3B: Part I Causes of the Civil War (Sectionalism)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Sectionalism
Loyalty to one's own region of the country, rather than to the nation as a whole
Popular Sovereignty
The idea that people living in a territory should vote on whether to allow slavery.
Abolitionism
A movement that sought to end slavery in the United States.
Free Soil Party
A political party dedicated to stopping the expansion of slavery. Wanted no slavery in free territories in the west because they wanted to preserve it for white farmers. If slavery was allowed then the white farmers would have a hard time finding work.
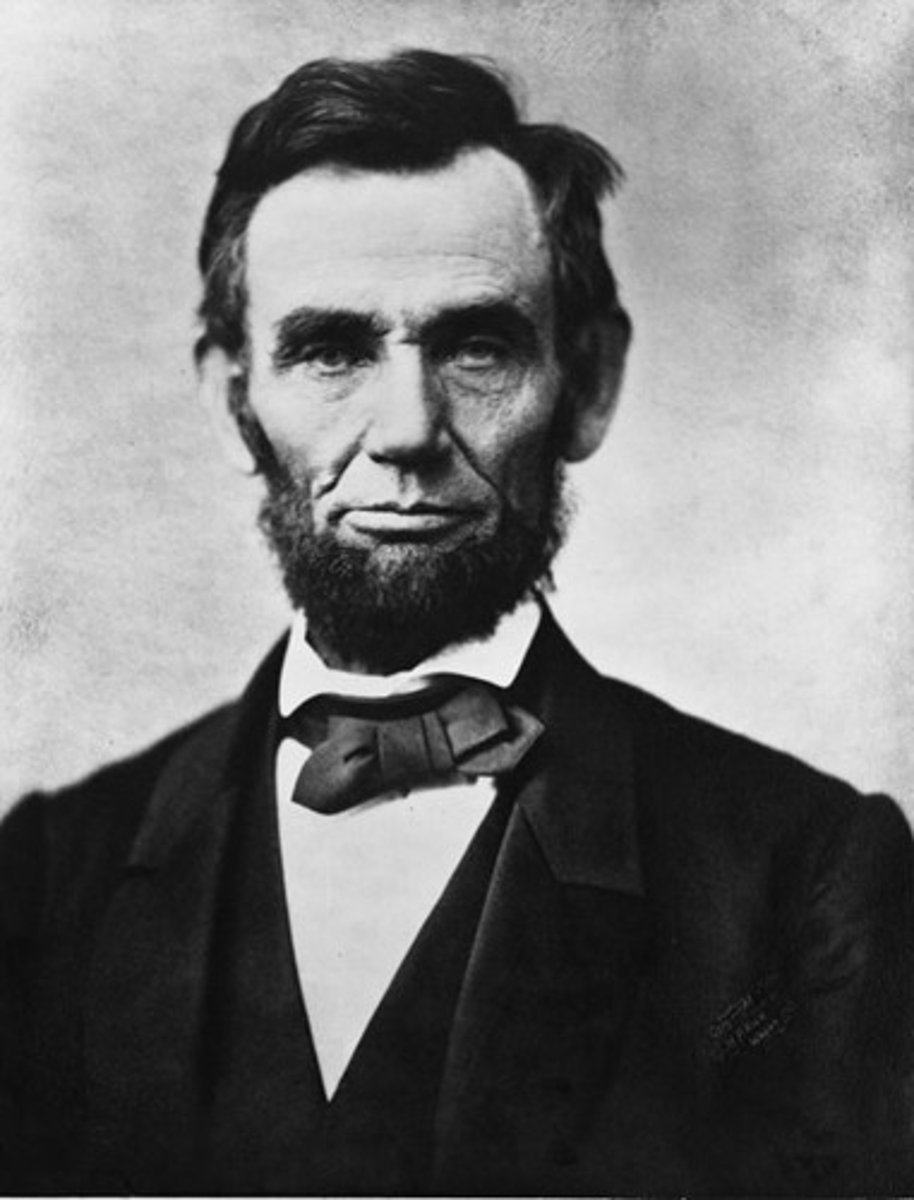
Abraham Lincoln
16th President of the United States saved the Union during the Civil War and emancipated the slaves. First Republican president.

