Personal Health and Wholeness NSG-1410 Full Review (In Progress)
1/74
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
social determinants of health
Income and social status
Employment and working conditions
Education and literacy
Childhood experiences
Physical environments
Social supports and coping skills
Healthy behaviours
Access to health service
Biology and genetic endowment
Gender
Culture
Race/racism
Reconciliation
The process of establishing and maintaining respectful relationships
Repair trust through apologies, amends and following through
Recognizing rights, partnerships
Ongoing process
policy and system change
engaging community
maintaining indigenous safe and healthcare providers
anti-racism and cultural safety education
improving indigenous client care
What are the calls to action relating to health?
maintenance of physiological functional norms
medical interventions of curing diseases
reactive healthcare
less emphasis on health promotion and disease prevention
what is the medical approach?
Lalonde report promoted individual responsibility for health
Emphasis on health and disease prevention
Development of food guides
Determinants of health
what is the behavioural approach?
Thinking about context
Health is tied to social structures
Led to Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion
what is the Socio-environmental approach?
what does the Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion outline as the prerequisites for health?
Prerequisites for health:
Peace
Shelter
Education
Food
Income
A stable ecosystem
Sustainable resources
Social justice and equity
Based on a holistic model of health
Relationships and integrating culture
Balance of physical, mental, emotional and spiritual health
What is the Indigenous health model?
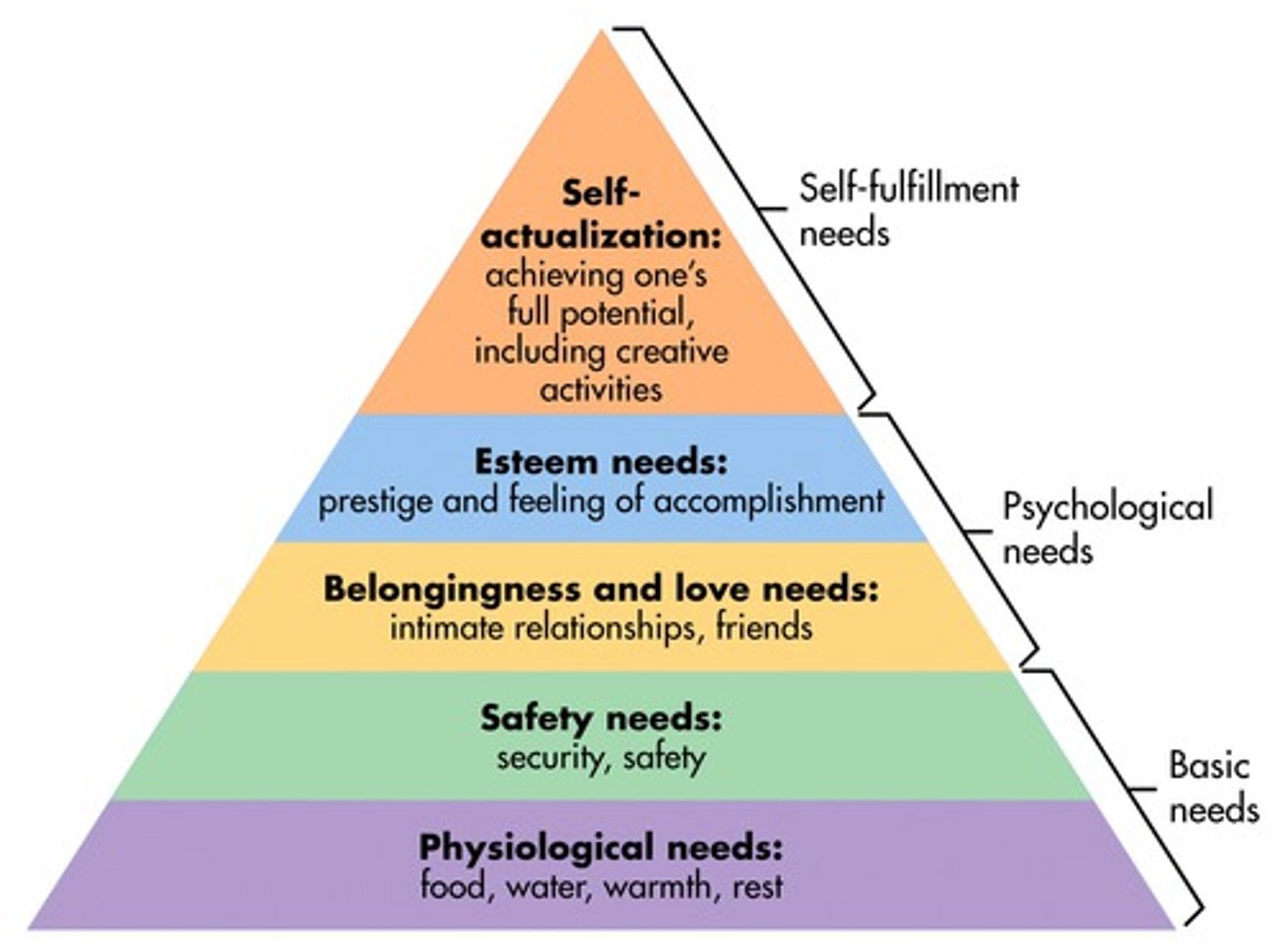
physiological
safety
love/belonging
esteem
self-actualization
what are the tiers to Maslow's Hierarchy? (#1 being at the bottom)
The art and science of teaching children
Teacher is central power role
Learners are told what to know, word for word
Dependent on instructor information
Extrinsic motivation (grades)
pedagogy
The art and science of helping adults learn
Focuses on the learner and their needs
Uses personal experiences in learning process
Learners are responsible for knowledge
Learning through application and questioning
andragogy
Individuals take on the responsibility for their own learning process based on:
Personal needs
Goals
Resources
Strategies
self-directed learning
Responsibility of learning is on the learner
Instructors provide guidance, feedback, and resources
Based on experience
self-determined learning
Impacts judgement
Impacts mental capacity
Increases risk of mistake (impacts everything)
what are the impacts of being unfit to practice?
Incapacitated
Fatigue
Substance use
Disability
Stress
what factors risk fitness to practice?
benefits of exercise
Increases energy
Reduces stress
Stimulates endorphins
Reduces risk of diseases
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Realistic
Timely
what are do the letters in SMART goal stand for?
emotional wellness
Ability to express and manage feelings
Ability to enjoy life
Ability to adjust to challenges
Ability to cope with stress and trauma (resilience)
Emotional Intelligence (EI)
