ARCH 2040 Unit 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Last updated 1:42 PM on 11/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
institution
system of rules that structure social interaction, governs a set of behaviors by individuals, transcends individuals and are identified with a social purpose (ex religion, family,
2
New cards
consequences of industrial revolution
major changes in every aspect of everyday life, unprecedented population growth, shift from agriculture to industry, population growth, urban growth, paves the way toward mass production and assembly lines, as well as new building materials and techniques
3
New cards
Neo-classicism
(originates in France) Western cultural movement manifested in architecture,
visual and decorative arts, music, theater that draws inspiration form
the culture of classical antiquity; the revival of the classical styles of
antiquity
visual and decorative arts, music, theater that draws inspiration form
the culture of classical antiquity; the revival of the classical styles of
antiquity
4
New cards
differences between neoclassicism and Renaissance
in the 19th c there is better knowledge of documentary
sources i.e. ancient ruins (excavations at Pompeii and Herculaneum)
new technologies
new building materials
aspirations for an architecture accessible to all
sources i.e. ancient ruins (excavations at Pompeii and Herculaneum)
new technologies
new building materials
aspirations for an architecture accessible to all
5
New cards
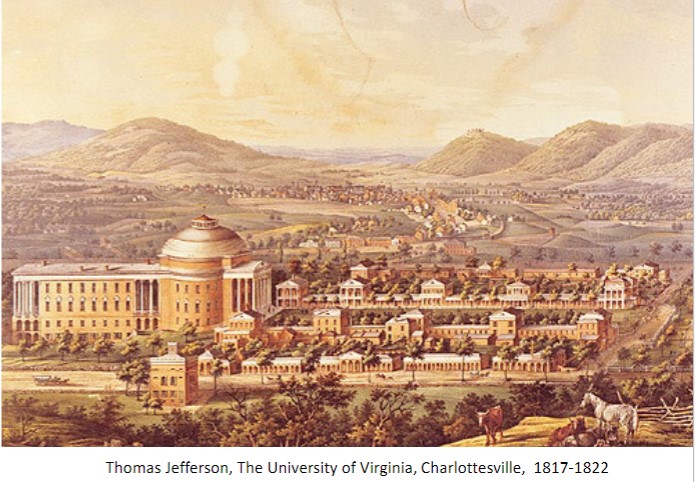
academic village
by Thomas Jefferson- university of Virginia- secular education
Masterplan: central axial lawn flanked by interlinked
colonnaded pavilions, with the Rotunda (library) at one end
(Rotunda – inspired by the Pantheon, Rome)
Masterplan: central axial lawn flanked by interlinked
colonnaded pavilions, with the Rotunda (library) at one end
(Rotunda – inspired by the Pantheon, Rome)

6
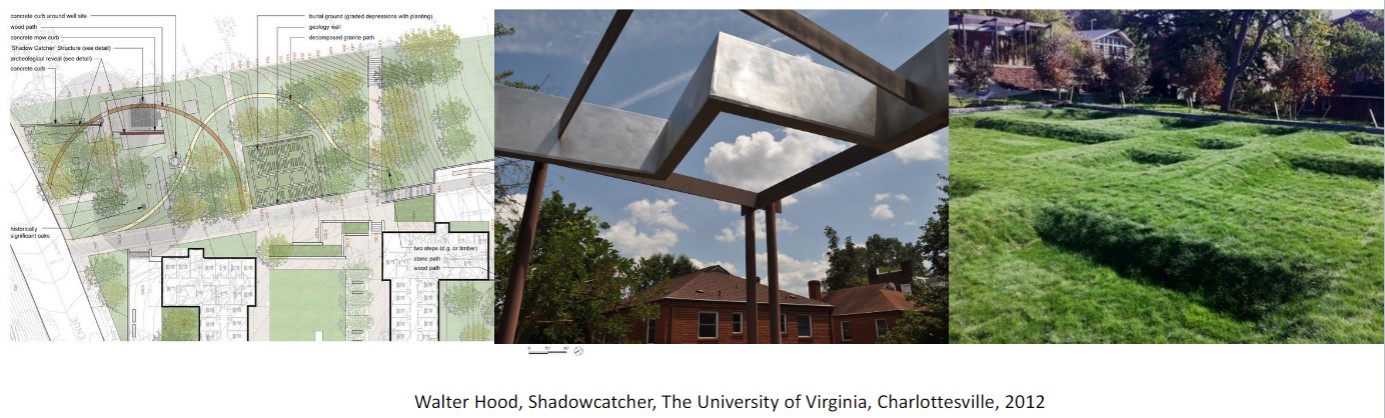
New cards
Shadowcatcher
by Walter Hood - UVA expansion
marks the homestead and cemetery remains of an African American family
marks the homestead and cemetery remains of an African American family