Confederate States of America
A republic formed in February of 1861 and composed of the eleven Southern states that seceded from the United States
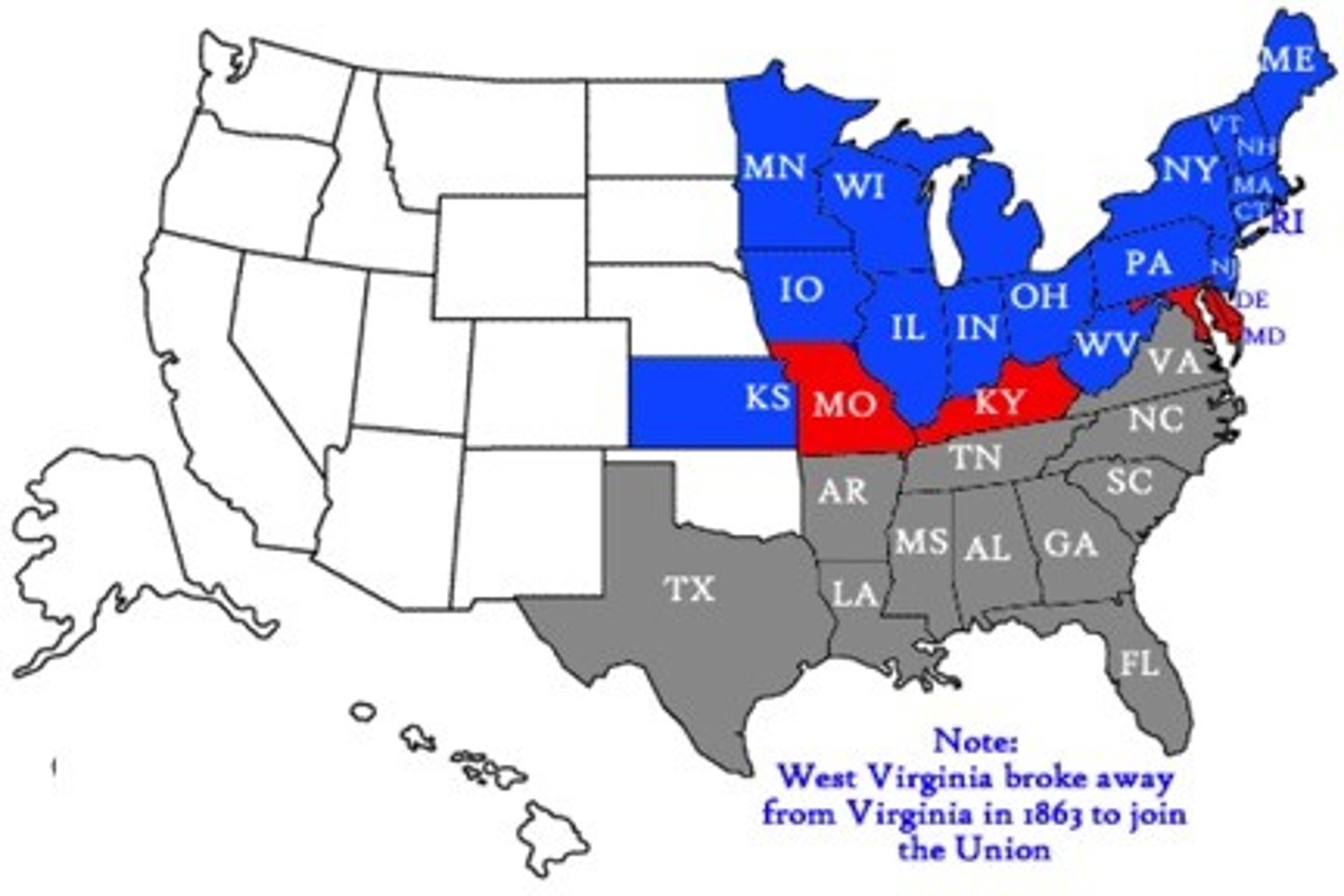
Mason-Dixon Line
Originally drawn by surveyors to resolve the boundaries between Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania and Virginia in the 1760s, it came to symbolize the North-South divide over slavery.
Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857)
Supreme Court case that decided that the US Congress did not have the power to prohibit slavery in federal territories- which made the 36-30 line of the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional. Also, slaves were private property and could not be taken away without due process - basically slaves would remain slaves in non-slave states and slaves could not sue because they were not citizens
Election of 1860
Lincoln, the Republican candidate, won because the Democratic party was split over slavery. As a result, the South no longer felt like it has a voice in politics and a number of states seceded from the Union.
Republican Party
Organized in 1854 by anti-slavery Whigs and Democrats, Free Soilers and reformers in response to the Kansas Nebraska Act; wanted to keep slavery out of the territories.
Chief Justice Roger Taney
Chief Justice of the Supreme Court during the Dred Scott decision. Argued that Congress could not ban slavery in the territories due to property rights.
Wilmot Proviso
1846 proposal that outlawed slavery in any territory gained from the War with Mexico. Never passed.
Compromise of 1850
(1) California admitted as free state, (2) Utah and New Mexico to use popular sovereignty to decide the issue of slavery, (3) resolution of Texas-New Mexico boundaries, (4) federal assumption of Texas debt, (5) slave trade abolished in DC, and (6) new fugitive slave law.
