Brominating Alkenes & IR Spectroscopy
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Applications of halogenation of alkenes (example)
The Halogenation of Alkene reaction called “Addition of Cl2 to Ethylene” produces a product that is used to prepare Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) which is used in house plumbing
Halogenation of Alkenes Using Iodine (I2)
Endothermic and very Sluggish process that produces vicinal dihalides that end up reverting back to their original alkene form.
(that’s why we typically use Br or Cl instead for Halogneation of alkene reactions in the lab)
How to Tell if a Halogenation Reaction will Produce Enantiomers?
Trans Alkenes produce Meso Compounds THAT ARE CIS (no enantiomers)
Cis Alkenes Produce Racemic Mixture THAT ARE TRANS (Enantiomers)
Erthro vs Threo
Also Describe How these Differ in terms of R and S
These are all just fancy foreign words to refer to concepts we already know
Erthro = Meso
Compound A: (R, S)
Compound B: (S, R)
(You know its meso bc the compound PHYSICALLY looks symmetrical)
Threo = Enantiomers
Compound A: (R, R)
Compound B: (S, S)
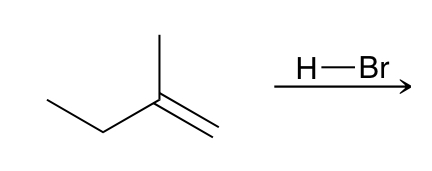
Draw the Mechanism and Product for a BASIC Electrophilic Anti-Addition Mechanism

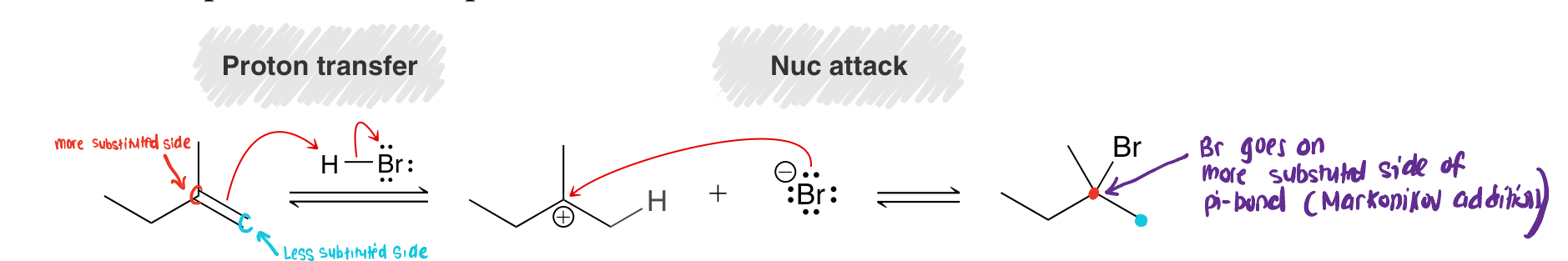
Markovnkov Anti Addition (Br on more substituted Side of 2x-bond, and H on less substituted side)
2 Steps (& an Carbocation Intermediate)

Halogenation Mechanism (using Br2 as the Halogen)
What product does it form?
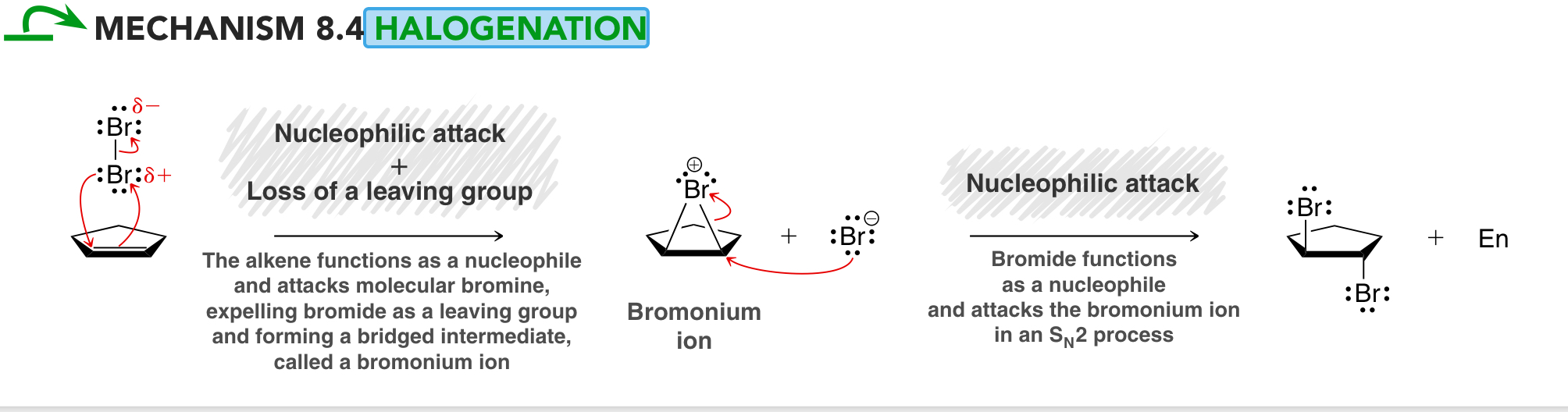
Forms trans vicinal Dihalides