7
New cards
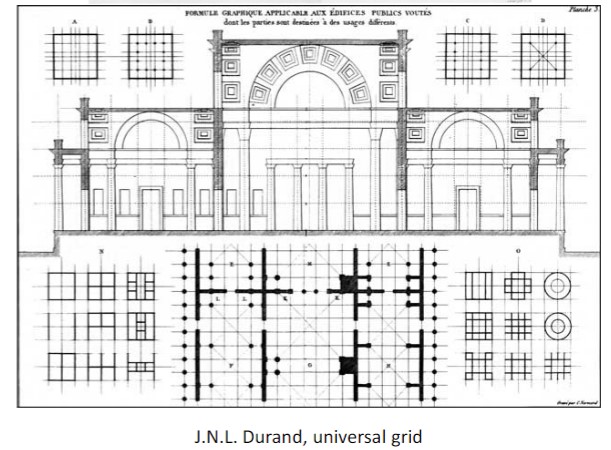
J.-N.-L. Durand
RATIONAL APPROACH TO ARCHITECTURE
Replaces the Vitruvian triad firmitas – utilitas – venustas (solidity – utility – beauty) with economy – simplicity – convenience
uses grids, graph paper, standardized parts
logical, simple forms, basic relationships
BEGINNING OF STANDARDIZATION
grid as method of standardization and control
basic design comes first
Replaces the Vitruvian triad firmitas – utilitas – venustas (solidity – utility – beauty) with economy – simplicity – convenience
uses grids, graph paper, standardized parts
logical, simple forms, basic relationships
BEGINNING OF STANDARDIZATION
grid as method of standardization and control
basic design comes first
8
New cards
Neo-Gothic or Gothic Revival
[originates in Germany and England]
cultural movement emerging in the late 18th century as a
form of resistance to Neo-classical styles
cultural movement emerging in the late 18th century as a
form of resistance to Neo-classical styles
9
New cards
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe writes what essay?
On German Architecture
10
New cards
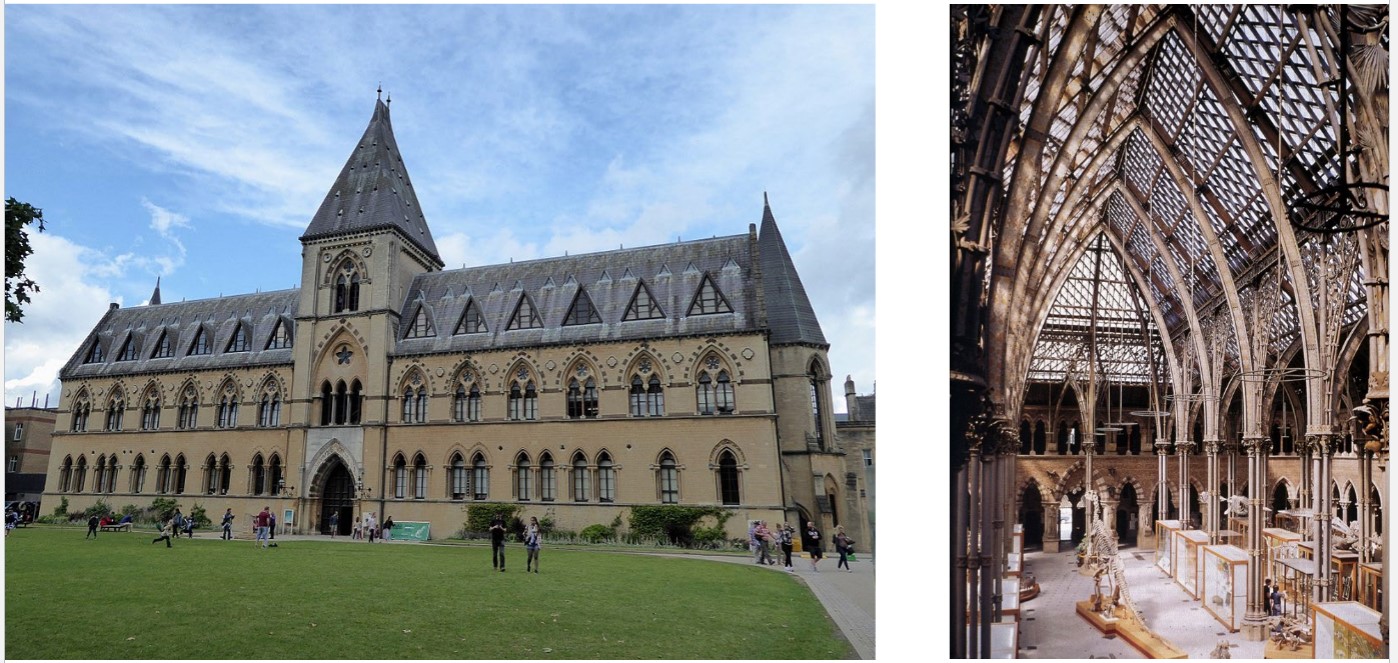
John Ruskin
inspired by Italian gothic
traveled the grand tour
PUBLISHED: The Seven Lamps of Architecture
(1849) and The Stones of Venice (1853)
emphasis on return to midevil craft
thinks structure should always be visible
traveled the grand tour
PUBLISHED: The Seven Lamps of Architecture
(1849) and The Stones of Venice (1853)
emphasis on return to midevil craft
thinks structure should always be visible

11
New cards
John Ruskin wrote what?
the Seven lamps of architecture, The Stones if Venice
12
New cards
Eugene-Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc
restorations of buildings to an idealized state that actually differ from the original (things around this time having been destroyed, then the concept of preserving architectural heritage emerges)
Restores over 200 structures – idealized version of a French vernacular
STRUCTURAL RATIONALISM
Restores over 200 structures – idealized version of a French vernacular
STRUCTURAL RATIONALISM

13
New cards
Eugene-Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc wrote what?
Dictionary of French Architecture, Discourses on Architecture-
Theoretical explorations that propose a new architecture based
on modern materials, inspired by the principles of Gothic
architecture
Theoretical explorations that propose a new architecture based
on modern materials, inspired by the principles of Gothic
architecture
14
New cards
Henri Labrouste
Innovative cast-iron frames + masonry piers + arches

15
New cards
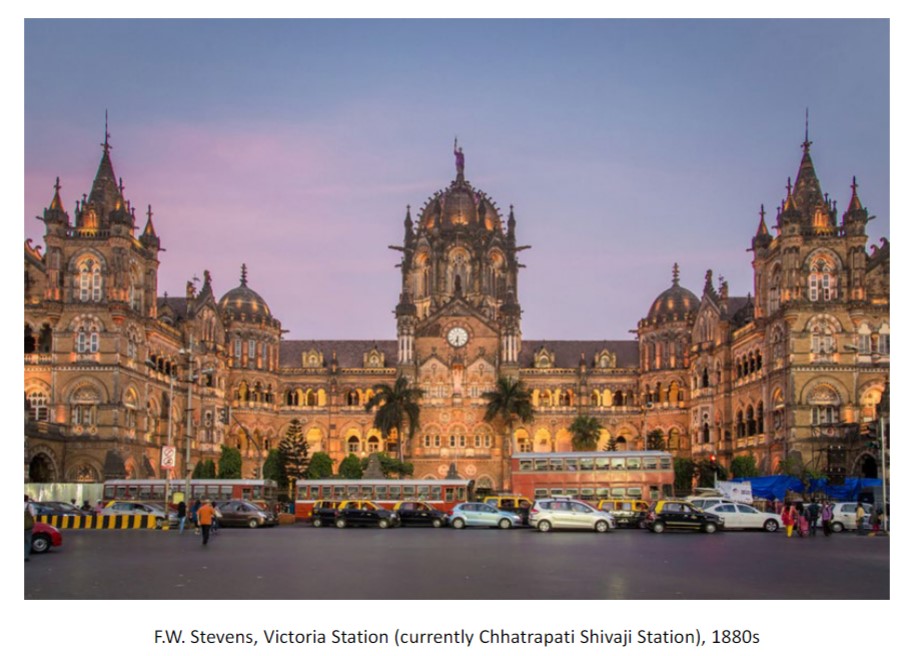
Victoria Station
in india, inspired by John Ruskin’s work, Neo-Gohic decoration

16
New cards
New Iron Age
With the Industrial Revolution: new materials (iron and glass) and new building techniques
New building typologies: Industrial buildings (factories, warehouses, train station) + cultural buildings (St. Genevieve Library, Paris) + commercial spaces (covered galleries) + suspension bridges
New building typologies: Industrial buildings (factories, warehouses, train station) + cultural buildings (St. Genevieve Library, Paris) + commercial spaces (covered galleries) + suspension bridges
17
New cards
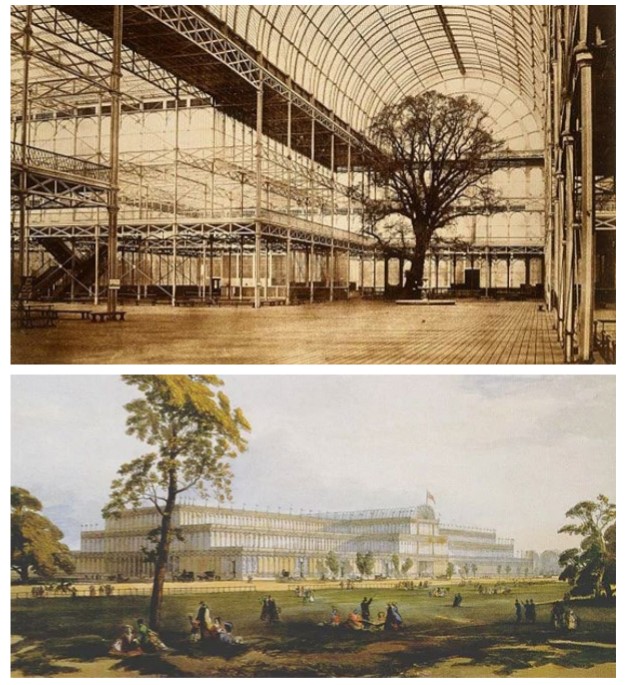
John Paxton
architect, parliament member, gardener
uses standardized measurements of iron and glass
illustrated division of labor
uses standardized measurements of iron and glass
illustrated division of labor

