Neuro-muscular disorders
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
How many bones in the body
206....207 if im hard ;)
Axis
Bone in your neck that helps the head turn freely. C2 bone.
Aging and vertebral column
Aging can cause herniated intervertebral discs.
the disc can push some of its softer interior jellylike substances through a crack in the exterior of the disc. The result is pressure against the spinal nerves and pain that radiates out from the spinal cord.
What is a Intervertebral disc:
a small pad or disc of rubbery-like cartilage (nucleus pulposus) located between two vertebrae.
Herniated disc tx:
Laminectomy, Diskectomy, Spinal Fusion
Classification of bones:
Long, short, flat, Irregular
sesamoid bones
type of irregular : bones the develop within joints & tendons (patella is the largest one)
Function of muscle:
body movement, blood circulation, and heat production
Ossification
Process of bone formation
Vitamin D increase in calcified tissue is ossification
Occipital lobe
Visual transmission and interpretation occur in the visual areas.
Direct visual experiences
temporal lobe
Controls the sensations of hearing, auditory interpretation, smell, and some memory
Auditory areas both receive and interpret transmissions
parietal lobe
Speech and some Sensory area
Interprets sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain, which are received from the skin
Spatial ability (the ability to recognize shapes and sizes) is also located in this area.
Cerebellum
muscle control
Pons
carries messages between cerebellum and medulla, responsible for resp.
Broca's area:
area of cerebrum.
Associated with speech .
CVA affects ability to speak clearly
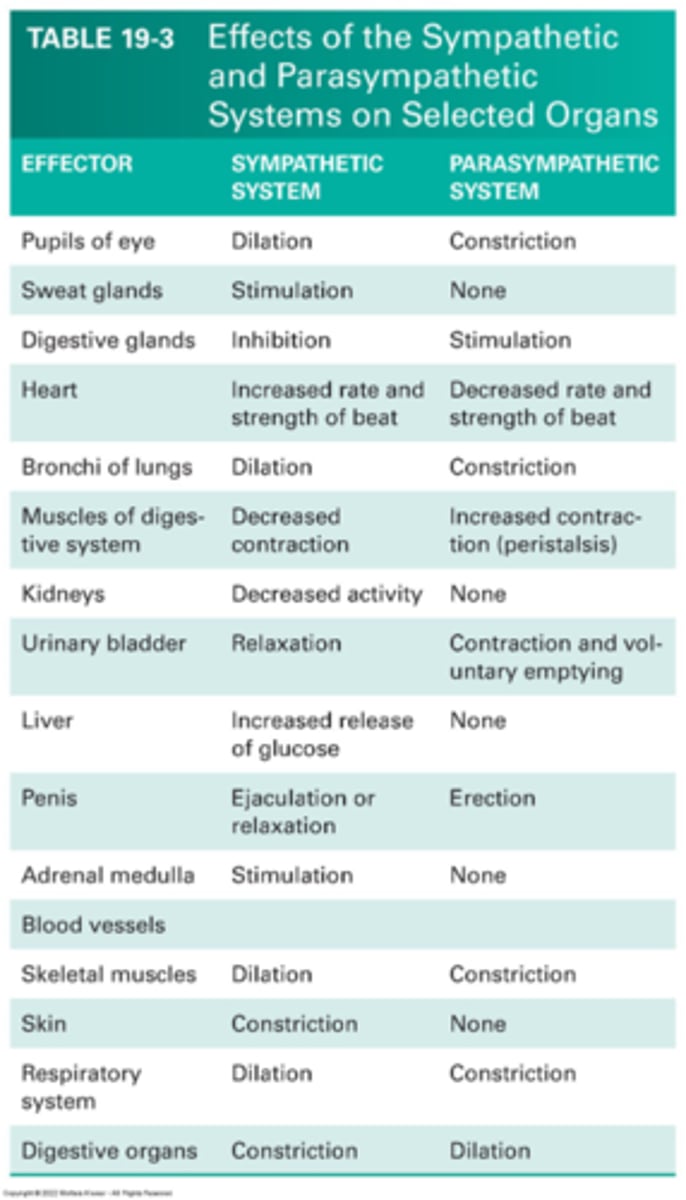
Sympathetic nervous system (look at flashcard outside of Learn)
Fight or flight.
Example- involuntary defecation and urination, tachycardia.
how to promote healing in severe joint pain
Hot compress
Arthroscopy
Endoscope used to visualize joints for diagnostics and treatments. Done in the OR, can remove loose objects such as bone spurs or pieces of cartilage
Arthroscopy Considerations
Elevate extremity, apply ice to area, monitor for signs of infection
What do we need to know about CSF?
Cerebral spinal fluid
contains glucose
What are Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), Rheumatoid factor (RF), Creatine Kinase (CK) tests used for?
show inflammation related to an infection or inflammatory condition
what are CBC, uric acid, calcium, and phosphorus levels tests used for?