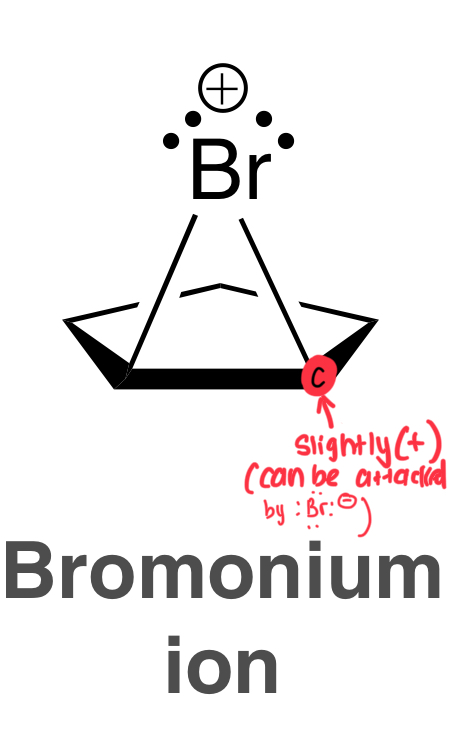
Draw the Bromonium Ion Intermediate of an Alkene Halogenation using Br2
more stable than a normal carbocation intermediate bc all atoms in the bromonium ion have full octets
The Common Pro of Using Halogenation of Alkenes Using Chlorine (Cl2) or Bromine (Br2)
Halogenation of alkenes occurs rapidly at room temperature, producing STABLE, trans vicinal dihalides
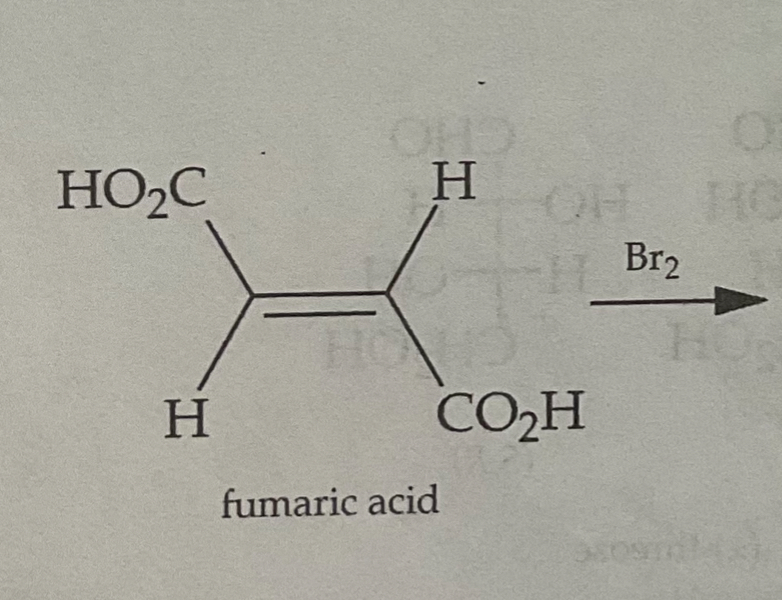
Trans Alkenes form ___(cis/trans)_______ bromonium ions
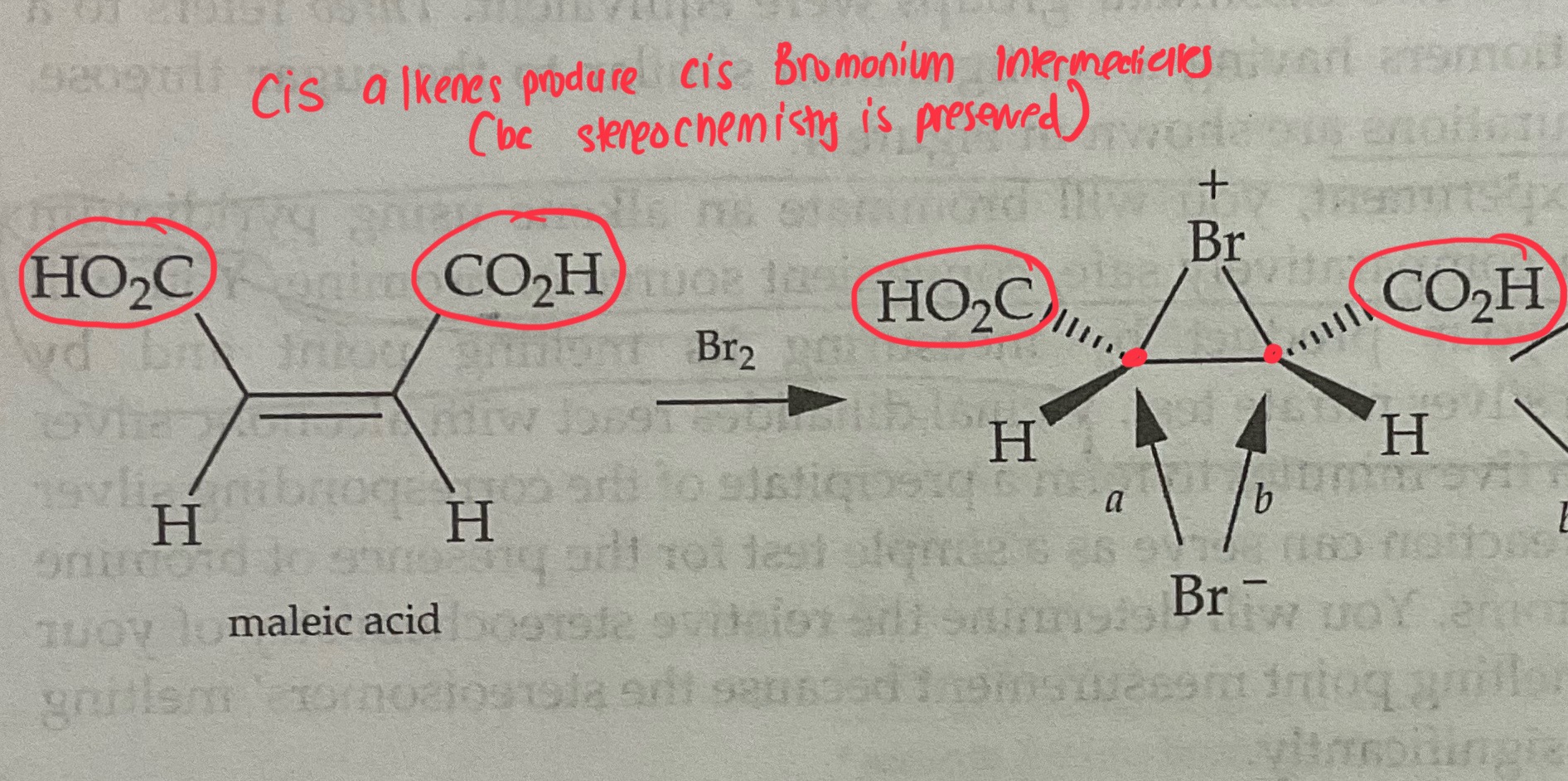
Cis Alkenes form ___(cis/trans)_______ bromonium ions
Explain why?
Trans Alkenes form ___trans______ bromonium ions
Cis Alkenes form __cis_______ bromonium ions
The Process of Bromonium Ion Formation Preserves the stereochemistry of the original molecule
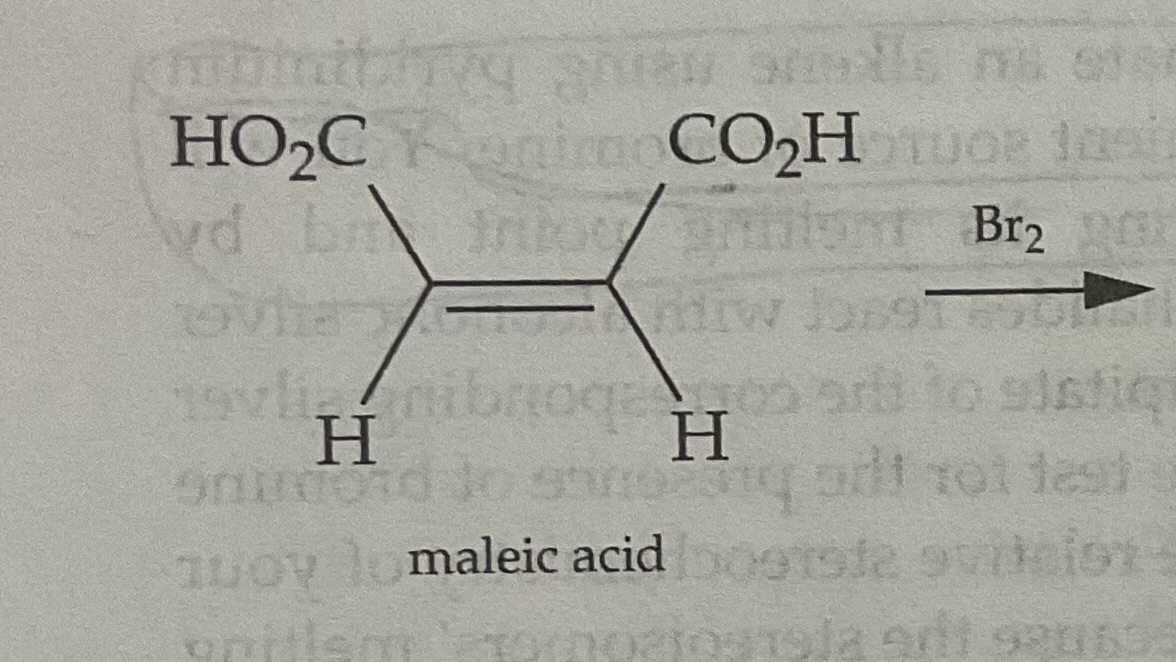
Draw the Bromonium Ion Intermediate for a Cis Alkene

Draw the Bromonium Ion Intermediate for a Trans Alkene
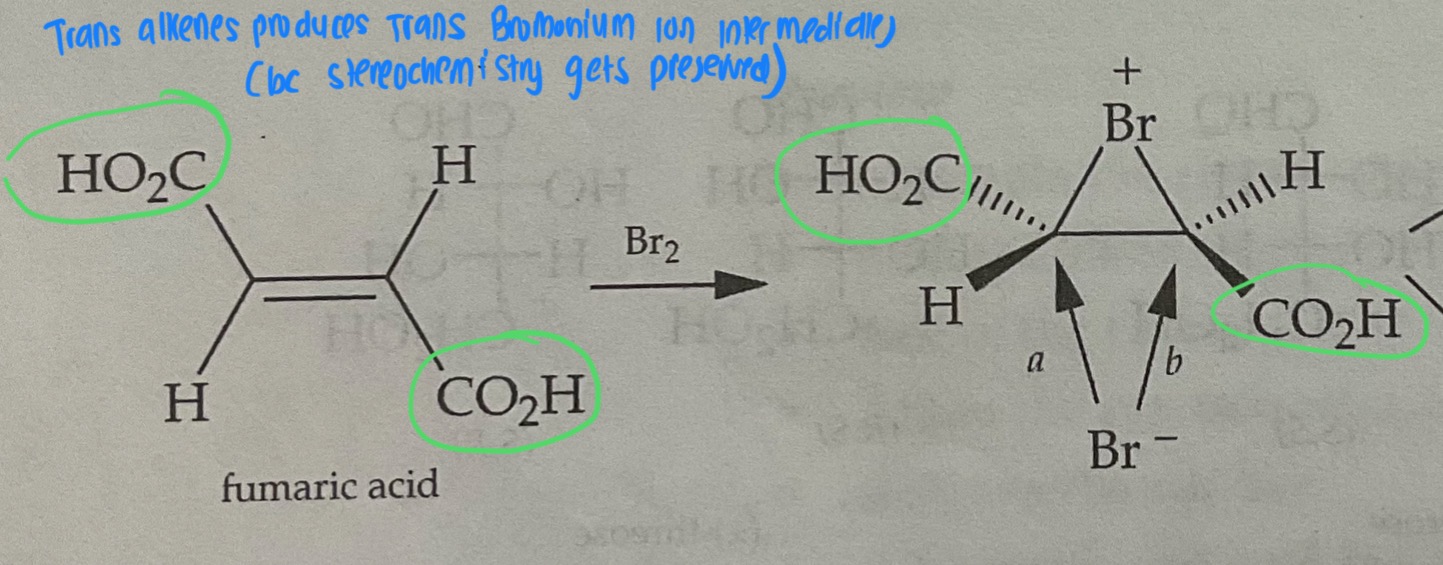

