IB Psychology Test Prep - Terms to Know (copy)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Behavioral Genetics
Study of how both genetics and environment contribute to individual variations in human behavior
Social Psychology
Field of study that examines role that groups and environmental factors that play in shaping human behavior
Prosocial behavior
Voluntary behavior intented to benefit others
Social Identity
How we see ourselves and relate to the world around us, impacted by groups we belong too that create schemas and ways of thinking through social learning and observations
Social Cognitive Theory
We learn prosocial and antisocial behaviors by watching others in the world
Emotion
Conscious mental reaction experienced as a strong feeling, usually directed toward a specific reason accompanied by physiological and behavioral changes in body
Amygdala
Responsible for stress (fight, flight, freeze) and threat analysis
Frontal Lobe
Helps with self control (emotions, impulses), social interactions, empathy, and planning and decision making
fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging scan that shows activity in specific areas of brain
Gene
Working subunits of DNA, each gene contains a particular set of instructions, usually coding for a particular protein or for a particular function
Inheritance
Each offspring inherits half of their DNA from each parent (46 chromosomes total with 23 from female and 23 from male)
MAOA Gene
Codes for an enzyme that breaks down neurotransmitters in brain, low activity gene-low reaction to serotonin, high amounts of dopamine and adrenaline, high activity gene-high reaction of seratonin, low amounts of domapine and adrenaline
Neurotransmitter
Chemical that is exchanged between neurons that allow them to communicate
Evolutionary Psychology
one of many biologically informed approaches to study of human behavior. Evolutionary psychologists propose that much, if not all, of our behavior can be explained by appeal to internal biological functions. What distinguishes evolutionary psychologists from many psychologists is the proposal that relevant biological functions are adaptations—products of natural selection—that helped our ancestors get around the world, survive and reproduce.
Biophilia Hypothesis
suggests that humans possess an innate tendency to seek connections with nature and other forms of life. We see the biological benefits of being in nature because humans have evolved to be in nature. When we are detached from nature, our biological systems may struggle.
Enculturation
process by which an individual learns traditional content of a culture and assimilates its practices and values. This happens as a result of...
Direct Tuition: Learning Through Instruction/Language/Telling.
Participatory Learning: Learning through Doing.
Observational Learning: Learning through Watching.
Modeling: Acting with intention of helping someone learn.
Theory of Reconstructive Memory
Our past experiences and beliefs shape creation of our memory
Schema Theory
A generalization of past experiences that forms a scripted pattern of thinking.
Flashbulb Memories
Highly accurate and exceptionally vivid memories of learning about a shocking or emotional event. Elements of a flashbulb memory include place they were, what they were doing, who told them information, how others felt, and importance of event
Stereotype
A generalization that is made about a group and then applied to individual members of that group. They can be either positive or negative.
Localization of function
Brain parts have specific functions
Cultural Dimension
Ways that how people can measure cultural groups differening (individualism vs collectivism)
Cortisol
Stress Hormone
Oxytocin
“Cuddle Hormone”
Acculturation
The process of social, psychological and cultural change that results from blending between cultures. Stages include…
Separation
Marginalization
Assimilation
Integration
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
a machine that takes photos of the brain structure
Multistore model of memory
memory consists of three stores: a sensory register, short-term memory (STM), and long-term memory (LTM).
Working model of memory
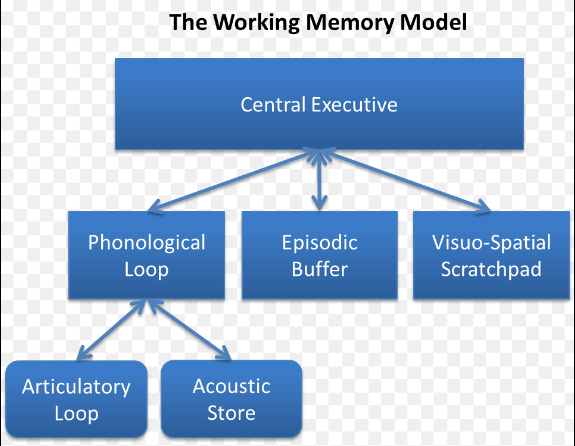
Neuroplasticity
the brain changes and continuously adapting throughout an individuals life, happens as neurons make connections between each other and for network
Myelination
a fatty substance that builds up around neural networks to help them send information faster and more effieciently
Pruning
the Brain’s ability to remove neural networks that are underused in order to strenghten ones that are
Serotonin
Mood stabilizer, sleep and digestive system - usually inhibitory
Hormones
chemical messengers that are released from glands in the body and serve to change psycological and physical functioning based on experiences
Encoding
The process of storing memories. Rooted in neuroplasticity.
Retreival
The process of activating memories.
Distortion
Remembering the main idea but forgetting small details.
Assimilation
Modifying details of a memory to fit within our worldview or perspective.
Reuptake
after connecting with the receptors, the neurotransmitters are released, travel back through the synapse and are reabsorbed by the reuptake transporter on the original neuron
Cortisol
stress hormone
Norepinephrine
increases blood flow and concentration
Acetylcholine
learning and memory - activates muscles in the body - excitatory
Hippocampus
Storage and Formation of new memories and stress Inhabition
Neuron
Brain cell designed for communication
Epigenetics
factors beyond genes, including traumas, diet, stress, lack of exercise, or living with an abusive parent, get inside genes and alter their function in the body - our expiriences change out genes
Adrenaline
increases heart rate, awareness and physical abilities (fight or flight)
Stereotype threat
situation in which an individal is at rist of conforming, as self characteristic, a negative stereotype about ones group. During these times, they often preform worse due to stress and anxiety of conforming stereotypes