A&P Eye Iris and Ciliary Body
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/154
Last updated 11:17 PM on 4/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
1
New cards
very fast; sphincter
Parasympathetic innervation of the CB and iris have a (very slow/very fast) latency. This innervation innervates the iris (sphincter/dilator) muscle and innervates choroidal vessels.
2
New cards
1. Zonules
2. Vitreous base
The non-pigmented ciliary epithelium serves as an attachment site for what 2 structures?
3
New cards
iris
Found in anterior portion of globe that divides anterior and posterior chambers of anterior segment; anterior most part of uveal tract
4
New cards
collarette
Where is the thickest part of the iris?
5
New cards
iris root
Where is the thinnest part of the iris?
6
New cards
nasal; inferior
The pupil is slightly (nasal/temporal) and (superior/inferior) to dead center.
7
New cards
pupil
Controls amount of light let into the eye
Allows aqueous to flow from posterior to anterior chamber
Reduces spherical and chromatic abberation
Increases depth of focus
Allows aqueous to flow from posterior to anterior chamber
Reduces spherical and chromatic abberation
Increases depth of focus
8
New cards
increases; reduces; increases
The pupil (increases/decreases) depth of focus. It also (increases/reduces) the extra light in photopic (bright) conditions and (increases/reduces) available light in scotopic (dark) conditions.
9
New cards
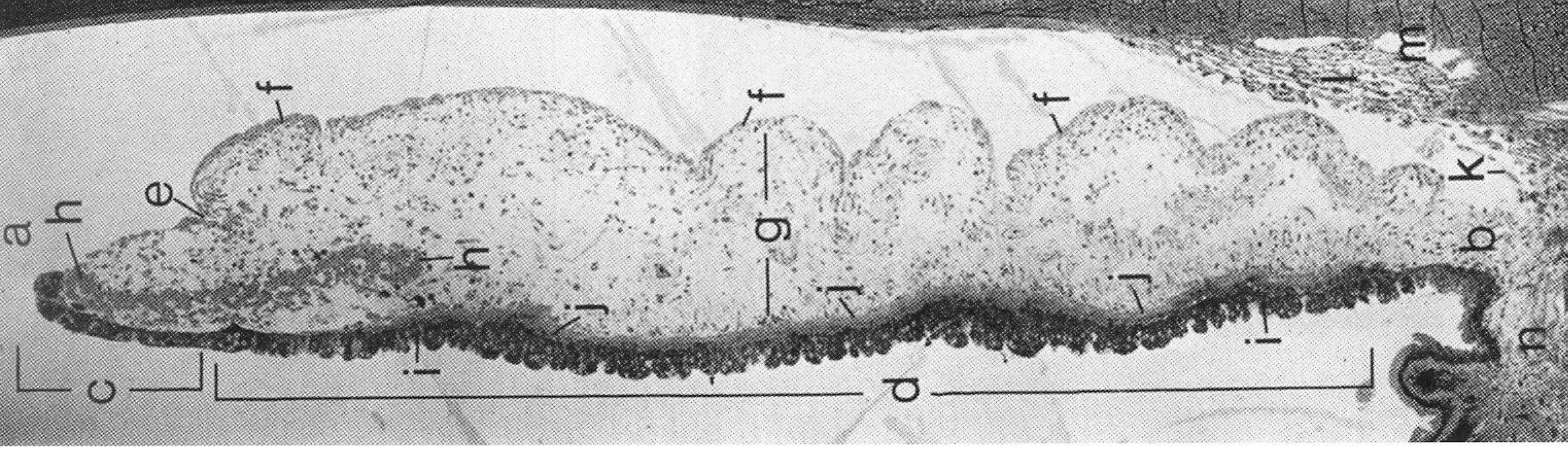
a. pupil and pupillary ruff
b. iris root
c. pupillary portion
d. ciliary portion
e. collarette
f. anterior border layer
g. stroma
h. iris sphincter muscle
i. posterior epithelium
j. anterior epithelium
k. anterior chamber angle
l. trabecular meshwork
m. Canal of Schlemm
n. ciliary bodt
b. iris root
c. pupillary portion
d. ciliary portion
e. collarette
f. anterior border layer
g. stroma
h. iris sphincter muscle
i. posterior epithelium
j. anterior epithelium
k. anterior chamber angle
l. trabecular meshwork
m. Canal of Schlemm
n. ciliary bodt
Identify the following structures in the image of the iris.
10
New cards
collarette
Structure that divides the ciliary from the pupil portion of the iris
11
New cards
1. collarette
2. crypts
3. collarette
4. ruff
Identify the missing structures in the image (1-4).
