Lecture 8: Haemoglobin and Myoglobin
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
In muscle tissue
myoglobin tissue
Haemoglobin
RBC
Why are haemoglobin and myoglobin essential for the transport of molecular oxygen?
• Oxygen is non-polar = poorly soluble in water
• Oxygen is poorly diffusible = oxygen will not reach target tissues by diffusion alone
• Globin has evolved to transport molecular oxygen
Haldane effect
Haemoglobin gives up CO2 when pO2 rises (lungs)
Haemoglobin binds CO2 when pO2 falls (tissues)
Haem structure
Poryphrin ring and an Fe atom bound to 4 Nitrogen atoms of the ring
1 molecule of oxygen binds to the ___ group in myoglobin and haemoglobin
haem
Fe atom is bound to the protein via ___ residue (proximal ___) on the other side of the ring
histidine
Features of myoglobin structure
- 153 a.a. long
- Compact, tightly folded
- 75% alpha-helixes (8 helices)
- Histidine-93 in the 8th a-helix is covalently linked to Fe
- Haem is linked into Fe helix by proximal and distal histidine
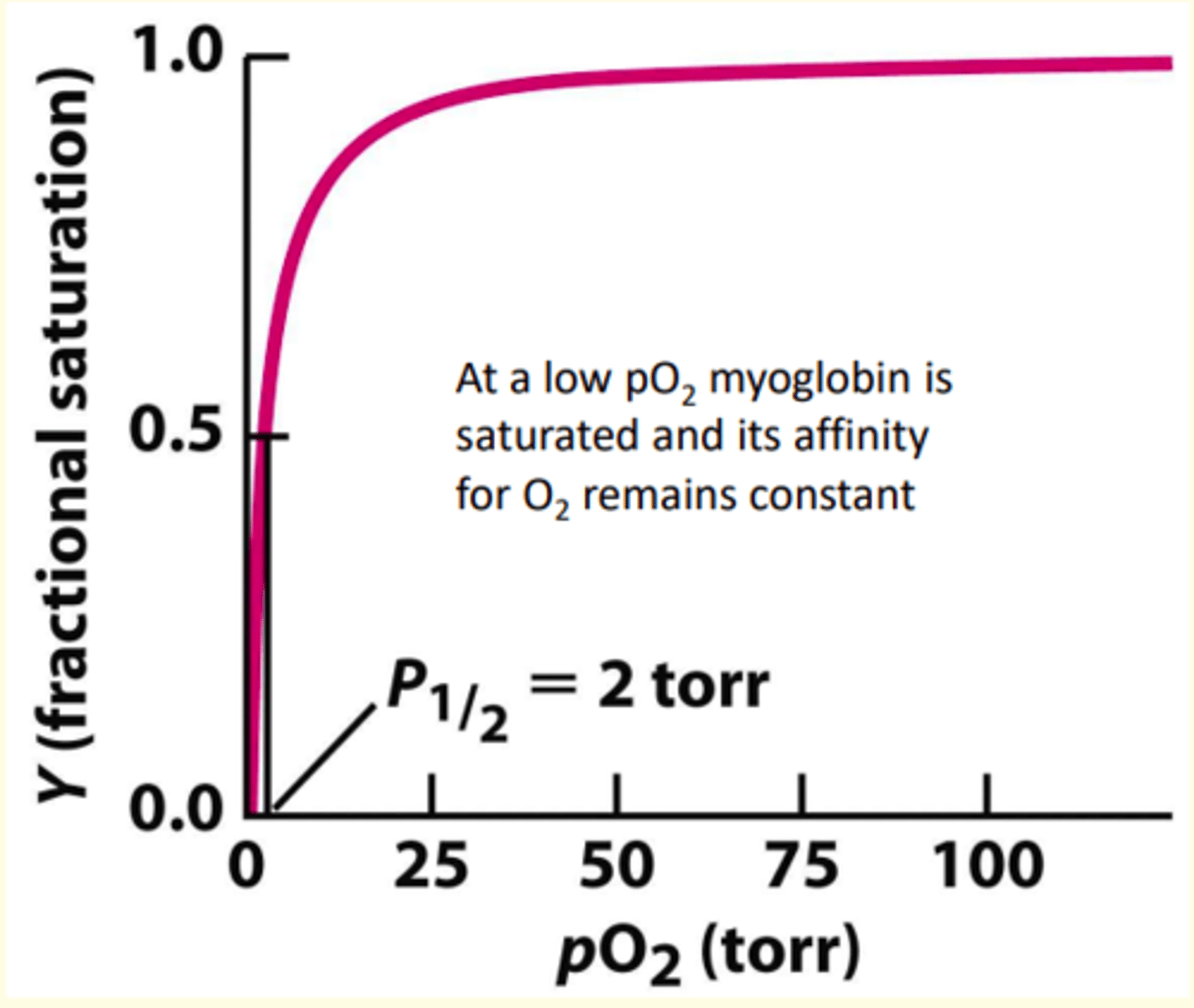
The binding of oxygen by myoglobin shows what type of curve?
