Humidity and Aerosol Therapy in Medical Practice
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Humidity
Water that exists in the form of individual molecules in the vaporous or gaseous state.
Size of Water Molecules
Molecules of water are about 0.001 µm.
Medical Aerosols
Medical aerosols can range from 0.2 to 50 µm.
Atomizers
Devices used to generate medical aerosols.
Nebulizers
Devices used to generate medical aerosols.
Inhalers
Devices used to generate medical aerosols.
Condensation
Occurs when vapors cool and collects in the lowest point of the circuit.
Relative Humidity (RH)
As temperature increases, the amount of water a gas can hold increases, decreasing its Relative humidity (RH).
Humidity Management Methods
Condensation is managed by placing water traps at the lowest point in the circuit or using a heated wire circuit.
Heat Moisture Exchange
A primary function of the respiratory tract that adds heat and humidity during inspiration and retains it during exhalation.
Humidity Therapy
Involves adding water vapor to inspired gas.
Isothermic Saturation Boundary
Point in airway where inspired gas is saturated with humidity at body temperature, usually occurring 5 cm below carina.
Indications for Humidification Therapy
Primary: Humidifying dry medical gases; Overcoming humidity deficit created when upper airway is bypassed.
Secondary Indications for Humidification
Treating bronchospasm caused by cold air.
Inspissated Secretions
Thick pulmonary secretions that occur as the production of mucus increases.
Humidity Injury Threshold
When the RH of inspired gas is greater than 60% of Body temperature and pressure saturated (BTPS) conditions, no injury is believed to occur in normal lungs.
Contraindications for Humidity Therapy
Humidity devices may be contraindicated in patients with upper airway hyperresponsiveness or at risk for bronchoconstriction.
Humidifiers
Devices that add molecular water (vapor) to gas.
Factors Affecting Humidifier Performance
Time of contact, temperature, surface area of contact, and thermal mass.
Contact Time
The longer the time of contact, the more time for evaporation to occur.
Temperature Effect on Humidity
As temperature increases, capacity (potential humidity) will increase.
Surface Area Effect on Humidity
The greater the surface area, the more potential for evaporation.
Thermal Mass
The more water in the humidifier, the more potential for transfer of heat.
Types of Humidifiers
Humidifiers are either active (actively adding heat or water) or passive (recycling exhaled heat and humidity).
Active Humidifiers
Include bubble humidifiers, passover humidifiers, nebulizers of bland aerosols, and vaporizers.
Passive Humidifiers
Refer to typical heat and moisture exchangers (HMEs).
Bubble Humidifiers
Break underwater gas stream into small bubbles to increase surface area for gas/water interaction.
Unheated Bubble Humidifier Output
Can provide an absolute humidity level of 10 to 20 mg/L.
High-Flow Humidifiers
Used with mechanical ventilation and designed to accommodate flow rates of gas delivered up to 100 L/min.
Passover Humidifiers
Directs gas over water surface and includes simple reservoir type, wick type, and membrane type.
Heated Humidifiers
Devices that increase humidity for respiratory patients.
Absolute Humidity
Amount of water vapor in a gas.
Mechanical Ventilation
Assisted breathing using machines for patients.
Airway Burns
Injuries caused by heated inhaled gases.
Large Bore Heated Tubing
Reduces condensation and obstruction in humidifiers.
Optimum Humidity
Ideal humidity levels for airway conditions.
AARC Guidelines
Recommendations for respiratory care practices.
Humidity Level for Intubated Patients
At least 30 mg/L of humidity required.
High-Flow Heated Humidifiers
Used with high-flow systems for ventilation.
Water Reservoir
Large container for humidifier water supply.
Gravity Feed System
Uses gravity to maintain water levels automatically.
Manual System
Requires manual refilling of humidifier water.
Wick Humidifier
Gas passes through water-saturated material.
Heat-Moisture Exchangers (HMEs)
Passive devices that recycle exhaled humidity.
Simple Condenser Humidifier
Traps heat and humidity from exhaled gas.