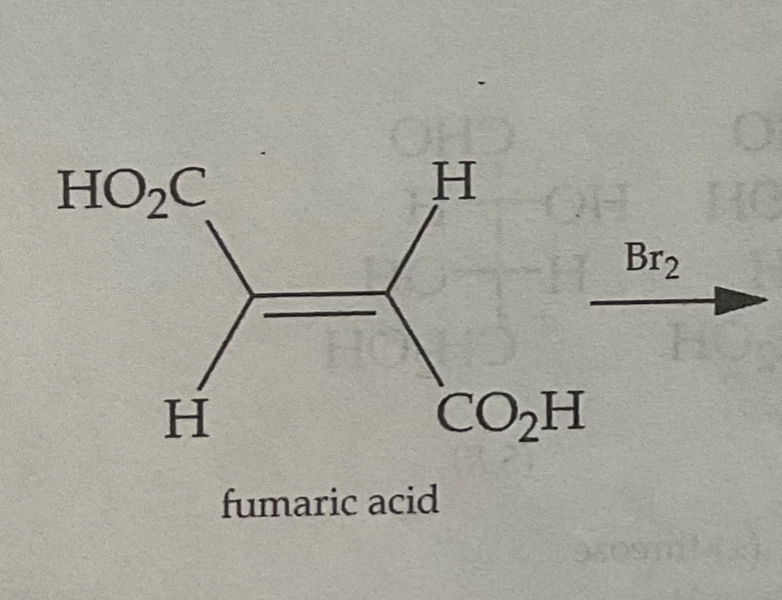
Draw the Products of a Bromination Mechanism involving Trans Alkenes

PRODUCTS ARE MESO
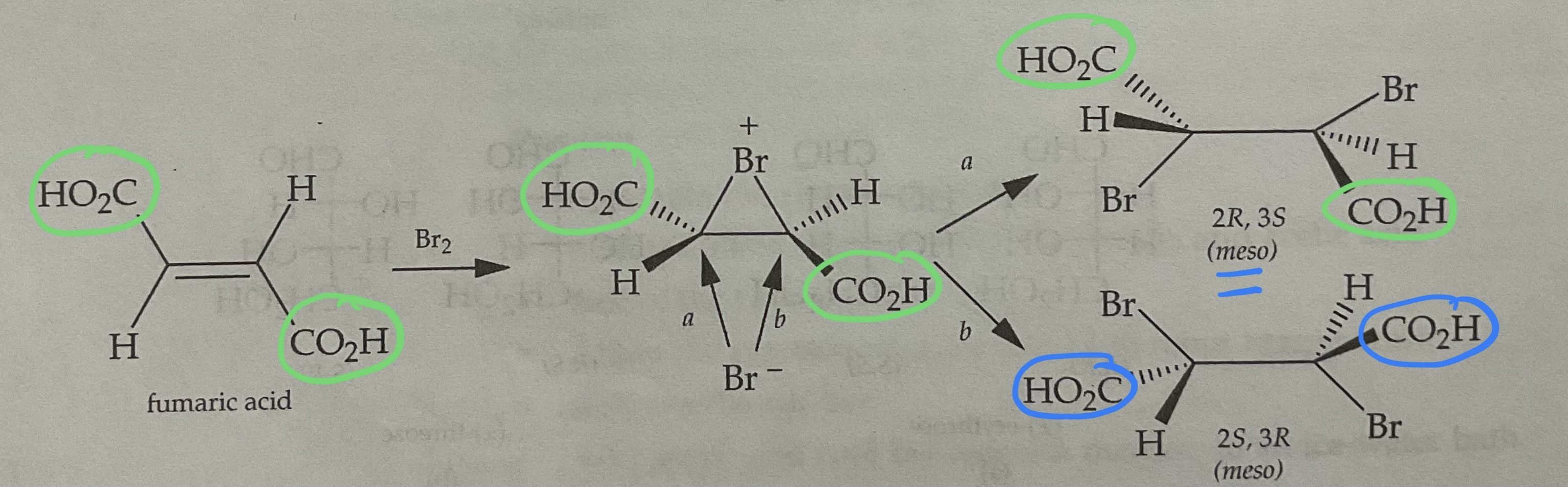
Meso Configuration
(R, R) and (S,S)

Draw the Products of a Bromination Mechanism involving Cis Alkenes
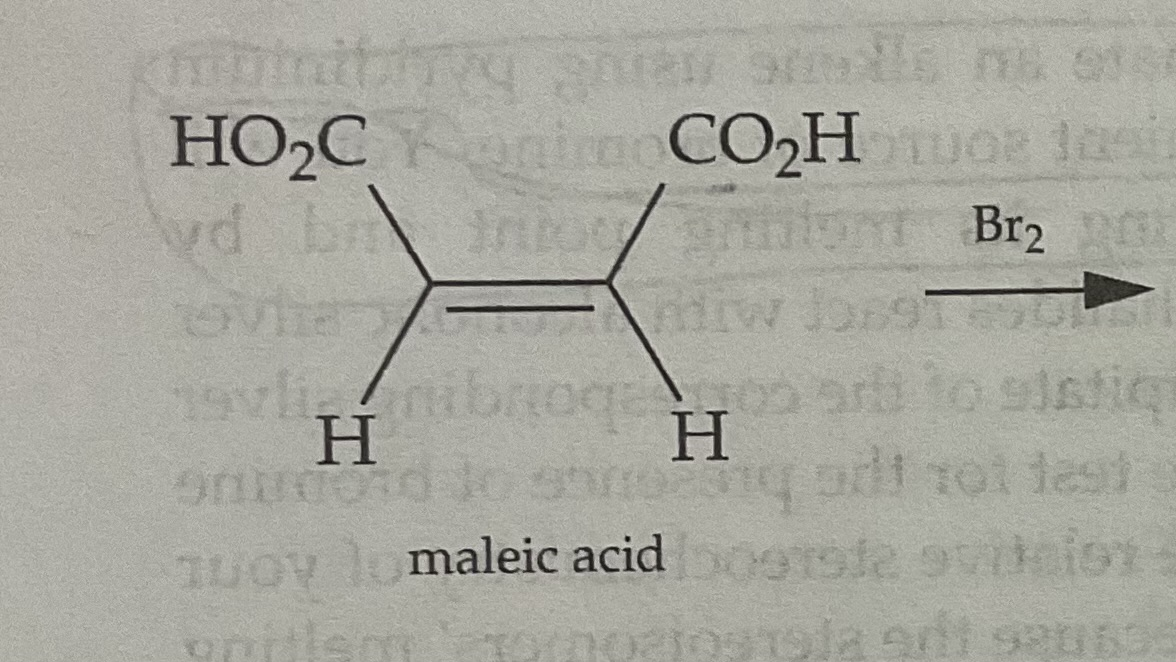
Products are ENANTIOMERS
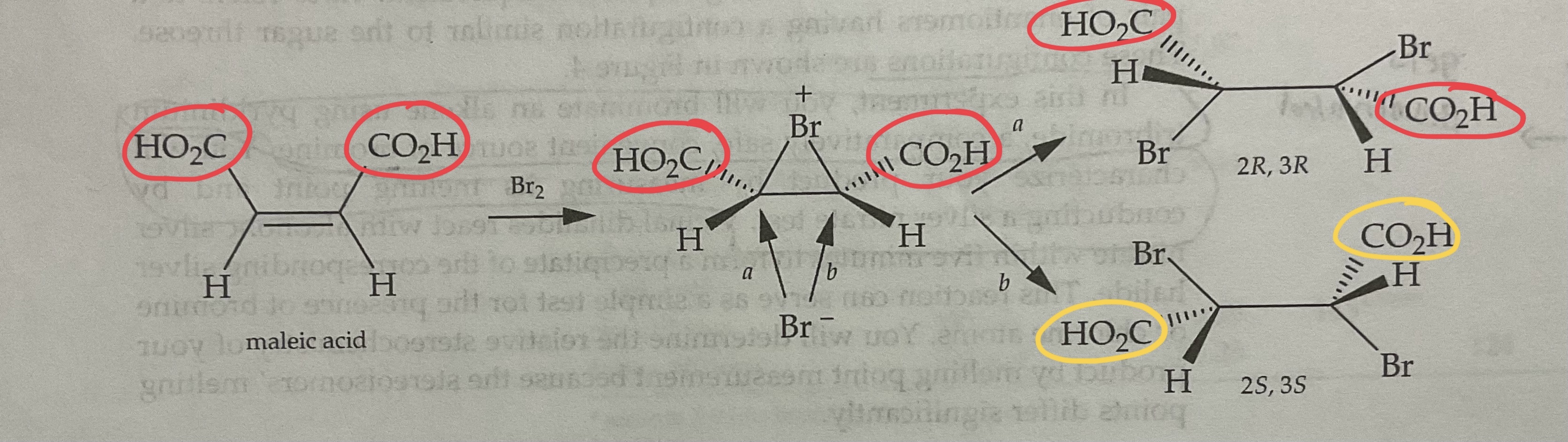
Ie. (R,S) and (S,R) = Enantiomer

