natural landscapes terms
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
global climate systems
encompass atmosphere, hydrosphere (water), cryosphere (ice) lithosphere (land), biosphere (living things)
ex. wind circulation, global conveyor belt w ice
causes of natural climate change
milankovitch cycles, volcanic eruptions, fluctuations in solar radiations, tectonic shifts
abedo-effect
a surface’s ability to reflect sunlight (high albedo = reflecting more, ex. snow and ice, causing cooling) (low albedo = reflecting less, ex. dark surfaces such as water absorb more, causing warming)
milankovitch
eccentricity - changes in shape of earth orbit, elliptical shape
obliquity - changes in tilt of earth’s axis
precession - changes in direction of earth’s axis
pleistocene
the first epoch of the quaternary period, before holocene
glaciation
the process or state of being covered by glaciers or ice sheets
glacial
period with when polar and mountain ice sheets were unusually extensive across the earth’s surface, relatively colder
interglacial
relatively warmer interval between glacial periods within an ice age (retreat of glaciers, rising sea levels, increased global temperatures)
global conveyor belt
impact of climate change
proxy records
stratigraphic subdivisions
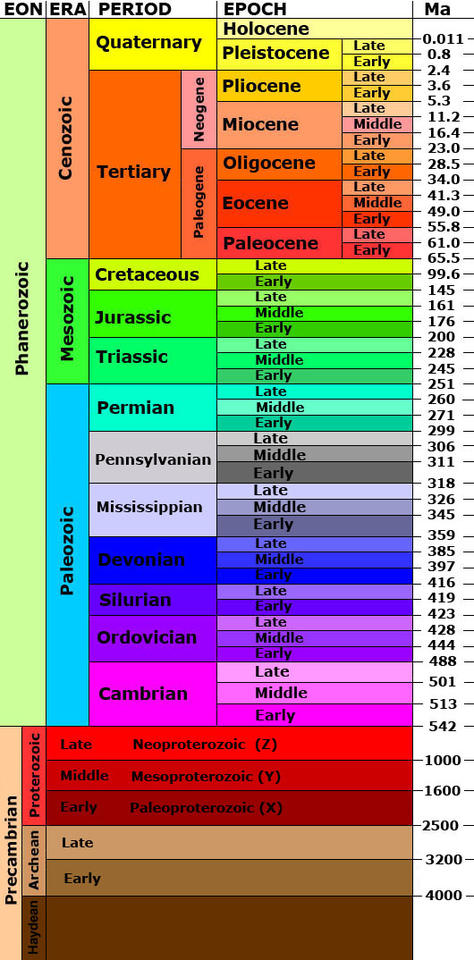
geological time scale
international system classifying earth’s 4.6 billion year history into hierarchial framework of units (eons, eras, periods, epochs, ages)
based on relative placement of rock layers and biostratigraphy
concept of time in sedimentary sequence
hiatus
one of the ways sedimentary environments are characterised by time and space, a period of time when sedimentation stops or where previosuly deposited sediments are removed by erosion resulting in a gap in the rock record, indictes missing time in sequence of rock layers
palimpsest
one of the ways sedimentary environments are characterised by time and space, a deosit where material from different past events or time periods is superimposed or mixed, creates complex and possibly confusing record due to the layers having been disturbed or reworked
superposition
correlation (in context of stratigraphy)
process of matching or proving equivalence of rock layers from different locations by comparing their characteristics (physical continuity, lithology, fossil content)
index species
fossils of animals/plants that were alive for only a certain period of geological time, easily identifiable
lithostratigraphy
chronostratigaphy
biostratigraphy
constraints of a stratigraphical subdivision
boundary types
reflection of time and events in a landscape
scientific dating methods
paleomagnetism
how does it work (basic level)? …
when can it be used? …
what can go wrong? …
dendrochronology
how does it work (basic level)? …
when can it be used? …
what can go wrong? …
luminescence dating (OSL)
how does it work (basic level)? …
when can it be used? …
what can go wrong? …
14-C dating (radiocarbon)
how does it work (basic level)? …
when can it be used? …
what can go wrong? …
calibration
how does it work (basic level)? …
when can it be used? …
what can go wrong? …
sampling (what should an archaeologist know?)