18
New cards
École des Beaux Arts [School of Fine Arts], Paris (France)
(for painting, sculpture and architecture)
(for painting, sculpture and architecture)
Promoter of classical aesthetic traditions and ideals
- Promoter of specific instruction methods – atelier (studio)
- The most powerful entity that ever existed for training high-skilled architects
- Promoter of specific instruction methods – atelier (studio)
- The most powerful entity that ever existed for training high-skilled architects
19
New cards
parti
(from prendre parti – to take a stand)
Basic scheme of the building and fundamental solution of the functional program
Basic scheme of the building and fundamental solution of the functional program
20
New cards
Eclecticism
combination of elements from different historical styles into one work
21
New cards
Atelier (studio)
educational system at the Ecole; students work in the atelier of a senior patron; younger students help older ones to prepare projects for the Prix de Rome competition
22
New cards
Julien Guadet
promotes eclecticism, study of classical and gothic structures
23
New cards
Charles Garnier
builds opera house in paris (becomes an institution within itself)
he designs it according to how people walk in pairs, spatial and social heriarchy
he designs it according to how people walk in pairs, spatial and social heriarchy

24
New cards
Benjamin Henry Latrobe
British-American architect
works first in London in an architecture and engineer firm
Bank of Pennsylvania: ionic temple fronts – central dome over the rotunda (first true masonry vault in the US) – establishes the temple type as an appropriate form for American banks
DESIGNS CAPITOL BUILDING IN DC
works first in London in an architecture and engineer firm
Bank of Pennsylvania: ionic temple fronts – central dome over the rotunda (first true masonry vault in the US) – establishes the temple type as an appropriate form for American banks
DESIGNS CAPITOL BUILDING IN DC
25
New cards
William Strickland
Studied with Benjamin Latrobe
Active mainly in Philadelphia and Nashville
promoted Greek Revival
early example of use of structural iron (Tennessee State Capitol)
Active mainly in Philadelphia and Nashville
promoted Greek Revival
early example of use of structural iron (Tennessee State Capitol)

26
New cards
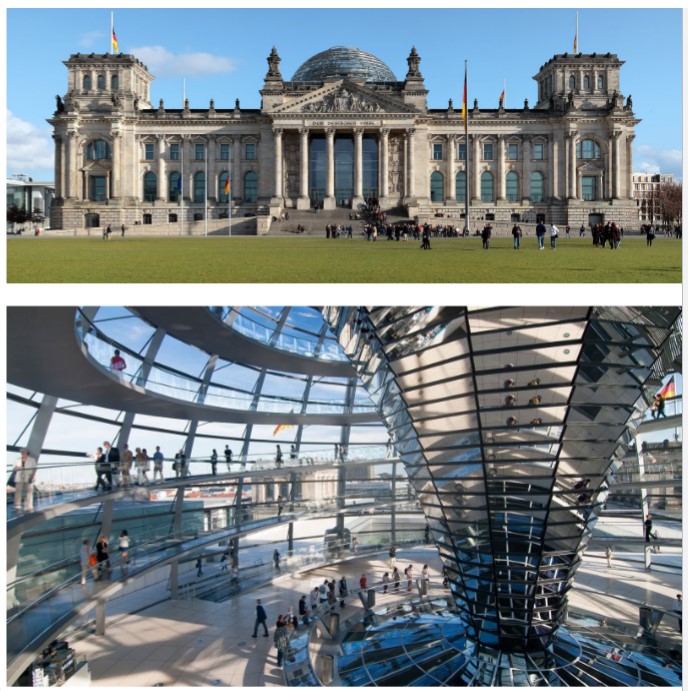
Reichstag Building- who worked on it
Paul Wallot, Paul Baumgarten restores it after it is almost destroyed, Norman Foster finished it

27
New cards
Johan Sigfrid Siren built
finnish Parliment Building
Architectural style that combines Neo-Classicism and early modernism: simplified columns, less decoration
Architectural style that combines Neo-Classicism and early modernism: simplified columns, less decoration

28
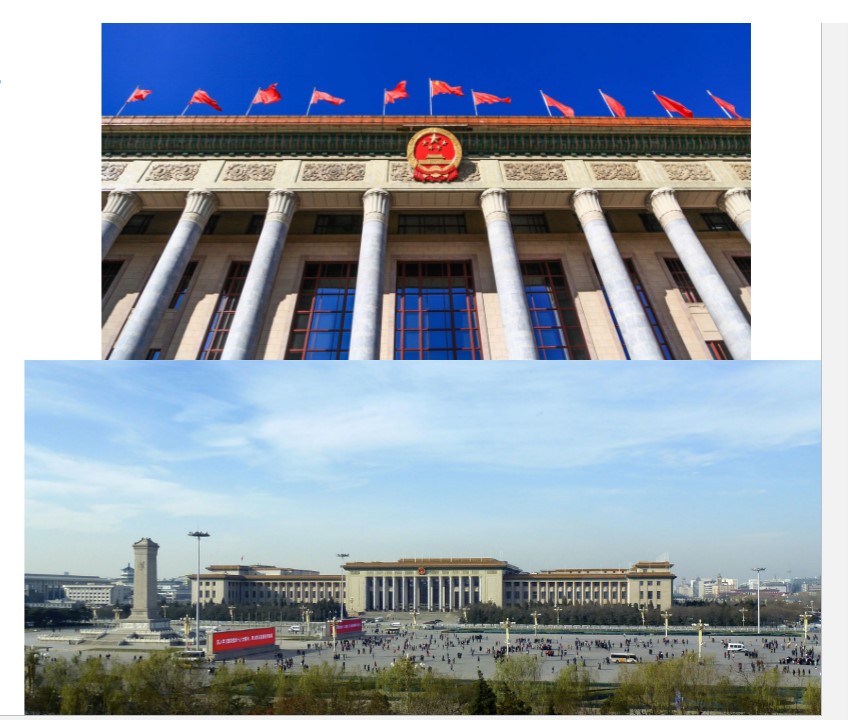
New cards
Zhang Bo built
Great Hall of the People, Beijing
example of Chinese Neo-Classicism, built in 10 months
example of Chinese Neo-Classicism, built in 10 months