hyperbolic binding curve
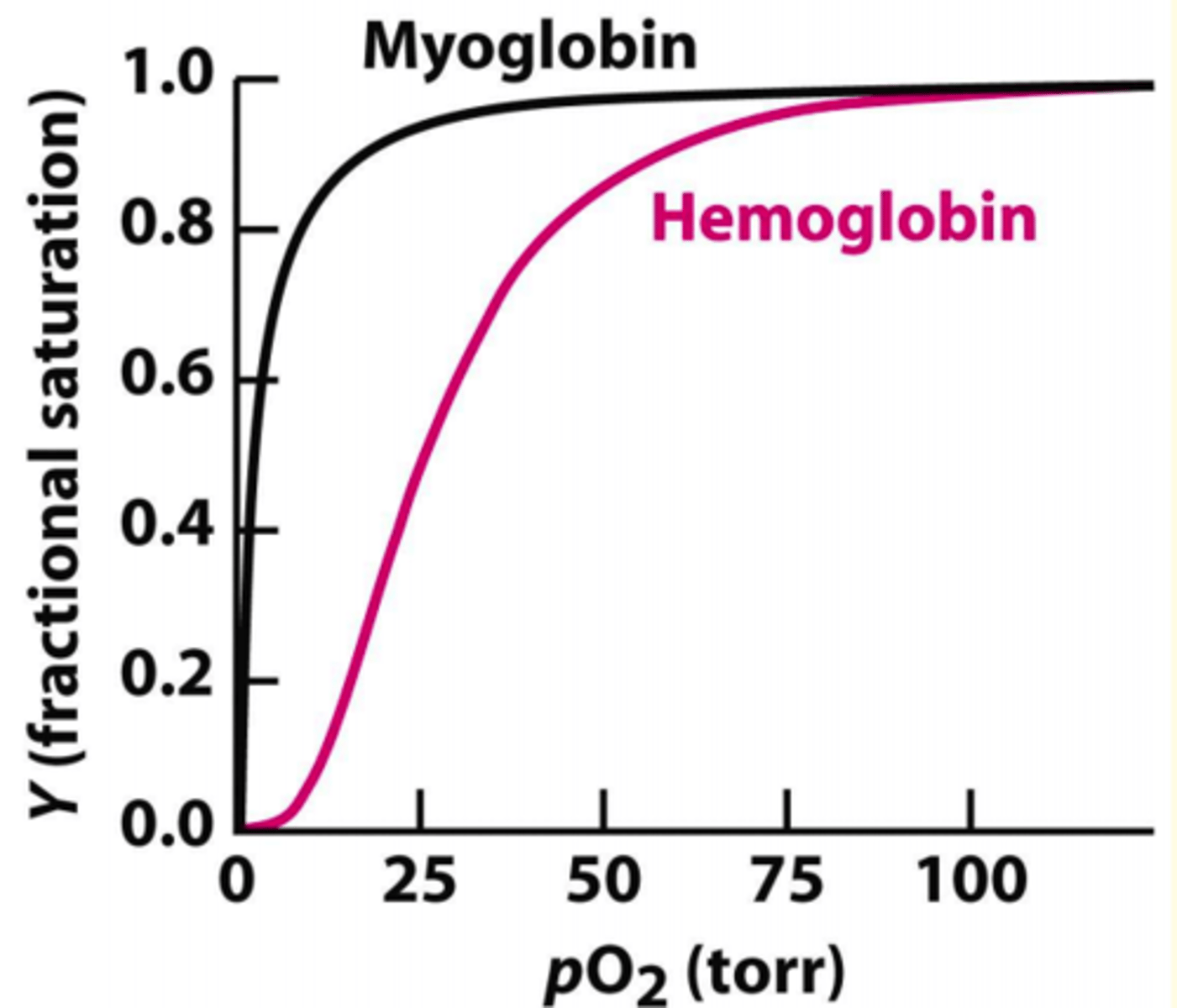
The binding of oxygen by haemoglobin shows what type of curve?
sigmoidal
Features of haemoglobin structure
• a2b2 tetramer
• 2 polypeptide chains = alpha (141 a.a.) and beta (146 a.a.)
