bonding, structure and properties of matter
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
ions are ________ particles
charged
how do atoms become an ion
gain or lose an electrons to get a full outer shell
atoms with full outer shells are very…
stable
noble gases on the periodic table are group
O
When metals form ions they _____ electrons from their outer shell to form _______ ions
lose positive
When non-metals form ions they _____ electrons from their outer shell to form _______ ions
gain negative
which two groups of elements are metals which lose electrons to form positive ions (cations)
group 1+2
which two groups of elements are non-metals which gain electrons to form negative ions (anions)
group 6+7
group 1 elements form
1+ ions
group 2 elements form
2+ ions
group 6 elements form
2- ions
group 7 elements form
1- ions
the column number is how many electrons
in the outer shell
what is ionic bonding
when a metal and a non-metal react together
in ionic bonding the oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to each other by
electrostatic forces
ionic compounds have a structure called
a giant ionic lattice
do ionic compounds have high or low melting and boiling point + why?
high because of the strong bonds between the ions so lots of energy is needed to overcome it
when ionic compounds are solid to they conduct electricity
no
when ionic compounds are melted to they conduct electricity + why
yes because they’re free to move so can carry electric charge
when dissolved in water can ionic compounds carry electrical charge?
yes as they’re free to move
what are the three steps to work out empirical formula
1- work out what ions are in the compound
2- what out what charges the ions will form
3- balance the charges so the charge of the empirical formula is zero
what is covalent bonding
where non-metal atoms bond together and 5hey share a pair of electrons to make covalent bonds
the positively charged nuclei of the bonded atoms are attracted to the shared pair of electrons by electrostatic forces making the covalent bonds very…
strong
in which shell to atoms share their electrons
outer shell
how many shared electrons does a single covalent bond provide for each atom
one
having a full outer shell gives atoms the electronic structure of a
noble gas which is very stable
substances containing covalent bonds usually have…
simple molecular structure
atoms within simple molecular structures are held together by …
very strong covalent bonds
the forces of attraction between molecules in simple molecular substances are…
very weak
to melt or boil a simple molecular compound you need to break the ___________ ______ not the __________ _____
intermolecular forces covalent bonds
simple molecular substances have a _______ ______ melting and boiling point
very low
what state of matter are most molecular substances at room temp
gases or liquids
As molecules get bigger the strength of the intermolecular forces _______ so ____ energy is needed to break them and melting and boiling points ________
increases more increase
do molecular compounds conduct electricity and why
no because they aren’t charged so there are no free electrons or ions
What is this describing
lots of small units which are linked together to form a long molecule that has repeating sections
a polymer
all the atoms in a polymer are joined together by
strong covalent bonds