Used to indicate the overall condition of MS system
arthrogram
Study of a joint by injecting a radiopaque substance
(check for iodine & shellfish allergies)
Myelogram
Exam of the spinal cord and vertebral canal after contrast is injected into the subarachnoid space.
Checks spinal cord for abnormalities caused by tumors, herniated intervertebral disks, or other lesions
Electromyogram
Test of electrical conductivity in the muscles both at rest and activity
Immobilization device complication
-Pressure from swelling.
-Edema
-Blanched, mottled or cyanotic skin color
-Numbness, tingling, or the inability to move
-Cold fingers
-Severe pain
-Lack of digital pulse
-Slow capillary refill
Activity and exercise for casts or splints to reduce immobilization
-Elevate
-Wiggle exposed fingers or toes
-Isometric exercise
-Use assistive devices as needed
Amputations levels
BEA: below elbow amputation
AEA: Above elbow amputation
BKA: Below knee amputation
AKA: Above knee amputation
Amputations considerations
-Protects limb
-Promotes healing
-Controls edema
-Minimize pain & trauma
Amputations complications
-Observe for bleeding
-Monitor drains
-Avoid dislodging drains
-Check incision closely when changing dressing:
-With leg amputation: Have patient lie in prone position to prevent contractures
Most at risk of an amputation
homeless with DM
phantom limb pain Tx.
pain meds
Replantation post op care
-Anticoagulation therapy
-Caffeine-free diet (prevents vasospasm)
-Wound care
-Antibiotics
-Frequent neuro vascular checks
-Monitor for bleeding, arterial or venous compromise, infection, decrease ROM
Lordosis
Curvature of lumbar vertebrae
kyphosis
Curvature of thoracic spine often caused by osteoporosis, hump back
Lordosis & kyphosis edu
Have patient make frequent position changes in bed
Lumbar decompression concerns
-Nerve damage
-Edema:
-Change in level of consciousness:
-Muscle spasms:
-Thrombophlebitis:
-Infection
Muscle Dystrophies:
chronic, degenerative diseases of skeletal muscles that are often inherited.
These disorders are characterized by various degrees of progressive weakening and wasting of the muscles.
Muscular dystrophy complication education
Prevent upper respiratory infections
Carpal tunnel syndrome test
-Test for Tinel sign
-Tinel sign: When the provider taps the median nerve, the client experiences paresthesia and pain in the thumb and first three fingers.
Carpal Tunnel Tx:
wrist splinting, rest, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections, surgery.
What is a Bursa
The bursa is a sac filled with synovial fluid that pads bony prominences in the joints.
Bursitis, care, gout
inflammation of a bursa related to mechanical irritation, bacterial infection, trauma, or gout. In response to inflammation, fluid increases, causing distention.
Bursitis S/S & Tx.
S/S: With chronic inflammation, calcification may result. Pain and tenderness in the joint limit movement.
Tx: heat, rest, anti-inflammatory medications.
Tenosynovitis
Inflamm of tendon sheath
Tenosynovitis S/S
Pain, tenderness.
Tenosynovitis Tx
Rest, ice for 1-2 dyas, NSAIDs, surgery, antibodies
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
A type of arthritis
The characteristic sign of SLE is a butterfly rash on the face.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) cause
damage to the collagen sys.
Arthritis Tx:
Arthroplasty or joint replacement.
Scleroderma
Hard skin caused by a collagen disorder
Chronic hardening & shrinking of connective tissues
Care for sprained ankle
Keep area immobilized with elastic bandage
Fractures: greenstick
One side of bone breaks, one side bends
Fractures: compression
Bone collapses in itself
Cast removal education
-Explain skin under may be covered with scales or crusts of dead skin
-Wear gloves, protective eye-wear, and mask
-Removed with a cast saw
Plaster Case nursing consideration
If dried edges are rough, cover with tape for protection
Skin traction
the pull is applied to the client's skin, which transmits the pull to the musculoskeletal structures
Skin traction types
-Bucks (A): One or both legs wrapped with bandage. Applied with weight attached below the foot
-Bryant (B): Variation of bucks for child 2 years and younger
-Cervical Halter (C): Used for neck pain, neck strain, or whiplash
Skin traction; Dunlop (Side-Arm)
Fractures of upper arm and shoulder dislocation prior to surgery
Skin traction; Russell (Balanced)
Balanced pulley system for leg traction. Femur
Skin traction Nursing alert
monitor for difficulty swallowing. indicates signs that the vertical bar of the device is too long.
External Fixator
Device used for complex fractures
Observe closely for infection.
Hip surgery care
-Do not bed body more than 90 degrees
-no 90 degrees turn frequently in bed
What is osteomyelitis
-Serious bone infection that is curable if it is detected early and treated appropriately.
-Modern antibiotics have greatly improved the chances for recovery from this infection.
Acute osteomyelitis
may result from a compound fracture that exposes bone to infection. Because blood supply to the bone is compromised, the bone becomes necrotic. Pus drains through the primary wound.
Embolism
A sudden blockage of one or more arteries by a piece of foreign material.
Fat embolism
most common embolism associated with fractures. Involves a bolus of fat.