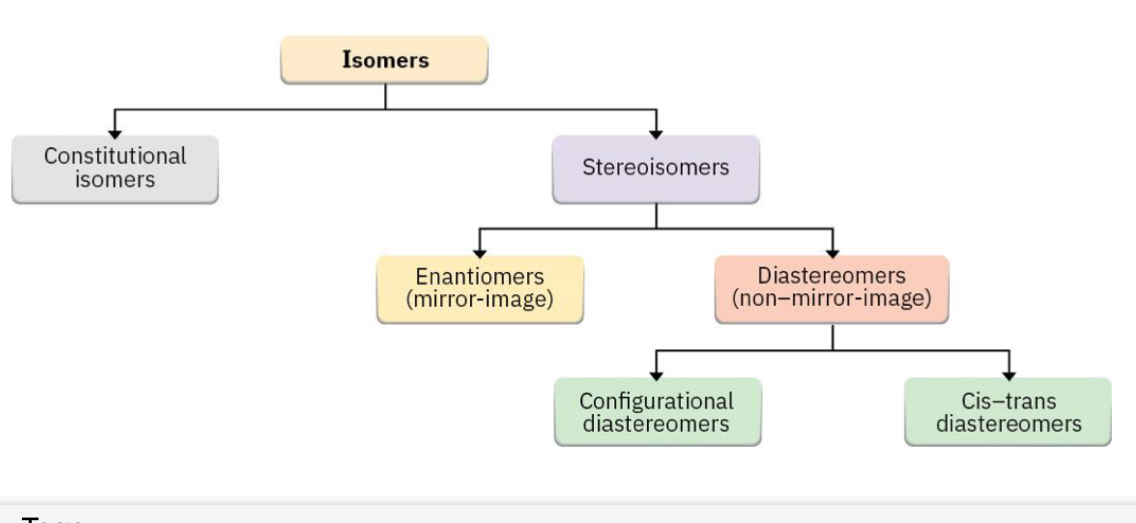
What is the relationship between the
(1) Isomers as a whole,
(2) Constitional Isomers,
(3) Stereoisomers,
(4) Enatiomers
(5) Diastereomers
(6) cis and trans
(7) confugurational diasteriomers

What are Enantiomers?
mirror-image molecules that cannot be superimposed, like left and right hands.
They look exactly the same except all the dashes on 1 Compound are wedges on the other compound
Thus, Pairs of enantiomers have opposite configurations at every stereocenter.
So the enatiomer of 2S,3S, 5R has a stereochemistry of ..
2R,3R, 5S
What are Meso Compounds?
Meso compounds are molecules with an even # of chiral centers.
(ie. 2 chiral centers, 4 chiral centers, etc. ) and have a plabe a symmetry. These properties cause the mirror image of a meso compound to simply be itself
Thus, a meso compound has chiral centers, but is ACHIRAL

Rules for Identifying if a Compound is Chiral Or Not
0 chiral centers = not a chiral compound
1 chiral center = chiral compound
2 or more chiral centers = may or may not be chiral...(2 cases)
- case 1: If it has a plane of symmetry = achiral (ex: cis stereoisomers, or meso compounds )
- case 2: If its asymmetrical = chiral (ex. trans stereoisomers)

Whats a Racemic Mixture?
a 50/50 blend of two mirror-image versions (called enantiomers) of the same molecule.
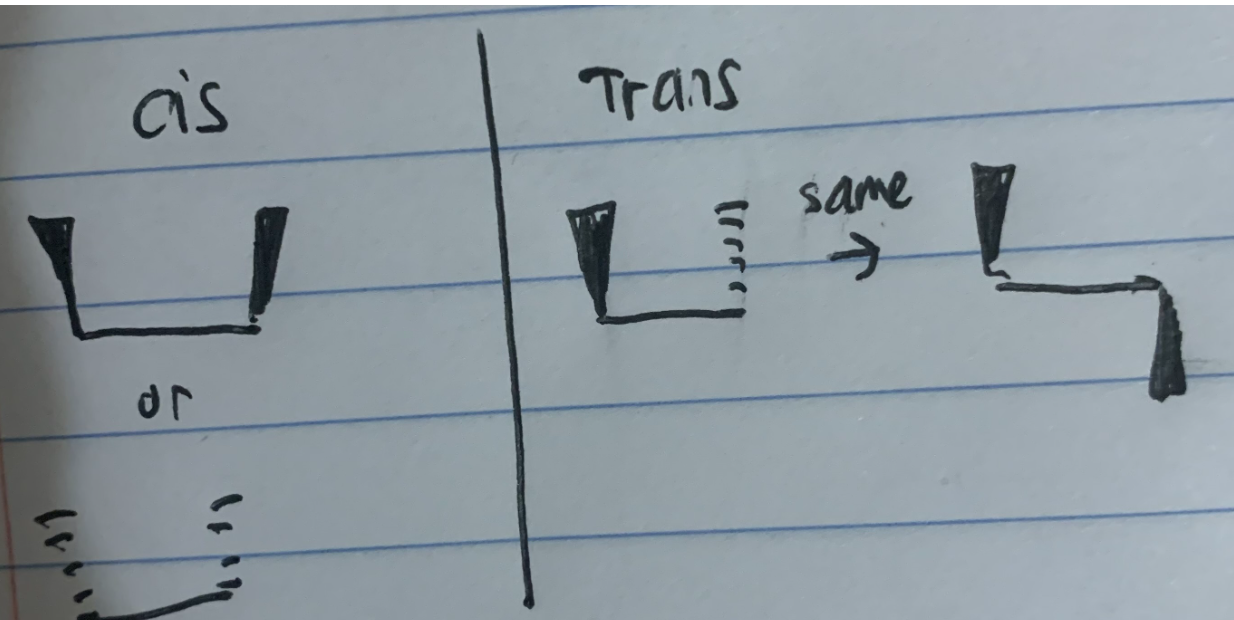
Draw What Cis and Trans Look Like

