Chemistry Redox and Cells and Electrolysis notes and mistakes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
when we have charge and know the equation at the fuel cell, what is the percent efficiency (can be charge or elec) what do we use
Using Q = n(e-) x F, from redox
when balancing the half equation and there is like some random ion in there, like Pb (s) → PbS04(s)
Add the ion to the side which does not have it.
You must add the SO4 2- (aq) ion to the side which does not have it.
Important derivation/shortcut formula for n(e-)
n(e-) = I t / F ,
I - current (A)
t - time (s)
F- Faradays constant, 96500 C
when it says there is a semipermeable membrane
it allows only some certain substances to pass through
what is green hydrogen
A form of hydrogen produced through electrolysis, using renewable energy sources, resulting in zero net contribution to greenhouse gases
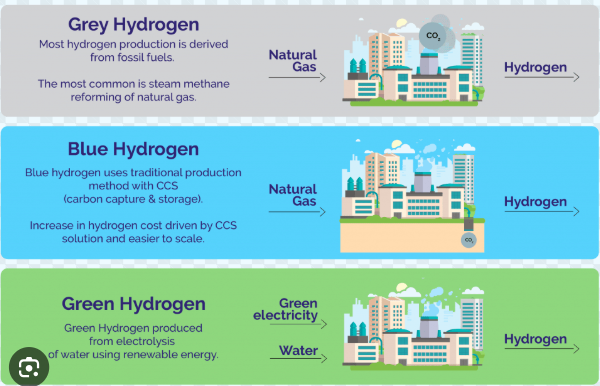
Method to produce green hydrogen
electrolysis of water, through
—alkaline electrolysis circuit
purposes of membranes
-acts as a selective barrier preventing ions from contaminating another solution.
e.g “in membrane cells, stopping Cl'- from contaminating NaOH soln”
-to prevent a spontaneous reaction
-to prevent the excessive release of thermal energy
-to prevent direct contact between oxidant and reductant.
what is molten
when there is liquid without water and very hot
the energy/voltage required to make a recharge reaction
GREATER than E (reduction) - E (oxidation).
OR E( higher/more pos value) - E (more/neg value)
MUST SAY GREATER than this voltage required
if an electrolytic cell with Br- (aq) and Sn 2+ (aq) what will the reductant and oxidant be?
Sn 2+ will be both the oxidant and reductant, as there are two equations
Do the polarities switch during recharge?
NO, it does NOT, the electrode polarity does not change from recharge to discharge.
All that changes is the direction of the electron flow,
HOWEVER, what once was the cathode (site of reduction) is now the anode (site of oxidation)
IT is STILL positive!!!
What do you assume if there is concentrated NaCl and Brine or 5M NaCl
This means that chloride oxidation is preferred over water oxidation,
chloride undergoes oxidation in this situation
EVEN THOUGH water is a stronger reductant in the electrochemical series and still stronger,
BECAUSE of the non SLC concentrated conditions we must use 2Cl- (aq)
Cls (g) + 2 e- => 2Cl- (aq),
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- => 2 H20 (l)
despite this, you must choose 2Cl- (aq) as a preferred reductant for the anode.
ONLY SPECIAL CONCENTRATION CASE YOU MUST MUST MUST KNOW.
Disadvantages of fuel cells in motor vehicles
expensive,
flammable as it is in hydrogen
Advantages of fuel cells
more energy efficient as directly chemical to electrical energy.
When balancing with an oxygen, and there’s multiple which do you use
The one which gives a stronger reaction/gradient
This is identified as a reducing agent, which version should you use to balance half equation ‘ 2Fe (s) or Fe(s)
Fe(s)
The electrolyte in the equation is
The ion in the question, and it needs to be bonded to something to be used as an electrolyte.
K + for OH-
If something is molten what is the state?
Liquid
What is the name of the fuel cell correspond to
The electrolyte
where does the co2 go in molten carbonate fuel cell? Out of cell?
No it gets recycled from the anode to the cathode
Why are the two half cells separated in fuel cell?
to ensure electrons flow across the circuit and harness electrical energy
To avoid reduction and oxidation to happen spontaneously and stopping the flow of electrons
Compare question layout
Define both things in context!
Then difference, then similarity.