29
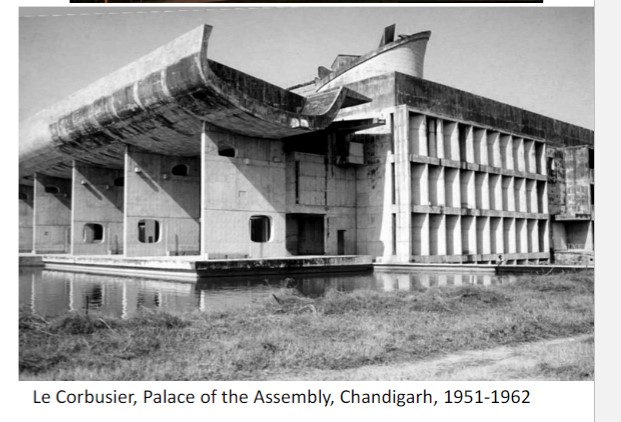
New cards
Le Corbusier built (In india)
palace of assembly, palace of justice, monument to the open hand

30
New cards
Louis Khan built
National Assembly Buidling, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Modernist building rooted in its context
Main idea: to create an identity to the newly established country of Bangladesh
Poured in place concrete with inlaid white marble
Modernist building rooted in its context
Main idea: to create an identity to the newly established country of Bangladesh
Poured in place concrete with inlaid white marble

31
New cards
Enric Miralles and Benedetta Tagliabue built
scottish parliament building
Incorporates elements of Scottish heritage: landscape, forms of
upturn boats in a nearby shoreline, floral paintings by Charles
Rennie Mackintosh (revered Scottish architect and painter)
Incorporates elements of Scottish heritage: landscape, forms of
upturn boats in a nearby shoreline, floral paintings by Charles
Rennie Mackintosh (revered Scottish architect and painter)

32
New cards
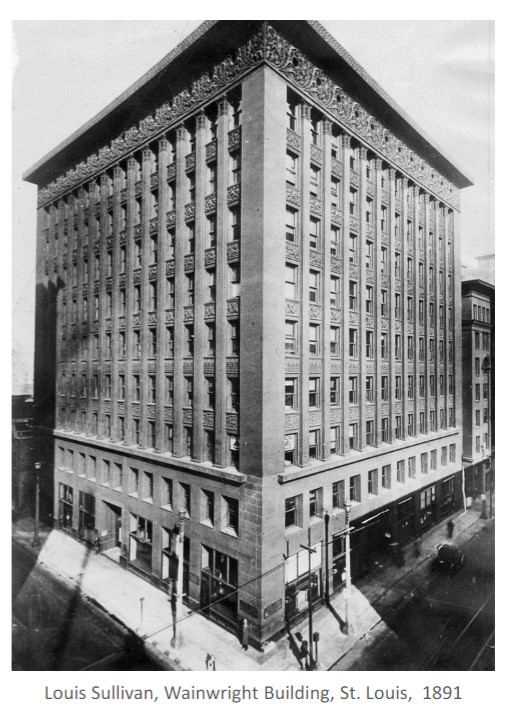
Louis Sullivan wrote and built
writes the first theoretical piece on tall-buildings – “The Tall
Office Building Artistically Considered” (1896) – Forms follows function.
configuration reminiscent of a classical column
Form ever follows function.
Organic: evolutionist ornament
Function leads to form organically and evolutionistically
built wainwright building
Office Building Artistically Considered” (1896) – Forms follows function.
configuration reminiscent of a classical column
Form ever follows function.
Organic: evolutionist ornament
Function leads to form organically and evolutionistically
built wainwright building

33
New cards
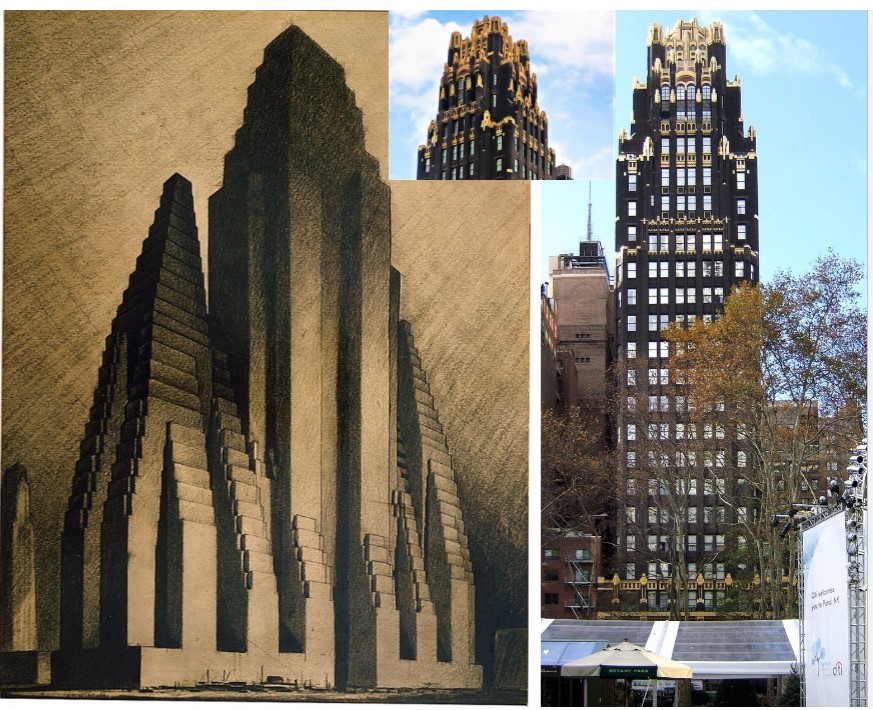
Raymond Hood built
American Radiator Building
steel frame cladded in black bricks to reduce the contrast between the dark window hollows and the walls
golden finials capping each structural bay repeat the geometry of the tower’s stepped forms
steel frame cladded in black bricks to reduce the contrast between the dark window hollows and the walls
golden finials capping each structural bay repeat the geometry of the tower’s stepped forms

34
New cards
Hugh Ferriss wrote what?
Metropolis of Tomorrow (book of drawings depicting visions of future skyscrapers generated by the 1916 Zoning Law)
35
New cards
Plinth
a heavy base supporting a statue / vase / building
36
New cards
Finial
distinctive ornament at the top of a roof / pinnacle / tower
37
New cards
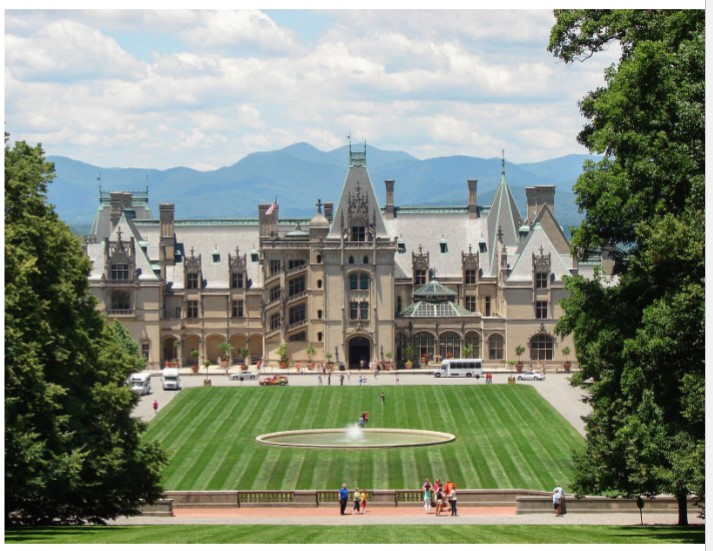
Richard Morris Hunt
First American architect trained at the Beaux Arts in Paris
built the Biltmore estate
built the Biltmore estate