Equation for finding the maximum number of stereoisomers

In which, n = # of chiral centers in a given molecule
If n = 3, 2^(3) = 8 total stereoisomers (1 being the original diagram, the others being the ones you draw out)
**Cannot be applied to Meso Compounds
What does R and S stand for?
What do they even mean?
R - “Rectus”
S - “Sinister”
These represent the only 2 configurations possible for a chiral center
Halogenation of Alkenes Using Fluorine (F)
F is highly reactive and exothermic, so it produces a VERY VIOLENT reaction thats accompanied by other side reactions
Vicinal Dihalides vs Geminal Dihalides?
(See pic)
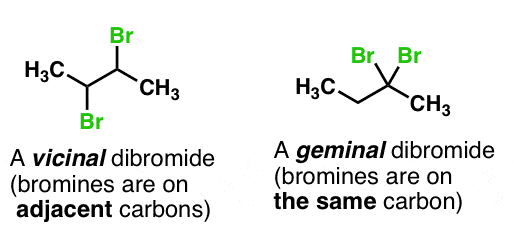
Halogenation of Alkenes produces
Vicinal Dihalides
Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) Test - What is it?
confirms the presence of halide ions in a solution by forming a AgX precipitate product
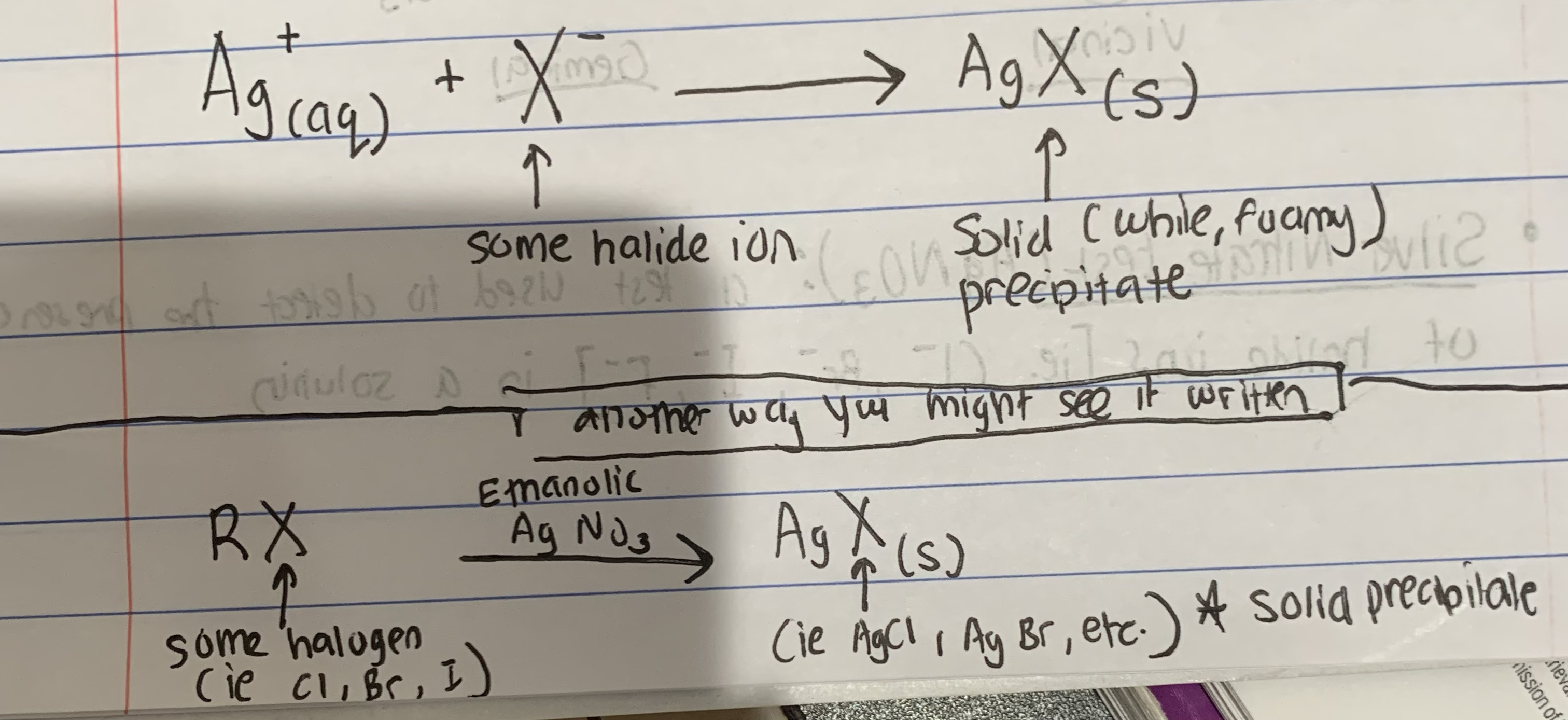
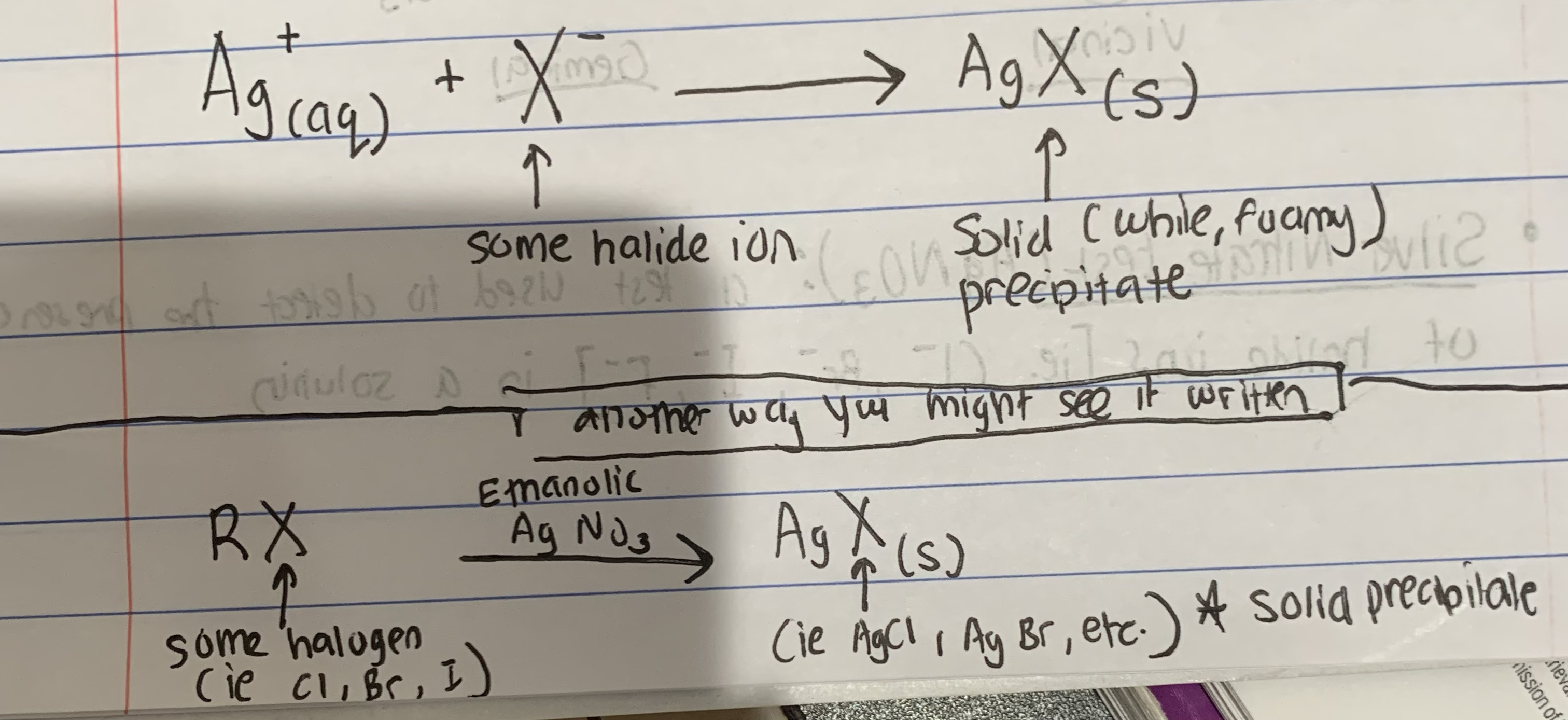
Write the Basic Chemical Equation for the Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) Test (2 ways to represent it)
(see pic)
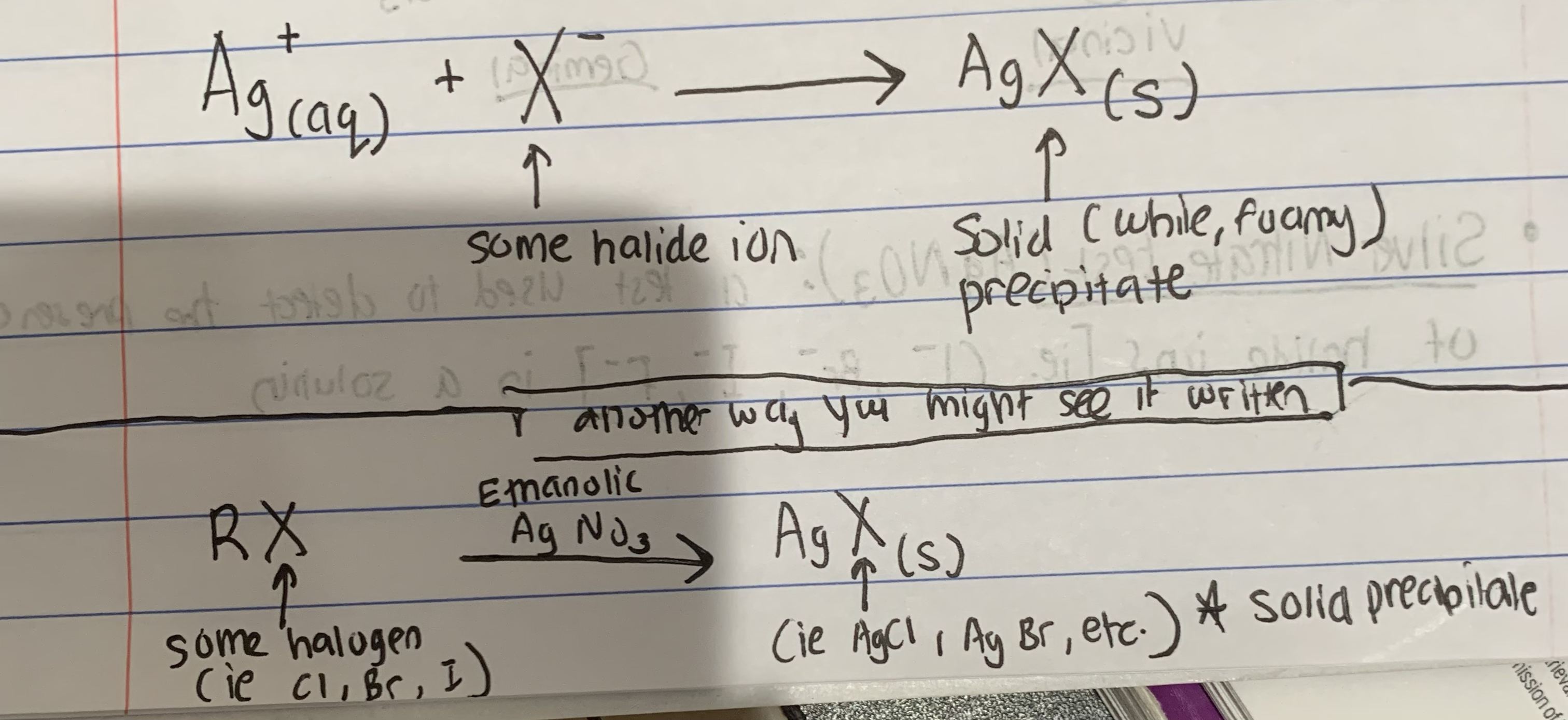
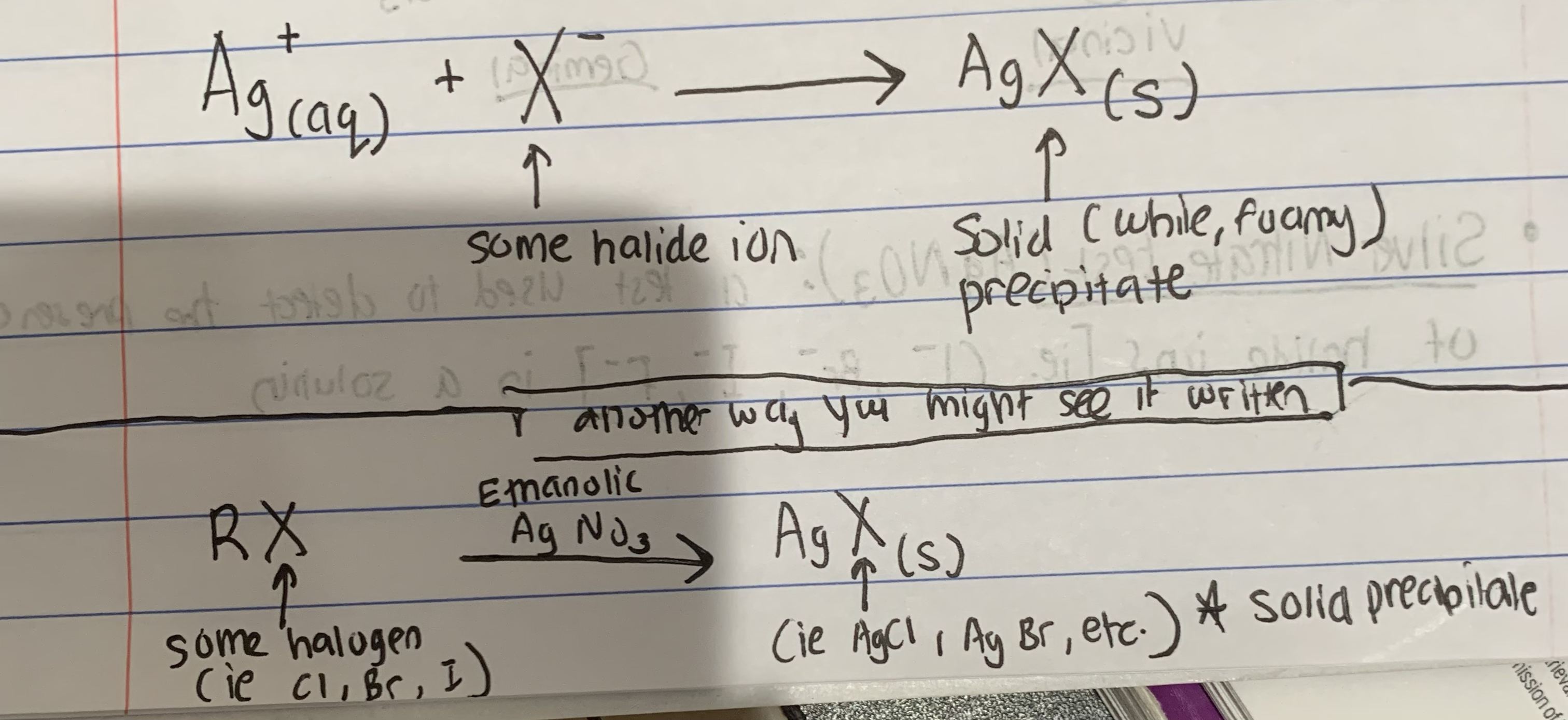
How does the Silver Nitrate Test (AgNO3) work?
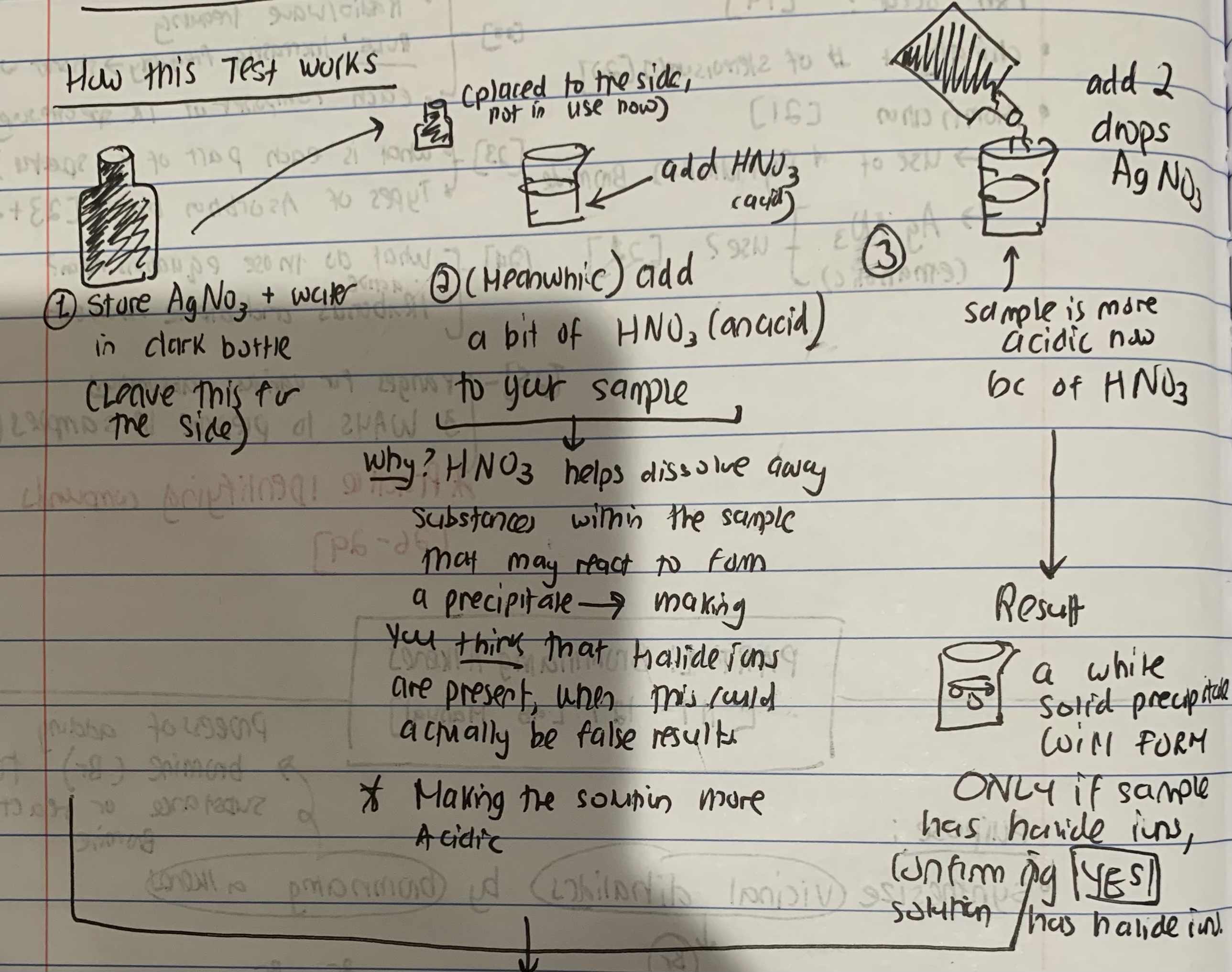