12
New cards
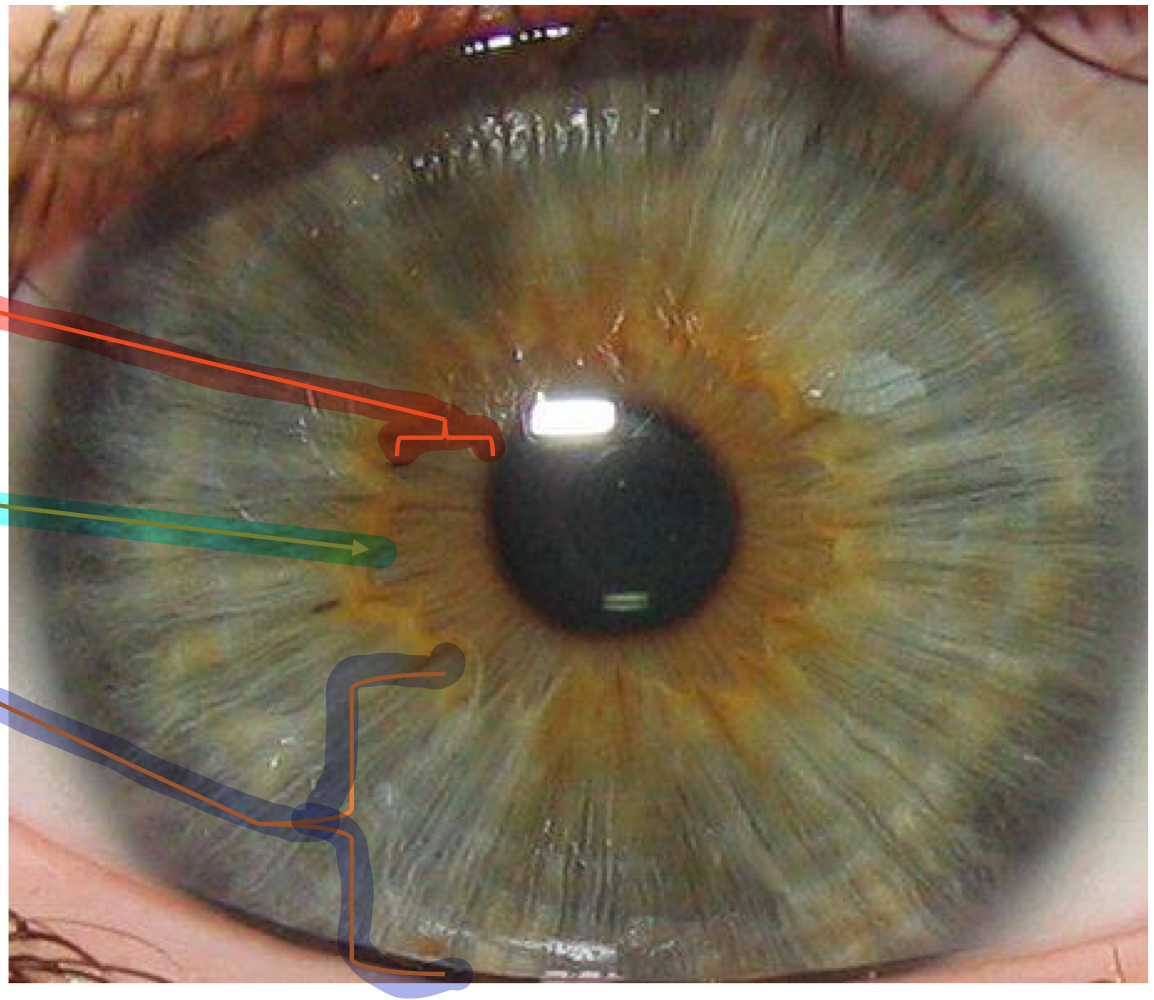
pupillary zone
What structure within the iris is the red line pointing to?
13
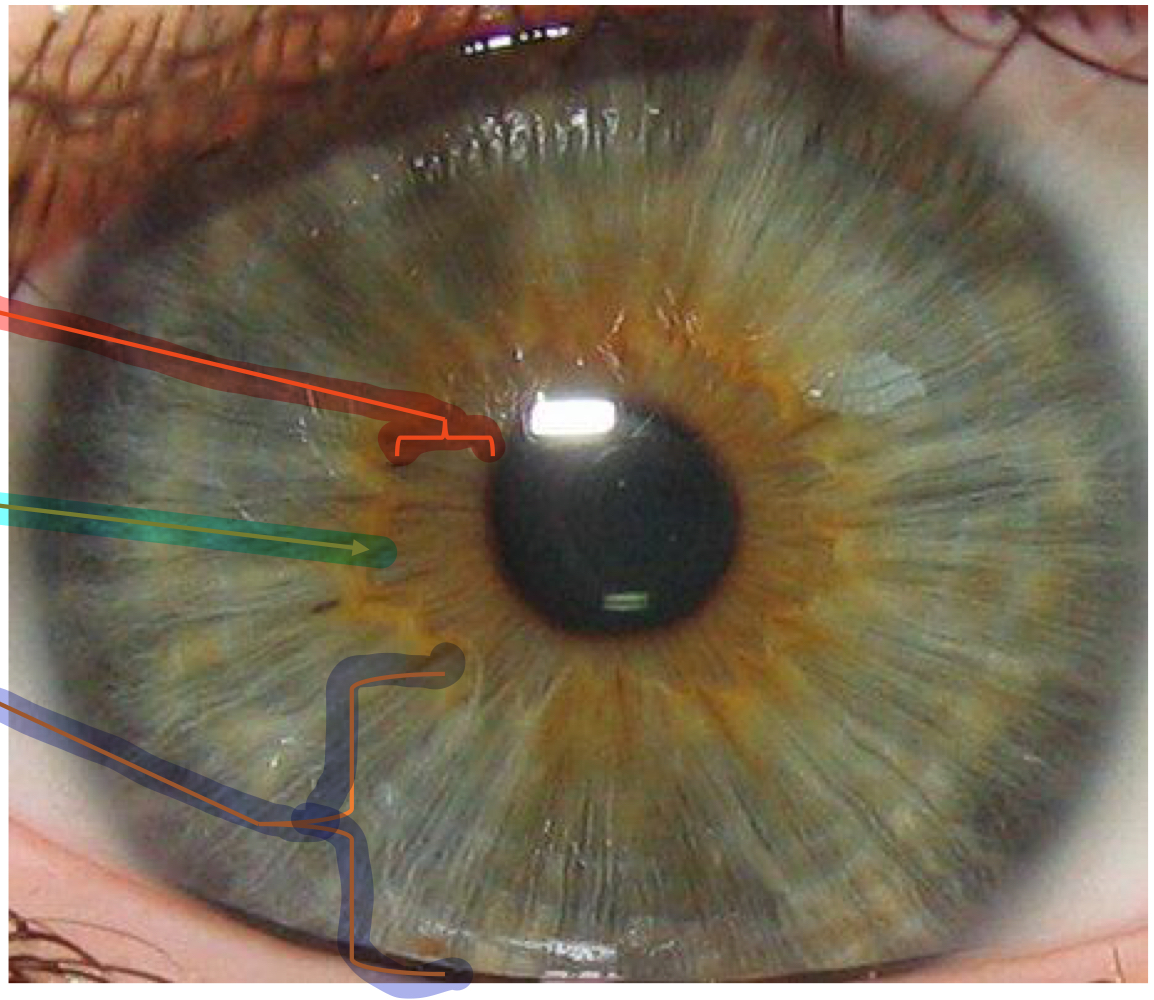
New cards
collarette
What structure within the iris is the light blue line pointing to?