38
New cards
McKim, Meade and White built
Boston Public Library
inspired by St. Genevieve Library in Paris [note
the vaulted ceilings, the large windows, bookshelves inserted into wall
thicknesses, Neo-Classical language]
inspired by St. Genevieve Library in Paris [note
the vaulted ceilings, the large windows, bookshelves inserted into wall
thicknesses, Neo-Classical language]
![Boston Public Library
inspired by St. Genevieve Library in Paris [note
the vaulted ceilings, the large windows, bookshelves inserted into wall
thicknesses, Neo-Classical language]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f93c60aca96746daa17d88e72e72668e.jpeg)
39
New cards
Thomas Jefferson Building, Library of Congress
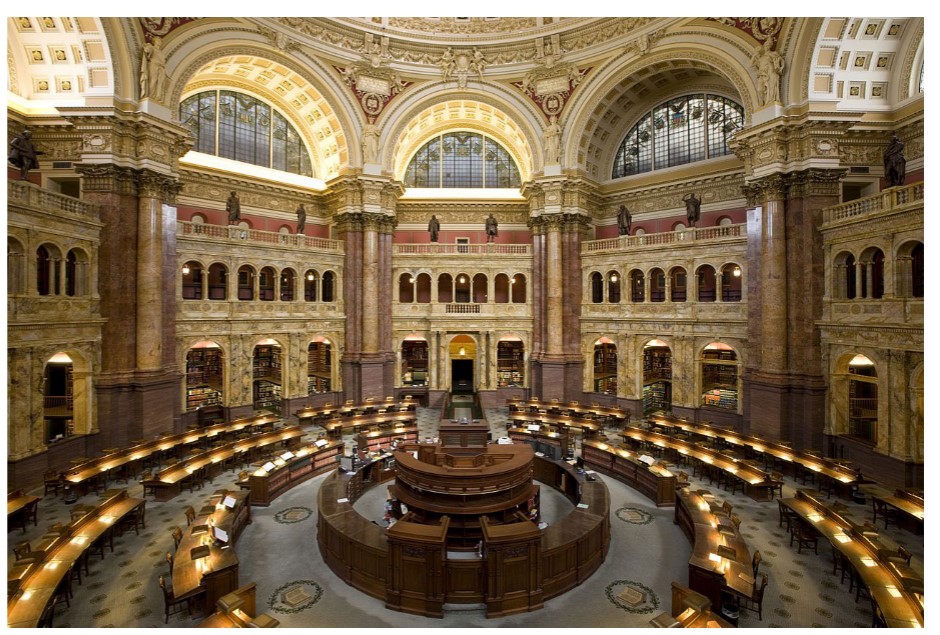

40
New cards
Gunnar Asplund built
Stockholm Public Library

41
New cards
Mecanoo built
TU Delft Library
Sits opposite a concrete Brutalist building
Tilted lawn – creates spaces for the library underneath
A cone pierces the lawn and the library
Sits opposite a concrete Brutalist building
Tilted lawn – creates spaces for the library underneath
A cone pierces the lawn and the library

42
New cards
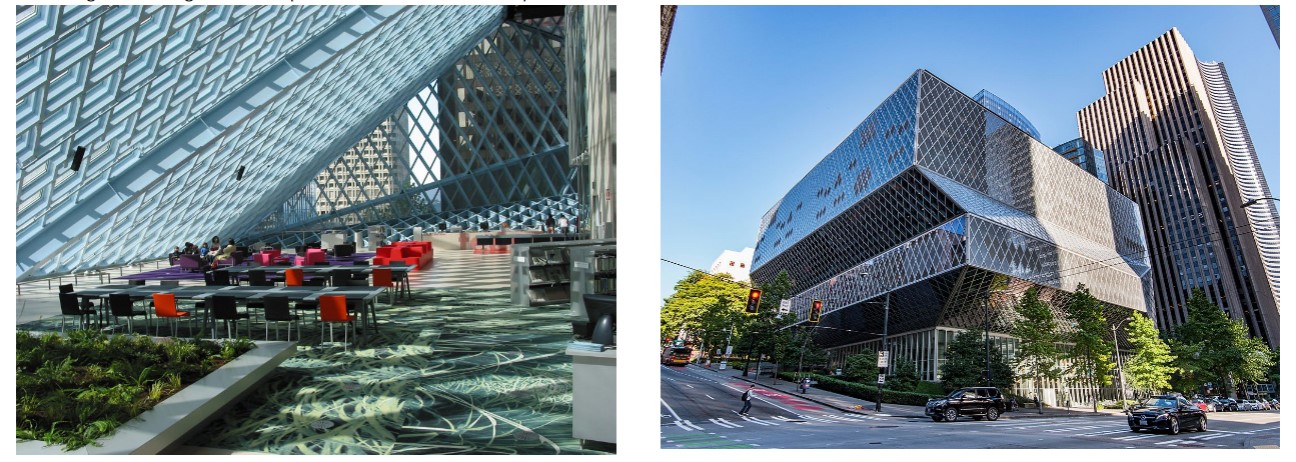
Seattle Public Library
Library as civic space – people go there to study, but also to gather, attend
different events and simply hang out
Circulation of knowledge in all media
The Book Spiral: innovative organizing system for an ever-growing physical collection
different events and simply hang out
Circulation of knowledge in all media
The Book Spiral: innovative organizing system for an ever-growing physical collection

43
New cards
Henry Hobson Richardson
Studies for 6 years at the Beaux Arts in Paris –learns about architectural polychromy [use of multiple colors]
Interest in medieval architecture and medieval masonry – Romanesque cathedrals
built Trinity Church in Boston
Interest in medieval architecture and medieval masonry – Romanesque cathedrals
built Trinity Church in Boston
![Studies for 6 years at the Beaux Arts in Paris –learns about architectural polychromy [use of multiple colors]
Interest in medieval architecture and medieval masonry – Romanesque cathedrals
built Trinity Church in Boston](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1a73f862f6214b43b374b48897e915d9.jpeg)
44
New cards
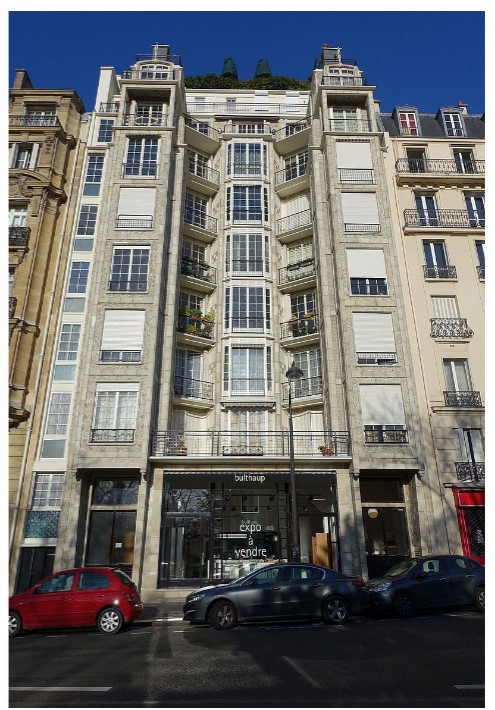
Auguste Perret
he used reinforced concrete- included it in the facade of buildings
built Rue Franklin Apartment Building (pictured), Notre Dame de Raincy
built Rue Franklin Apartment Building (pictured), Notre Dame de Raincy