Describe how the reflux reaction works
a technique where a reaction mixture is continuously boiled and the vapors are condensed and returned to the reaction flask, allowing the reaction to proceed at a constant temperature without solvent loss
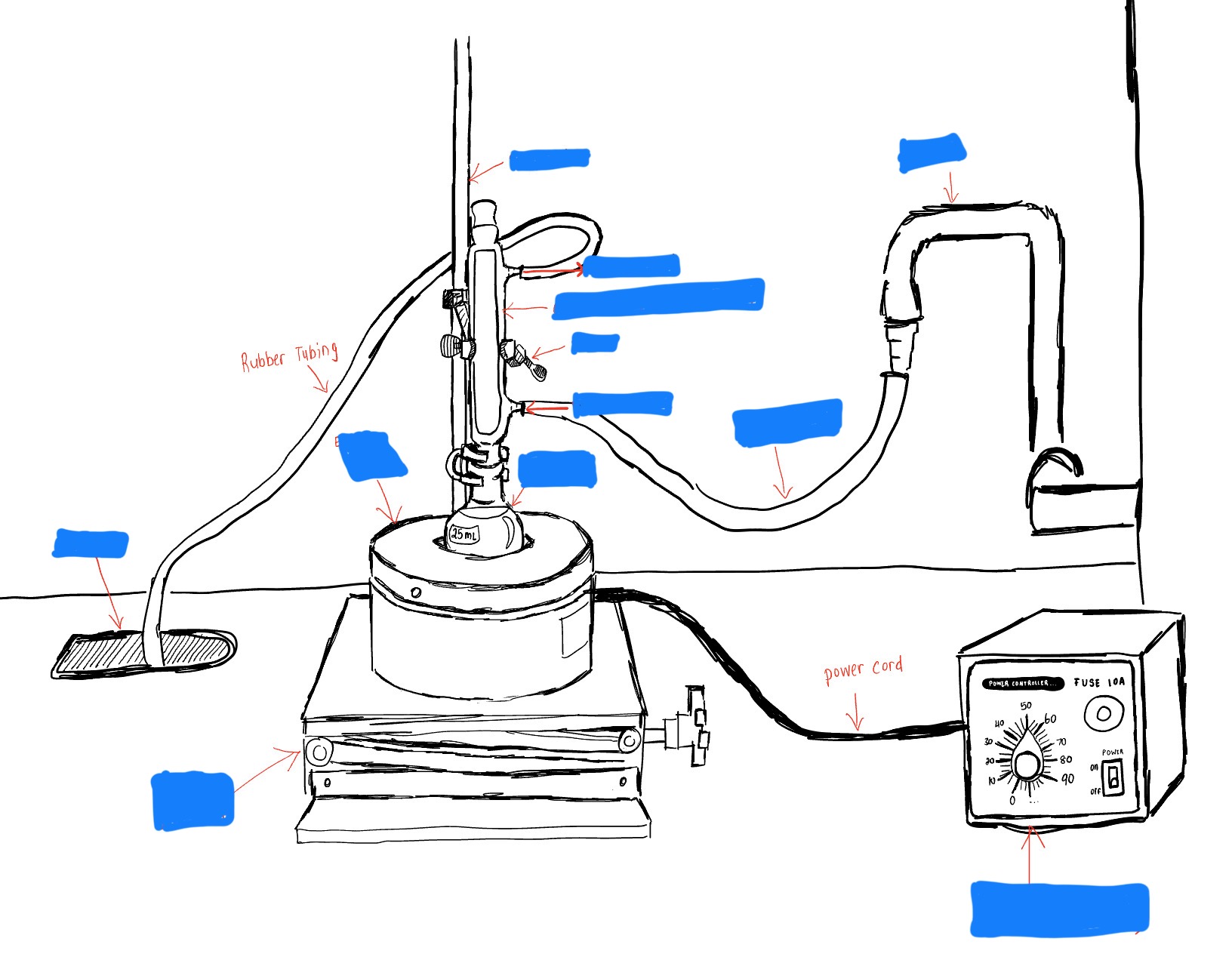
Label the Parts of a Reflux Apparatus