14
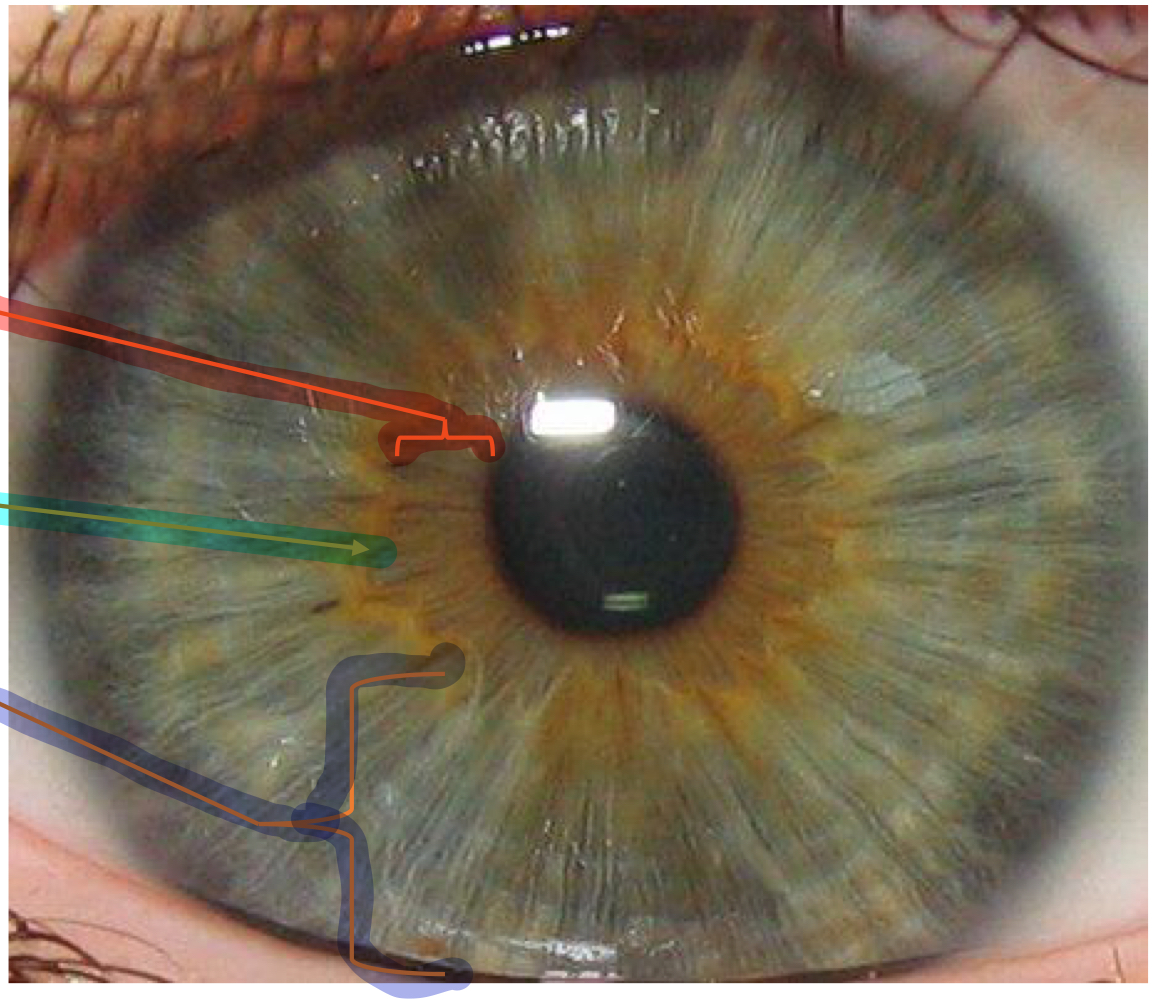
New cards
ciliary zone
What structure within the iris is the indigo line pointing to?
15
New cards
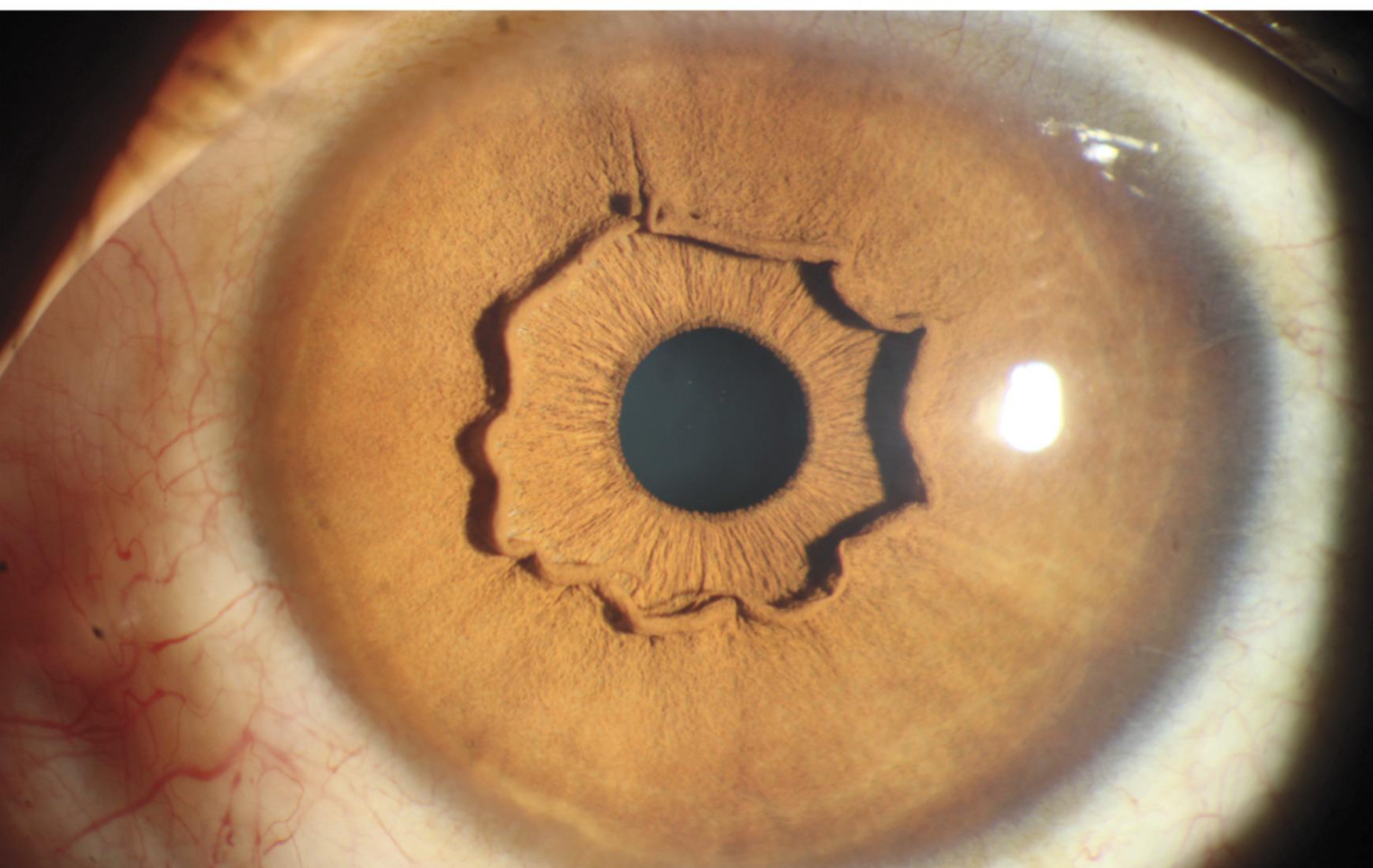
asymptomatic; abnormal collarette
Is the iris in the image asymptomatic or symptomatic? What abnormality is seen here?