45
New cards
Notre Dame de Raincy (building)
built by Auguste Perret
exposed concrete structure – raw expression of materials –technology and construction materials drive the aesthetics of the building
Re-interpretation of Gothic elements: slender columns, large glazed walls, dominant tower
exposed concrete structure – raw expression of materials –technology and construction materials drive the aesthetics of the building
Re-interpretation of Gothic elements: slender columns, large glazed walls, dominant tower
46
New cards
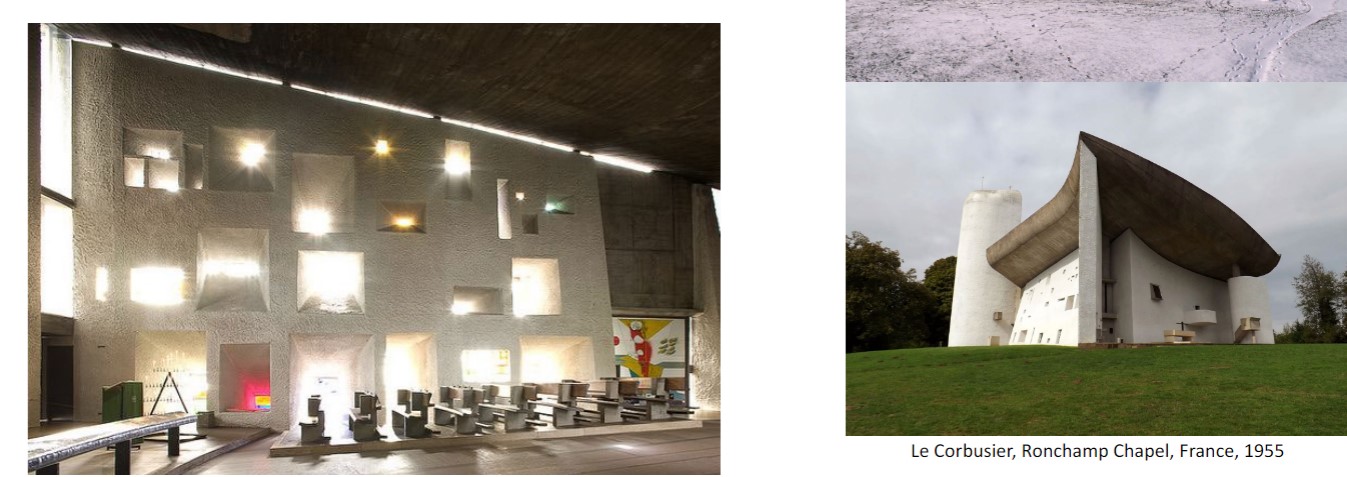
Ronchamp Chapel
built by Le Corbusier
he studied under Perret and learned about reinforced concrete
he studied under Perret and learned about reinforced concrete

47
New cards
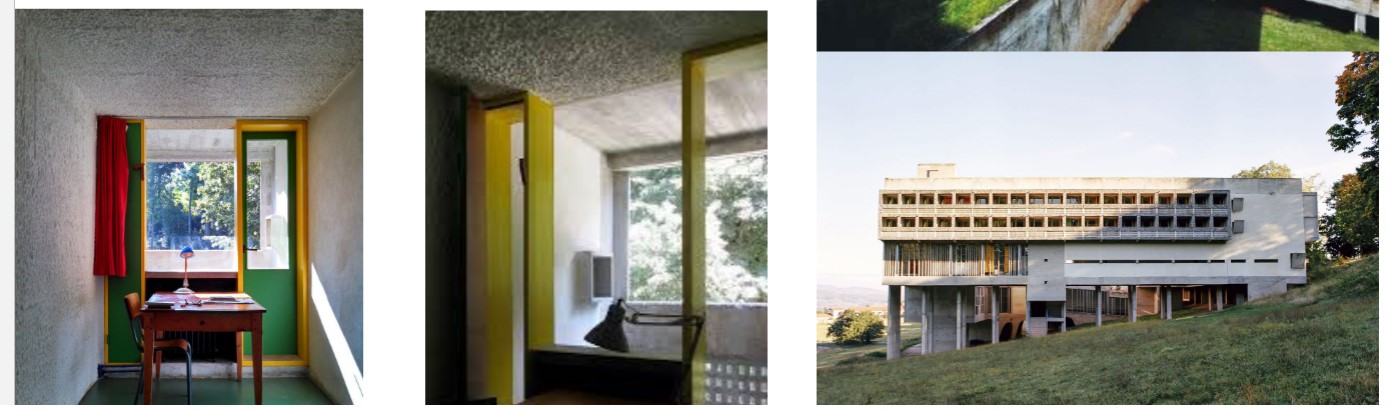
La Tourette Monastery
built by Le Corbusier
housed monks
Skylights bring daylight and color into spaces
Individual cells: narrow, austere units with views toward the landscape
housed monks
Skylights bring daylight and color into spaces
Individual cells: narrow, austere units with views toward the landscape

48
New cards
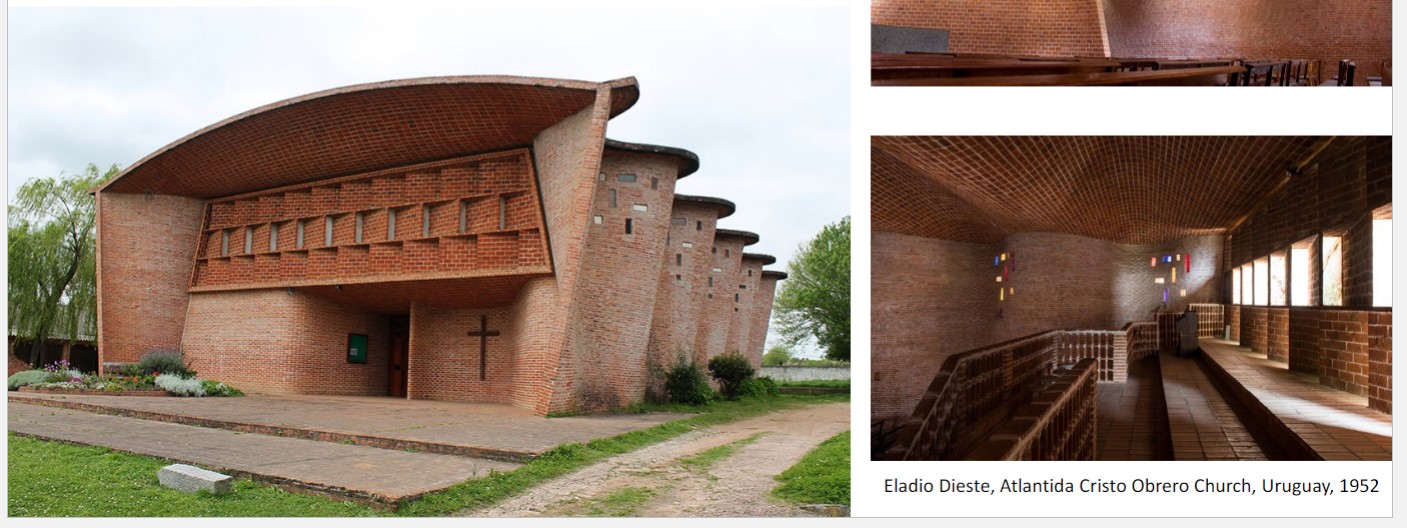
Eladio Dieste built
Atlantida Church, Uruguay,
engineer – innovative brickwork
Structure: curved brick walls + vaulted roof – walls + vault form a type of shell frame
engineer – innovative brickwork
Structure: curved brick walls + vaulted roof – walls + vault form a type of shell frame