• Each chain contains haem prosthetic group which binds an oxygen
• Shape of each polypeptide chain of haemoglobin is very similar to myoglobin (similar amino acids)
X-ray crystallography shows that deoxyhaemoglobin can exist in a tense state (T) which is ___ affinity for oxygen or
a relaxed state (R) which is ___ affinity for oxygen
X-ray crystallography shows that deoxyhaemoglobin can exist in a tense state (T) which is low affinity for oxygen or
a relaxed state (R) which is high affinity for oxygen
Oxygen binding to deoxyhaemoglobin promotes ___ of the R state and a ___% rotation in the molecule
Oxygen binding to deoxyhaemoglobin promotes stabilisation of the R state and a 15% rotation in the molecule
Why is the oxygen binding curve for haemoglobin sigmoidal shaped?
- Cooperative binding = binding of 1st oxygen is hard (low affinity), but the binding of the last oxygen is very easy (high affinity)
- Binding affinity for oxygen increases as more oxygen molecules bind to Hb subunits
Cooperative binding
Each successive oxygen bound to hemoglobin increases the affinity of the other subunits, while each successive oxygen released decreases the affinity of the other subunits
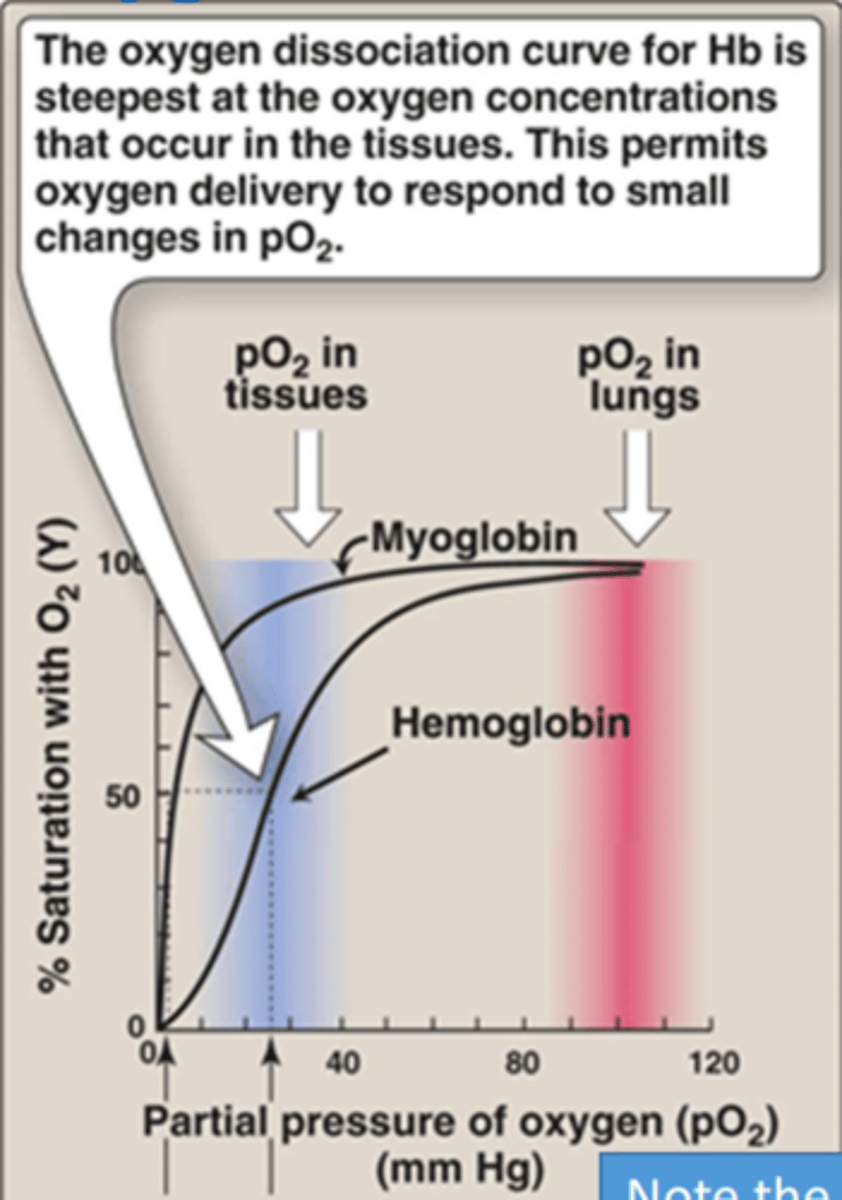
Why is the sigmoidal oxygen dissociation curve useful for haemoglobin's function in the body?