the ability to understand, use and manage emotion in positive ways
social network and emotion wholeness
sense of purpose, belonging and safety
humour
laughter is the best medicine - enjoy and express feelings of joy and happiness- stimulates endorphins
intellectual health and wholeness
creativity, mental activities, learning, increased knowledge, problem solving , awareness
lifelong learning
the continuing development of knowledge and skills that people experience after formal education and throughout their lives
cognitive, affective, psychomotor
3 domains of learning
cognitive learning
knowledge (head/brain) -blooms taxonomy
affective learning
attitudes or heart - feelings, values, motivation, appreciation
psychomotor learning
skills or hands - 3 A's (accept, apply, adapt)
social health and wholeness
our ability to effectively express ourselves and interest with people around us - support system (family and friends)
loneliness
discrepancy between ones desired and actual level of social connection - satisfaction with quality of connections
social isolation
few social contacts, low meaningful interactions, lack of mutually rewarding relationships
healthy relationships
based on equality and respect, support, trust and belonging
environmental health
External physical, chemical, and biological factors impacting health, focusing on their assessment, control, disease prevention, and creation of health-supportive environments.
spiritual health and wholeness
The integration of body, mind, and spirit, fostering a sense of connection to self, others, and a higher power to achieve wholeness and well-being.
Income and Social Status
Maria works part-time at a grocery store and earns minimum wage. Her paycheck barely covers rent and utilities, so she often skips meals to ensure her children eat first. What SDoH is most at play?
education and literacy
Jason grew up in a low-income neighborhood with underfunded schools. His high school had limited science classes and no college counseling. What SDoH is most at play?
physical environments
Ahmed lives near a busy industrial area with poor air quality and no green spaces. The nearest grocery store is 10 miles away, but fast food is everywhere. What SDoH is most at play?
Social Supports and coping skills
Evelyn is an elderly widow living alone in a rural town. Her children live far away, and she has limited social interaction. What SDoH is most at play?
Access to Health Services
Luis doesn’t have health insurance because his job doesn’t offer benefits. When he experiences chest pain, he delays going to the doctor due to cost. What SDoH is most at play?
Gender
Anna, a 45-year-old woman, reports chronic chest pain. When she visits her local clinic, her symptoms are dismissed as “anxiety,” and she is not referred for further testing. Which SDoH is most at play?
Culture
Li is a recent immigrant who believes strongly in traditional herbal medicine. She avoids Western doctors because she fears being misunderstood or disrespected for her cultural practices. Which SDoH is most at play?
Race/Racism
Marcus, a Black man, visits multiple clinics for high blood pressure management. He notices shorter appointment times and fewer explanations than his White colleagues receive at the same practice. Which SDoH is most at play?
