pH, pOH, pKa
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Ionization of water
Ionization of water leads to a Hydronium ion being formed (H3O+) and a Hydroxide ion being formed (OH-)
This is when one water molecule nabs a hydrogen from another water molecule, leading to autoionization of water
How much hydronium is in one liter of water?
One litre has roughly 1×10-7 M of hydronium
Whats a Molar (M)
M = mole/L
This is also known as the concentration of something
How to calculate concentration of a substance?
C = mass (in moles or grams) / volume (in liters usually)
Acidic solution
The Concentration of H3O+ > OH-
Basic solution
The Concentration of H3O+ < OH-
pH
p is the -log10
so pH is just the -log10[H+]
(we use H+ and H3O+ synonymously, they mean the same thing)
pOH
This is the -log10 [ OH- ]
pH and pOH
For any aqueous solution at 25*C pH + pOH = 14
Find concentration of H+ or OH- using pH and pOH
[ H+ ] = 10-pH
[ OH- ] = 10-pOH
Ka
This is the acid ionization constant (also known as the acid dissociation constant)
Bronsted-Lawry Base
If a molecule is acting as a BLB, than it will accept an electron from another molecule
Bronsted-Lawry Acid
If a molecule is acting as a BLA, then it will donate an electron to another molecule
Weak acid vs Strong acid (Ka)
As a strong acid fully dissociates in water, it has a large Ka (greater than 1)
Weak acids, on the other hand, do not dissociate well, thus having a small Ka (less than 1)
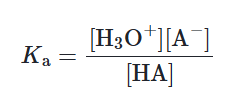
Weak base vs Strong base (Kb)
As a strong base fully dissociates in water, it has a large Kb (greater than 1)
Weak bases, on the other hand, do not dissociate well, thus having a small Kb (less than 1)
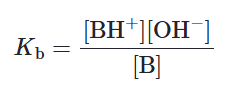
pKa ( Applies to pKb )
pKa = -log[Ka]
This, unlike Ka, is inversely related to the strength of an acid; a lower pKa value suggests a stronger acid
% Ionization or dissociation
% = X / HA
X represents amount of acid that was dissociated (usually the H3O+ concentration and for bases its the OH- concentration)
HA is just the concentration of the acid or the base (on the reactant side)
Acetic acid (Weak or Strong acid)
Weak acid
Steps in solving the pH of a weak acid
If dissociation constant is given, firstly write the formula out
Then, using ICE, write the equation using Ka
Solve for x
If Ka is small, in the denominator of the equation, you can ignore the value of X and solve it that way. Otherwise, use the quadratic formula.
Use the pH = -log [H+] to find the pH using the concentration of hydronium