AP Calculus AB Flashcards
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Volume of Sphere
\frac43\pi r^2
Volume of rectangular prism/cube
lwh
Volume of cone
\frac{\pi r^2h}{3}
volume of cylinder
\pi r^2h
area of right triangle
\frac12bh
area of semi-circle
\frac{\pi r^2}{2}
area of quarter-circle
\frac{\pi r^2}{4}
area of circle
\pi r^2
area of square
s^2
area of rectangle
wl
area of trapezoid
\frac{\left(a+b\right)}{2}h
equation of semi-circle function
\sqrt{r^2-\left(x-h\right)^2}+k , where the center of the circle is (h,k) and the radius is r
equation of a circle function
\left(x-h\right)^2+\left(y-k\right)^2=r^2 , where the center of the circle is (h,k) and the radius is r
distance formula
d=\sqrt{\left(x_2-x_1\right)^2+\left(y_2-y_1\right)^2} (this is an application of the Pythagorean theorem!)
height of equilateral triangle and relation to 30-60-90 triangle
\frac{a\sqrt3}{2} , an equilateral triangle split in half is a 30-60-90 triangle
tangent line/point slope form
y_2-y_1=m\left(x_2-x_1\right)
local linearity
y-y_1=m\left(x-x_1\right)
tangent line
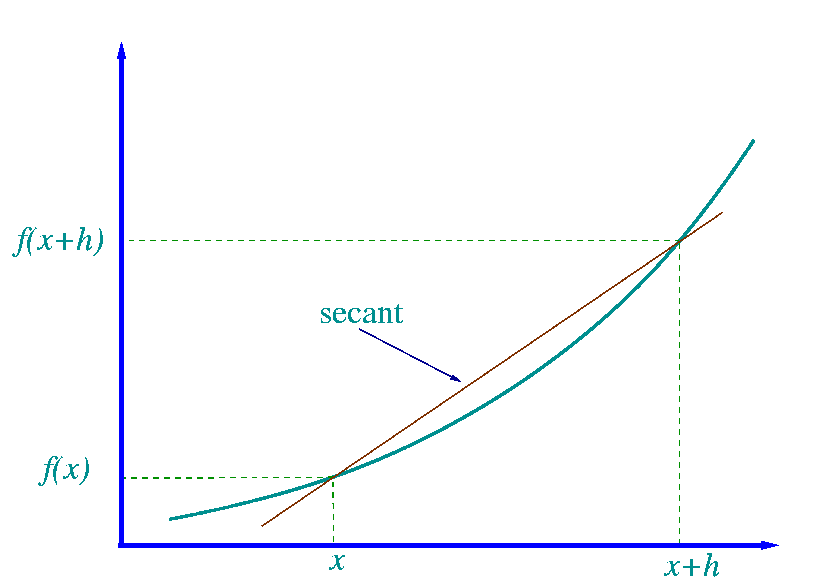
instantaneous rate of change (IROC): slope from one point
mean value theorem
f^{\prime}\left(c\right)=\frac{f\left(b\right)-f\left(a\right)}{b-a} , IROC = AROC if… f(x) is continuous on [a,b] abd differentiable on (a,b), then somewhere IROC = AROC
![<p>$$f^{\prime}\left(c\right)=\frac{f\left(b\right)-f\left(a\right)}{b-a}$$ , IROC = AROC if… f(x) is continuous on [a,b] abd differentiable on (a,b), then somewhere IROC = AROC</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d1b7e49d-6353-4b50-8a37-67bf266fe7ae.png)
first derivative tells you…
increasing/decreasing — first thing you notice from just looking at if f’(x) is neg/pos
definition of derivative
\lim_{h\rightarrow0}\frac{f\left(x+h\right)-f\left(x\right)}{h} , h= smallest gap from IROC you are solving for
secant line
AROC: slope from 2 points
infinite limit of sin(x)/x
\lim_{x\rightarrow\infty}\frac{\sin\left(x\right)}{x}=0\cup\lim_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\frac{\sin\left(x\right)}{x}=0
Differentiability
\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{-}}f\left(x\right)=\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{+}}f\left(x\right)=f\left(a\right) — continuous
\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{-}}f^{\prime}\left(x\right)=\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{+}}f^{\prime}\left(x\right) — smooth at x=a, right and left limits approaching the same value
definition of continuity
\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{-}}f\left(x\right)=\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{+}}f\left(x\right)=f\left(a\right)
intermediate value theorem
if f(x) s continue on [a,b] and k is any value between f(a) and f(b), then there is at least one value c in the interval [a,b] such that f (c ) = k
![<p>if f(x) s continue on [a,b] and k is any value between f(a) and f(b), then there is at least one value c in the interval [a,b] such that f (c ) = k</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7fcdce52-b3b4-4922-8d74-0c58dc81b9bf.png)
