Introductory Physics- Chapter 4- Newton's Second Law of Motion
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:43 AM on 9/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1
New cards
What is acceleration directly proportional to?
* net force
* Increasing acceleration of object also increases net force
* Increasing acceleration of object also increases net force
2
New cards
What does the force of friction depend on?
* type of material and how much they’re pressed together
* due to tiny surface bumps and to “stickiness” of atoms on material’s surface
* Ex: Friction between crate on smooth wooden floor is less than that on rough floor
* due to tiny surface bumps and to “stickiness” of atoms on material’s surface
* Ex: Friction between crate on smooth wooden floor is less than that on rough floor
3
New cards
What is mass?
* quantity of matter in an object
* also measure of inertia or sluggishness that object has in response to any effort made to start it, stop it, or change its state of motion in any way
* does not depend on gravity like weight
* is constant- same mass everywhere
* the greater the inertia, the greater the mass
* Unit: Kg
* also measure of inertia or sluggishness that object has in response to any effort made to start it, stop it, or change its state of motion in any way
* does not depend on gravity like weight
* is constant- same mass everywhere
* the greater the inertia, the greater the mass
* Unit: Kg
4
New cards
What is weight?
* force upon an object due to gravity or if suspended in supporting string
* depends on location: Different weight on Earth, Moon, etc
* Unit: N
* Another common unit is lbs
* Formula: W=mg(mass\*gravity)
* depends on location: Different weight on Earth, Moon, etc
* Unit: N
* Another common unit is lbs
* Formula: W=mg(mass\*gravity)
5
New cards
What is acceleration inversely proportional to?
* mass; resists acceleration
* Ex: twice the mass produces half the acceleration
* Ex 2: three times the mass produces one third the acceleration
* Ex: twice the mass produces half the acceleration
* Ex 2: three times the mass produces one third the acceleration
6
New cards
What does Newton’s second law state?
* Acceleration→ produced by a net force on object→ directly proportion to net force, is the same direction as net force, and is inversely related→ mass of object
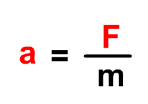
7
New cards
What does Free Fall suggest?
* **a=g; acceleration of an object is approximately equal to acceleration due to gravity**
* **the greater the mass of object:**
* the __greater its force of attraction toward Earth__(meaning the greater its weight)
* __the smaller its tendency to move; the greater its inertia__
* __acceleration of any object regardless of weight is approximately 10 m/s^2__
* Ex: coin and feather fall together in a vaccum chamber because there is no air→no air resistance
* **the greater the mass of object:**
* the __greater its force of attraction toward Earth__(meaning the greater its weight)
* __the smaller its tendency to move; the greater its inertia__
* __acceleration of any object regardless of weight is approximately 10 m/s^2__
* Ex: coin and feather fall together in a vaccum chamber because there is no air→no air resistance
8
New cards
What does non free fall suggest?
* **a does not = g**
* when an object falls downward through air, it experiences *gravity* and *air drag*
* **air resistance is negligible-depends on two things:**
* __speed__ and __frontal surface area__
* **When object is moving fast, air resistance builds up to balance(F net = 0) the force of gravity(R=mg), meaning**:
* __no net force, no acceleration, velocity doesn’t change__
* Ex: rock hits ground before feather when air is present; rock takes more time for air resistance to balance its weight
* when an object falls downward through air, it experiences *gravity* and *air drag*
* **air resistance is negligible-depends on two things:**
* __speed__ and __frontal surface area__
* **When object is moving fast, air resistance builds up to balance(F net = 0) the force of gravity(R=mg), meaning**:
* __no net force, no acceleration, velocity doesn’t change__
* Ex: rock hits ground before feather when air is present; rock takes more time for air resistance to balance its weight
9
New cards
What is terminal speed and terminal velocity in non-free fall?
* **Terminal speed**- when __acceleration terminates__(air resistance balances weight, so that net force=0)(R=mg)
* **Terminal velocity**- __terminal speed__ along with __direction of motion__(which is downward)
* **Terminal velocity**- __terminal speed__ along with __direction of motion__(which is downward)