- Sigmoidal binding curve of haemoglobin means that oxygen can be efficiently carried from the lungs to the tissues
- More sensitive to small difference in oxygen concentrations
In the alveolus, mixed venous blood pO2 of 40mmHg/O2 saturation is ___%
75%
In comparison to haemoglobin, myoglobin's oxygen dissociation curve has...
- Higher O2 affinity
- Responds to muscle's oxygen needs rapidly
The plateau of oxygen dissociation Hb is approximately ___mm Hg on the graph
60mm Hg
2-3 Biphosphoglycerate (2-3 BPG) ___ haemoglobin's oxygen affinity
decreases
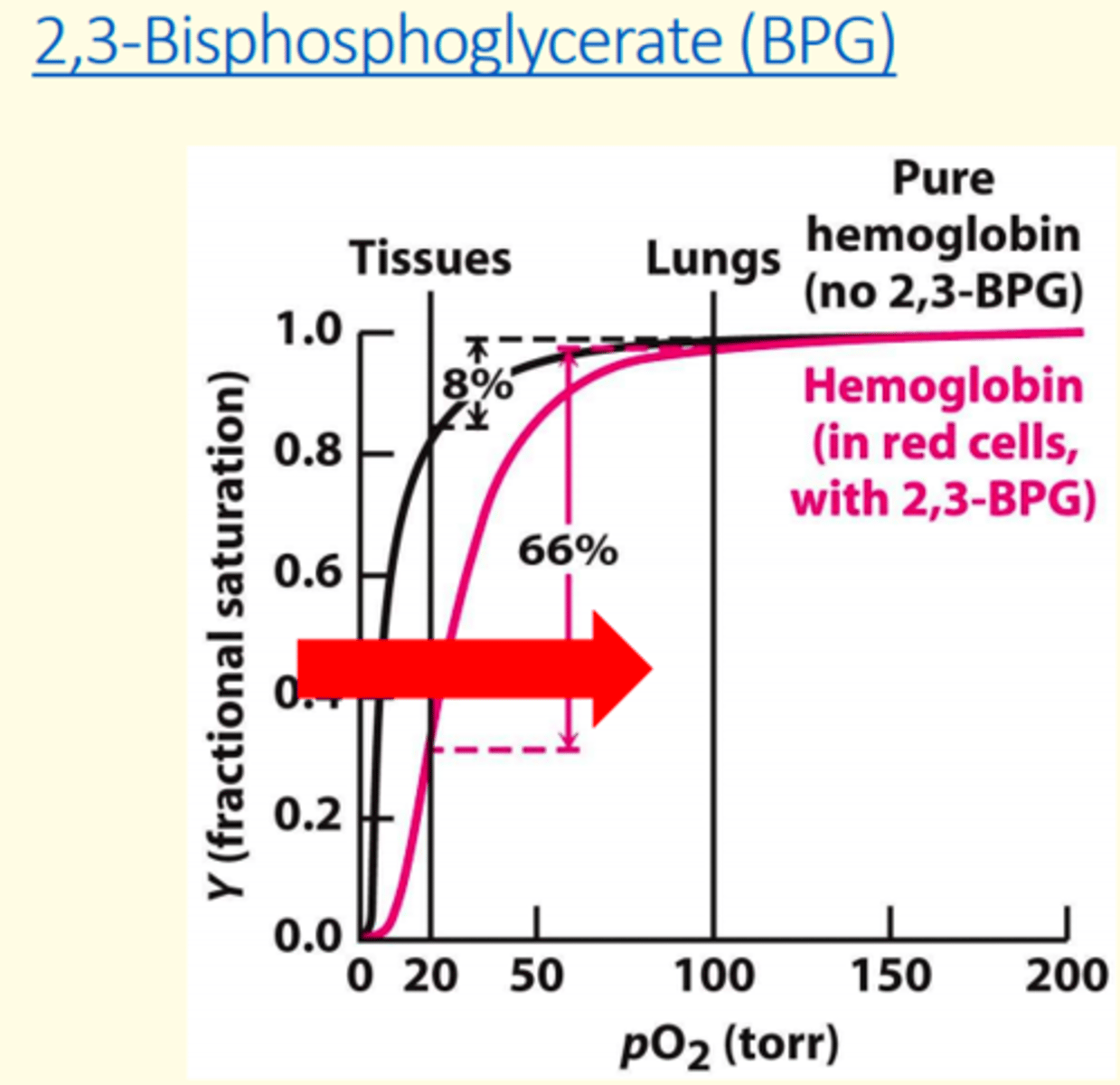
What two conditions stimulate 2-3 BPG?