squeeze theorem
f\left(x\right)\le g\left(x\right)\le h\left(x\right)\cup\lim_{x\rightarrow C}f\left(x\right)=L,\lim_{x\rightarrow C}h\left(x\right)=L\Rightarrow\lim_{x\rightarrow C}g\left(x\right)=L
infinite limit: same degrees
\frac{x^2}{x^2}\rightarrow\frac{c}{c}=\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f\left(x\right)
infinite limit: higher degree in numerator
\frac{x^2}{x}\rightarrow\frac{big}{small}\rightarrow\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f\left(x\right)=\pm\infty
infinite limit: lower degree in numerator
\frac{x}{x^2}\rightarrow\frac{small}{big}\rightarrow\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f\left(x\right)=0
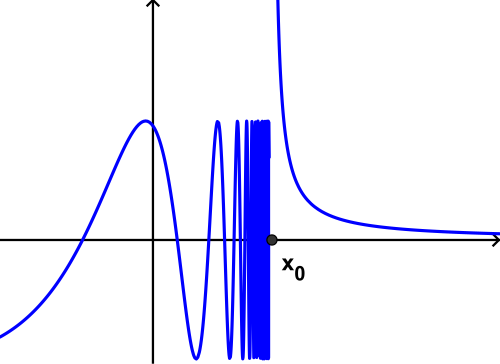
infinite/essential/asymptotic discontinuity
\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{-}}f\left(x\right)\ne\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{+}}f\left(x\right) AND one or both DNE (*can be continuous at other points)
jump discontinuity
\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{-}}f\left(x\right)\ne\lim_{x\rightarrow a^{+}}f\left(x\right)
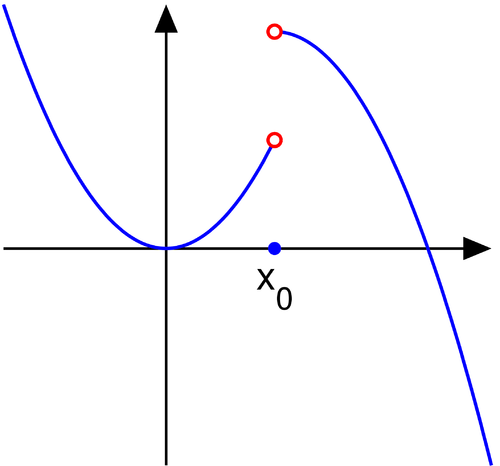
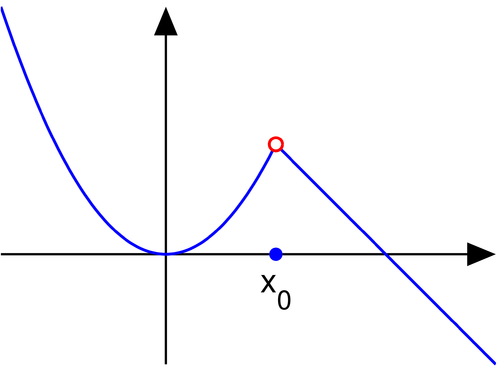
removable discontinuity
\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f\left(x\right)\ne f\left(a\right)
power rule of limits
\lim_{x\rightarrow a}\left\lbrack f\left(x\right)\right\rbrack^{n}=\left\lbrack\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f\left(x\right)\right\rbrack^{n}
root rule of limits (application of the power rule)
\lim_{x\rightarrow a}\left\lbrack\sqrt{f\left(x\right)}\right\rbrack=\lim_{x\to a}\left\lbrack f\left(x\right)\right\rbrack^{\left(\frac12\right)}=\left\lbrack\lim_{x\to a}f\left(x\right)\right\rbrack^{\left(\frac12\right)} a square root is the same as the power of 1/2, so you can adapt all radical functions using the power rule of limits
sum and difference rule of limits
\lim_{x\to a}\left\lbrack f\left(x\right)\pm g\left(x\right)\right\rbrack=\lim_{x\to a}f\left(x\right)\pm\lim_{x\to a}g\left(x\right)
constant multiple rule of limits
\lim_{x\to a}\left\lbrack cf\left(x\right)\right\rbrack=c\cdot\lim_{x\to a}f\left(x\right)
product rule of limits
\lim_{x\to a}\left\lbrack f\left(x\right)g\left(x\right)\right\rbrack=\lim_{x\to a}f\left(x\right)\cdot\lim_{x\to a}g\left(x\right)
quotient rule of limits
\lim_{x\to a}\left\lbrack\frac{f\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}\right\rbrack=\frac{\lim_{x\to a}f\left(x\right)}{\lim_{x\to a}g\left(x\right)}
sum and difference rule of derivatives
\frac{d}{\differentialD x}f\left(x\right)\pm g\left(x\right)=f^{\prime}\left(x\right)\pm g^{\prime}\left(x\right)
product rule of derivatives
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\left\lbrack f\left(x\right)\cdot g\left(x\right)\right\rbrack=f\left(x\right)\cdot g^{\prime}\left(x\right)+f^{\prime}\left(x\right)\cdot g\left(x\right)
quotient rule of derivatives