49
New cards
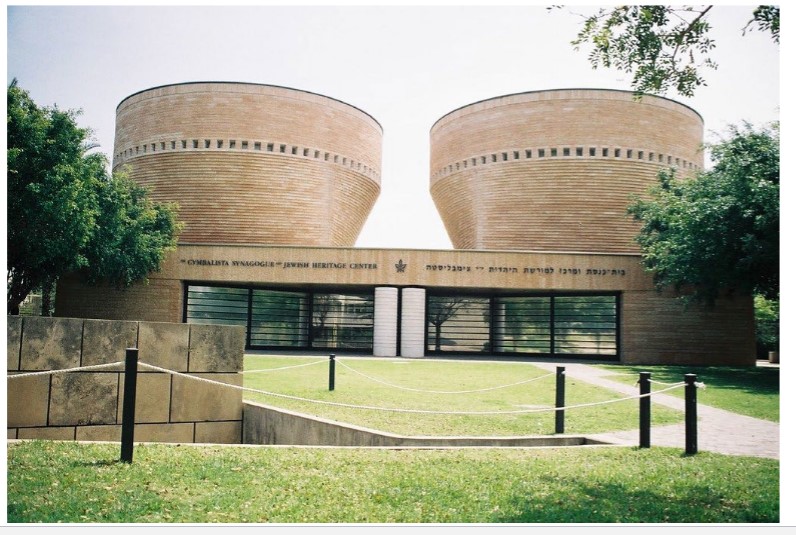
Mario Botta built
Cymbalista Synagogue and Jewish Heritage Center
Rectangular volumes rotate and open up into a circular shape – transition from Earth
(symbolized by the square) to Heavens (symbolized by the circle)
Inscribed square roof within the circle creates arched segments that filter light down into spaces
interior: gold sandstone
exterior: red sandstone
Rectangular volumes rotate and open up into a circular shape – transition from Earth
(symbolized by the square) to Heavens (symbolized by the circle)
Inscribed square roof within the circle creates arched segments that filter light down into spaces
interior: gold sandstone
exterior: red sandstone

50
New cards
Robert Robinson Taylor
"soldier's home" thesis
taught at Tuskegee Institute
Early examples of design-built projects: students design the campus buildings in studio, make the bricks in the workshops and work on the construction sites
taught at Tuskegee Institute
Early examples of design-built projects: students design the campus buildings in studio, make the bricks in the workshops and work on the construction sites
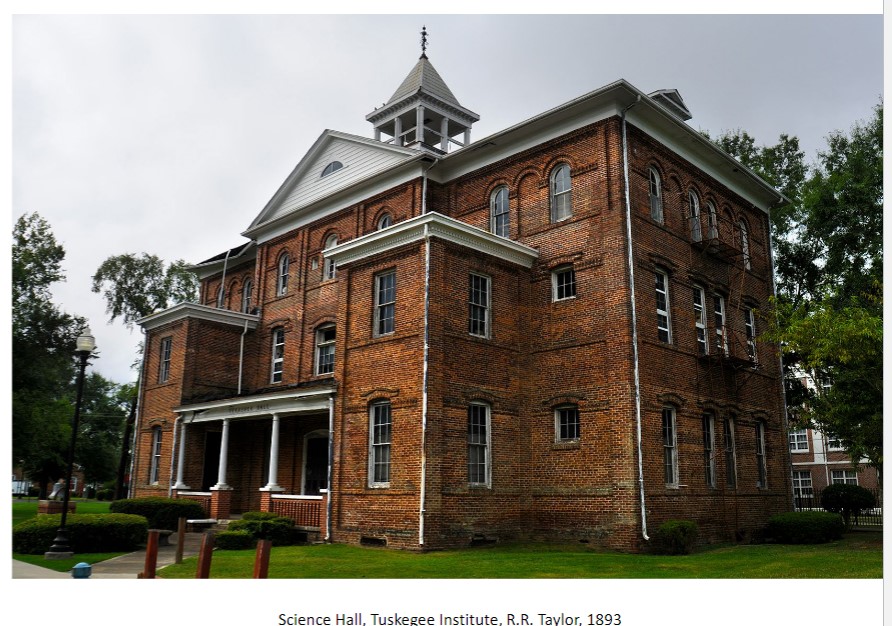

