Q3: FINAL DISS MIDTERMS Reviewer
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Humanities
generally refers to art, literature, music, architecture, dance, and theater — areas in which human subjectivity is emphasized and individual expensiveness is dramatized
importance of human being an feelings
records man’s experiences, values, sentiments, ideas, and goals
Social
relating to human society and how it is organized
Science
study of physical/natural world and phenomena using systematic observation and experiment
Social Science
deals with human behavior in its social and cultural aspects
Applied Social Science
the study of society we live in and the relationships people have in the society
Sociology
study of human societies, their interactions, and the processes that preserves them and changes them
Anthropology
study of the cultural, social, and physical development of humans
Psychology
study of mental states and processes and behavior in humans and other animals
Demography
statistical study of human populations
Political Science
systematic study of governance by the application of empirical and generally scientific methods of analysis
Economics
study of how people allocate scarce resources for production, distribution, and consumption
History
study of past happenings in all aspects
Linguistics
study of languages
Micro Level Approach
individuals as level of analysis
social interactions
small patterns
Rational Choice Theory and Symbolic Interactionism
Micro Level Approach ideas and concepts:
Macro Level Approach
social aggregate (collection of people who share physical location)
social structure, social institutions, political and economic change
large patterns
broader social phenomena = whole social structure & system and phenomena
Structural Functionalism
Macro Level Approach ideas and concepts:
Large Systems
nations
legal systems
economies
Small Systems
families
relationships
individuals
Rational Choice Theory
why people act or behave in the way they do
people usually do what they believe to have the overall best outcome
individuals’ actions are based on their preferences, beliefs, and feasible strategies
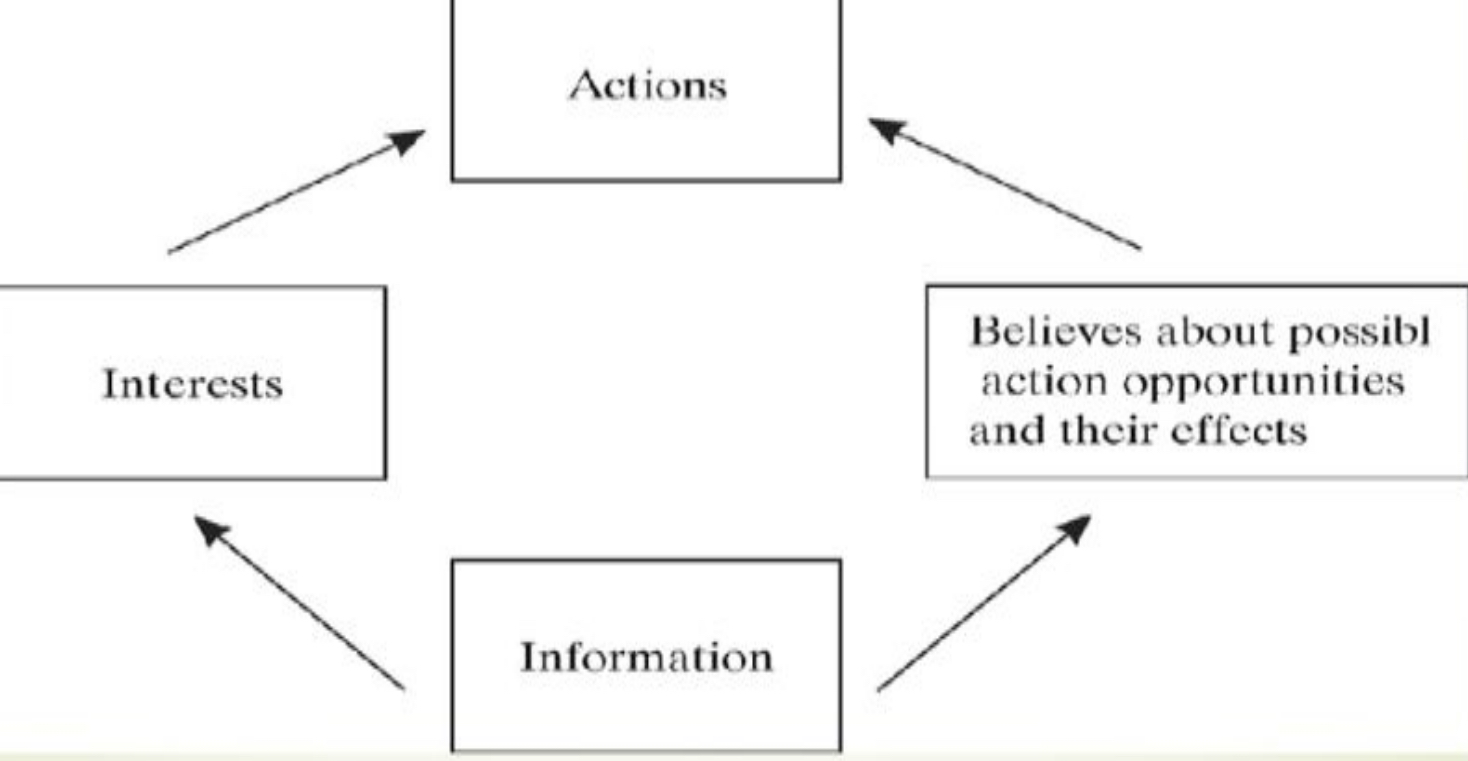
3 Pillars of RCT
strategies/courses of action
preferences over the end-statesto which combinations of actions chosen by the various players lead
beliefs about important parameters
Symbolic Interactionism
sociological framework that focuses on different meanings individuals attach to objects, peoples, and interactions.
Gestures
Posture, tone of voice, voice interactions, hands and facial movements
conveys significance
they can either accentuate or contradict what we are saying
unintentional and without conscious meaning
Gestures according to mead:
Self
The subject of one’s own experience of phenomena, perceptions, emotions, and thoughts.
Definition of one’s character, abilities, and attitude, especially in relation to persons or things outside oneself.
Consist of self-knowledge, self-esteem, self-concept and social self.
Threefold Gesture