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\left\lbrack\frac{f\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}\right\rbrack=\frac{g\left(x\right)\cdot f^{\prime}\left(x\right)-f\left(x\right)\cdot g^{\prime}\left(x\right)}{\left\lbrack g\left(x\right)\right\rbrack^2}
chain rule
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\left\lbrack f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)\right\rbrack=f^{\prime}\left(g\left(x\right)\right)\cdot g^{\prime}\left(x\right)
l’hopitals rule
\lim_{x\to a}\frac{f\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}=\frac00\cap\frac{\infty}{\infty}\Rightarrow\lim_{x\to a}\frac{f^{\prime}\left(x\right)}{g^{\prime}\left(x\right)}=L
first derivative test
tells you relative extrema. plug in numbers on either side of candidates, pos to negative = maximum, neg to positive = minimum
second derivative test
tells you relative extrema. plug in candidates to f’’(x), if positive = minimum, if negative = maximum
\frac{\differentialD p}{\differentialD t}=kt\ldots
\ldots P=P_0e^{rt}
volumes of revolution formula
\pi\int_{a}^{b}\left(f\left(x\right)-a\right)^2-\left(g\left(x\right)-a\right)^2\differentialD x
area between curves formula (terms of x)
\int_{a}^{b}f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)\differentialD x
area between curves formula (terms of y)
\int_{c}^{d}f\left(y\right)-g\left(y\right)\differentialD y
indefinite integral
\int_{\placeholder{}}^{\placeholder{}}f\left(x\right)dx
definite integral
\int_{a}^{b}f\left(x\right)\differentialD x
average value formula
\frac{1}{b-a}\int_{a}^{b}f\left(x\right)\differentialD x
fundamental theorem of calculus part one
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\int_{a}^{t}f\left(x\right)\differentialD x=f\left(t\right) , derivatives and integrals are inverse operations
fundamental theorem of calculus part two
\int_{a}^{b}f\left(x\right)\differentialD x=F\left(b_{}\right)-F\left(a\right)
extreme value theorem
If a function is continuous on [a,b], then it must have a maximum and a minimum on that interval.
![<p><span>If a function is continuous on [a,b], then it must have a maximum and a minimum on that interval.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c5ffecf6-d6e0-44e6-b9f2-86977666d337.png)
power rule of derivatives
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}x^{n}=nx^{n-1}
reverse power rule of integrals
\int_{a}^{b}x^{n}dx=\frac{1}{n+1}x^{n+1}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\log_{a}x
\frac{1}{\ln\left(a\right)\cdot x}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}a^{x}
a^{x}\cdot\ln\left(a\right)
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\sin^{-1}\left(x\right)
\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\cos^{-1}\left(x\right)
\frac{-1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\csc^{-1}\left(x\right)
\frac{-1}{\left\vert x\right\vert\sqrt{\left(x^2-1\right)}}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\sec^{-1}\left(x\right)
\frac{1}{\left\vert x\right\vert\sqrt{\left(x^2-1\right)}}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\cot^{-1}\left(x\right)
\frac{-1}{1+x^2}
\frac{\differentialD y}{\differentialD x}\tan^{-1}\left(x\right)
\frac{1}{1+x^2}