Hygroscopic Condenser Humidifier
Uses hygroscopic materials to enhance humidity.
Hydrophobic Condenser Humidifier
Water-repellent element that retains humidity.
Flotation Valve
Maintains fluid volume in humidifier reservoir.
Vapotherm 2000i
Device for heating and humidifying oxygen.
Condensation Prevention
HMEs with filters reduce infection risks.
Maximum Absolute Humidity
Upper limit of humidity in gas delivery.
Thin-Film Boiler
High-surface area device for humidification.
Heating Elements
Components that require energy to heat water.
Inspiratory Line
Pathway for gas delivery to patients.
Cross-Contamination
Unwanted transfer of pathogens between systems.
Molecular Humidity
Humidity that decreases infection risk.
Heat Moisture Exchanger (HME)
Device that conserves heat and moisture in gas.
Mechanical Dead Space
Volume added by HMEs, 30 to 90 mL.
Uncuffed Endotracheal Tubes (ETTs)
ETTs allowing gas leakage, reducing HME efficiency.
Heated Humidity
Humidity provided at temperatures below 35°C causes obstruction.
Active HMEs
Devices adding heat or humidity to inspired gas.
Relative Humidity
Amount of moisture in gas, 100% at BTPS.
Minute Volume
Total gas volume breathed per minute, 4 to 20 L.
Humid-Heat System
Absorbs expired moisture, releases into inspired gas.
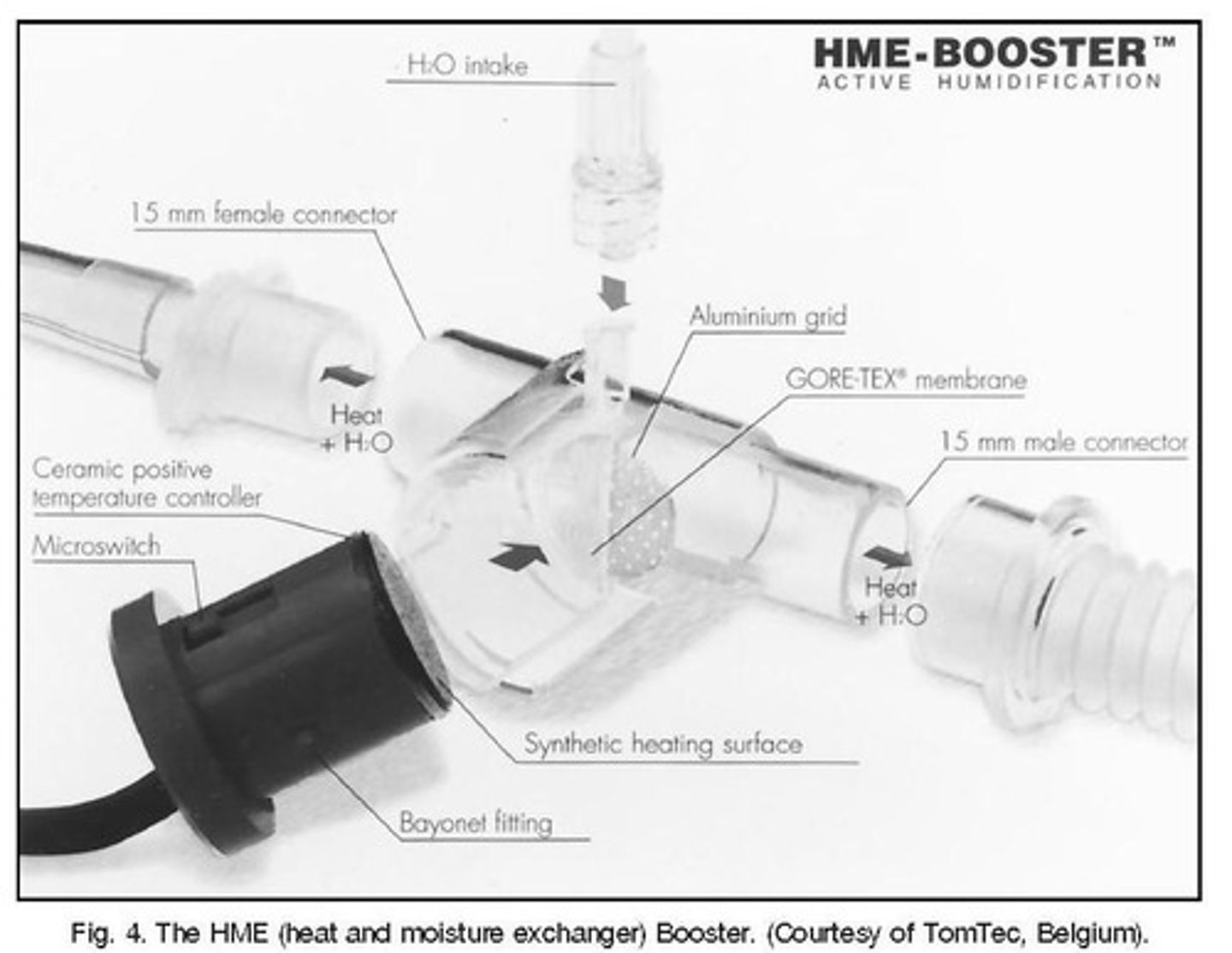
HME Booster
T-piece with heated element for specific patient volumes.
Contraindications for HMEs
Conditions where HMEs should not be used.
Tidal Volume
Volume of air per breath, >700 mL contraindicates HMEs.
Cross Contamination
Risk of infection from humidification systems.
Bland Aerosol Therapy
Therapy using liquid particles in gas.
Indications for Cool Bland Aerosol
Conditions like laryngotracheobronchitis requiring humidification.
Large-Volume Nebulizers
Devices generating bland aerosol using Bernoulli principle.
Air:Oxygen Ratios
Proportions of air to oxygen for different FiO2 levels.