Biology and genetic endowment
Sara has a family history of breast cancer. Genetic testing reveals she carries the BRCA1 mutation. Which SDoH is most at play?
Childhood experiences
Jamal grew up in a home with domestic violence and neglect. As an adult, he experiences chronic anxiety and substance misuse. Which SDoH is most at play?
Healthy Behaviours
Sofia lives in a walkable community with parks, affordable gyms, and fresh produce markets. She exercises regularly, eats balanced meals, and avoids smoking. Which SDoH is most at play?
Employment and Working Conditions
Carlos works in a large warehouse where he lifts heavy boxes for 10-hour shifts, six days a week. The workplace has poor ventilation, limited breaks, and minimal safety training. His supervisor discourages workers from taking sick leave, warning that “absences affect job security.” Which SDoH is most at play?
pure fresh air
pure water
effective draining
cleanliness
light
What are the 5 factors in Nightingale’s environmental theory of health?
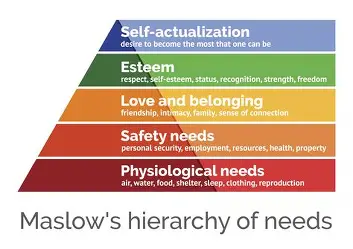
We must first meet our physiological and biological needs to begin building up the ladder to our social and emotional needs
Describe how Maslow’s Hierarchy effects health outcomes
social
emotional
intellectual
physical
occupational
spiritual
what are the 6 dimensions of wellness?
Occupational
Rina feels constantly stressed and unmotivated at her job. She often brings work home and misses family time. What dimension of wellness is most affected?
Physical
Jordan works late shifts and relies heavily on caffeine to stay awake during the day and has begun to regularly skip breakfast. Which dimension of wellness is most affected?
social
Taylor recently moved to a new city and has felt very isolated since. what dimension of wellness is most affected?
Intellectual
Amir feels bored at work, watches TV all day outside of work, and avoids new challenges. what dimension of wellness is most affected?
Spiritual
Jade feels lost and unsure of her purpose in life and lacks a clear sense of values, morals, and inner peace. what dimension of wellness is most affected?
Emotional
Liam experiences frequent panic attacks and is uncomfortable expressing emotions resulting in impulsivity when he is upset. what dimension of wellness is most affected?
Exercise
mindfulness
therapy
social support
adequate rest
What are some coping mechanisms for chronic stress?
It can disrupt physical, emotional, and social well-being, affecting the body’s ability to maintain homeostasis.
how does stress influence overall health?
A state of balance and integration of body, mind, and spirit.
What does wholeness mean in a health context?
By reducing stress, improving emotional regulation, and enhancing self-awareness.
How can mindfulness promote wholeness?
Emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced sense of accomplishment.
What are signs of nurse burnout?
It can impair judgment, concentration, communication, and patient safety.
How can stress affect nursing performance?
Emotional exhaustion from caring for others in distress, often linked to chronic occupational stress.
What is compassion fatigue?
Through self-care, peer and mentor support, healthy boundaries, mindfulness, emotional intelligence, spiritual reflection, ongoing education, and advocating for supportive workplace environments.
What are some ways that we can promote resiliency for nurses to combat burnout?
decreased psychological distress
self confidence
reduce risk factors
reduced GI symptoms
pain management
decreased headaches
What are some health benefits to Mindfulness Based Stress-Reduction (MBSR)?
freedom from any cognitive, physical, psychological or emotional condition and dependence on alcohol or drugs that impairs ones ability to practice nursing
What does it mean to be “fit to practice”?
S- Stop and take stock
T- Take a mindful breath or two
O- Open and Observe
P- Proceed with new possibilities
What does the STOP Acronym mean?
Income and Financial Stability
What is the most influential SDoH?
Financial aid
What is a resource at the Polytech that can help you with financial struggles?
Seeking to learn more
What is the key point of self-directed learning?
Self-directed learning
when we ask ourselves “what do I need or want to learn?” this an example of…
Nurses assess themselves
Who assesses nurses for fitness to practice?
Psychomotor learning
When you physically practice a new clinical skill, such as venipuncture, you are engaging in which learning domain?
Affective learning
Developing a professional attitude towards patient confidentiality is an example of growth in which learning domain?
cognitive learning
During a shift, a nurse encounters a patient presenting with sudden shortness of breath. The nurse assesses the patient's vital signs, reviews their medical history, and synthesizes this information to identify potential causes and determine the most appropriate immediate interventions. This process of critical thinking, data interpretation, and decision-making to plan care exemplifies cognitive learning in action.
Cognitive learning
Which domain of learning categorizes intellectual skills using Bloom's Taxonomy?
Remembering…
What are the levels of blooms taxonomy