51
New cards
Julian F. Abele built
Philadelphia Museum of Art
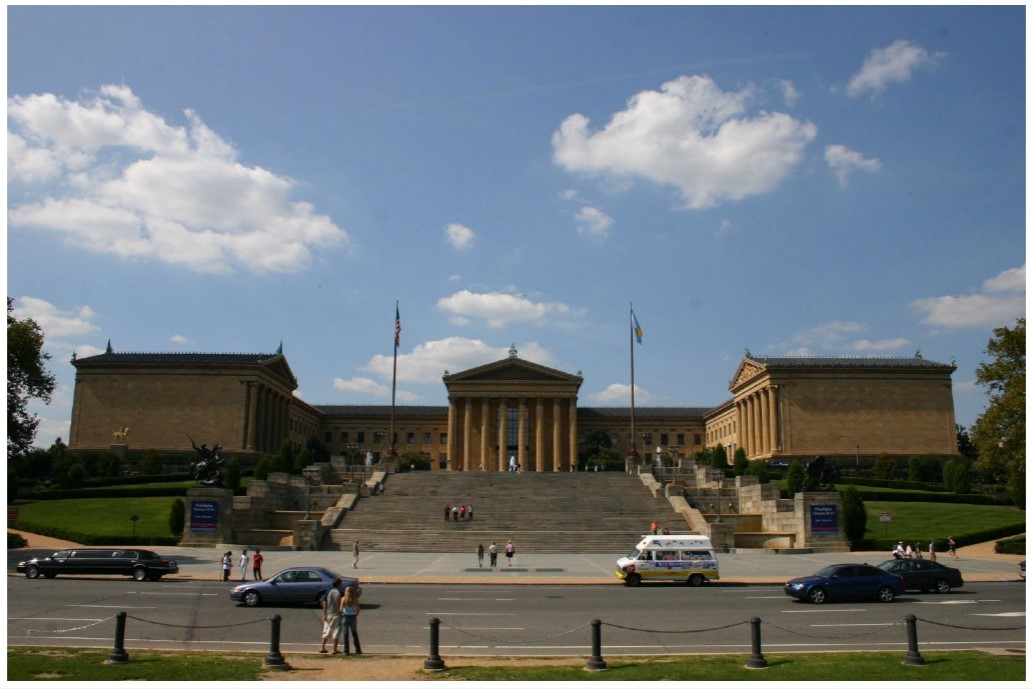

52
New cards
Post WWII
The birth of the “Third World”
Nations in Africa and the Indian subcontinent win independence from colonial powers
Overall trend: postcolonial architects often return to indigenous models as a means of showing independence
Architecture will become a major ideological tool in affirming different political positions
Main issue: the question of identity
Nations in Africa and the Indian subcontinent win independence from colonial powers
Overall trend: postcolonial architects often return to indigenous models as a means of showing independence
Architecture will become a major ideological tool in affirming different political positions
Main issue: the question of identity
53
New cards
Anthropology center, mexico city
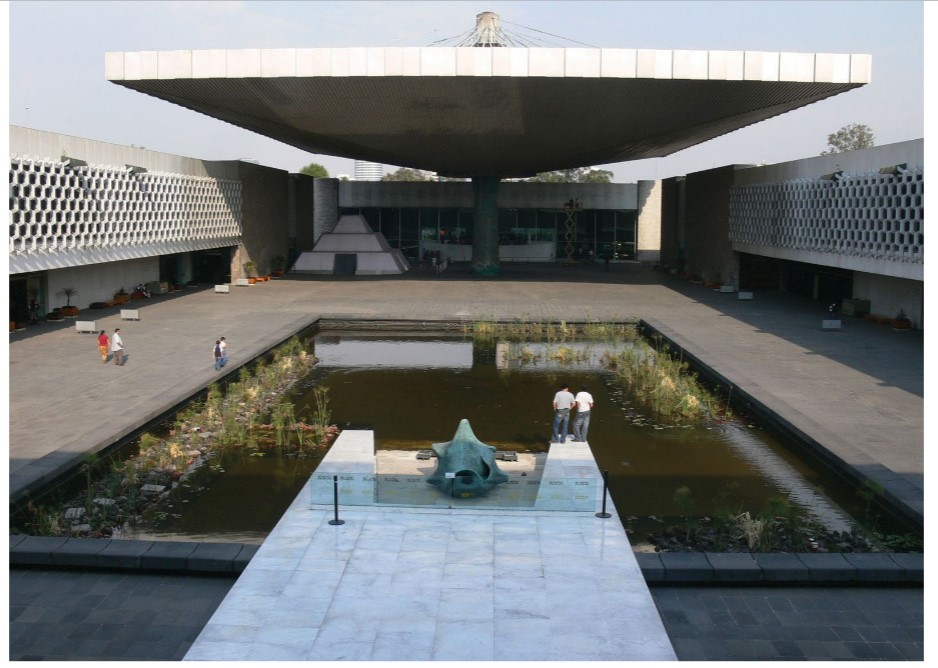

54
New cards
Lina Bo Bardi built
Sao Paolo Museum of Art
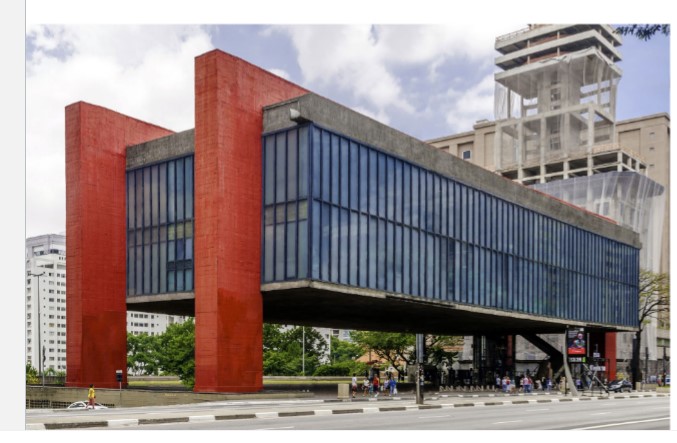

55
New cards
Kimbell Art Museum
built by Louis Kahn and Harriet Pattison
Landscape: key aspect of the project – landscape architect Harriet Pattison
Creates the impression of enclosed spaces by placing top-lit vaults over the
galleries
Structural innovation: post-tension concrete vault-shaped beams span the 102
ft spaces
Landscape: key aspect of the project – landscape architect Harriet Pattison
Creates the impression of enclosed spaces by placing top-lit vaults over the
galleries
Structural innovation: post-tension concrete vault-shaped beams span the 102
ft spaces

56
New cards
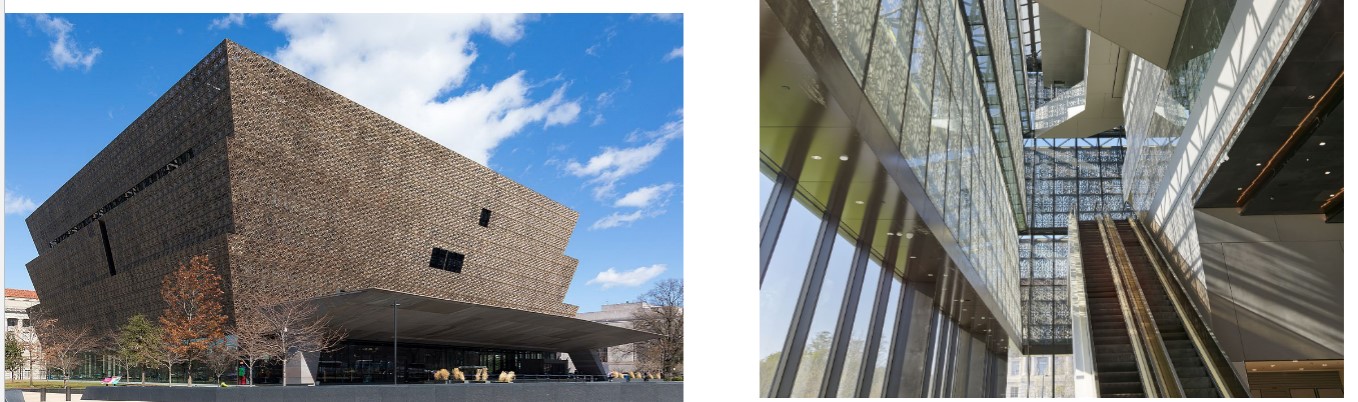
Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture
built by David Adjaye
Operates simultaneously as a museum + memorial + space for cross-cultural community building
Main design elements: overall “corona” shape + the porch(extension of the building into the landscape) + filigree envelope (bronze-coated aluminum lattice)
Envelope pattern: reference to African American craftsmanship
Operates simultaneously as a museum + memorial + space for cross-cultural community building
Main design elements: overall “corona” shape + the porch(extension of the building into the landscape) + filigree envelope (bronze-coated aluminum lattice)
Envelope pattern: reference to African American craftsmanship