16
New cards
1. Radial folds
2. Circular contraction folds
What are the 2 types of folds/wrinkles in the iris?
17
New cards
radial contraction furrows
What type of wrinkles in the iris are present on the posterior surface and run from the margin to the collarette?
18
New cards
radial structural furrows
What type of wrinkles in the iris are present on the posterior surface and run from the collarette, past the iris root, and into pars plicata?
19
New cards
Fuch’s crypts
What type of crypt is indicated by the pink circle?
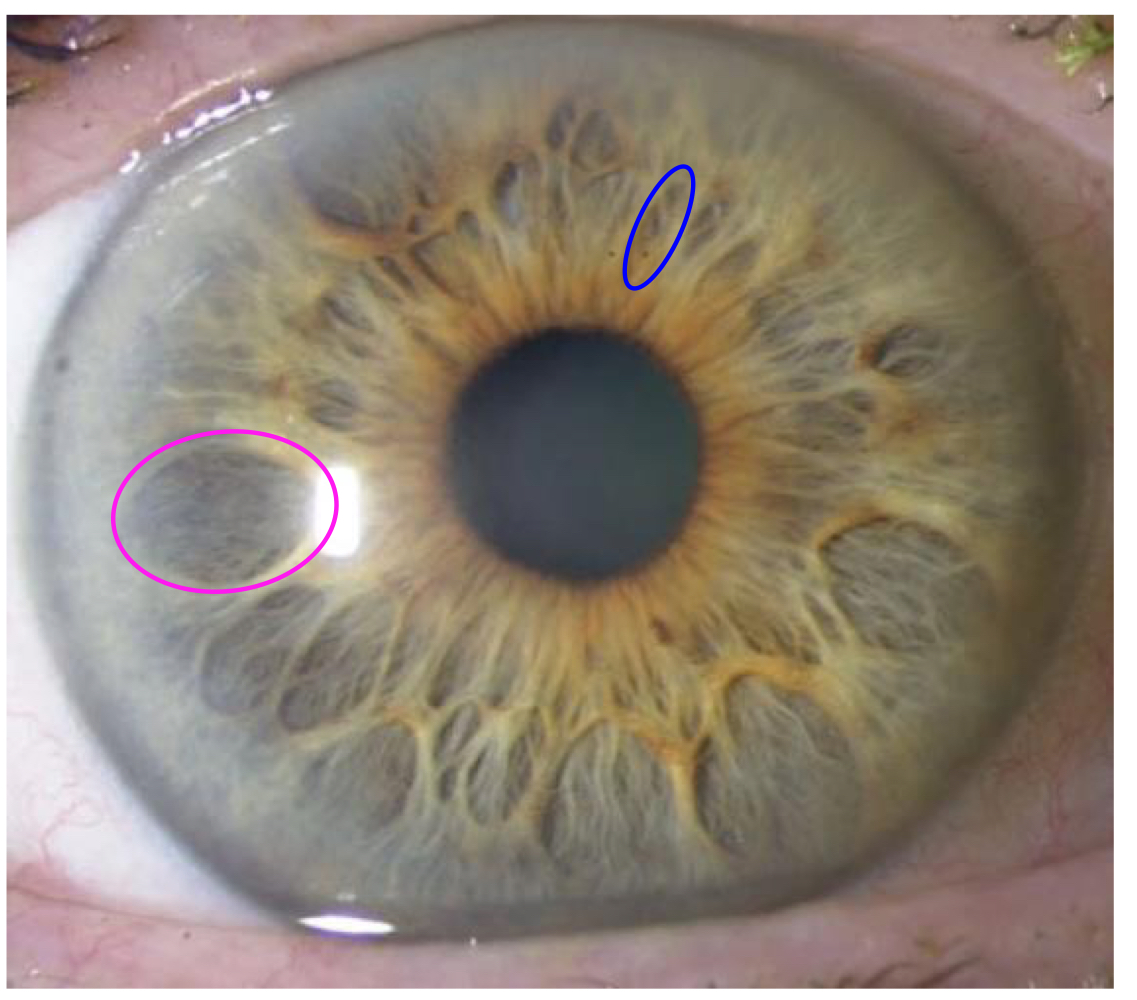
20
New cards
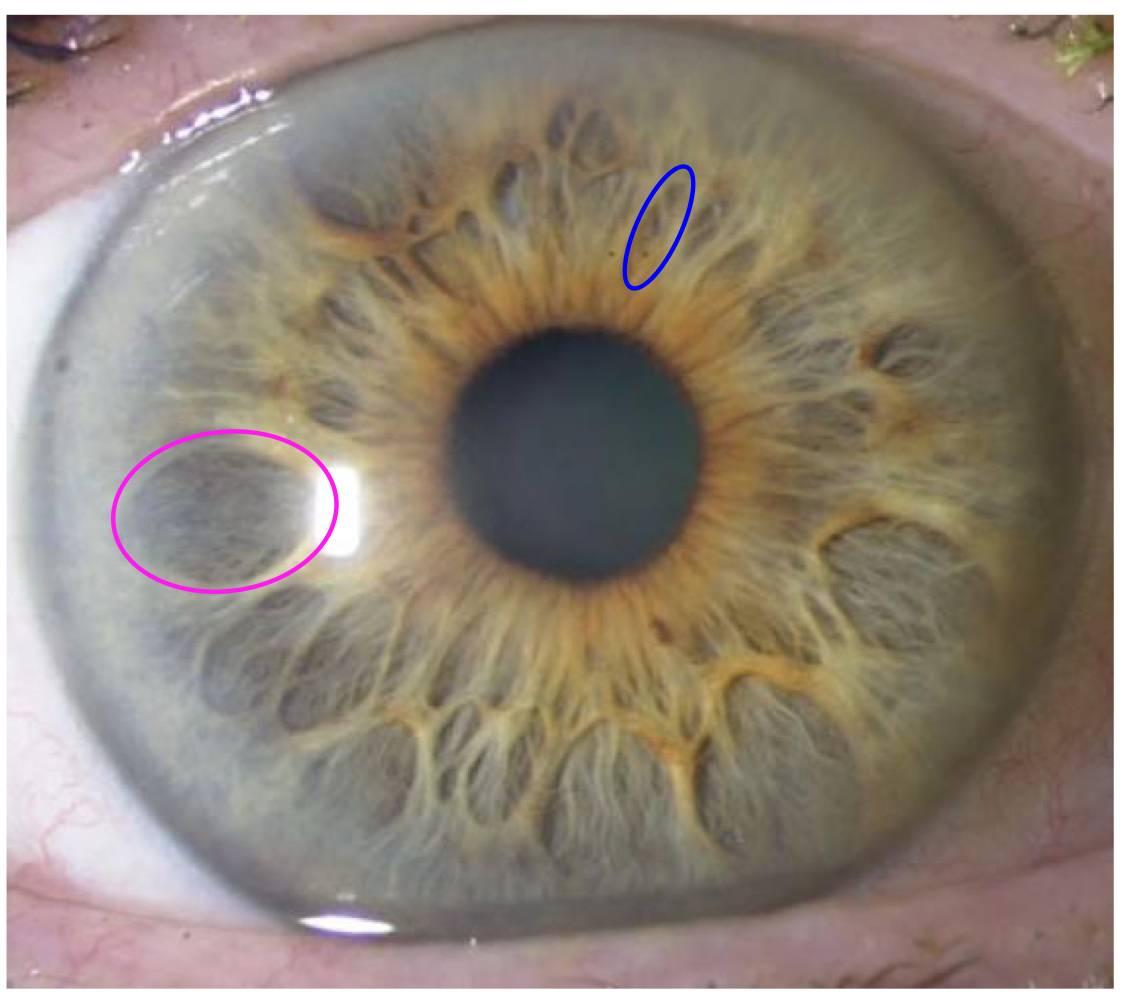
Ciliary crypts
What type of crypt is indicated by the blue circle?
21
New cards
Fuch’s crypts
What type of crypt is deeper and allows aqueous into the stroma?
22
New cards
ciliary crypts
What type of crypt is smaller and is found in the ciliary zone?
23
New cards
trabeculae
Loosely arranged stroma connective tissue radial columns
24
New cards
pupillary ruff
Posterior pigmented epithelium that wraps around the anterior surface (brown fluff)
25
New cards
crenations
Lobules in the pupillary ruff; continuation of radial contraction furrows
26
New cards
1. Anterior border layer
2. Iris stroma/sphincter muscle
3. Anterior eptihelium/dilator muscle
4. Posterior pigment epithelium
List the four layers of the iris from front to back.
27
New cards
1. Melanocytes
2. Fibroblasts
What 2 types of cells made up the anterior border layer of the iris?
28
New cards
anterior border layer
Thin condensation of stroma (may not be a separate layer, not an epithelium)