Fat embolism S/S
dyspnea, tachycardia, fever, petechial rash, hypoxemia, chest pain, pulmonary edema.
extra info about Embolus
can travel to heart, lung, or brain
Prevention for DVT & Pulmonary Embolism
Sequential Compression Devices (SCDs), subcutaneous heparin, ambulation.
Compartment syndrome
inadequate or obstructed blood flow to muscles, nerves and tissue. Medical emergency- damage can occur in 4-6hrs.
Compartment syndrome S/S
The cardinal symptom is pain that is unrelieved by medications and aggravated by passive stretching of the ischemic muscle.
Tightness, swelling, numbness and tingling of affected extremity.
Compartment syndrome Tx.
Fasciotomy (excision of the fascia)
Angiogram- Dye
Encourage fluid intake due to injected dye
radiopaque dye used- drink fluids. Cerebral arteriography- obtain baseline neuro status
Arteriography
obtain baseline neuro assessment
Thrombus can become dislodged during exam
Elderly with contrast dye
Monitor the older adult client's blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine before and after any procedure that uses dye.
The aging population is at increased risk for kidney damage; promptly report any elevations in BUN and creatinine.
types of brain scans
CT & MRI
Brain Scan evaluates for
-Vascular lesions
-Neoplasms
-Abscesses
-Areas of ischemia
Lumbar Puncture
(LP, spinal tap) involves the insertion of a hollow needle with a stylet (guide) into the subarachnoid space of the lumbar region of the spinal canal.
CSF contains glucose.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Used in the diagnosis of:
Seizures, brain tumors, intracranial lesions, blood clots, infections, sleep disorders, and confirmation of brain death
Paraplegia neuro chair
-Provides a comfortable place to rest out of bed,
-Adjusts to various positions: Fowlers, Trendelenburg,
-Place chair flat first, Reposition to desired position,
-Lock the wheels,
-Obtain additional help when moving.
Cephalgia
Headache
Most common symptoms of neurologic disorder. Not a disease, a symptom of underlying disorder. Not the same as an occasional HA that responds to meds
Migraine S/S
Sensory warnings (Aura)
Mood changes
Anorexia
Numbness or body part
Visual symptoms: Flashing lights, floating spots
Throbbing or steady pain
N/V
Trigeminal neuralgia
the root of the trigeminal (fifth cranial) nerve becomes painful.
Cause: unknown
generally occurs in the older population.
pain is excruciating and comes in spasms that can last for seconds to hours, occurring in the jaw and parts of the face.
Trigeminal neuralgia trigger
slightest touch to various parts of the face, or even by a breeze, a change in temperature, or a mouthful of food, depending on the trigger zone's location.
Bell's Palsy
temporary, partial, one-sided facial paralysis and weakness caused by ischemia or inflammation of the seventh cranial nerve.
Bell's Palsy S/S
temporary, partial, lopsided facial appearance, The eye on the affected side will not close. caused by ischemia or inflammation of the seventh cranial nerve.
A Bell palsy-type syndrome may result from?
a brain lesion
Spinal cord function & extra info
Communication between the brain and body
Spinal cord cannot regenerate
Transection of spinal cord causes permanent paralysis
Paraplegia care
Immobility: Beds and chairs with special features, Prevents skin breakdown, Reduces pain
Parkinson disease- S/S
Bradykinesia (slow movements), fine, rhythmic tremors of hands, arms, legs, jaw, face, limbs and trunk rigid and stiff
Parkinson disease- Tx
Levodopa (replaces missing dopamine), Carbidopa-levodopa, Dopamine agonists, MAO B Inhibitors, Anticholinergics
Myasthenia Gravis- S/S
Double vision (diplopia), Drooping face/lids (ptosis), Sleepy, Expressionless, Difficulty breathing, Dysphagia, Dysphasia, Weaker arms than legs
Myasthenia crisis
life threatening complication of Myasthenia
severe muscle weakness, particularly of the respiratory muscles, requiring mechanical ventilation
Epilepsy
CNS disorder in which nerve cell activity in the brain becomes disrupted, causing periods of unusual behavior. Sometimes loss of consciousness.
Huntington disease
Chronic, progressive, Hereditary, Brain cells in basal ganglia prematurely die, physical, intellectual, emotional symptoms
Child has 50-50 chance of inheriting gene: Will develop disease, Can pass to next generation, Age on onset varies, Symptoms about 30-40 years old
ALS- Lou Gehrig disease
Destruction of motor neurons: Cortex, brain stem, spinal cord,
ALS- Lou Gehrig disease S/S & onset
Voluntary movement degenerates, Always progresses to respiratory dysfunction and death,
onset at 50-70 yrs., more men than women
Brain abscess can lead to?
meningitis if untreated
Positive Brudzinski sign
The client lies on the back and brings the head forward toward the chest.
-Pain or resistance indicates meningeal irritation, arthritis, or a neck injury.
-If the person responds by flexing the hips and knees, meningeal inflammation is indicated.