Process of self-discovery is enacted through this:
Play Stage; Game Stage; Generalized Other
Enumerate the 3 (three) steps of Threefold Gesture in order:
Play Stage
Young children identify key features with their environments to which they have been exposed and replicate the behaviors that correspond with such roles.
e.g. a child applies lipstick with a object mimicking its mother or rubbing face with object to mimick father shaving
Game Stage
Children extrapolate from the vantage point of the roles they have simulated by assuming the roles that their counterpart concurrently undertake.
Generalized Other
Refers to widespread cultural norms and values we use as reference in evaluating ourselves.
Symbol
Stimuli that is abstract and abritrary
Sign
fixed single and concrete meaning regardless of context
Mead
According to ___:
1. Humans act toward things based on the meanings they give to it
2. The thing’s meaning is derived from social interaction that one has with others
3. The meaning is handled and modified through an interpretative process
Meaning is important; symbolic references are molded through Socialization; cultural dimension intertwines with symbolic educational development.
Enumerate the 3 (three) overarching Principles of Symbolic Interactionism ACCORDING TO MEAD:
MII; SRAMTS; CDIWSED
Blummer
According to __:
- Meaning isn’t inherent in objects
- Humans adjust meaning they assign to people
Meaning; Language; Thought
Enumerate the 3 (three) overarching Principles of Symbolic Interactionism ACCORDING TO BLUMMER:
Meaning
People act towards other things based on this:
Language
This provides meaning to humans by means of symbols
Thought
Interpretations assigned to symbols
Structural Functionalism
➔ Parts of the whole system may vary in terms of function but they are related to each other.
➔ One goal is needed to maintain or keep the whole system.
➔ Working on one part would affect other parts.
Parsons, Weber, & Durkheim
Developed Structural Functionalism
Family; Government; Education; Religion; Economy
Enumerate the five (5) social institutions:
Family
the basic unit of society and the educational system where the child begins to learn.
Government
institution which solves the conflicts that are public in nature and involve more than one people.
Education
form of learning in which knowledge, skills, and habits of groups of people are transferred from one generation to the next through teaching, training or research.
Religion
system of belief and rituals that serve to bind people together through shared worship
Economy
An economic system encompasses many institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes, and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community.
Robert Merton
He expanded the concept of social structure, wherein any social structure may have function
Everything that existed had a reason
Manifest and Latent
Enumerate the 2 (two) types of functions:
Manifest Function
recognized and intended consequence
Latency Function
unrecognized and unintended consequence