Gravitational fields
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Force field definition
A region in which a body experiences a non-contact force
Gravitational field definition
A region in which mass experiences a non-contact force
What is gravity
It is a universal attraction between two masses
It is quite a weak force so is only noticed in large objects like planets and stars
gravitational field strength definition
The force per unit mass on a small test mass placed in the field
the test mass must be small otherwise it will pull too much on the other object, making it change its position and alter the field
Gravitational field strength equation
g = grav field strength = 9.81 Nkg-1 on earth
F = gravitational force
m - mass
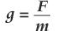
Newtons law of gravitation
he reasoned that the gravitational pull exerted on a body needs to be proportional to its mass, as 3rd law states these forces are equal, force between masses must be proportional to both
assumes that F is - always an attractive force, proportional to mass of each object, proportional to 1/r2
Newtons law of universal gravitation (Force between 2 masses) equation
F = Gravitational force
G = gravitational constant = 6.67×10-11 Nm2kg-2
m = mass
r = radius
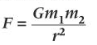
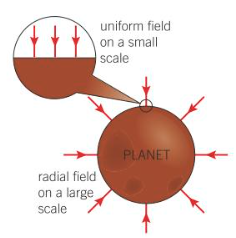
Radial and uniform field patterns
Radial - Field lines directed towards centre of an object
this occurs on a large scale
Uniform - g is the same magnitude and direction, field lines equally spaced an parallel
occurs on small scale
Gravitational potential energy definition
Energy of an object due to its position in a gravitational field
infinity has 0 GPE as object is so far from gravitational force that it is negligible
GPE is negative at the surface so work needs to eb done to leave the surface
Gravitational potential definition
the work done per unit mass to move a small object from infinity to that point
Gravitational potential equation
V = gravitational potential = Jkg-1
W = work done
m = mass
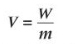
Equipotential definition
surfaces on constant potential, so no work needs to be done to move along the surface as they are along the same potential gradient
horizontal movement at the same point on a field line when in a surface over a small region
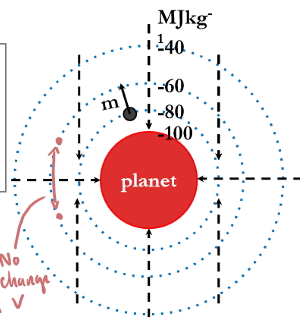
Potential gradient definition
the change of potential energy per metre at that point
potential gradient = change in V/change in r
grav field strength is negative of potential gradient
how does g vary with distance from centre of planet
inverse square law relationship 1/r2
Gravitational potential of spherical object equation
V - gravitational potential
G - gravitational constant
M - mass of planet
r - distance from centre of planet (radius)
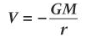
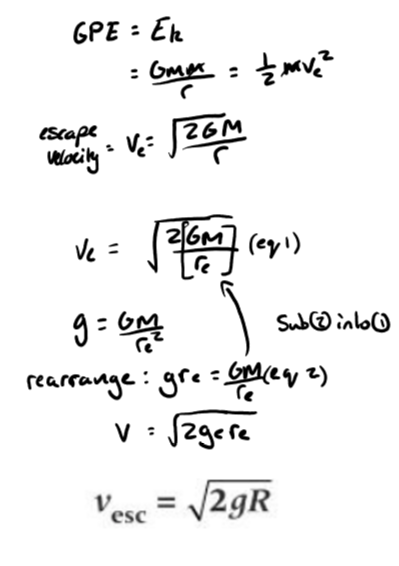
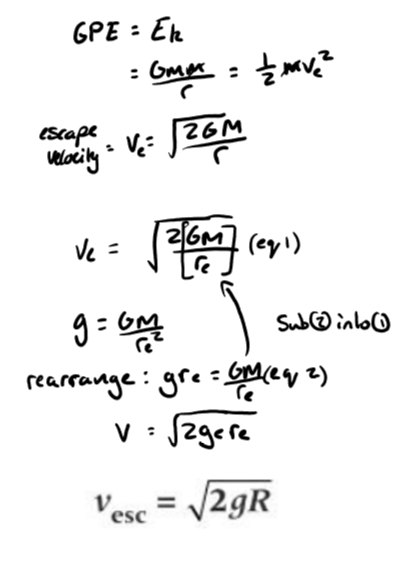
Escape velocity definition
minimum velocity an object must be given to escape from the planet when projected vertically from the surface
escape velocity equation
g - grav field strength
R - radius of planet
Derived from work done = mV = gmm/R
and Ek = 1/2mv2 = Work done
v2 = 2GM/R
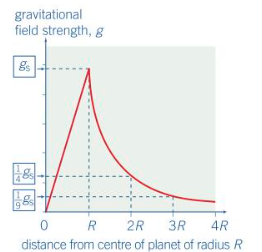
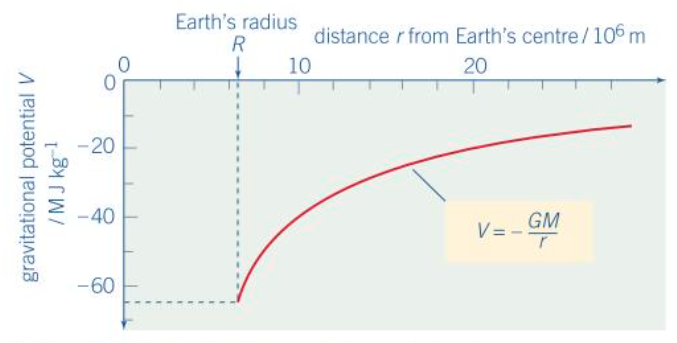
Potential gradient near spherical planet of a graph
Its an inversely proportional relationship (1/r)
How does energy of a satellite work
Total energy is constant and is equal to GPE and KE
How do satellites act in orbit
They need to be travelling at the correct speed for the orbit
Their speed increases as they move close to the earth
Its period will decrease as it moves closer to the earth as its orbit is shorter
Measurement of distance of orbit should be from the centre of the earth
Eccentric orbit
orbits where the altitude varies
Polar orbits
Orbit that passes over north and south poles
as the earth spins on its axis this can scan the entire earth in a few revolutions
spy and weather satellites use this orbit
Low earth orbit satellites
these are easy to access and are used for space stations
Geostationary orbit satellites
These are 35,900km about the equator and take 24 hours to complete an orbit
The satellite is fixed but the earth spins round it to orbit
They are used for communication (INTELSAT) or weather monitoring (METEOSTAT)
Radius of orbit is calculated using the equation
Energy of an orbiting satellite equation