Then link to context o
Green chemistry principles linking to fuel cells
Catalysis- electrodes contain catalysis which improve the rate of reaction and improve efficiency.
Design for energy efficiency- direct conversion of chemical to electrical energy.
Prevention of waste- no production of CO2 use of renewable feedstocks
02 produced via photosynthesis, to renewable
H2 electrolysis of H20. Energy provided by renewables
Green hydrogen
Green electricity and water resulting in green hydrogen
Issues with hydrogen
explosive and flammable
Colourless odorless
Storage and transport difficult due to the great volume it takes up, it requires high compression,
Differences between fuel cells and galvanic cells
Fuel cells are a continuous supply,
Porous electrodes
Secondary cells
rechargeable cells,
Electrical to chemical
Non spontaneous
Reluctant above oxidant
Discharge (like a galvanic)
Generates electricity, and is spontaneous
Chemical to electrical
Ph as H+ products would result in what?
H+ consumed means that the acidic nature of the cell would reduce and it would become more neutral hence increasing its pH
If substance solid can you break into ion for oxidising agent or reducing agent?
No, you must include the whole thing if not aqueous
Redox flow battery, how is this a hybrid of fuel and secondary cell
Because of a continuous supply of reactants, it is a fuel cell
Because it can be recharged,
Function of membrane
Transport electrons between electrodes
To prevent a spontaneous redox reaction
What would happen if the barrier was removed between two half cells
Current stops
Spontaneously react, (Release thermal E, confirm first so don’t say this till confirmed)
Stops thinning reductant, thing undergoing oxidation
Stops thickening oxidant, thing undergoing reduction
Why is the hydrogen half cell assigned a 0.00 value, what is its role in other voltages
It is a benchmark and reference, to compare other voltages
For example, Ni half cell E is lesser than the hydrogen half cell at -0.28, hence it is a stronger reducing agent than hydrogen and Ni 2+ is a weaker oxidising agent than 2H+.
Advantages of lead acid cell
Rechargeable, long life, reliable, high currency
Disadvantages of lead acid cell
Lead is poisonous, heavy, acid is corrosive, low energy density.
Why are fuel cells more efficient than thermal power stations?
Fuel cells - directly from Chem to electrical
Thermal power from - Chem to thermal to mechanical to electrical,
in each step there is a energy loss, so the more steps, the more energy loss and lesser efficiency
Sources of hydrogen gas
Mostly from fossil fuels.
Steam reforming of fossil fuels
Steam reforming of biogas
Decomposing of water,electrolysis
GCP’s pertinent to fuel cells
Design for energy efficiency-
Designing safer chemicals-
Catalysis- incorporates catalysts into the porous electrode to speed up rate of reaction by reducing the activation energy required for a successful collision/
Use of renewable feedstocks- (for microbial fuel cells)
How is design for energy efficiency pertinent to fuel cells?
because the direct conversion of chemical to electrical energy, MUST LINK TO ALL PARTS OF QUESTION, SO THE ECONOMIC AND/OR ENVIORNMENTAL
allows a higher energy efficiency for the same fuel used. This is compared to the comparatively less efficient coal powered stations with multiple steps and lower energy efficiencies.
→releasing lesser GHG’s like CO2 in the atmosphere, reducing GHG effect,( MINIMISES NEGATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS)
→More efficienct means less fuel used, hence lesser economic cost
How is designing safer chemicals used in regards to fuel cells
The fuel cells achieve their function and minimise toxicity and enhance safety by producing H20 a relatively harmless chemical as a product.
Contrarily, you can talk about how hydrogen fuel cells, are sourced from flammable and combustible hydrogen and can be unsafe as a result.
How does use of renewable feedstocks relate to MICROBIAL fuel cells
MICROBIAL Fuel cells can be derived from renewable feedstocks such as soils, wastewater,
Why is a cell not at 100% efficiency
Because of side reactions, forming products, giving resistance to the cell, reducing energy efficiency as a result
Features of fuel cells which are good
Porous electrode- the porousity increases the surface area
Catalyst- the catalyst increases rate of reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway which reduces the required activation energy and increases the proportion of successful collisions
Heat siphoning - capture and reuse excess heat, enhancing overall efficiency