Thickest at collarette, not present at the crypts
May form iris processes--attach to the trabecular meshwork
Ends at the root
Thickest at collarette, not present at the crypts
May form iris processes--attach to the trabecular meshwork
Ends at the root
29
New cards
Density of meshwork
What is the main influence of iris color?
30
New cards
Fibroblasts; melanocytes
What cells are present at the surface of the anterior border layer? Underneath the anterior border layer?
31
New cards
2-7 cells thick
How many cells thick is the anterior border layer?
32
New cards
iris nevus
Accumulation of melanocytes in anterior border layer
33
New cards
iris stroma
What layer of the iris is continuous with the stroma of the ciliary body & is HIGHLY vascular?
34
New cards
1. Collagen fibrils & ground susbtance
2. Pigmented cells
3. Non-pigmented cells
4. Vessels
What are the 4 main components of the iris stroma?
35
New cards
collagen fibrils & ground substance
What component of the iris stroma allows aqueous to flow within the stroma?
36
New cards
pigmented cells
What component of the iris stroma contain clump cells (large, round, dark) that are scavengers of free pigment and are usually found in the pupillary portion near the sphincter?
37
New cards
Non-pigmented cells
What component of the iris stroma involves fibroblasts, lymphocytes, macrophages, and mast cells?
38
New cards
1. Anterior border layer
2. Iris stroma
3. Sphincter muscle
4. Clump cell
5. Anterior iris epithelium
6. Posterior iris epithelium
Identify the structures in the image of the iris.