Calculation for Air:Oxygen Ratios
Liters air = (100-O2%); Liters O2 = (%O2-21).
Variable Air-Entrainment Port
Allows air mixing to adjust flow rates and FiO2.
Heated Nebulizers
Produce 35 to 55 mg H2O/L due to vapor capacity.
Self-Filling Humidifiers
Reduce cross contamination in humidification systems.
Water Traps
Placed in circuits to minimize condensation risks.
Temperature Probes
Ensure accurate temperature readings in humidification systems.
Wick Humidifiers
Lower infection risk by preventing bacterial aerosols.
Aerosol Face Mask
Device for delivering aerosol therapy to patients.
Postextubation Edema
Swelling after extubation requiring humidification support.
Large-Volume Jet Nebulizers
Generate liquid particles using high-velocity gas.
Babington Nebulizer
Uses glass sphere to produce high-density aerosol.
Spinning Disk Device
Centrifugal nebulizer for home aerosol delivery.
Ultrasonic Nebulizers
Use vibrations to create high-density aerosol.
Particle Size
Inversely proportional to transducer's signal frequency.
Aerosol Production Rate
Directly related to transducer's signal amplitude.
Sputum Induction
Diagnoses diseases using hypertonic saline aerosols.
Airway Appliances
Devices for delivering bland aerosol therapy.
Aerosol Mask
Short-term therapy for patients with intact airways.
Face Tent
Used for patients intolerant to masks.
Tracheostomy Mask
Designed for patients with tracheostomy.
T-tube
Used for tracheostomy patients needing oxygen.
Mist Tents
Deliver aerosol therapy to infants and children.
Cross-contamination
Risk minimized by proper cleaning of equipment.
Environmental Concerns
Aerosol exposure can trigger asthma symptoms.
Inadequate Mist Production
Caused by flow issues or system leaks.
Overhydration Risk
Greatest in infants; requires careful monitoring.
Bronchospasm Monitoring
Risk increases with hypotonic aerosol solutions.
Negative Pressure Room
Prevents airborne infection spread; HEPA filters used.