1) Chronic hypoxemia caused by pathological lung conditions
2) High altitudes
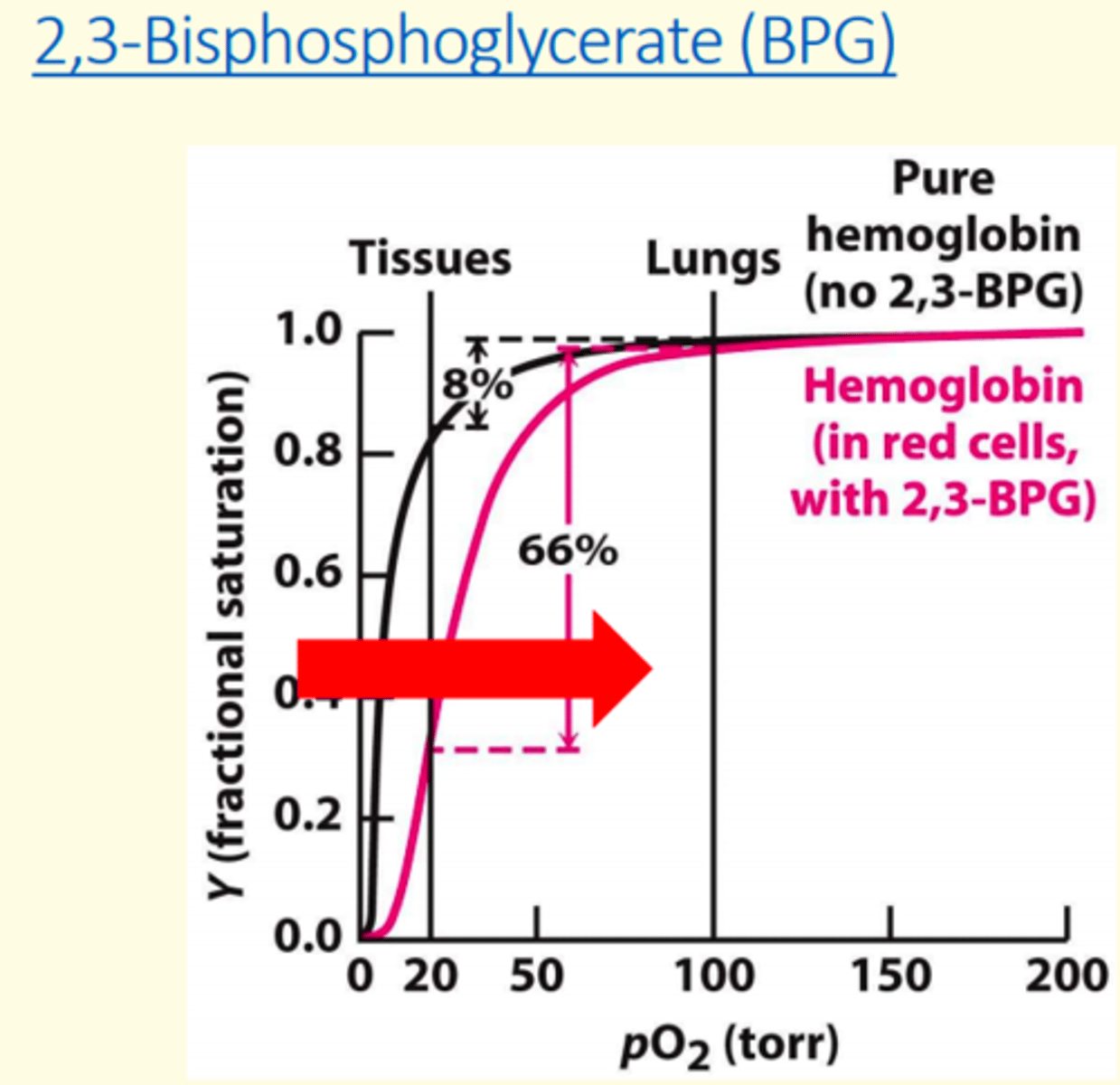
2-3 Biphosphoglycerate (2-3 BPG) shifts the oxygen curve to the ___
right
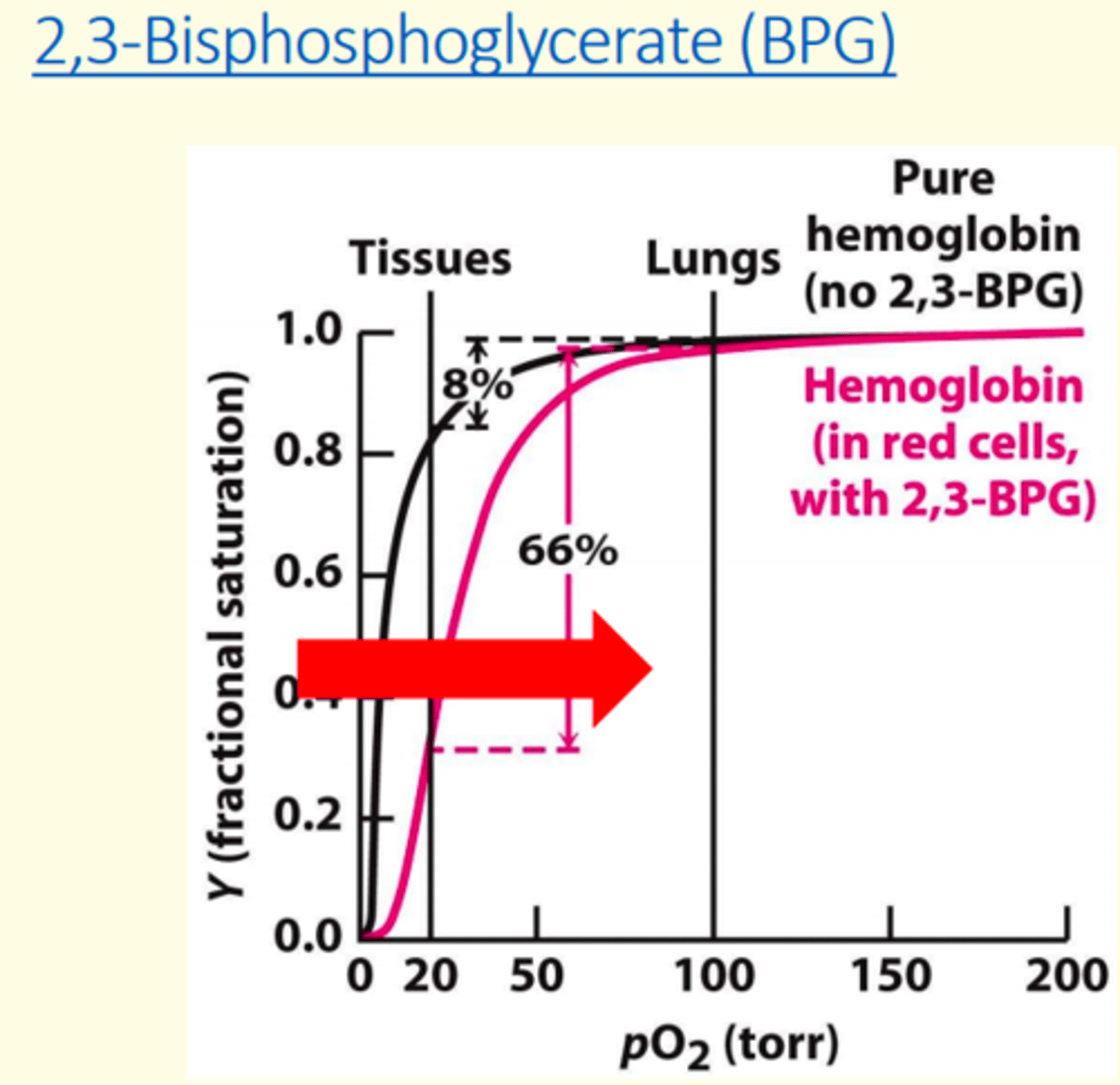