Kansas Nebraska Act (1854)
Created Nebraska and Kansas as states & gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be either a free or slave state through popular sovereignty. Repealed the Missouri Compromise;
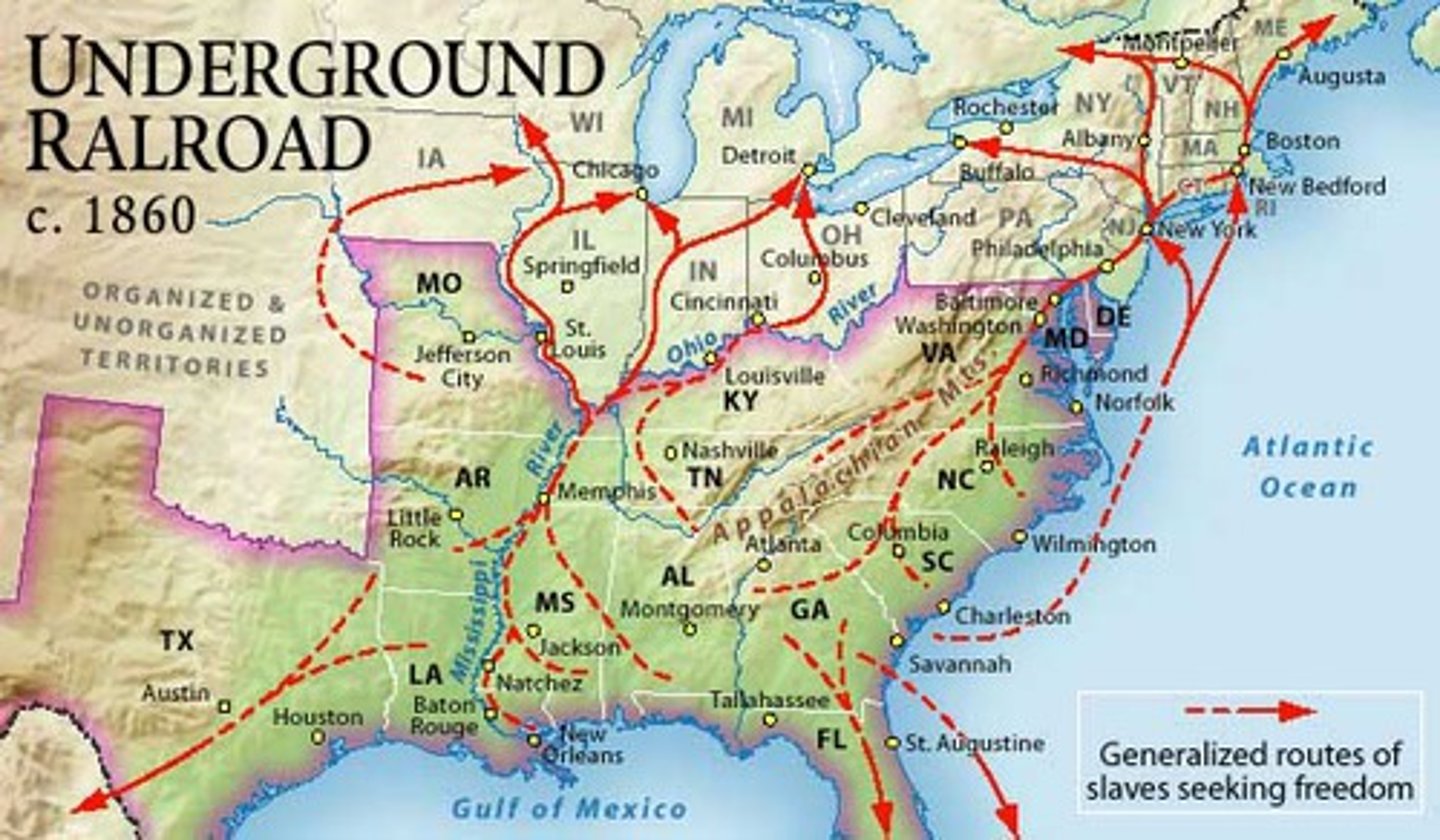
Underground Railroad
A system of secret routes used by escaping slaves to reach freedom in the North or in Canada
Uncle Tom's Cabin
Written by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1853. It promoted abolition.
Fugitive Slave Law
Enacted by Congress in 1793 and 1850, these laws provided for the return of escaped slaves to their owners. The North was lax about enforcing the 1793 law, with irritated the South no end. The 1850 law was tougher and was aimed at eliminating the Underground Railroad.
King Cotton
Expression used by Southern authors and orators before Civil War to indicate economic dominance of Southern cotton industry, and that North needed South's cotton.
The Union
A term used to describe the northern states during the Civil War.