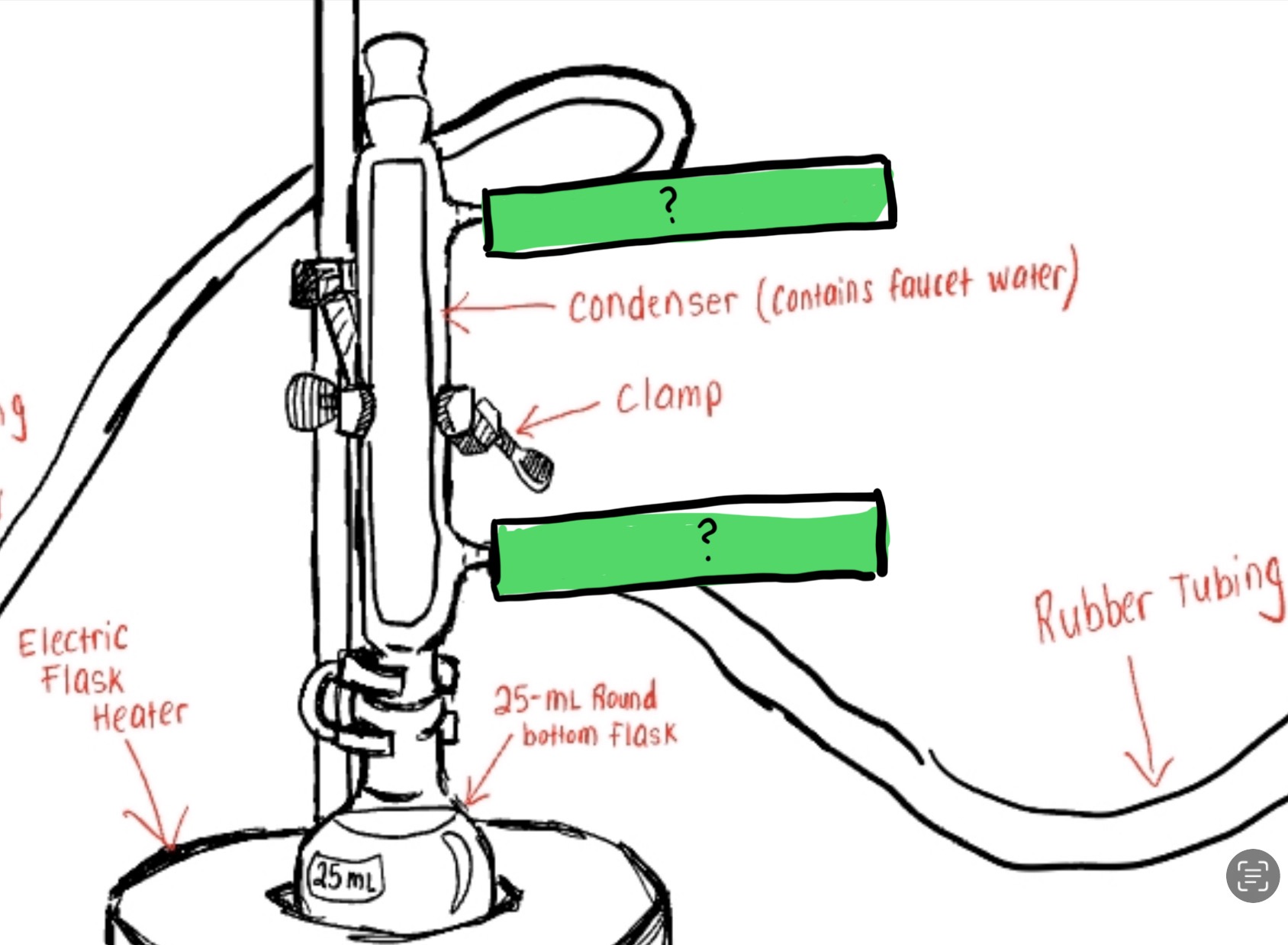
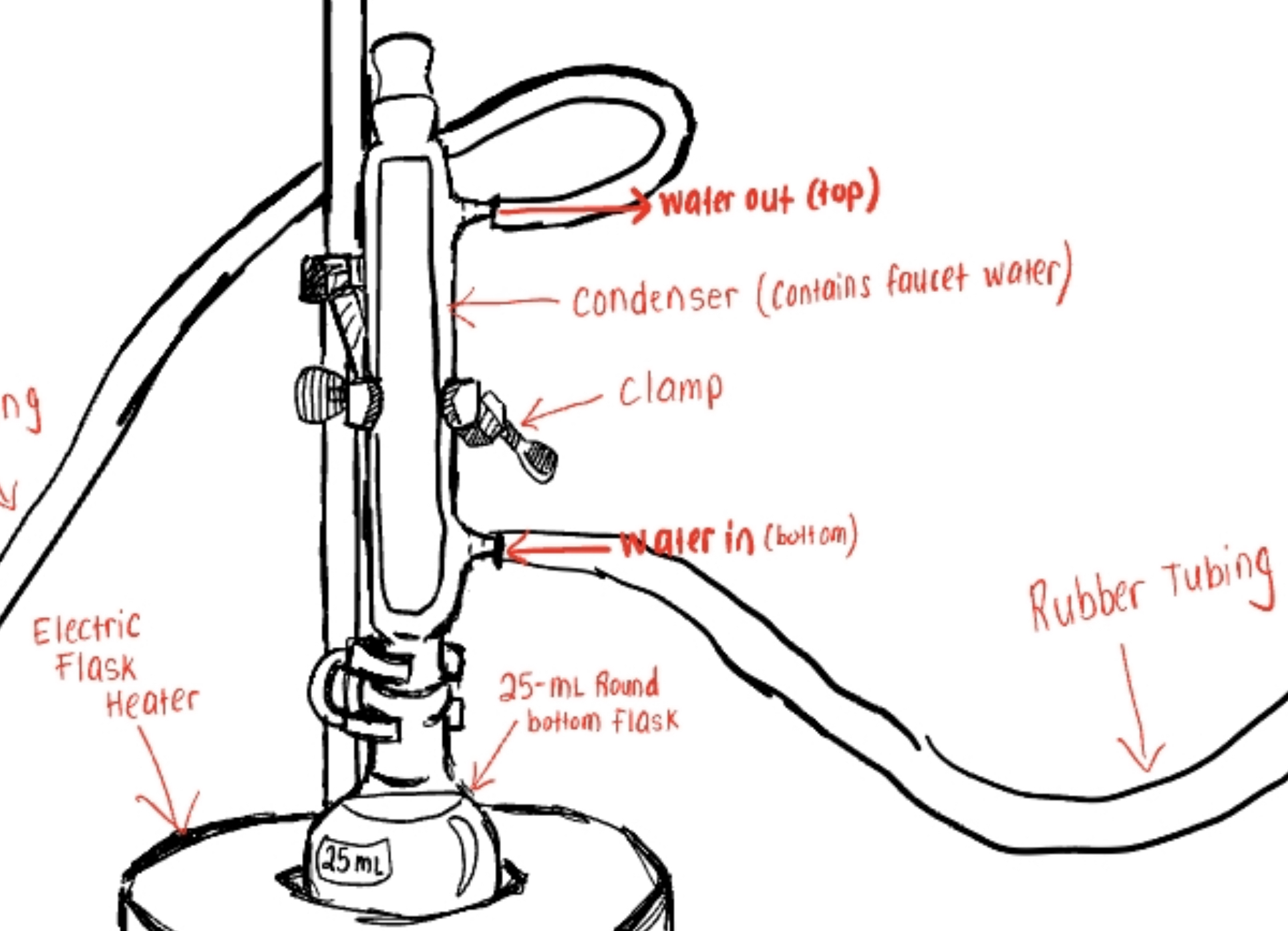
Label The Parts for How Water Goes In/out In the Diagram of this Reflux Apparatus (See Pic)

Describe the contents of this 25-mL Round Bottom Flask and each of their roles
trans-cinnamic acid (the alkene you want to brominate)
90 percent PBP (source of bromides)
Acetic Acid (Solvent)

What is this?

