pediatrics JCCC EMT (EMS 132)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
neonate age
0-28 days
infant age and considerations
1 month-1 year - keep equipment warm. If stable do toe to head exam. Older than 6 months have seperation anxiety.
Toddler age and considerations
1-3
dont like being touched or having clothing removed
preschoolers age and considerations
3-6
concrete thinking “take your blood pressure”
explain what you will do, then do immediately
fear pain and may think it is punishment
school age and considerations
6-12
explain each procedure
afraid of disability
BP vitals sign hacks
lower limit= 70 + (age x 2)
median= 80 + (age x 2)
upper limit= 90 + (age x 2)
diastolic = 2/3 of systolic
newborn blood volume
about 350 ml (a can of soda)
pediatric airway considerations
bigger tongue
smaller airway diameter
epiglottis is higher in the neck
can kink airway if overextended
excessive pressure on chin can block airway (use good BVM technique)
the lungs are the last to develop- more fragile tissue
soft spots on infant heads and when they close
fontanelles
anterior 18 months
posterior 6 months
pediatric ribs
bend rather than break - can cause internal damage with no external signs
more horizontal ribs (dont protect liver and spleen as much)
underdeveloped chest muscles (lack protection)
pediatric tidal volume formula
5-7cc/kg
pediatric emergencies considerations
treat airway management aggresively
compensate a lot, then crash (dont let vitals fool you)
hypotension is a later sign of decompensation
bones and muscles in pediatrics
splinter rather than snap
motor development occurs from head to toe
metabolism
o2 and glucose burn up faster
unable to store glucose as much
body surface area (skin)
child body surface area is large compared to overall body size
skin is thinner with less fat and muscle
initial assessment for a child
PAT- pediatric assessment triangle
1st look at Work of breathing
then circulation (skin color, temp, moisture, cap refill)
then apearence (acting normal? Gaze? Limp posture, etc)
it starts with WOB normally
PAT apearence mneumonic
TICLS
Tone
interactivity and irritability
Consolability (think breast feeding for babies)
look or gaze
speech or cry
AVPU for young child
A- awake, curious, interested, attentive
V- turns his head to sounds
P- moans or cries to pain
U- unresponsive
breathing assessment considerations
obtan RR before touching them
obtain breath sound first or last (dont want them upset)
history for pediatrics (and exp ?s)
they can start answering questions around 4
talk to parents
who was taking care of them
sickness at school?
progression of illness
dehydration?
poopy/wet diaper? How many?
Are they acting normal- toys, games, activity?
breathing emergencies with peds considerations
humidify o2 if possible
remember that they may contine to compensate even through failure
croup
Infection of upper airway causes swelling & airway narrowing beneath the glottis (larynx).
Signs & symptoms are slow in onset & include:
•Hoarse cough with “seal bark”quality
•Stridor
•Restlessness
walk outside in cool air
high flow 02- humidify
ALS
epiglottitis
×RARE Bacterial infection that causes inflammation & swelling of the epiglottis (Hib vaccine—2 months)
×Age: 3 - 7 years (usually)
×Rapid onset accompanied by a high fever
s/s
•Pain on swallowing
•High fever
•Drooling
•Tripod position
Inspiratory stridor
suction mouth or nose first in babies?
mouth
bronchiolitis
Viral infection of the bronchioles resulting in inflammation
usually from RSV
Signs & Symptoms:
•Poss fever, cough, rhinorrhea, swelling of tongue/lips, rash, labored breathing, FBAO
•Dyspnea
•Possible hx of: prematurity, respiratory illnesses, contact w/others who are ill
•Family history of asthma, allergies, eczema
•Ask about changes in feeding patterns & wet diapers
•Children < 2 years almost always have bronchiolitis & not asthma
•Children > 2 years almost always have asthma & not bronchiolitis
•Emergency Care:
•Supplemental O2
•Suction secretions
•HFNC , CPAP, SGA considered situationally
meningitis
×Infection of the brain & spinal cord - can be fatal.
×Fever in an infant under the age of 3 months is considered meningitis until proven otherwise!
×Signs & symptoms include:
×Ear or respiratory tract infection
×High fever & rash
×Lethargy, irritability, AMS, nausea, vomiting
×Bulging anterior fontanelle if adequately hydrated
×Stiff neck - generally not observable in infant
SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome)
also- what to look for
×The sudden & unexpected death of an infant in which autopsy fails to identify the cause of death.
×Usually between 1 month & 1 year.
×Peak incidence at 4 months.
×Most cases involve a previously healthy infant, often born prematurely.
look for scene clues
-sleep enviornment (sleep on stomach or side, with lots of blankets?)
-maternal risk factors
-sleeping with parents
-siblings with sids
-male baby?
Care:
ask the time the baby was put to bed- they should sleep in short increments
CPR unless obvious signs of death
care for family
BRUE/ALTE
Brief Resolved Unexplained Event/Apparent Life-Threatening Event:
×Age: <1 year
×Time: <1 minute
•Breathing change (absent, decreased, irregular)
•Color change (central cyanosis or pallor)
•Marked change in muscle tone (hyper/hypotonia)
•Altered level of responsiveness (increased irritability or decreased)
death of a child care for family
•Use the child’s name
•Use the word “dead” or “died”
•Acknowledge feelings, avoid “I know how you feel”
•Offer to call family members or religious support
•Keep instructions short, simple
•Ask each adult family member individually if he/she wants to hold the child
shaken baby syndrome
•Shaken-Baby Syndrome: Abuser violently shakes infant or small child, creating whiplash-type motion that causes acceleration-deceleration injuries.
DOPE
used for trouble shooting tracheostomy tubes
×DOPE = Dislodgement, obstruction, pneumothorax, equipment.
Long term venous access device permits administration of medications, fluids, etc., into the child’s bloodstream.
name and complications
central lines
×Most common complications:
×Infection at site
×Occlusion
×Bleeding at site
×Air embolus
where do we transport children
childrens mercy missouri
Neisseria Meningitides
a bacterium that causes rapid onset of meningitis symptoms leading to shock or death. Comes with rash
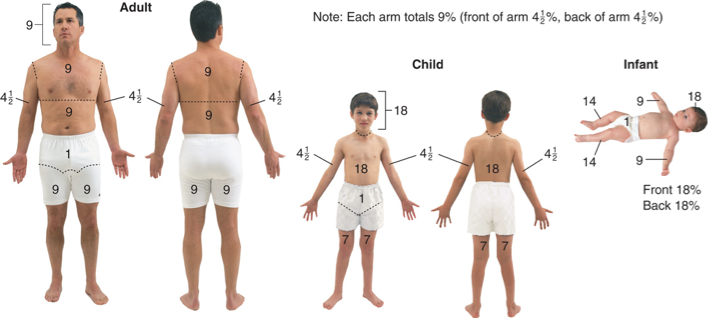
rule of nines