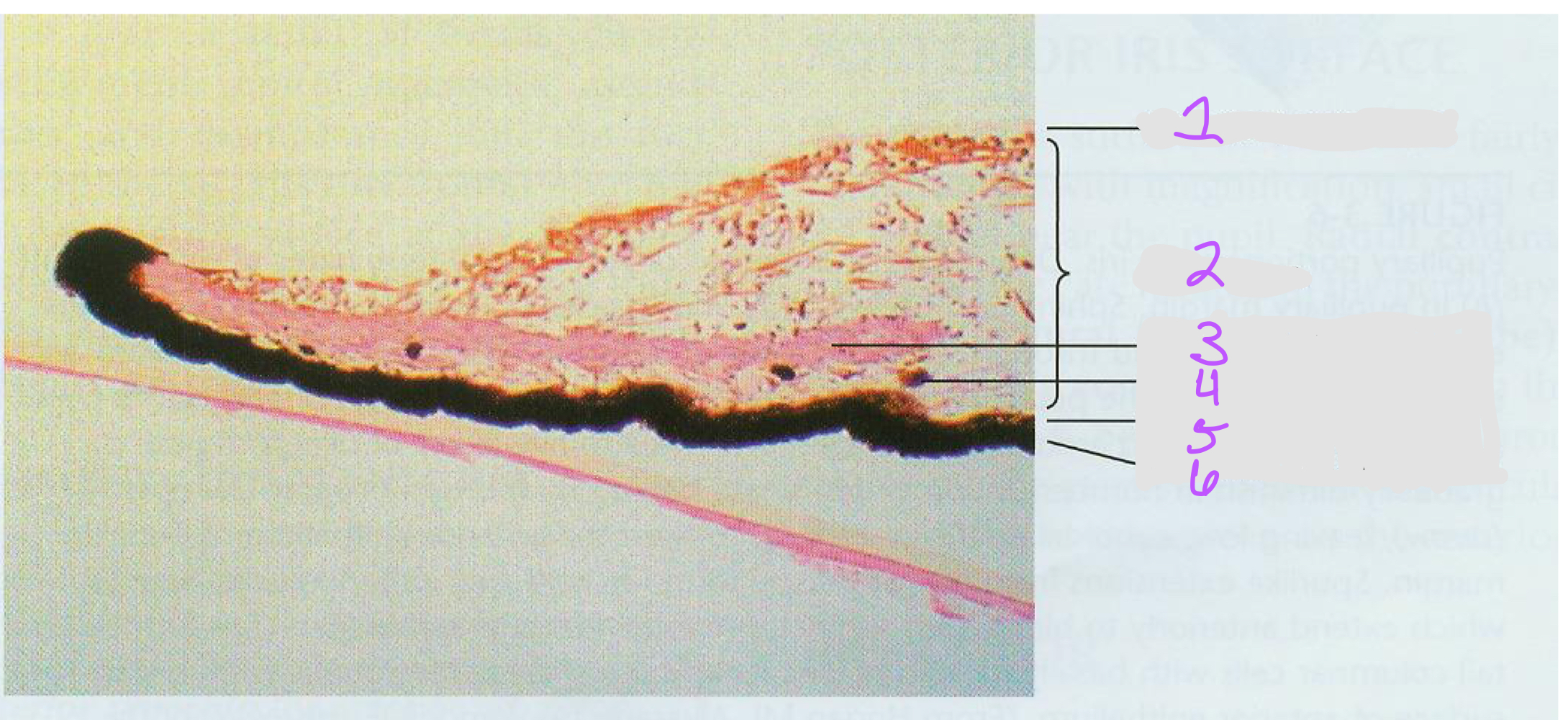
39
New cards
trabeculae
Collagen fibrils arranged in radial columns within the iris stroma
40
New cards
iris stroma
Which has less melanocytes & fibroblasts--the iris stroma or anterior border layer?
41
New cards
radially
Vessels that branch off of the major circle of the iris will run (radially/circularly) through the stroma.
42
New cards
iris stroma; pupillary region
What layer of the iris contains the iris sphincter muscle? In what region is the iris dilator muscle contained?
43
New cards
constriction
The iris sphincter muscle causes pupillary (dilation/constriction) in response to bright light or accommodation.
44
New cards
smooth muscle cells
What type of cells make up the iris sphincter muscle and are joined together by tight junctions?
45
New cards
parasympathetically; short
The iris sphincter muscle is (sympathetically/parasympathetically) innervated by the (long/short) ciliary nerves.
46
New cards
iris stroma & collagen around the iris dilator muscle
What is the iris sphincter firmly attached to?
47
New cards
False
True/False: The iris sphincter muscle cannot function with radial tears.
48
New cards
anteriorly
During contraction of the iris sphincter, the pupil margin pulls (posteriorly/anteriorly).
49
New cards
False
True/False: Anterior epithelium/iris dilator muscle is located on anterior iris.
50
New cards
anterior epithelium/iris dilator muscle
The ________________ layer of the iris is just anterior to the posterior epithelium.
51
New cards
myoepithelial cells
What type of cells make up the anterior epithelium/iris dilator muscle layer of the iris?
52
New cards
basal
The (apical/basal) side of the anterior epithelium/iris dilator muscle layer is anterior.
53
New cards
cuboidal pigmented epithelium; tight junctions & desmosomes
How would you classify the apical portion of cells in the anterior epithelium/iris dilator muscle layer? What joins these cells together?
54
New cards
Elongated, contractile smooth muscle processes
What composes the basal portion of the anterior epithelium/iris dilator muscle layer?
55
New cards
dilator
The iris (dilator/sphincter) is a poorly developed smooth muscle.
56
New cards
sympathetically; stroma
The iris dilator muscle is (sympathetically/parasympathetically) innervated and attaches to the _______ and some of the sphincter muscle.
57
New cards
3-5
Muscle fibers of the iris dilator muscle extends into the stroma, forming _____ layers.
58
New cards
anterior epithelium
What layer of the iris runs the whole length of the iris, is pigmented, but not as much as posterior epithelium, and continues posteriorly with pigmented epithelium of the ciliary body?
59
New cards
densely; larger
The posterior epithelium of the iris is (sparsely/densely) pigmented and contain (smaller/larger) cells than the anterior iris epithelium.
60
New cards
columnar
What are the shape of the posterior iris eptihelial cells?
61
New cards
tight junctions & desmosomes
What holds posterior epithelium cells together within the iris?
62
New cards
apical; desmosomes
The apical ends of the posterior epithelium faces the (apical/basal) ends of the anterior epithelium and is held together by _____________.
63
New cards
posterior
The basal side of the posterior epithelium faces the (anterior/posterior) chamber.
64
New cards
posterior
The (anterior/posterior) epithelium of the iris has a well-defined basement membrane.