Electric Flask Heater
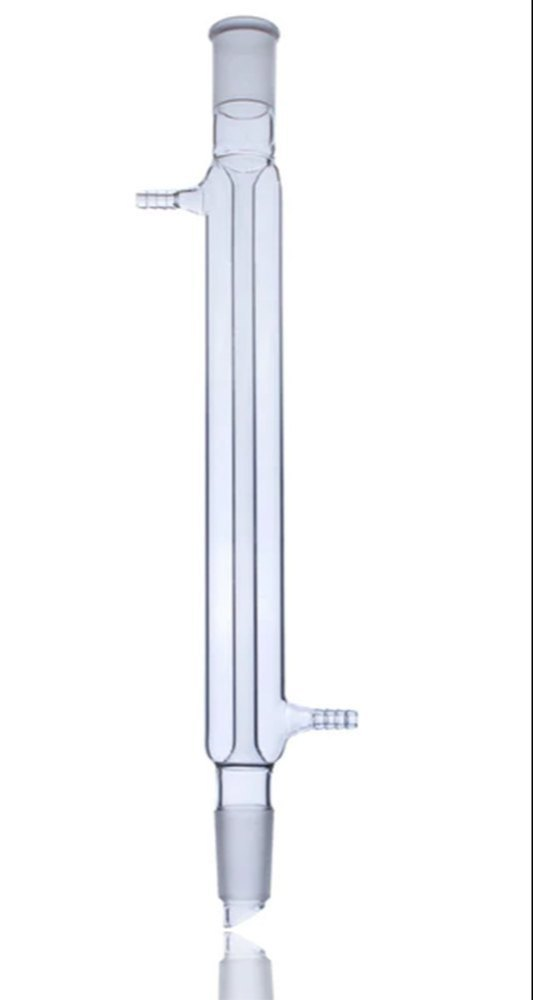
What is this?
Condenser
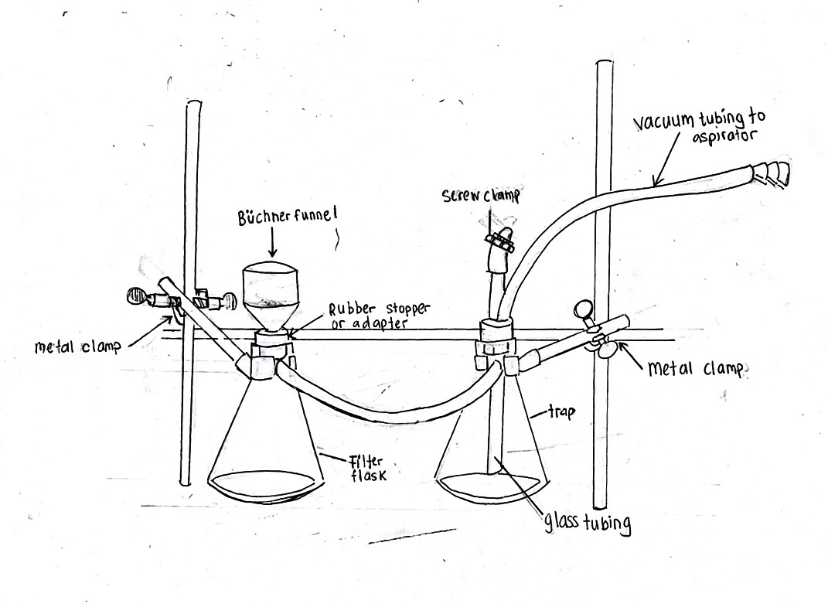
Label the Parts of this Vacuum Apparatus Setup
Difference between the Trap Flask and the Filter Flask in a Vacuum Filtration Apparatus
Filter Flask:
Collects Filtrate (Has Büchner Funnel w/ Rubber Adapter)
Trap Flask:
Prevents Liquid Backflow
(this means that the trap flask acts as the “middle monkey” preventing the liquid filtrate thats poured into the Büchner funnel from getting COMPLETLEY SUCKED into the vacuum source)
Presence of alkyl Cl or Br atoms in organic compounds can be tested with
an ethanolic solution of AgNO3
Bromination will be performed with __________________. This is a convenient, safer source of bromine.
pyridinium tribromide (aka pyridinium bromide perbromide).
Name the Strength of Different Waves in Order from Least Strongest to Most Strongest
"Rebecca Makes Icecream Very Unusually for Xylophone-loving George"
R = Radio = Rebecca Rabbit
M = Microwave = Makes
I = Infrared = Icecream
V = Visible = Very
U = UV = Unusually
X = X-ray = for Xylophone-loving
G = Gamma = George
What is Wave number?
Frequency of the radiation (Wavelengths per cm)
It is the X-axis for the IR spectrum
What is % Transmittance?
the percentage of light that passes through a sample (which is not reflected off, scattered, or absorbed.
It is the y-axis of the IR Spectra
What are the two big branches of “peaks or Absorption bands” on an IR spectra?
stretching and bending
(each have their own subtypes)
What are the 2 main types of stretching frequencies?
Symmetric and Asymmetric
What are the 2 main types of bending frequencies?
What are Each and What are their subtypes?
Out-of-Plane:
What: 3D motions (atoms move above/below the molecular plane)
Sub-Types: Twisting and Wagging
In-Plane:
What: 2D motions (atoms stay within the same plane)
Sub-Types: Rocking and Scissoring

What’s the difference between in-plane and out-of-plane molecular vibrations?
In-plane: Atoms move within the plane (flat) of the molecule — includes rocking and scissoring
Out-of-plane: Atoms move above and below the molecular plane — includes wagging and twisting
Sample placed in the path of IR radiation has a range of _______
400–4000 cm–1.
How are gas samples prepared for IR spectroscopy?
Gases are expanded into an evacuated gas cell with IR-transparent windows (like NaCl or KBr).
Ideal for small, volatile molecules.
Requires special equipment due to long path lengths and pressure control.
What are three ways to prepare liquid samples for IR?
A:
Neat sample – Place a drop between NaCl plates (no solvent).
Solution – Dissolve in IR-transparent solvent (e.g., CCl₄) and use in a liquid cell.
Thin film – Dissolve in solvent, spread on NaCl plate, and evaporate solvent.
What are the main methods for preparing solid IR samples?
KBr pellet – Grind with dry KBr and press into a pellet.
Thin film – Dissolve solid, evaporate on NaCl plate.
Nujol mull – Mix with mineral oil to make a paste, place between IR plates.
Why are NaCl and KBr commonly used in IR sample prep?
They are transparent to IR light in most regions, allowing accurate detection of sample vibrations.
⚠ Both are water-sensitive and should be kept dry.
What is an Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) spectrophotometer?
A type of IR spectrophotometer that uses internal reflection through a crystal (e.g., diamond) to measure sample absorbance via an evanescent wave.
✅ Great for solids, liquids, pastes — minimal sample prep.
How does ATR spectroscopy work?
IR light reflects within a crystal in contact with the sample. A shallow evanescent wave penetrates the sample surface and is absorbed, creating the IR spectrum.
What is a Double Beam Spectrophotometer used for?
Used in UV-Vis or IR analysis, it splits the light beam between a sample and a reference to correct for variations.
✅ Ideal for quantitative analysis and kinetics.
What makes double beam spectrophotometers better than single beam?
They allow real-time correction for lamp intensity and solvent effects by comparing sample and reference simultaneously.
What is an FT Spectrophotometer (Fourier Transform)?
An IR spectrometer that uses an interferometer to collect data at all wavelengths at once and applies Fourier Transform math to produce a spectrum.
Why is FT-IR preferred over traditional IR?
✅ Faster scans
✅ Higher resolution
✅ Better signal-to-noise ratio
Especially useful for trace analysis and complex molecules.
What is the relationship between 1x-bond, 2x-bond and 3x-bonds with peaks and why?
Single bonds are the longest and require less energy to bend
Triple bonds are the shortest and require MORE energy to bend (more s-character) HAS HIGHER WAVENUMBER VALUES ON IR
Relationship between hybridization and Wavenumber
Hybridization affects C-H stretches:
sp³ C-H: Below 3000 cm⁻¹ (ie. single bonds)
sp² C-H: 3000–3100 cm⁻¹ (ie. Double bonds)
sp C-H: ~3300 cm (ie. Triple Bonds)
Relationship between electronegativity of an atom and Absorbtion Values on IR spectra
Higher Electronegativity of Atom (ie O) —> has a shorter bond (wants to get close) —→ Harder to bend, and thus has HIGHER ENERGY/ABSORPTION values (cm-1)
Will Br2 show up on IR spectra?
No, bc compounds that don’t have a dipole moment might not show up on the IR spectra (but may still exist in the mixture itself)
Formula for Hexane
C₆H₁₄
Formula for Hexene
C₆H₁₂
Formula for Cyclohexane
C₆H₁₂ (its formula is identical to that of Hexene)
Formula for Cyclohexene
C₆H₁₀