BPG concentration increases at ___ altitudes, promoting oxygen release at tissues
high
Bohr effect
The binding of H+ and CO2 lowers the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen - shifts curve to the right
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning
blocks oxygen transport (binds to haemoglobin)
CO binds to haemoglobin ___x more readily than oxygen
250x
CO poisoning is fatal when COHb is >___%
>50%
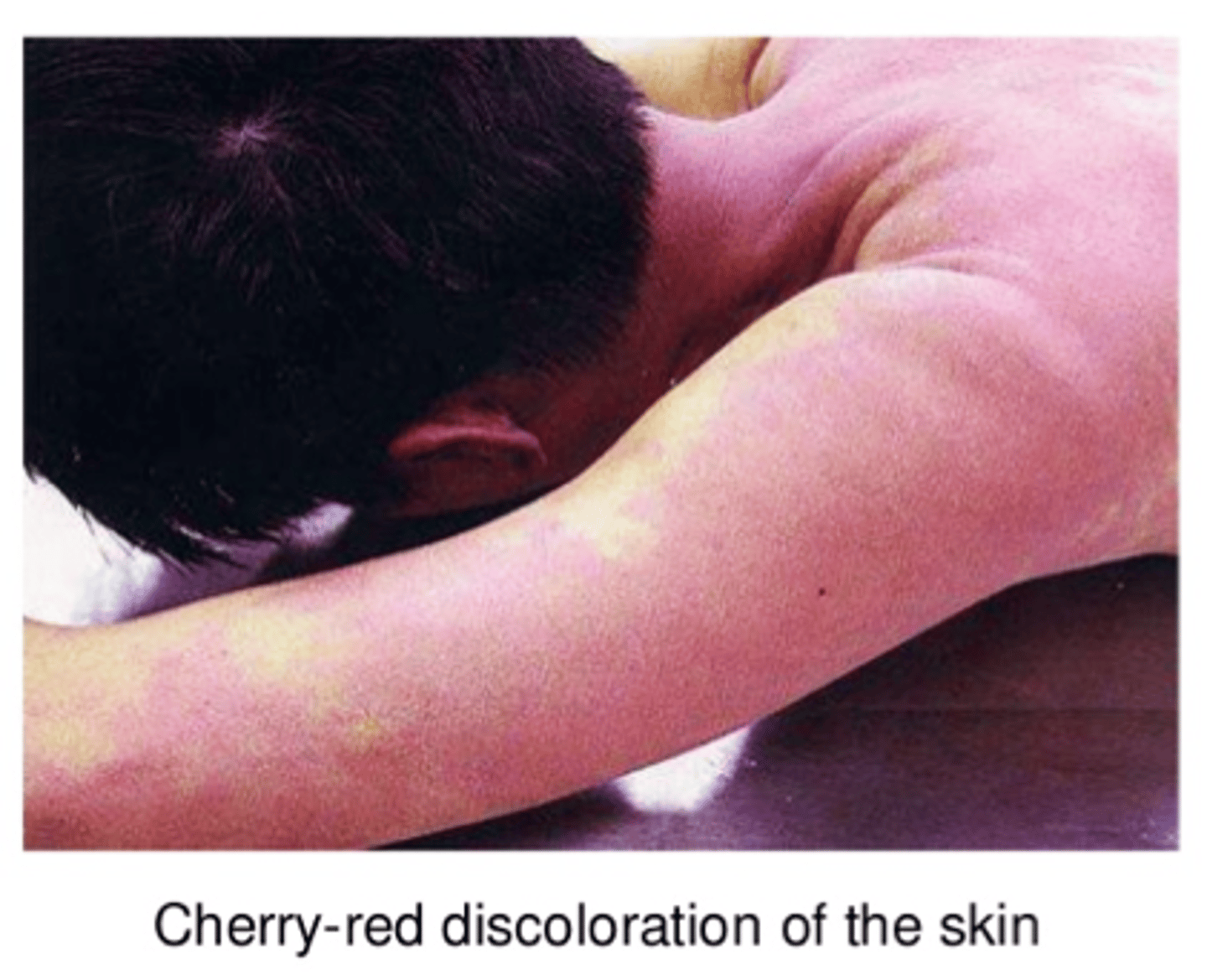
Symptom of CO poisoning
skin turns a cherry red colour that persists after death