65
New cards
radially; circularly
The iris dilator is (circularly/radially) oriented while the iris sphincter is (circularly/radially) oriented.
66
New cards
pigmented; posterior
In all individual (besides albanism) irises, the epithelial layers will be (non-pigmented/pigmented). The (posterior/anterior) epithelial layer is more so pigmented.
67
New cards
True
True/False: The number of melanocytes is fairly consistent between different eye colors.
68
New cards
False
True/False: The number of melanin granules within the melanocytes is fairly consistent between different eye colors.
69
New cards
1. Anterior border layer
2. Iris stroma
Most of the iris color is probably due to what 2 layers of the iris?
70
New cards
collagen trabeculae
What component of the iris is more apparent in lighter colored irises?
71
New cards
Shorter wavelengths are scattered more due to the arrangement and density of connective tissue.
What often causes lighter irises to appear blue?
72
New cards
Long wavelengths
In lighter irises, what wavelength of light is more absorbed?
73
New cards
albinism
Lack of pigment results in transillumination (light passes through)
Reduced acuity due in part to poorly functioning aperature
Reduced acuity due in part to poorly functioning aperature
74
New cards
Heterochromia
Different color irises; melanocytes develop asymmetrically as babies mature
Can occur later due to injury, inflammation, etc.
Can occur later due to injury, inflammation, etc.
75
New cards
ciliary body
Ocular structure that appears round when viewed from front to back
Middle portion of the uvea
Triangular in cross section
Middle portion of the uvea
Triangular in cross section
76
New cards
1. Ciliary stroma
2. Ciliary muscle
3. Supraciliaris
4. Pigmented epithelium
5. Nonpigmented epithelium
6. Pars plana
7. Pars plicata
Identify the structures of the ciliary body (1-7).
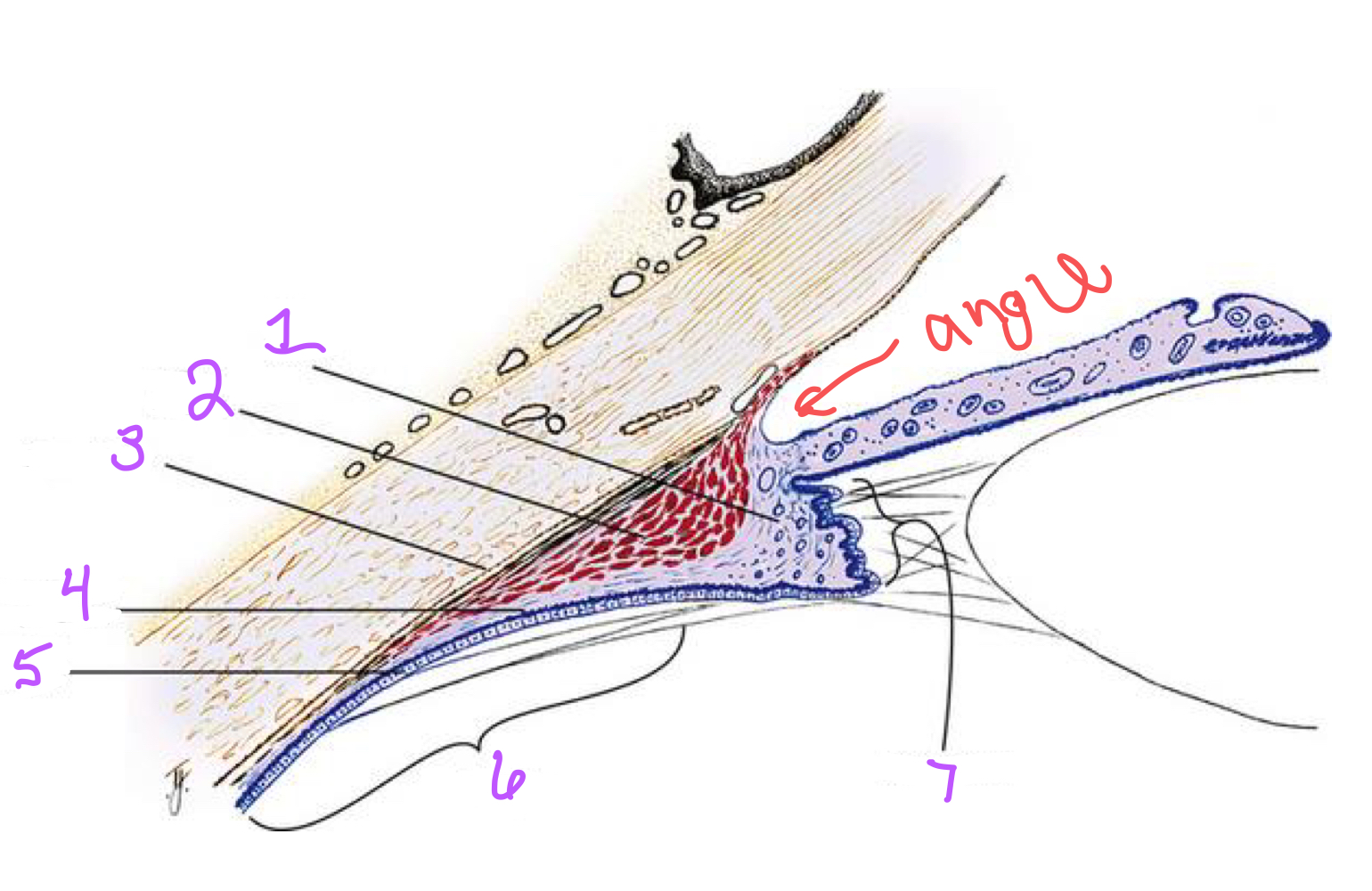
77
New cards
1. Accommodation
2. Production of aqueous humor
3. Contribution to vitreous production
What are the 3 main functions of the ciliary body?
78
New cards
1. Pars plana
2. Pars plicata
What are the 2 main parts of the ciliary body?
79
New cards
pars plana
Posterior flat part of the ciliary body
Meets the retina at the ora serrata
Meets the retina at the ora serrata
80
New cards
ora serrata; pars plicata
The pars plana extends from the _______ to the posterior edge of the ________________.
