynthesis
nutrient cycling
What are provisioning services?
the products obtained from ecosystems:
food
medicine
fuel
biochemicals
What are regulating services?
benefits obtained from the regulation of the ecosystem:
climate regulation
air quality regulation
pest regulation
disease regulation
What are cultural services?
non-material benefits obtained
spiritual enrichment
recreation
aesthetics
cognitive development
Name a small scale ecosystem in the UK. Give some information.
Studland Bay sand dunes
Dorset coast
Embryo Dunes
closest to shore
marram grass colonised
Fore Dunes
stabilised by marram grass
Yellow Dunes
further inland
higher vegetation cover
Grey Dunes:
more stable
heather and gorse
Climatic Climax Community
naturally oak + pine
Hosts range of species
dunes shaped by wind and water influenced sand movement
organic matter accumulation affects nutrient cycling
water percolation supports diverse vegetation
What is the effect of humans on biodiversity in Studland Bay’s dunes?
tourism → trampling → disturbs nesting sites
introduction of invasive species can outperform natural flora and fauna
conservation efforts aims to protect but can alter natural dynamic
What is the effect of humans on flows in Studland Bay’s dunes?
paths and infrastructure disturb natural percolation and water patterns
boardwalks stabilise dunes, reducing sand movement
What is the effect of humans on cycles and process in Studland Bay’s dunes?
trampling → reduces vegetation cover → soil erosion → loss of biomass