BIOL 12 Protein Structure and Function
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
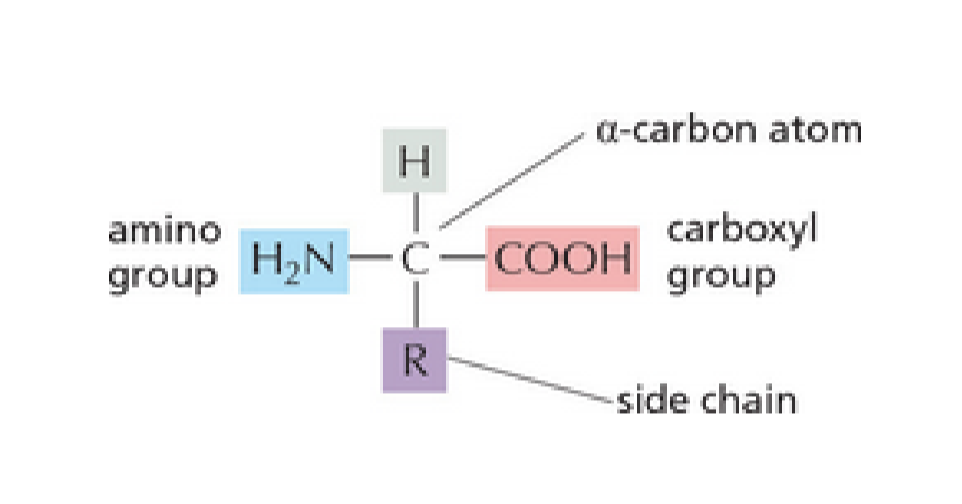
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
Alpha carbon atom, amino group, carboxyl group, R group side chain, H atom
What is the charge of the amino and carboxyl group at pH 7?
The amino group is protonated and has a +1 charge, the carboxyl group is deprotonated and has a -1 charge
What are the 4 categories of R groups?
Non polar (hydrophobic)
Polar charged (hydrophilic)
Polar uncharged (hydrophilic)
Unique
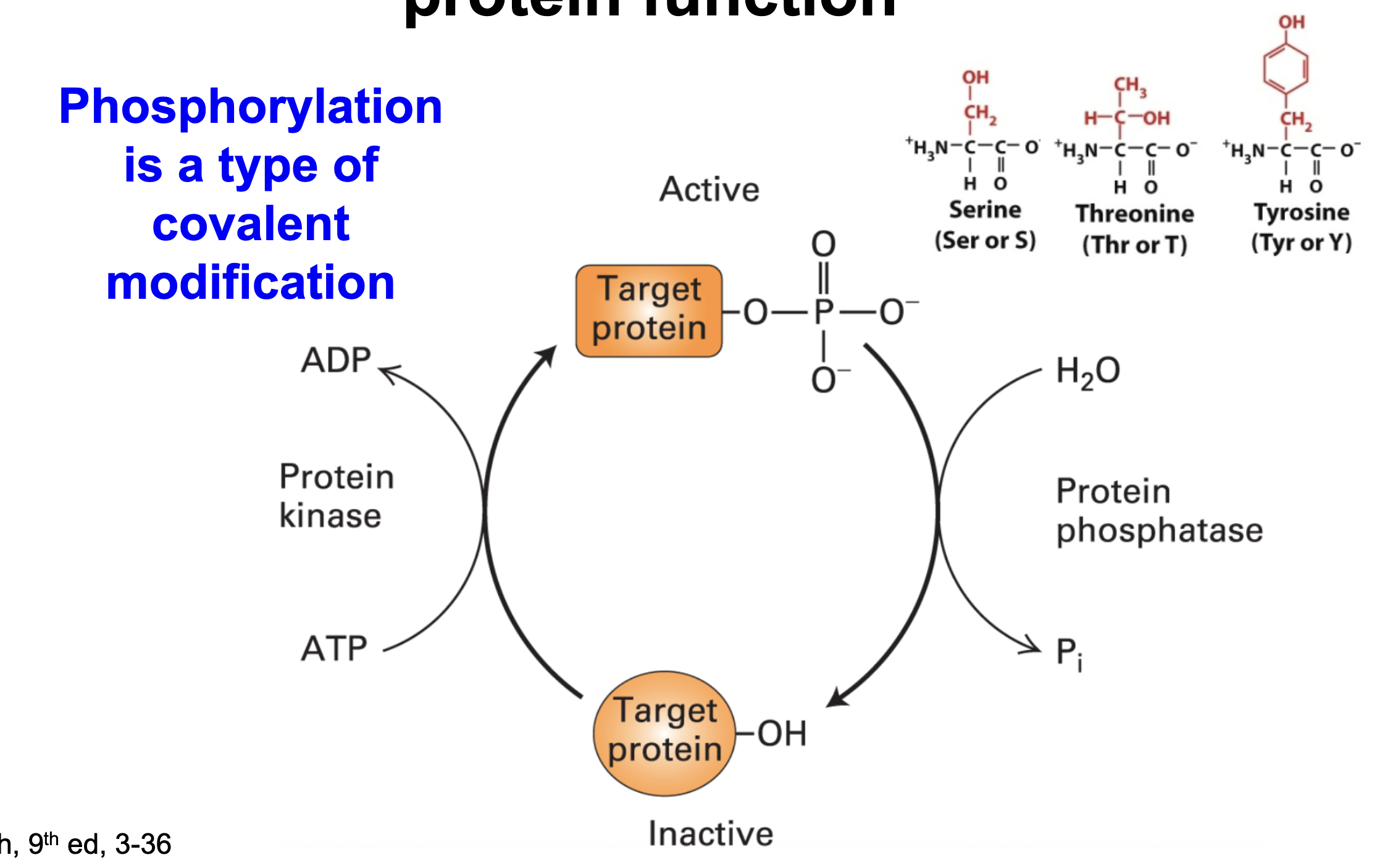
What three amino acids can be phosphorylated?
Serine, threonine, tyrosine (all polar uncharged)
What are the amino acids with unique properties?
Glycine
Single H for R group
Fits into either hydrophobic or hydrophilic environment
Often resides where 2 polypeptides come into close contact
Cysteine
Side chain is polar uncharged
Can bond w/ another cysteine to form a disulfide bond
Proline
Hydrophobic character
Creates kinks in polypeptide chains (helix breaker)
Rigid structure due to 2 covalent attachment to backbone
How are polypeptides formed?
Condensation reaction → peptide bond
What are the two ends of a polypeptide?
N (amino) terminus and C (carboxyl) terminus
What are the 4 stages of protein structure?
Primary — amino acid residues (sequence)
Secondary — alpha helixes, beta sheets
Tertiary — Polypeptide chain and 3D structure
Quaternary — Assembled subunits
What are alpha helixes important for? Would you expect an alpha helix spanning the lipid bilayer to have mostly hydrophobic or hydrophilic R groups?
Important for integral membrane proteins
Hydrophobic
What bonds connect beta strands?
H-bonds
What do multiple beta strands make?
Beta sheets
Antiparallel vs. parallel beta sheets?
Antiparallel → NC CN NC
Parallel → NC NC NC
What forces maintain a tertiary structure?
Non covalent forces:
Van der Waals forces, H-bonds, ionic bonds
Covalent:
Disulfide bonds between cysteine residues (inter or intramolecular)
What is a homodimer vs. heterdimer vs. homotetradimer?
Homodimer — two of the same subunits
Heterodimer — two different subunits
Homotetradimer — four of the same subunits
Explain the components of phosphorylation