81
New cards
posteriorly; anteriorly
The pars plana thins (anteriorly/posteriorly) and thickens (anteriorly/posteriorly).
82
New cards
ciliary bays
Rounded edges of ciliary tissue
83
New cards
dentate processes
Tooth-like extensions of retina in between ciliary bays
84
New cards
striae ciliaris
Linear striations in the pars plana
Extends from the apex of dentate processes into the pars plicata
Site of attachments of initial fibers that coalesce to form ciliary zonules
Extends from the apex of dentate processes into the pars plicata
Site of attachments of initial fibers that coalesce to form ciliary zonules
85
New cards
pars plicata
Anterior portion of the ciliary body; contains the ciliary processes (70-80) and extends into the posterior chamber
Gets smaller with age
Gets smaller with age
86
New cards
Valleys of Kuhnt
What lies between the pars plicata?
87
New cards
1. lens
2. ora serrata
3. sclera
4. ciliary process
5. pars plicata
6. pars plana
Identify the numbered structures in the image.
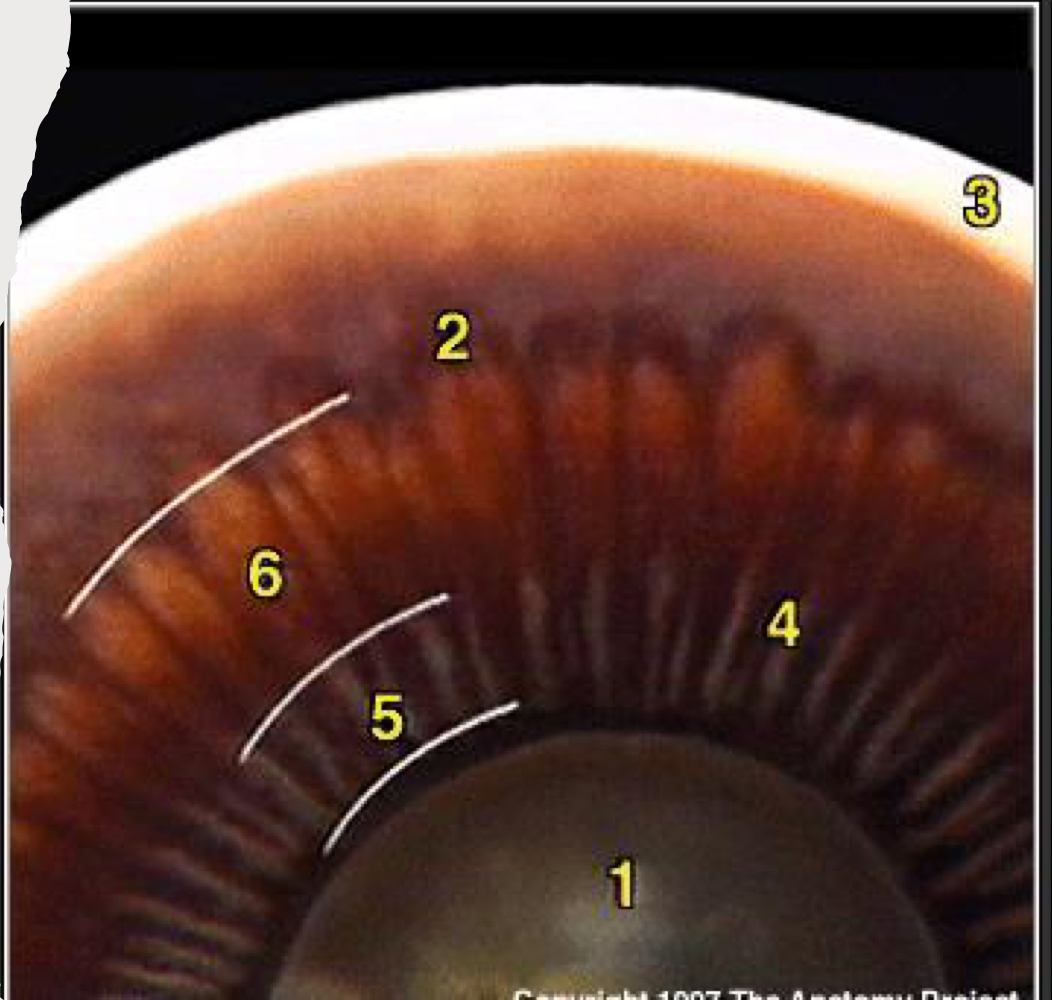
88
New cards
anteriorly; rounder; scleral spur; trabecular meshwork
During accommodation, the ciliary body shifts (posteriorly/anteriorly) and rotates outward slightly, allowing zonules to relax. This allows the lens to become more (flatter/rounder). This also pulls on the ______ and _______________, which can reduce intraocular pressure.
89
New cards
zonules
Fibers that suspend the lens in place
90
New cards
1. Pars plana
2. Valleys of pars plicata
What are the 2 locations in which zonules attach?
91
New cards
1\.5
Zonules start about ____ mm from the ora serrata.
92
New cards
1. Supraciliaris (supraciliary lamina)
2. Ciliary muscle
3. Ciliary stroma
4. Ciliary epithelia
List the 4 layers of the ciliary body from outer to inner.
93
New cards
1. Pigmented epithelium
2. Nonpigmented epithelium
What are the 2 sublayers of the ciliary epithelia layer of the ciliary body?
94
New cards
supraciliaris
What layer of the ciliary body is adjacent to the sclera, is the transition layer between the sclera & ciliary body, is continuous with the suprachoroid, and contains ribbon-like layers?
95
New cards
1. Melanocytes
2. Collagen bands
3. Fibroblasts
What are the 3 main components of the supraciliaris layer of the ciliary body?
96
New cards
lamina fusca
The supraciliaris merges with the __________ _________ of the sclera.
97
New cards
supraciliaris
What layer of the ciliary body allows the ciliary body to slide against the sclera without detaching/stretching (imp. for accommodation)?
98
New cards
supraciliaris
What layer of the ciliary body allows fluid into spaces?
99
New cards
1. Longitudinal
2. Radial
3. Circular
What are the 3 portions of the ciliary muscle?
100
New cards
scleral spur
All 3 portions of the ciliary muscle attach at the _________.