what can you do instead of drawing out the entire polymer molecule
draw the shortest repeating section like this
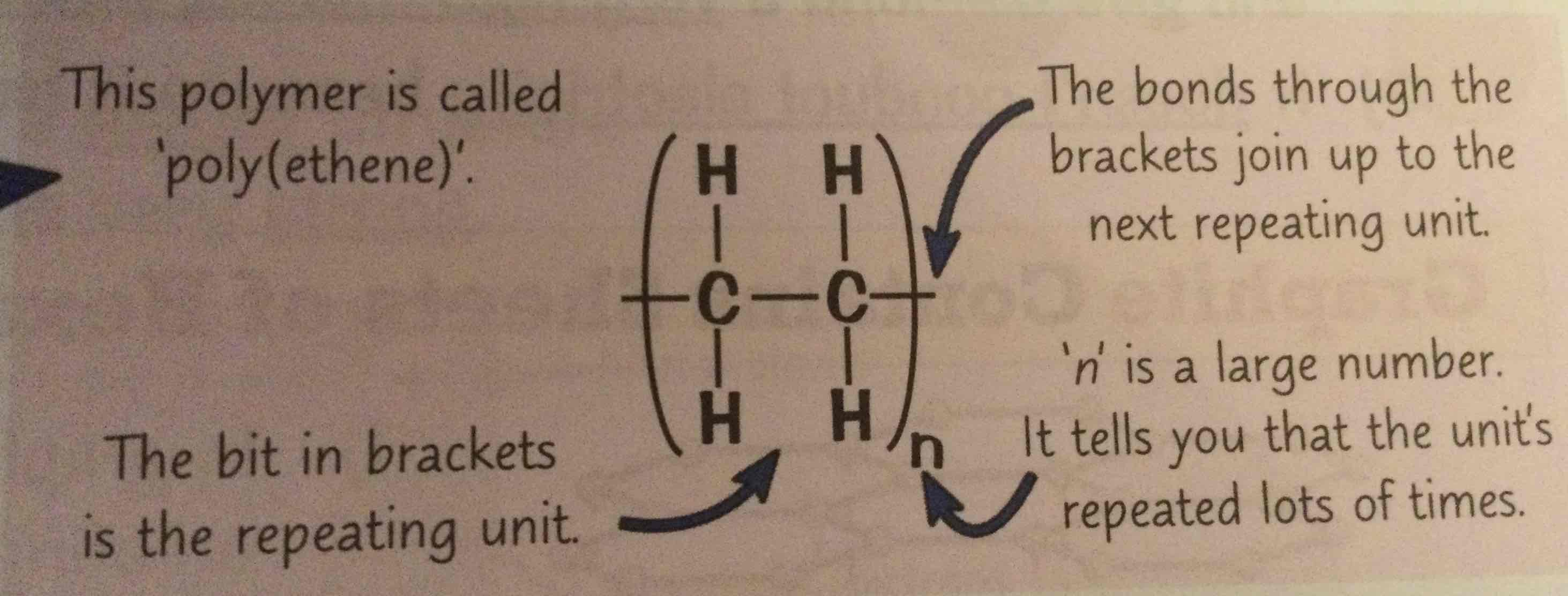
how do you find the molecular formula of a polymer
write down the molecular formula of the repeating unit in brackets and put an ‘n’ outside
are the intermolecular forces between polymer molecules larger or smaller than simple covalent molecules and what does this mean to break them?
larger and more energy is needed to break them
what state of matter are most polymers at room temperature
solid
polymers intermolecular forces are still ______ than ionic or covalent bonds, so they generally have _____ boiling points
weaker lower
In giant covalent structures all the atoms are bonded to each other by
strong covalent bonds
how high or low are giant covalent structures melting and boiling points
very high
do giant covalent structures conduct electricity?
no as they don’t contain charged particles apart from a few exceptions such as graphite, diamond and silicon dioxide
(in diamonds) each carbon atom form ____ covalent bonds in a very _____ giant covalent structure
four rigid
(in graphite) each carbon atom forms _____ covalent bonds to create _______ of _________ each carbon atom also has one ___________ electron
three layers hexagons delocalised
(in silicon dioxide) this is what ____ is made of, each grain of ____ is one giant structure of silicon and oxygen
sand sand
what structure does diamond have?
giant covalent made up of carbon atoms that each form four covalent bonds
how high or low is diamonds boiling/melting point
very high
do diamonds conduct electricity
no
in graphite are their any covalent bonds between the layers
no they’re held together very weakly so they’re free to move over each other
how high or low is graphites melting point
very high
can graphite conduct electricity
yes as one of the 4 electrons is delocalised
graphene is ___ layers of graphite
one
how thick is graphene
1 atom thick
can graphene conduct electricty
yes it can be used in electronics
is graphene strong?
yes
what are fullerenes
molecules of carbon, shaped like closed tubes or hollow balls.
what are fullerenes mainly made up of and how are they arranged
carbon atoms arranged in hexagons but also can be in pentagons and heptagons
the fullerene structure can trap another atom or molecule inside how could this be used
to deliver a drug inside the body
how big is fullerenes surface area
huge
fullerenes can form
nanotubes - tiny carbon cylinders
can nanotubes conduct electricity and thermal energy
yes
what are 4 uses of fullrenes
lubricants catalysts drug delivery to strengthen materials
metals also consist of…
a giant structure
the electrons in the outer shell of the metal atoms are
delocalised
their are strong forces of electrostatic attraction between the positive metal ions and
the shared negative electrons
is metallic bonding strong
yes
metallic bonding is held together by
forces of electrostatic attraction
which substances are held together by metallic b9nding
metallic elements and alloys
do compounds with metallic bonds have high or low boiling/melting points
high
metals are good _________ of electricity and heat
conductors
most metals are m________
malleable
alloys are harder than
pure metals
most pure metals are too
soft
if solids have a strong force of attraction between particles what is a gas’ like
very weak