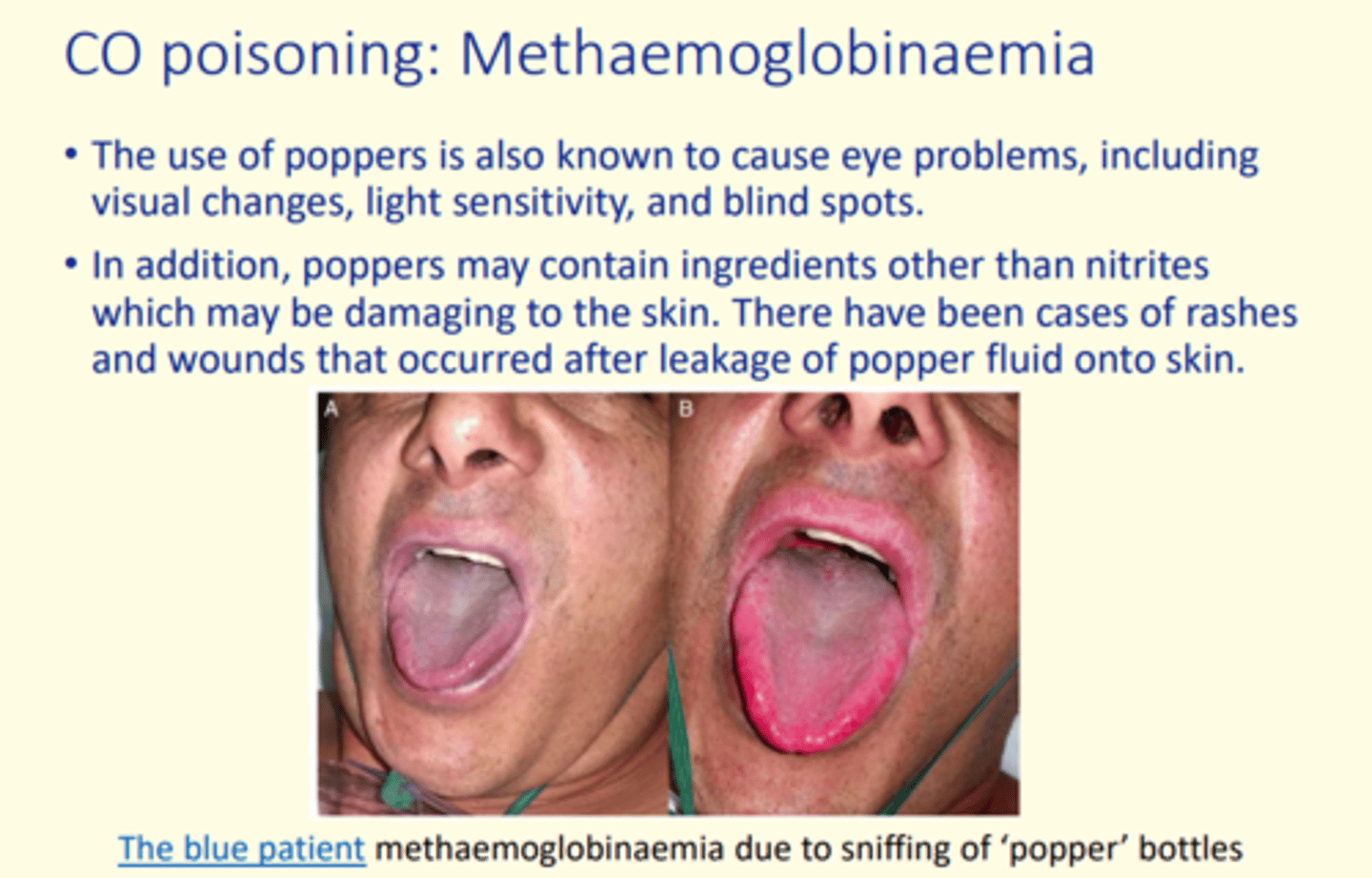
Methaemoglobinaemia
Excessive levels of methaemoglobin in the blood which is an oxidised form of haemoglobin and has a lower oxygen affinity
The use of popper bottle has been linked to causing ___
methaemoglobinaemia